Our parents had learned some wrong lessons from the ’20s, ’30s, and ’40s. They learned to love government too well. They learned that government was what rescued you from depression and war. Our parents were very trusting of large governmental institutions. The liberalism that was a seed of the radicalism to come was in our parents, even when our parents were Republicans. They had taken large government for granted.
P.J. O’Rourke, interviewed by Scott Walter, “The 60’s Return”, American Enterprise, May/June 1997.
April 19, 2024
QotD: The “Greatest Generation”
April 18, 2024
Wagner’s Ring Cycle, summarized
I have to admit that aside from some amazing helicopter music, most of Wagner’s music isn’t my cup of tea drinking horn of mead. As a result, I didn’t know what the whole Ring Cycle was all about and mostly didn’t care. Coming to my rescue, Kulak provides a summary for my fellow non-Wagner fans:
So researching my epic length piece on female warriors, pre-Christian sexual politics, and the unique development of North European culture I got really into Richard Wagner’s Ring Cycle after stumbling on Arthur Rackham’s gorgeous illustrations to the English translations of the text of the operas (Link 1, Link 2).
And one of the things that immediately jumped out to me, even beyond everything listed in the long piece, is how weird and unique the sexual politics of Pagan Germanic culture is.
Sure it’s Wagner, it’s not a primary source. It’s a 19th century romantic composer interpreting several different legends of pagan era Germany and Scandinavia, as record by Christian monks and scholars 100s of years after the fact. So academically not the most accurate thing to draw conclusions from, however if you subscribe to any blood memory, or spirit of a people, or eternal culture theory … it’s almost better.
This is the version of the tale that’s survived and been refined across first oral, then written traditions, then preserved by Christian monks, then revived by high Victorian romantics into one of the most celebrate and popular operas of all time. If there’s anything we could learn about the eternal character of North European women, sexuality, and sexual politics (and by extension modern sexual politics, we’re all North Europeans now) it is here.
And damned … what a datapoint.
What follows is a MeToo story on hyperborean crack.
The Female lead Brunhilde starts out as a Valkyrie who disobeys her master/father the god Wotan (Odin) in a matter of divine importance so as to save a mortal man. For her disobedience Wotan strips her of her divine nature and curses her to sleep on the earth as a mortal woman until such a time as the first man to find her wakes her, then she is to be his wife. However, taking pity Wotan lays out an magical wall of fire to guard her so no coward, only a great hero, would ever succeed. (end opera 1/3).
20-ish years later Siegfried, the son of the man Brunhilde saved, finds her (she hasn’t aged a day), and perfectly fearless he braves the fire to wake her, where-upon they fall in love (end opera 2/3)… then taking leave for more adventure Siegfried takes off promising to return and remember their. Where-upon he meets the King Gunther and his sister Gutrune, who seduces Siegfried and makes him forget Brunhilde. Making friends with Gunther, Siegfried conspires with him that he should have Brunhilde for a wife (given she’s the best woman he can think of for his friend), but there’s a problem … Gunther cannot brave the fire, he’s not fearless like Siegfried. So Siegfried, conspires to impersonate Gunther using his magic, brave the fire again, seduce Brunilde again, get her to consent to marry him in the Guise of Gunther, spend the night using his sword to divide himself from Brunhilde. Then in the morning swap back, Siegfried Married to Gutrune, Gunther to Brunhilde … The plan worked perfectly.
Then Brunhilde found out.
Learning what had been done she conspires with Siegfried’s enemies to have him killed, falsely accuses him of rape, and successfully maneuvers him into admitting to lying in an oath he wasn’t even aware was a lie … so that his fearless perfect life can end with a stab in the back.
So you may ask: Having avenged herself does she settle-down with her husband?
Hell no! You think you could fill the shoes of Siegfried you curr, you coward, you beta-cuck?! You will NEVER be Siegfried.
Instead she gives the mother of all angry speeches denounces Gertrude and everyone else of the court to their face, and then rides Siegfried’s horse onto his funeral pyre, determined it is better to die with Chad than live with Brad.
THE END.
Of the entire opera cycle. No more.
The Fat Lady has sung.
Your 4 day trip into the German mountains to experience 3 1/2 Operas over as many days and a combined 15 hours has concluded. Go Home.
I’m Sorry bros, the hoes have always been like this.
Even in the mythical past of high Germanic mythology … the hoes were like this.
What to do if Romans Sack your City
toldinstone
Published Jan 12, 2024Chapters:
0:00 Introduction
0:34 Progress of a siege
1:55 Looting and violence
3:42 Recorded atrocities
4:45 Captives
5:27 BetterHelp
6:36 Surviving a Roman sack
7:13 Where to hide
8:27 What to do if you’re captured
9:20 Advice for women
10:09 The fate of captives
(more…)
April 17, 2024
Soviet Berlin Offensive Begins – WW2 – Week 294B – April 16, 1945
World War Two
Published 16 Apr 2024The final Soviet assault on Berlin begins today. The Soviets have two million men supported by tens of thousands of guns, tanks, and aircraft. Opposite them stand millions of men and boys of the German Wehrmacht, Waffen SS, Volkssturm, and Hitler Youth. The forces of Nazism are weakened and disorganised but determined to fight on as long as possible.
00:41 Roosevelt’s death
03:09 Preparations for the Soviet drive on Berlin
08:49 Zhukov’s Offensive
12:48 Konev’s Offensive
14:57 Summary & Conclusion
(more…)
French M14 Conversion – the Gras in 8mm Lebel
Forgotten Weapons
Published May 16, 2016The French adopted the Gras as their first mass-issued metallic cartridge rifle in 1874, replacing the needlefire 1866 Chassepot. Quite a lot of Gras rifles were manufactured, and they became a second-line rifle when the 1886 Lebel was introduced with brand-new smokeless powder and its smallbore 8mm projectile. When it became clear that the quick and decisive war against Germany was truly turning into the Great War, France began looking for ways to increase the number of modern Lebel rifles it could supply to the front.
One option that was used was to take Gras rifles from inventory and rebarrel them for the 8mm Lebel cartridge (which was based on the Gras casehead anyway). These could be issued to troops who didn’t really need a top-of-the-line rifle (like artillery crews, train and prison guards, etc). Then the Lebel rifles from those troops could be redirected to the front.
The rebarreling process was done by a number of contractors, using Lebel barrels already in mass production. The 11mm barrel from the Gras would be removed, and only the front 6 inches (150mm) or so kept. A Lebel barrel and rear sight would be mounted on the Gras receiver, and that front 6 inches of Gras barrel bored out to fit tightly over the muzzle of the new 8mm barrel. This allowed the original stock and nosecap to be used (the 8mm barrel being substantially smaller in diameter, and not fitting the stock and hardware by itself). It also allowed the original Gras bayonet to be fitted without modification, since the bayonet lug was also on that retained section of barrel. In addition, a short wooden handguard was fitted. This was designated the modification of 1914, and an “M14” was stamped on the receivers to note it.
These guns are of dubious safety to shoot, since the retain the single locking lug of the Gras, designed for only black powder pressures. However, this was deemed safe enough for the small amount of actual shooting they were expected to do.
QotD: The mid-life crisis, male and female versions
Most men get over the strippers-and-sports-cars overreaction pretty quickly, generally to be replaced by a new outlook on life. The guys who have come through the midlife crisis are generally a lot better people — more focused, more outgoing, far less materialistic — because they’ve taken up, however briefly, the perspective of Eternity. If you’re religious, you wonder if you’ll merit heaven. If you’re not, you wonder how you’ll be remembered. Either way, you start thinking about the kind of world you want to leave behind you, and what you’re going to do to achieve it with whatever time is left to you.
Which is why I’ve found the COVID overreaction so bizarre. Realizing your own mortality changes things. You can always tell, for instance, when it has happened to a younger person — when they come home, combat vets often act like middle-aged men going through a midlife crisis. Readjustment to civilian life is hard. Read the great war narratives, and it’s clear that none of them ever really “got over it”. Robert Graves and Ernst Junger, for instance, both lived to ripe old ages (90 and 103, respectively), and were titans in fields far removed from battle … and yet, the war WAS their lives, in some way we who haven’t been through it will never understand, and it comes through in every line they wrote.
If the Covidians were really freaking out about COVID, then, I’d expect one of two broad types of reaction: Either party-hearty midlife crisis mode, or a new determination to get on with whatever’s left of life. Obviously neither of those are true, and I just can’t grasp it — these might be your last few weeks on Earth, and that’s how you’re going to spend them? Sitting in your apartment like a sheep, wearing a mask and eating takeout, glued to a computer screen?
If you want a measure of just how feminized our society has become, there you go. Call this misogyny if you must, but it’s an easily observed fact of human nature — indeed, it has been observed, in every time, place, and culture of which we have knowledge — that post-menopausal women go a bit batty. Though a man might know for certain that he dies tomorrow, he can still keep plugging away today, because he’s programmed to find real meaning in his “work” — we are, after all, running our snazzy new mental software over kludgy old caveman hardware.
Women aren’t like that. They have one “job”, just one, and when they can’t do it anymore, they get weird. In much the same way high-end sports cars would cease to exist if middle aged men ceased to exist, so there are entire aspects of culture that don’t make sense in any other way except: These are channels for the energies of post-menopausal, and therefore surplus-to-requirements, women. You could go so far as to say that pretty much everything we call culture — traditions, history, customs — exist for that reason. Women go from being the bearers, to being the custodians, of the tribe’s future.
Severian, “Life’s Back Nine”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-05-11.
April 16, 2024
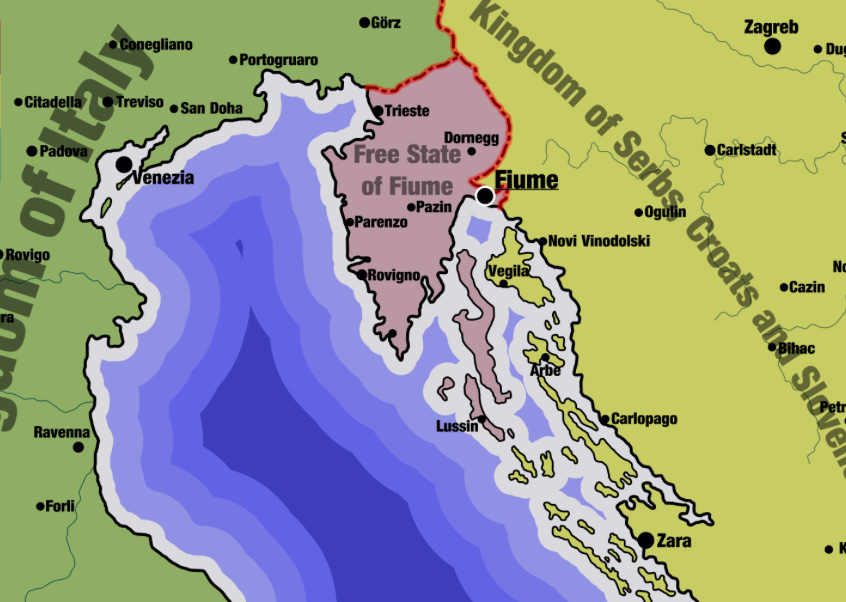
Gabriele D’Annunzio’s Impresa – the 1919 occupation of Fiume
Ned Donovan on the turbulent history of the Adriatic port of Fiume (today the Croatian city of Rijeka) after the end of the First World War:
Fiume was a port on the Adriatic coast with several thousand residents, almost half of whom were ethnic Italians that had been under Austro-Hungarian rule for several hundred years after it once having been a Venetian trade port. By some quirk, Fiume was missed in the Treaty of London, probably because it had never been envisioned by the Allies that the Austro-Hungarian Empire would ever truly disintegrate and the rump of it that would remain required a sea port in some form. The city’s other residents were ethnically Serbian and Croatian, who knew the city as Rijeka (as you will find it named on a map today). All of this complexity meant that the fate of Fiume became a major topic of controversy during the Versailles Peace Conference. President Woodrow Wilson had become so unsure of what to do that he proposed the place become a free city and the headquarters of the nascent League of Nations, under the jurisdiction of no country.
By September 1919 there was still no conclusion as to the fate of Fiume. Events had overtaken the place and through the Treaty of St Germain, the Austro-Hungarian Empire had been dissolved after the abdication of the final Habsburg Emperor Charles I. Once again, Fiume had not been mentioned in the treaty and the country it had been set aside for no longer existed. The city’s fate was still at play.
Enter Gabriele D’Annunzio, an aristocrat from Abruzzo on the eastern coast of Italy. Born in 1863, he was a handsome and intelligent child and was nurtured by his family to be exceptional, with a predictable side effect of immense selfishness. As a teenager, he had begun to dabble in poetry and it was praised by authors unaware of his age. At university he began to be associated with Italian irredentism, a philosophy that yearned for all ethnic Italians to live in one country – by retaking places under foreign rule like Corsica, Malta, Dalmatia and even Nice.
[…]
The Italian government’s lack of interest [in Fiume] was unacceptable to D’Annunzio and he made clear he would take action to prevent it becoming part of Yugoslavia by default. With his fame and pedigree he was able to quickly assemble a small private force of ex-soldiers, who he quickly took to calling his “legionaries”. In September 1919 after the Treaty of St Germain was signed, his small legion of a few hundred marched from near Venice to Fiume in what they called the Impresa – the Enterprise. By the time he had reached Fiume, the “army” numbered in the thousands, the vanguard crying “Fiume or Death” with D’Annunzio at its head in a red Fiat.
The only thing that stood in his way was the garrison of the Entente, soldiers who had been given orders to prevent D’Annunzio’s invasion by any means necessary. But amongst the garrison’s leaders were many [Italian officers] sympathetic to D’Annunzio’s vision, some even artists themselves and before long most of the defenders had deserted to join the poet’s army. On the 12th September 1919, Gabriele D’Annunzio proclaimed that he had annexed Fiume to the Kingdom of Italy as the “Regency of Carnaro” – of which he was the Regent. The Italian government was thoroughly unimpressed and refused to recognise their newest purported land, demanding the plotters give up. Instead, D’Annunzio took matters into his own hands and set up a government and designed a flag (to the right).
The citizens of what had been a relatively unimportant port quickly found themselves in the midst of one of the 20th Century’s strangest experiments. D’Annunzio instituted a constitution that combined cutting-edge philosophical ideas of the time with a curious government structure that saw the country divided into nine corporations to represent key planks of industry like seafarers, lawyers, civil servants, and farmers. There was a 10th corporation that existed only symbolically and represented who D’Annunzio called the “Supermen” and was reserved largely for him and his fellow poets.
These corporations selected members for a state council, which was joined by “The Council of the Best” and made up of local councillors elected under universal suffrage. Together these institutions were instructed to carry out a radical agenda that sought an ideal society of industry and creativity. From all over the world, famous intellectuals and oddities migrated to Fiume. One of D’Annunzio’s closest advisers was the Italian pilot Guido Keller, who was named the new country’s first “Secretary of Action” – the first action he took was to institute nationwide yoga classes which he sometimes led in the nude and encouraged all to join. When not teaching yoga, Keller would often sleep in a tree in Fiume with his semi-tame pet eagle and at least one romantic partner.
If citizens weren’t interested in yoga, they could take up karate taught by the Japanese poet Harukichi Shimoi, who had translated Dante’s works into Japanese. Shimoi, who quickly became known to the government of Fiume as “Comrade Samurai” was a keen believer in Fiume’s vision and saw it as the closest the modern world had come to putting into practice the old Japanese art of Bushido.
The whole thing would have felt like a fever dream to an outsider. If a tourist was to visit the city, they would have found foreign spies from across the world checking into hotels and rubbing shoulders with members of the Irish republican movement while others did copious amounts of cocaine, another national pastime in Fiume. The most fashionable residents of Fiume carried little gold containers of the powder, and D’Annunzio himself was said to have a voracious habit for it. Sex was everywhere one turned and the city had seen a huge inward migration of prostitutes and pimps within days of D’Annunzio’s arrival. Almost every day was a festival, and it was an odd evening if the harbour of Fiume did not see dozens of fireworks burst above it, watched on by D’Annunzio’s uniformed paramilitaries.
D’Annunzio himself lived in a palace overlooking the city, Osbert Sitwell describes walking up a steep hill to a Renaissance-style square palazzo which inside was filled with plaster flowerpots the poet had installed and planted with palms and cacti. D’Annunzio would cloister himself in his rooms for 18 hours a day and without food. Immaculate guards hid amongst the shrubs to ensure he would not be disturbed. In D’Annunzio’s study, facing the sea, he sat with statutes of saints and with French windows onto the state balcony. When he wanted to interact with his people he would wait for a crowd to form over some issue, walk to the balcony and then ask what they wanted.
April 15, 2024
Simon & Schuster, founded 1924
In the latest SHuSH newsletter, Ken Whyte provides a thumbnail history of the American publishing house Simon & Schuster:
The firm was started by Richard Leo Simon, a Great War veteran and piano salesman, and his partner, Max Lincoln Schuster, an auto magazine editor. They had met when Simon failed to sell Schuster a piano. They scraped together $8,000 in savings and loans from friends, family, and a telephone operator, and launched their first title in 1924: The Cross Word Puzzle Book, a collection compiled by the editors of the New York World, which was reputed to have the best crossword of the day. Each copy of the book came with a pencil and an eraser.
Messrs. Simon and Schuster initially called themselves The Plaza Publishing Company (something S&S doesn’t mention on its history webpage). They didn’t want to be personally associated with a novelty publishing project.
The novelty project sold 40,000 copies in three months and just under half a million in its first year, earning the boys a profit of $100,000, which has to be the fastest start ever for a book publisher. The Cross Word Puzzle Book was a cash cow for decades to come — there were at least fifty-six more editions, the vast majority published as S&S books. Its proceeds funded many better quality publishing initiatives.
Will Durant’s The Story of Philosophy was published in 1926 to critical success and impressive sales. Hervey Allen’s Anthony Adverse won the Pulitzer in 1934, as did Thomas Wolfe’s You Can’t Go Home Again in 1940. Will and Ariel Durant’s eleven-volume The Story of Civilization, which started publishing in 1935 and would take forty years to complete, also won a Pulitzer and was another huge seller.
By the time S&S acquired the paperback rights to Margaret Mitchell’s Gone with the Wind in 1942 and Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby in 1945, it was already the leading publisher in America. To make sure everyone knew it, the boys moved into a stunning new headquarters at one of the most expensive addresses in the world, 1230 Avenue of the Americas, part of Rockefeller Center.
While it was winning its share of literary awards and publishing some great books, Simon & Schuster never forgot its roots in commercial projects. In mid-life it was famous as the how-to publisher: How to Read a Book, How to Improve your Memory, How to Raise a Dog, How to Think Straight, How to Play Winning Checkers, and the bestselling granddaddy of them all, Dale Carnegie’s How to Win Friends and Influence People, which has sold a staggering thirty million copies and still routinely shows up on bestseller lists.
Interestingly, the operational brains behind S&S was an unnamed partner, Leonard Shimkin, who joined the company as business manager at age seventeen. It was largely at Shimkin’s initiative that S&S launched Pocket Books in 1939, establishing the concept of inexpensive paperbacks, which broadened the reading public and opened the door to the expansion of genre fiction. He was also the one who walked Dale Carnegie into S&S.
The boys sold the company to Marshall Field, owner of the Chicago Sun, in 1944 but continued to work at it. They bought it back when Field died in 1956, this time with Shimkin taking an equity position. Simon retired in 1957 and Schuster not long after, eventually leaving Shimkin with sole ownership.
Meanwhile, the hits kept coming. Joseph Heller’s Catch-22 in 1961, Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring in 1962, Capote’s In Cold Blood in 1966, Alex Haley’s Roots in 1976, Larry McMurtry’s Lonesome Dove in 1985, Stephen Hawking’s A Brief History of Time in 1988, and so on.
In 1975, Shimkin sold S&S to Gulf + Western, the first in a depressing series of corporate foster homes, none of which has known anything about or cared anything for books. G+W became Paramount in 1989, which was acquired by Viacom in 1994, which split into two companies in 2005, with Simon & Schuster becoming part of CBS Corporation, which in 2019 was merged back with Viacom, which in 2022 changed its name to Paramount Global and, after failing to unload S&S to Penguin Random House that same year, landed it with KKR the next. More on why all the corporate shuffling is far from over here.
Simon & Schuster and its subsidiary, Scribner, are the last great American-owned monuments to the golden age of American book publishing, which runs from about 1920 through to … I don’t know, the 1970s? All the others — Random House, Knopf, HarperCollins, Little, Brown & Co. — are owned by foreign conglomerates (HC’s owner, News Corp, is technically American but its controlling family, the Murdochs, are culturally British when they’re not being Australian).
The MOST INCOMPETENT Railroad You’ve Ever Seen!
Southern Plains Railfan
Published Jan 6, 2024In today’s video, we recount the time Penn Central let nearly all of Maine’s potato harvest rot in Selkirk yard; ruining thousands of lives and nearly taking down other railroads in the process.
Merch Shop: http://okieprint.com/SPR/shop/home
QotD: Cereal cultivation also helped grow the centralized state
Sumer just before the dawn of civilization was in many ways an idyllic place. Forget your vision of stark Middle Eastern deserts; in the Paleolithic the area where the first cities would one day arise was a great swamp. Foragers roamed the landscape, eating everything from fishes to gazelles to shellfish to wild plants. There was more than enough for everyone; “as Jack Harlan famously showed, one could gather enough [wild] grain with a flint sickle in three weeks to feed a family for a year”. Foragers alternated short periods of frenetic activity (eg catching as many gazelles as possible during their weeklong migration through the area) with longer periods of rest and recreation.
Intensive cereal cultivation is miserable work requiring constant toil with little guarantee of a good harvest. Why would anyone leave this wilderness Eden for a 100% wheat diet?
Not because they were tired of wandering around; Scott presents evidence that permanent settlements began as early as 6000 BC, long before Uruk, the first true city-state, began in 3300. Sometimes these towns subsisted off of particularly rich local wildlife; other times they practiced some transitional form of agriculture, which also antedated states by millennia. Settled peoples would eat whatever plants they liked, then scatter the seeds in particularly promising-looking soil close to camp – reaping the benefits of agriculture without the back-breaking work.
And not because they needed to store food. Hunter-gatherers could store food just fine, from salting animal meat to burying fish and letting it ferment to just having grain in siloes like everyone else. There is ample archaeological evidence of all of these techniques. Also, when you are surrounded by so much bounty, storing things takes on secondary importance.
And not because the new lifestyle made this happy life even happier. While hunter-gatherers enjoyed a stable and varied diet, agriculturalists subsisted almost entirely on grain; their bones display signs of significant nutritional deficiency. While hunter-gatherers were well-fed, agriculturalists were famished; their skeletons were several inches shorter than contemporaneous foragers. While hunter-gatherers worked ten to twenty hour weeks, agriculturalists lived lives of backbreaking labor. While hunter-gatherers who survived childhood usually lived to old age, agriculturalists suffered from disease, warfare, and conscription into dangerous forced labor.
Scott Alexander, “Book Review: Against The Grain“, Slate Star Codex, 2019-10-15.
April 14, 2024
Soviets Take Vienna and Königsberg – WW2 – Week 294 – April 13, 1945
World War Two
Published 13 Apr 2024The prizes of Vienna and Königsberg fall to the Soviets as they continue what seems an inexorable advance. In the West the Allies advance to the Elbe River, but there they are stopped by command. The big news in their national papers this week is the death of American President Franklin Roosevelt, which provokes rejoicing in Hitler’s bunker. The Allied fighting dash for Rangoon continues in Burma, as does the American advance on Okinawa, although Japanese resistance is stiffening and they are beginning counterattacks.
Chapters
00:32 Recap
01:05 Operation Grapeshot
01:57 Roosevelt Dies
06:01 Soviet Attack Plans for Berlin
12:45 Stalin’s Suspicions
14:31 The fall of Königsberg
17:02 The fall of Vienna
18:38 Japanese Resistance on Okinawa
20:34 The War in China
21:09 Burma and the Philippines
22:38 Summary
22:57 Conclusion
25:05 Memorial
(more…)
Elmer Keith’s Revolver Number 5
Forgotten Weapons
Published Feb 28, 2015Elmer Keith’s No.5 Single Action Army is arguably the most famous custom revolver ever made. Keith had it built in 1928 after developing a friendship with Harold Croft, another revolver enthusiast. Croft had shown Keith his own custom revolvers, which he had numbered 1 through 4. Croft had been trying to make an ideal pocket gun, and Keith used several of his ideas along with some of Keith’s own to put together a revolver for general-purpose field use. In recognition of Croft’s work, Keith called his gun Number 5. It featured an extended flat top with windage-adjustable sights, an improved mainspring, redesigned cylinder pin, custom hammer spur, and modified Bisley grip. It was chambered for the .44 Special/.44 Russian cartridges (the Russian being a slightly shorter version of the Special), and it was Keith’s favorite shooting piece until the .44 Magnum cartridge was introduced in the late 1950s. He described this gun in detail in a 1929 American Rifleman article entitled “The Last Word”.
http://www.forgottenweapons.com
Theme music by Dylan Benson – http://dbproductioncompany.webs.com
QotD: Imperium in the Roman Republic
What connects these offices in particular is that they confer imperium, a distinctive concept in Roman law and governance. The word imperium derives from the verb impero, “to command, order” and so in a sense imperium simply means “command”, but in its implication it is broader. Imperium was understood to be the power of the king (Cic. Leg. 3.8), encompassing both the judicial role of the king in resolving disputes and the military role of the king in leading the army. In this sense, imperium is the power to deploy violence on behalf of the community: both internal (judicial) violence and external (military) violence.
That power was represented visually around the person of magistrates with imperium through the lictors (Latin: lictores), attendants who follows magistrates with imperium, mostly to add dignity to the office but who also could act as the magistrate’s “muscle” if necessary. The lictors carried the fasces, a set of sticks bundled together in a rod; often in modern depictions the bundle is thick and short but in ancient artwork it is long and thin, the ancient equivalent of a policeman’s less-lethal billy club. That, notionally non-lethal but still violent, configuration represented the imperium-bearing magistrate’s civil power within the pomerium (recall, this is the sacred boundary of the city). When passing beyond the pomerium, an axe was inserted into the bundle, turning the non-lethal crowd-control device into a lethal weapon, reflective of the greater power of the imperium-bearing magistrate to act with unilateral military violence outside of Rome (though to be clear the consul couldn’t just murder you because you were on your farm; this is symbolism). The consuls were each assigned 12 lictors, while praetors got six. Pro-magistrates [proconsuls and propraetors] had one fewer lictor than their magistrate versions to reflect that, while they wielded imperium, it was of an inferior sort to the actual magistrate of the year.
What is notable about the Roman concept of imperium is that it is a single, unitary thing: multiple magistrates can have imperium, you can have greater or lesser forms of imperium, but you cannot break apart the component elements of imperium.1 This is a real difference from the polis, where the standard structure was to take the three components of royal power (religious, judicial and military) and split them up between different magistrates or boards in order to avoid any one figure being too powerful. For the Romans, the royal authority over judicial and military matters were unavoidably linked because they were the same thing, imperium, and so could not be separated. That in turn leads to Polybius’ awe at the power wielded by Roman magistrates, particularly the consuls (Polyb. 6.12); a polis wouldn’t generally focus so much power into a single set of hands constitutionally (keeping in mind that tyrants are extra-constitutional figures).
So what does imperium empower a magistrate to do? All magistrates have potestas, the power to act on behalf of the community within their sphere of influence. Imperium is the subset of magisterial potestas which covers the provision of violence for the community and it comes in two forms: the power to raise and lead armies and the power to organize and oversee courts. Now we normally think of these powers as cut by that domi et militiae (“at home and on military service”) distinction we discussed earlier in the series: at home imperium is the power to organize courts (which are generally jury courts, though for some matters magistrates might make a summary judgement) and abroad the power to organize armies. But as we’ll see when we get to the role of magistrates and pro-magistrates in the provinces, the power of legal judgement conferred by imperium is, if anything, more intense outside of Rome. That said it is absolutely the case that imperium is restrained within the pomerium and far less restrained outside of it.
There were limits on the ability of a magistrate with imperium to deploy violence within the pomerium against citizens. The Lex Valeria, dating to the very beginning of the res publica stipulated that in the case of certain punishments (death or flogging), the victim had the right of provocatio to call upon the judgement of the Roman people, through either an assembly or a jury trial. That limit to the consul’s ability to use violence was reinforced by the leges Porciae (passed in the 190s and 180s), which protected civilian citizens from summary violence from magistrates, even when outside of Rome. That said, on campaign – that is, militae rather than domi – these laws did not exempt citizen soldiers from beating or even execution as a part of military discipline and indeed Roman military discipline struck Polybius – himself an experienced Greek military man – as harsh (Polyb. 6.35-39).
In practice then, the ability of a magistrate to utilize imperium within Rome was hemmed in by the laws, whereas when out in the provinces on campaign it was far less limited. A second power, coercitio or “coercion” – the power of a higher magistrate to use minor punishments or force to protect public order – is sometimes presented as a distinct power of the magistrates, but I tend to agree with Lintott (op. cit., 97-8) that this rather overrates the importance of the coercive powers of magistrates within the pomerium; in any case, the day-to-day maintenance of public order generally fell to minor magistrates.
While imperium was a “complete package” as it were, the Romans clearly understood certain figures as having an imperium that outranked others, thus dictators could order consuls, who could order praetors, the hierarchy neatly visualized by the number of lictors each had. This could create problems, of course, when Rome’s informal systems of hierarchy conflicted with this formal system, for instance at the Battle of Arausio, the proconsul Quintus Servilius Caepio refused to take orders from the consul, Gnaeus Mallius Maximus, because the latter was his social inferior (being a novus homo, a “new man” from a family that hadn’t yet been in the Senate and thus not a member of the nobiles), despite the fact that by law the imperium of a sitting consul outranked that of a pro-consul. The result of that bit of insubordination was a military catastrophe that got both commanders later charged and exiled.
Finally, a vocabulary note: it would be reasonable to assume that the Latin word for a person with imperium would be imperator2 because that’s the standard way Latin words form. And I will say, from the perspective of a person who has to decide at the beginning of each thing I write what circumlocution I am going to use to describe “magistrate or pro-magistrate with imperium“, it would be remarkably fortunate if imperator meant that, but it doesn’t. Instead, imperator in Latin ends up swallowed by its idiomatic meaning of “victorious general”, as it was normal in the republic for armies to proclaim their general as imperator after a major victory (which set the general up to request a triumph from the Senate). In the imperial period, this leads to the emperors monopolizing the term, as all of the armies of Rome operated under their imperium and thus all victory accolades belonged to the emperor. That in turn leads to imperator becoming part of the imperial title, from where it gives us our word “emperor”.
That said, the circumlocution I am going to use here, because this isn’t a formal genre and I can, is “imperium-haver”. I desperately wish I could use that in peer reviewed articles, but I fear no editor would let me (while Reviewer 2 will predictably object to “general”, “commander” or “governor” for all being modern coinages).3
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: How to Roman Republic 101, Part IIIb: Imperium”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2023-08-18.
1. I should note here that Drogula (in Commanders and Command (2015)) understands imperium a bit differently than this more traditional version I am presenting (in line with Lintott’s understanding). He contends that imperium was an entirely military power which was not necessary for judicial functions and was not only indivisible but also, at least early on, did not come in different degrees. In practice, I’m not sure the Romans were ever so precise with their concepts as Drogula wants them to be.
2. Pronunication note because this bothers me when I hear this word in popular media: it is not imPERator, but impeRAtor, because that “a” is long by nature, and thus keeps the stress.
3. And yes, really, I have had reviewers object to “general” or “commander” to mean “the magistrate or pro-magistrate with imperium in the province”. There is no pleasing Reviewer 2.
April 13, 2024
When there was an active counterculture
Ted Gioia on a recent oral history of the countercultural touchstone, The Village Voice:
At the start of her oral history of The Village Voice, author Tricia Romano provides a “cast of characters”. It goes on for 15 pages, and includes 216 people — each with some connection to the alternative newspaper.
Many people nowadays have never lived in a society with such a vibrant counterculture. In a time when official sources all seem part of a predictable Disney-fied monoculture, just reading this list of names and mini-bios can be a revelation.
Many of these individuals are now revered as historic figures who changed society. They had power and prestige. It’s easy to forget that most of them operated as outsiders.
That’s how they wanted it.
These renegades at The Village Voice knew that working outside the system — and typically against the system — was their superpower. They could criticize ruling institutions. They could speak harsh truths. They could go against the grain.
One thing is certain: They didn’t align their interests with globalist corporate CEOs, billionaire technocrats, the surveillance state, and establishment bureaucracies. They would have laughed at journalists who did that — believing, rightly, that honest media requires distance, or even an adversarial stance, vis-à-vis entrenched powers.
Because that’s what a counterculture does. That’s what it’s expected to do.
Romano captures the peculiar vibe in the title of her book The Freaks Came Out to Write. She makes clear that The Village Voice wasn’t The New York Times and it definitely wasn’t The New Yorker.
Nobody ever stepped into its madcap offices and said “Ah, the Gray Lady”. No reader ever picked up a copy and expected to see Eustace Tilley on the cover.
And The Voice was heard. Even establishment insiders knew they needed to listen to these “Freaks”. Sometimes they feared The Voice, sometimes they secretly agreed with it, but they always treated it as a force deserving respect.
Until recently that’s how it worked. The tension between insiders and outsiders was a source of creative energy in society. The upstarts provided alternative views and new ideas. They kept everybody accountable.
I’m pointing this out because this no longer happens. This is the world we’ve lost.
The Death of Franklin Roosevelt
World War Two
Published 12 Apr 2024He lead his nation through the Great Depression, transformed it into a war-winning titan, and is working to shape the coming postwar world in his image. But today, 4,422 days into his record breaking presidency, Franklin Roosevelt dies. What was his final year really like?
(more…)