The first Great Commandment of scholarship is be honest; everything else is commentary. All the standards and methods that scholars have developed over the ages can be reduced to “be honest”.
Of course, fraudulent scholars have always existed, but it seems to me — not that I’ve conducted a study of the matter — that clear dishonesty by leading scholars no longer elicits widespread condemnation and no longer discredits the guilty parties to the extent that it used to. The Nancy MacLean affair [her book Democracy in Chains (2017) was an extended character assassination of Nobel Prize winning economist James M. Buchanan] is clear-cut. Thomas Piketty’s work is either blatantly dishonest or spectacularly incompetent. And many other examples might be adduced. Ideology, it seems, has overwhelmed scholars in the humanities and social sciences to an unprecedented degree.
Scholars should be seeking the truth, the whole truth, and nothing but the truth, however much they appreciate that this objective can never be attained fully. They are obliged to strive. If they clearly are not trying, indeed, are twisting and turning in the ideological wind above all, real scholars should drum them out of their professions as unworthy of recognition by genuine scholars.
Bob Higgs, Facebook, 2019-08-28.
February 27, 2024
QotD: The role of the scholar
February 7, 2024
As the media now tell us, it’s dangerous to do your own research and you should just trust them about everything
David Friedman has some timely tips on how you might go about determining the truth of an assertion offered in the legacy media or online source of undetermined trustworthiness:
Following up the claim you come across an article, perhaps even a book, which does indeed support that claim. Should you believe it?
The short answer for all of those examples, some of them claims I agree with, is that you should not. As I think I have demonstrated in past posts, claimed proofs of contentious issues are quite often wrong, biased, even fraudulent.
More examples from previous posts, here or on my old blog:
An estimate of the cost of a ton of carbon dioxide calculated with about half the total depending on the implicit assumption of no progress in medicine for the next three centuries.
A factbook on state and local finance that deliberately omitted the most important relevant fact that readers were unlikely to know.
A textbook, in its third edition, with multiple provably false claims.
The important question is how to tell. There are three answers:
1. Read the book or article carefully, check at least some of its claims — easier now that the Internet provides you with a vast searchable library accessible from your desktop — and evaluate its argument for yourself. Doing this is costly in time and effort and requires skills you may not have; depending on the particular issue that might include near-professional expertise in statistics, history, physics, economics, or any of a variety of other fields. I have taught elementary statistics at various points in my career, both in an economics department and a law school, but gave up on a controversy of considerable interest to me (concealed carry) when the statistical arguments got above the level I could readily follow.
2. Find one or more competent critiques of the argument and see if you find them convincing. This is the previous answer on easy mode. You still have to think things through but you don’t have to search out mistakes in the argument for yourself because the critic will point you at them, with luck offer evidence.
There are three possible conclusions that that exercise may support: that the argument is wrong. that it might be wrong, that it is probably right. The way you reach the last conclusion is from the incompetence or dishonesty of the critique; I am thinking of a real case.
John Boswell, a gay historian at Yale, argued that both the scriptures and early Christianity, unlike modern Christian critics of homosexual sex, treated it as no worse than other forms of non-marital intercourse. What convinced me that Boswell had a reasonable case was reading an attack on him by a prominent opponent which badly misrepresented the contents of the book I had just read. People who have good arguments do not need bad ones.
Of course, there might be other critics with better arguments.
An entertaining version of this approach is to find an online conversation with intelligent people covering a wide range of views and follow discussions of whatever issues you are interested in. With luck all of the good arguments for both sides will get made and you can decide for yourself whether one side, the other, or neither is convincing. Forty years ago I could do it in the sf groups on Usenet, which contained lots of smart people who liked to argue. Five years ago I could do it in the comment threads of Slate Star Codex. Currently Data Secrets Lox works for a few controversies but the range of views represented on it is too limited to provide a fair view of most.
The comment threads of this blog are at present too thin for the purpose, with between one and two orders of magnitude fewer comments than the SSC average used to be, but perhaps in another few years …
3. Recognize that you don’t know whether the claim is true and have no practical way of finding out, at least no way that costs less in time and effort than it is worth. This is the least popular answer but probably the most often correct.
February 3, 2024
QotD: The Postmodernist’s Dilemma
If Leftists could see the obvious consequences of their own positions, they wouldn’t be Leftists. We know this. But since it’s their world, and we have to live in it as best we can, it helps to go back and spell out those obvious consequences from time to time. The biggest, most obvious one of all is what I’m going to call The Great Contradiction. It’s the obvious next step from the Great Inversion: If “whatever is, is wrong”; then all authority, everywhere, is illegitimate — which includes the authority proclaiming The Great Inversion.
We could also call it “the PoMo’s Dilemma”, since this stuff originated in the ivory tower back in the Sixties, and finally broke containment in the late Seventies. Most intellectual fads quickly become caricatures of themselves, but in their haste to get to the next hot new thing the PoMos decided to cut to the chase. Postmodernism started as a self-parody. Put simply but not at all unfairly, PoMo is the assertion for a fact that there is no such thing as a fact. There is no Truth, just “truth”. No eternal verities, just perspective, just discourse; it’s all — say it with me now — “just a social construction”.
I suppose we must give the early PoMos credit for having — in a thoroughly Postmodern way – the courage of their convictions. When Alan Sokal invited the PoMos to try transgressing the Law of Gravity from his twenty-first floor apartment window, the goofs from Social Text published a “rebuttal” to Sokal, informing him, a working physicist, that they, the English Department, understood physics better than he did. He meant it as a joke, but he was really right all along about the so-called “law” of “gravity”.
That was 1996. At that point, any sane society would’ve had the editors of Social Text dragged out of the faculty lounge and shot in the middle of the quad, pour encourager les autres. But of course we chose not to. And why would we? Being close to three decades deep into the Great Inversion by then, we got much barmier stuff than anything Social Text published in freshman orientation. Stick it to The Man, we were told, and don’t trust anyone over thirty …
Severian, “Hoist on Their Own Petard”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-04-19.
January 25, 2024
QotD: How Meritocracy morphed into “Meritocracy”
The current meritocratic system began as an effort to open up a hereditary WASP elite to outsiders — and for a while, as immigrants, minorities, and women earned their way into America’s legacy campuses, writes Markovits, it looked like it was working more or less as intended. In the last few decades, however, the system has morphed into a do-or-die tournament for the prize of an Ivy League degree and a bonus-rich job at a swanky address. Instead of being democracies of talent, Harvard and Yale and their elite cronies are now quasi-exclusive clubs for the children of wealth. Money gives rich parents the means to groom their kids for these clubs as early as infancy with classes, books, and trips to museums meant to enhance kids’ development. They move to wealthy neighborhoods, where schools offer a vast array of (ahem) “enrichment” activities, including test prep and college-essay tutoring. Alternatively, they put their kids through 12 years of $40,000-a-year-plus private schools, whose administrators just happen to be chummy with Princeton admission officers.
Their efforts pay off for their progeny, but in the harsh competition that is the contemporary economy, they leave everyone else in the dust. Nourished in the hothouse of elite homes and communities, rich children have pulled away from their middle-class counterparts when it comes to academic performance, outscoring them on the SAT by twice as much as middle-class kids outscore poor students. The most elite colleges enroll more students from households in the top 1 percent than from the entire bottom half of the income scale. Those students are first in the pipeline to elite jobs. Top banks go only to the Ivy League, MIT, and Stanford for their recruiting. Top Five law schools are the training grounds for partners at the poshest firms. Meantime, middle-class kids are not only a rare sight on elite campuses; they’re also far less likely to get any college degree. Poor kids do worse still.
The result, says Markovits, is precisely the sort of dynastic elite that the putatively unbiased SAT was supposed to put out of business. To the dismay of his critics on the left, Markovits is not entirely unsympathetic to the winners of the tournament. The rich used to be indolent, he reminds us. The whole point of wealth was to be freed from toil, while peasants sweated in fields and manor kitchens to serve their betters and eke out a living for their undernourished families. These days, by contrast, the rich work 16-hour days and weekends under immense competitive pressure to close the deal, make partner, and take a conference call with Japanese businessmen. “No prior elite has ever been as capable or as industrious as the meritocratic elite that such training produces. None comes close,” Markovits asserts. Yes, a few actresses and real estate barons try to bribe and cheat their children into the palaces of learning, but most Ivy Leaguers have used their privileged upbringing to make their way into these bastions according to the rules of achievement. Given the expensive grooming required to make it to the top campuses, he implies, a squeaky-clean meritocracy would still favor the rich.
Kay S. Hymowitz, “Meritocrats versus Meritocracy”, City Journal, 2019-10-11.
January 20, 2024
January 2, 2024
December 31, 2023
QotD: Orwell as a “failed prophet”
Some critics do not fault [Nineteen Eighty-Four] on artistic grounds, but rather judge its vision of the future as wildly off-base. For them, Orwell is a naïve prophet. Treating Orwell as a failed forecaster of futuristic trends, some professional “futurologists” have catalogued no fewer than 160 “predictions” that they claim are identifiable in Orwell’s allegedly poorly imagined novel, pertaining to the technical gadgetry, the geopolitical alignments, and the historical timetable.
Admittedly, if Orwell was aiming to prophesy, he misfired. Oceania is a world in which the ruling elite espouses no ideology except the brutal insistence that “might makes right”. Tyrannical regimes today still promote ideological orthodoxy — and punish public protest, organized dissidence, and conspicuous deviation. (Just ask broad swaths of the citizenry in places such as North Korea, Venezuela, Cuba, and mainland China.) Moreover, the Party in Oceania mostly ignores “the proles”. Barely able to subsist, they are regarded by the regime as harmless. The Party does not bother to monitor or indoctrinate them, which is not at all the case with the “Little Brothers” that have succeeded Hitler and Stalin on the world stage.
Rather than promulgate ideological doctrines and dogmas, the Party of Oceania exalts power, promotes leader worship, and builds cults of personality. In Room 101, O’Brien douses Winston’s vestigial hope to resist the brainwashing or at least to leave some scrap of a legacy that might give other rebels hope. “Imagine,” declares O’Brien, “a boot stamping on a human face — forever.” That is the future, he says, and nothing else. Hatred in Oceania is fomented by periodic “Hate Week” rallies where the Outer Party members bleat “Two Minutes Hate” chants, threatening death to the ever-changing enemy. (Critics of the Trump rallies during and since the presidential campaign compare the chants of his supporters — such as “Lock Her Up” about “Crooked Hillary” Clinton and her alleged crimes — to the Hate Week rallies in Nineteen Eighty-Four.)
Yet all of these complaints about the purported shortcomings of Nineteen Eighty-Four miss the central point. If Orwell “erred” in his predictions about the future, that was predictable — because he wasn’t aiming to “predict” or “forecast” the future. His book was not a prophecy; it was — and remains — a warning. Furthermore, the warning expressed by Orwell was so potent that this work of fiction helped prevent such a dire future from being realized. So effective were the sirens of the sentinel that the predictions of the “prophet” never were fulfilled.
Nineteen Eighty-Four voices Orwell’s still-relevant warning of what might have happened if certain global trends of the early postwar era had continued. And these trends — privacy invasion, corruption of language, cultural drivel and mental debris (prolefeed), bowdlerization (or “rectification”) of history, vanquishing of objective truth — persist in our own time. Orwell was right to warn his readers in the immediate aftermath of the defeat of Hitler and the still regnant Stalin in 1949. And his alarms still resound in the 21st century. Setting aside arguments about forecasting, it is indisputable that surveillance in certain locales, including in the “free” world of the West, resembles Big Brother’s “telescreens” everywhere in Oceania, which undermine all possibility of personal privacy. For instance, in 2013, it was estimated that England had 5.9 million CCTV cameras in operation. The case is comparable in many European and American places, especially in urban centers. (Ironically, it was revealed not long ago that the George Orwell Square in downtown Barcelona — christened to honor him for his fighting against the fascists in the Spanish Civil War — boasts several hidden security cameras.)
Cameras are just one, almost old-fashioned technology that violates our privacy, and our freedoms of speech and association. The power of Amazon, Google, Facebook, and other web systems to track our everyday activities is far beyond anything that Orwell imagined. What would he think of present-day mobile phones?
John Rodden and John Rossi, “George Orwell Warned Us, But Was Anyone Listening?”, The American Conservative, 2019-10-02.
December 15, 2023
“Cletus is ’bout to go kinetic, y’all”!
Chris Bray turns to movie trailer analysis as a break from his usual work. Oh, wait, no it’s not really much of a break:
Cletus is ’bout to go kinetic, y’all. I got the news straight from brunch in Brentwood, where people really understand Middle America.
The trailer has dropped for a major new movie about an American civil war. No, not that one: the next one, with the dictatorial president who seizes an unconstitutional third term and refuses to leave the White House, and is an old white guy with big hair who drawls and thinks the world of himself and totally isn’t like any real person they’re trying to compare him to.
Note that the sniper in the thumbnail has camouflaged his rifle with a pile of spaghetti to avoid being seen, but is also wearing … nail polish? I am unfamiliar with this military doctrine, but if you ever find yourself in a war, wear bright shiny things so you blend in with the trees. I hope we’ve all seen the White House Christmas video this year, because I think they might also be gesturing at this brand of postmodern ghillie suit:
Civil War is Hollywood’s other “America collapsing soon” movie, behind the Obama-backed Leave the World Behind, which sounds like a form of torture. […]
You can watch the Civil War trailer to see how utterly dogshit banal it is, but my favorite detail is that Texas and California form an alliance against the US government and secede together. Yes, a long line of development executives said, Texas and California share a political agenda and would obviously make common cause in an insurgency.
I beg you to get drunk and discover on your own what professional entertainment journalists, a real category of human existence, are saying about this movie.
Severian also saw the trailer and as you’d guess it just blew him away:
So let’s see here … Florida and Texas seceding, necessitating the use of airstrikes — indeed, of all available force — against Americans? Check. Journalists as heroes? Check. Brown-skinned folks with funny accents as the only real Americans? Check. A rebel assault on the capitol, complete with explosions at the very heart of Our Democracy™? Check! I don’t think they actually said the names in the trailer — I kinda skimmed, because it’s nauseating — but whaddaya wanna bet the President of Real America has a name like, oh, I dunno … “Joe Ryder”, and the President of Godawful Redneckistan has a name kinda like “Ronald Rumph”?
They’re really steeling themselves to do Whatever It Takes, aren’t they?
Noted in the comments by Andrew: “Fun fact no. 1: there is only one facility in the US that manufactures explosive ordinance for the military. Fun fact no. 2: that facility is in Texas.”
Oh, and apparently red sunglasses are the new MAGA hat.
December 12, 2023
Canadian politics – if you don’t like something, call it some kind of “genocide”
Tristin Hopper on the political mis-use of the technical term “genocide”, to the point that it’s almost become routine to describe something you oppose as a “genocide”:
In recent weeks, it’s become popular among Canada’s activist groups and even mainstream politicians to accuse Israel of “genocide”. In a since-deleted Thursday evening social media post, for one, NDP MP Don Davies accused Israel of “cultural genocide” against Palestinians. The United Church of Canada has also begun using the g-word in its official literature.
The charge doesn’t hold up on any material grounds. Unlike most genocided people, the Palestinian population has been soaring dramatically ever since the 1960s — all while retaining their traditional language and religion. Israel’s prosecution of its current conflict against Hamas, meanwhile, has featured any number of factors that are markedly out-of-step with an attempted genocide, including detailed evacuation orders and a rate of civilian casualties markedly lower than the global average.
But the charge doesn’t need to make sense, because it turns out Canada has been abusing the term “genocide” for quite some time. Coined amidst the Second World War by Polish lawyer Raphael Lemkin, “genocide” refers to the intentional destruction of an entire demographic of people.
While the most notable genocides involve systematized mass-murder, it’s not a requirement. As per the official definition struck in the immediate aftermath of the Holocaust, genocide can also include attempts to erase a people via birth control or indirect methods such as famine. It’s on these grounds that Canada has officially accused China of genocide regarding its Uyghur minority. Although Beijing is not mass-murdering the Uyghurs, they are rounding them up into “re-education” camps and mandating forced sterilization with the explicit intention of destroying the Uyghur way of life.
But among Western academic and activist circles, “genocide” has now been stretched to apply to almost anything, from emissions policy to the ethnic ratios in prisons. Below, a not-at-all comprehensive list of just how much of Canadian life has been accused of being genocidal.
November 17, 2023
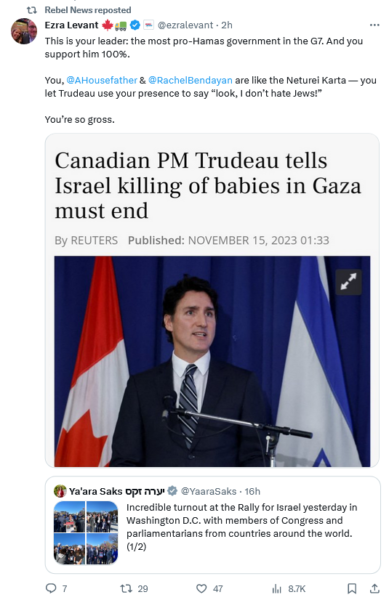
Israeli government responds strongly to Justin Trudeau’s accusations of deliberate killings of civilians
I guess the electoral calculus shows that there aren’t enough Jewish votes to be gained by backing Israel, so Justin Trudeau is going for the Islamic vote instead:
It’s not typical that an Israeli leader will issue an English-language excoriation of a friendly government in a time of war, but this week Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu made an exception for Prime Minister Justin Trudeau.
“While Israel is doing everything to keep civilians out of harm’s way, Hamas is doing everything to keep them in harm’s way,” said Netanyahu in a statement addressed to the Canadian leader. He added, “the forces of civilization must back Israel in defeating Hamas barbarism.”
.@JustinTrudeau It is not Israel that is deliberately targeting civilians but Hamas that beheaded, burned and massacred civilians in the worst horrors perpetrated on Jews since the Holocaust.
While Israel is doing everything to keep civilians out of harm’s way, Hamas is doing …
— Benjamin Netanyahu – בנימין נתניהו (@netanyahu) November 15, 2023
Netanyahu was reacting to prepared remarks Trudeau delivered in B.C. where he accused Israel of killing “women, children and babies”. The statement — which did not place any blame on Hamas for the carnage — urged Israel to exercise “maximum restraint” as “the world was watching”.
It’s but the latest incident in an official Trudeau government response to the Israel-Hamas conflict that has been checkered by confusion, contradiction — and a noticeable alienation from Canada’s usual international allies.
In the first days after the Oct. 7 massacres, Canada was left out of a strongly worded joint statement issued by five fellow members of the G7.
“The terrorist actions of Hamas have no justification, no legitimacy and must be universally condemned,” read the statement co-signed by the leaders of the U.S., U.K., Germany, Italy and France. The statement then urged Israel to “set the conditions for a peaceful and integrated Middle East region.”
Ottawa explained that the statement was issued by Quint – an organization of five countries separate from the G7 that has never included Canada.
But while it might make sense for Quint to exclude its other G7 ally, Japan, it’s more conspicuous that the co-signers never called the G7 member with a substantial Jewish population and a lengthy history of diplomatic support for Israel.
And while Trudeau’s official reaction to the Oct. 7 massacres carried much of the same sentiments, it did include a routine equivocation absent from the Quint statement: Israel had a right to defend itself “in accordance with international law”.
November 8, 2023
Sampling the alternate history field
Jane Psmith confesses a weakness for a certain kind of speculative fiction and recommends some works in that field. The three here are also among my favourites, so I can comfortably agree with the choices:
As I’ve written before, I am an absolute sucker for alternate history. Unfortunately, though, most of it is not very good, even by the standards of genre fiction’s transparent prose. Its attraction is really the idea, with all its surprising facets, and means the best examples are typically the ones where the idea is so good — the unexpected ramifications so startling at the moment but so obvious in retrospect — that you can forgive the cardboard characters and lackluster prose.
But, what the heck, I’m feeling self-indulgent, so here are some of my favorites.
- Island in the Sea of Time et seq., by S.M. Stirling: This is my very favorite. The premise is quite simple: the island of Nantucket is inexplicably sent back in time to 1250 BC. Luckily, a Coast Guard sailing ship happens to be visiting, so they’re able to sail to Britain and trade for grain to survive the winter while they bootstrap industrial civilization on the thinly-inhabited coast of North America. Of course, it’s not that simple: the inhabitants of the Bronze Age have obvious and remarkably plausible reactions to the sudden appearance of strangers with superior technology, a renegade sailor steals one of the Nantucketers’ ships and sets off to carve his own empire from the past, and the Americans are thrust into Bronze Age geopolitics as they attempt to thwart him. The “good guys” are frankly pretty boring, in a late 90s multicultural neoliberal kind of way — the captain of the Coast Guard ship is a black lesbian and you can practically see Stirling clapping himself on the back for Representation — but the villainous Coast Guardsmen and (especially) the natives of 1250 BC get a far more complex and interesting portrayal.1 Two of them are particularly well-drawn: a fictional trader of the thinly attested Iberian city-state of Tartessos, and an Achaean nobleman named Odikweos, both of whom are thoroughly understandable and sympathetic while remaining distinctly unmodern. The Nantucketers, with their technological innovations and American values, provide plenty of contrast, but Stirling is really at his best in using them to highlight the alien past.
- Lest Darkness Fall, by L. Sprague de Camp: An absolute classic of the genre. I may not love what de Camp did with Conan, but the man could write! One of the great things about old books (this one is from 1939) is that they don’t waste time on technobabble to justify the silly parts: about two pages into the story, American archaeologist Martin Padway is struck by lightning while visiting Rome and transported back in time to 535 AD. How? Shut up, that’s how, and instead pay attention as Padway introduces distilled liquor, double-entry bookkeeping, yellow journalism, and the telegraph before taking advantage of his encyclopedic knowledge of Procopius’s De Bello Gothico to stabilize and defend the Italo-Gothic kingdom, wrest Belisarius’s loyalty away from Justinian, and entirely forestall the Dark Ages. If this sounds an awful lot like the imaginary book I described in my review of The Knowledge: yes. The combination of high agency history rerouting and total worldview disconnect — there’s a very funny barfight about Christology early on, and later some severe culture clash that interferes with a royal marriage — is charming. Also, this was the book that inspired Harry Turtledove not only to become an alt-history writer but to get a Ph.D. in Byzantine history.
[…]
- Ruled Britannia, by Harry Turtledove: Turtledove is by far the most famous and successful alternate history author out there, with lots of short pieces and novels ranging from “Byzantine intrigue in a world where Islam never existed” (Agent of Byzantium) to “time-travelling neo-Nazis bring AK-47s to the Confederacy” (The Guns of the South), but this is the only one of his books I’ve ever been tempted to re-read. The jumping-off point, “the Spanish Armada succeeded”, is fairly common for the genre2 — the pretty good Times Without Number and the lousy Pavane (hey, did you know the Church hates and fears technology?!) both start from there — but Turtledove fasts forward only a decade to show us William Shakespeare at the fulcrum of history. A loyalist faction (starring real life Elizabethan intriguers like Nicholas Skeres) wants him to write a play about Boudicca to inflame the population to free Queen Elizabeth from her imprisonment in the Tower of London, while the Spanish authorities (represented, hilariously, by playwright manqué Lope de Vega) want him to write one glorifying the late Philip II and the conquest of England. Turtledove does a surprisingly good job inventing new Shakespeare plays from snippets of real ones and from John Fletcher’s 1613 Bonduca, but of course I’m most taken by his rendition of the Tudor world. Maybe I should check out some of his straight historical fiction …
1. Well, except for the peaceful matriarchal Marija Gimbutas-y “Earth People” being displaced from Britain by the invading Proto-Celts; they’re also “good guys” and therefore, sadly, boring.
2. Not as common as “the Nazis won”, obviously.
I agree with Jane about Island in the Sea of Time, but my son and daughter-in-law strongly preferred the other series Stirling wrote from the same start point: what happened to the world left behind when Nantucket Island got scooped out of our timeline and dumped back into the pre-collapse Bronze Age. Whereas ISOT has minimal supernatural elements to the story, the “Emberverse” series beginning with Dies the Fire went on for many, many more books and had much more witchy woo-woo stuff front-and-centre rather than marginal and de-emphasized.
While I quite enjoyed Ruled Britannia, it was the first Turtledove series I encountered that I’ve gone back to re-read: The Lost Legion … well, the first four books, anyway. He wrote several more books in that same world, but having wrapped up the storyline for the Legion’s main characters, I didn’t find the others as interesting.
October 31, 2023
QotD: Orwell’s “hero” in Nineteen Eighty-Four
Like virtually all utopian or anti-utopian satires, Nineteen Eighty-Four presents drab, flat characters living in a grim world. Their journeys are predictable because their freedoms are narrow, often nonexistent and merely imagined. You cannot judge this book by the conventional criteria signaling a “good” novel. Even the main characters are not three-dimensional figures.
That is how it should be. What would you expect? In a world like this, it would be inconsistent, if not contradictory, to portray human beings who are not stunted and who live exciting lives with unexpected plot twists and turns.
Yet there is a hero in this anti-utopia, and Orwell’s magnificent portrait exemplifies its consummate artistry. The multidimensional, richly drawn “hero” is none other than the setting — that is, the empire of Oceania itself. Its history, its corrupt and tyrannical ruling Party, its oppressive and terrifying technology, its ingenious propagandistic language (“Newspeak”), its hatred of the body and sexuality (Julia belongs to — and pretends to support — the Junior Anti-Sex League): all this makes it a rounded, fascinating, creatively elaborated “character”. And there is no room for any other. Because Oceania is omnipotent and omniscient, it determines that its citizenry — whether prole or Party leader — is a cipher. The setting is, as it were, the (pseudo-Marxist) substructure; the superstructure of character and plot are determined by and beholden to it, utterly secondary and “superfluous” by comparison.
Orwell created an unforgettable, terrifying character — Oceania — and showed its “development” (in the spheres of technology, language, warfare, geopolitics, state torture, social relations, and family and sexuality) with astonishing inventive prowess. That development is manifested above all in Oceania’s range of technological gadgets, Newspeak neologisms, and Party slogans and catchwords.
And that is why Nineteen Eighty-Four is a gripping “novel”. That is, moreover, why it not only became a runaway bestseller in the early Cold War era, but also why it has exerted a cultural impact greater than any work of fiction in the 20th century.
John Rodden and John Rossi, “George Orwell Warned Us, But Was Anyone Listening?”, The American Conservative, 2019-10-02.
October 18, 2023
George Orwell’s views on Rudyard Kipling’s worldview
David Friedman comments on Orwell’s essay “Rudyard Kipling“, published a few years after the poet’s death in Horizon, September 1941:
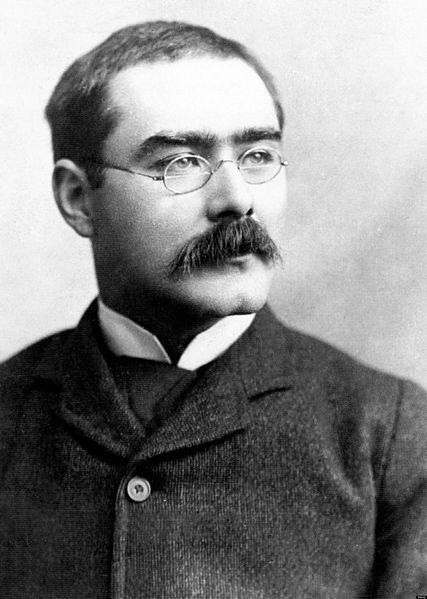

Portrait of Rudyard Kipling from the biography Rudyard Kipling by John Palmer, 1895.
Photo via Wikimedia Commons.
During five literary generations every enlightened person has despised him, and at the end of that time nine-tenths of those enlightened persons are forgotten and Kipling is in some sense still there.
Orwell’s essay on Rudyard Kipling in the Letters and Essays is both more favorable and more perceptive than one would expect of a discussion of Kipling by a British left-wing intellectual c. 1940. Orwell recognizes Kipling’s intelligence and his talent as a writer, pointing out how often people, including people who loath Kipling, use his phrases, sometimes without knowing their source. And Orwell argues, I think correctly, that Kipling not only was not a fascist but was further from a fascist than almost any of Orwell’s contemporaries, left or right, since he believed that there were things that mattered beyond power, that pride comes before a fall, that there is a fundamental mistake in
heathen heart that puts her trust
In reeking tube and iron shard,
All valiant dust that builds on dust,
And guarding, calls not Thee to guard,But while there is a good deal of truth in Orwell’s discussion of Kipling it is mistaken in two different ways, one having to do with Kipling’s view of the world, one with his art.
Orwell writes:
It is no use claiming, for instance, that when Kipling describes a British soldier beating a ‘nigger’ with a cleaning rod in order to get money out of him, he is acting merely as a reporter and does not necessarily approve what he describes. There is not the slightest sign anywhere in Kipling’s work that he disapproves of that kind of conduct — on the contrary, there is a definite strain of sadism in him, over and above the brutality which a writer of that type has to have.
There are passages in Kipling, not “Loot“, the poem Orwell quotes but bits of Stalky and Company, which support the charge of a “strain of sadism”. But the central element which Orwell is misreading is not sadism but realism. Soldiers loot when given the opportunity and there is no point to pretending they don’t. School boys beat each other up. Schoolmasters puff up their own importance by abusing their authority to ridicule the boys they are supposed to be teaching. Life is not fair. And Kipling’s attitude, I think made quite clear in Stalky and Company, is that complaining about it is not only a waste of time but a confession of weakness. You should shut up and deal with it instead.
A more important error in Orwell’s essay is his underestimate of Kipling as an artist, both poet and short story writer. Responding to Elliot’s claim that Kipling wrote verse rather than poetry, Orwell claims that Kipling was actually a good bad poet:
What (Elliot) does not say, and what I think one ought to start by saying in any discussion of Kipling, is that most of Kipling’s verse is so horribly vulgar that it gives one the same sensation as one gets from watching a third-rate music-hall performer recite ‘The Pigtail of Wu Fang Fu’ with the purple limelight on his face, AND yet there is much of it that is capable of giving pleasure to people who know what poetry means. At his worst, and also his most vital, in poems like ‘Gunga Din’ or ‘Danny Deever’, Kipling is almost a shameful pleasure, like the taste for cheap sweets that some people secretly carry into middle life. But even with his best passages one has the same sense of being seduced by something spurious, and yet unquestionably seduced.
I am left with the suspicion that Orwell is basing his opinion almost entirely on Kipling’s best known poems, such as the two he cites here, both written when he was 24. He was a popular writer, hence his best known pieces are those most accessible to a wide range of readers. He did indeed use his very considerable talents to tell stories and to make simple and compelling arguments, but that is not all he did. There is no way to objectively prove that Kipling wrote quite a lot of good poetry and neither Orwell nor Elliot, unfortunately, is still alive to prove it to, but I can at least offer a few examples …
October 15, 2023
QotD: The two eras of Jazz
In many ways, and for many people, jazz ended in the early Sixties, when Ornette Coleman, John Coltrane and Cecil Taylor suddenly became the avant-garde; in fact, almost everything that has happened to jazz in the last 50 years could be called “post-Coltrane” in much the same way that people use “postmodern”. Obviously, jazz was “free” and difficult (mad-looking Belgians with crazy hair, billowing luminescent smocks and angular, clarinet-looking instruments) or else it was nostalgic (Harry Connick Jr et al). Ironically, for a type of music so obsessed with modern and the “now”, jazz has always been preoccupied with the past, so much so that during the Eighties and Nineties it became less and less able to reflect modern culture. Everyone wanted to sound like Miles or Dizzy; either that or they went fusion mad and ended up sounding and looking like Frank Zappa on steroids.
Dylan Jones, “The 100 best jazz albums you need in your collection”, GQ, 2019-08-25.
October 9, 2023
“Wildly popular public sentiment is disorder, and has to be restrained”
Chris Bray outlines one of the many (many) ways that elected officials are insulating themselves from the voters who elected them to ensure that they only hear what they want to hear from the public … and as little of it as they can get away with:
Wildly popular public sentiment is disorder, and has to be restrained. So here, let’s start with something vital and interesting, and then work our way through the process a local government is using to kill it. As always, the point about this local story isn’t just the local story, since versions of this are happening all over the country (and with federal assistance).
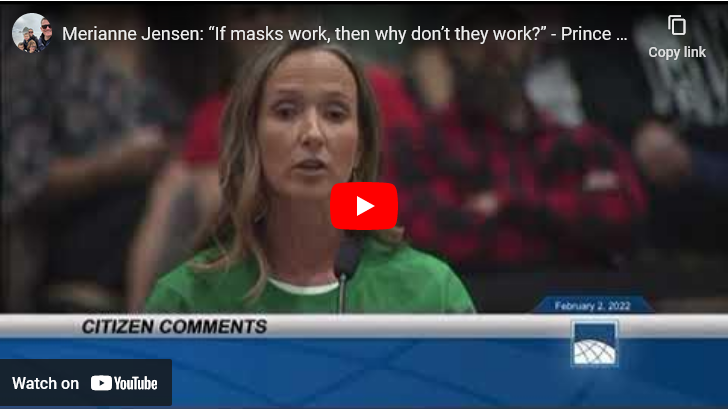
Early last year, an angry Virginia mom spoke to the Prince William County school board, blasting mask mandates in schools. Her fiery three-minute speech went viral, until YouTube, which now seems to mostly exist to prevent discussion, killed it:
It’s back, in a less-watched version that YouTube hasn’t gotten around to cancelling yet:
Here’s a version on Rumble, if you’d rather watch it there, but Substack doesn’t embed Rumble video.
The second thing to notice in that video, after you notice the clarity and strength of Merianne Jensen’s comments, is the response: an enormous audience of parents shouting and cheering in support as another parent sharply criticizes school district policy. The public is present for a government meeting, and the public is engaged. Citizens are participating, enthusiastically and in large numbers, which is supposed to be a thing we regard as an ideal.
[…]
Public comment is limited to one hour, full stop, no matter how many people wish to speak, and no matter how urgent a controversy before the board might be. The public — the entire public — gets an hour. But, second, that hour is alloted through an application process in which people who wish to speak to the school board fill out an online form that a clerk then evaluates and processes, deciding whether or not a request to speak will be granted. Detailed contact information is required before the school district will consider your request to speak, and national organizations and other outsiders have no right to speak at all, since public comment is limited to verified residents of the county. The form is a masterpiece of passive-aggressive nudging, communicating with great clarity that your desire to offer public comment is merely being tolerated. Read this carefully, because in a few minutes we’re going to get to the pernicious way this system is now being gamed:
This form does NOT confirm your request to be added to the list of speakers for Citizen Comment Time. You will receive a separate email indicating the status of your request. As a reminder, speakers are signed up to speak on a first-come, first-served basis.
Thank you again for your interest.
Citizens may sign up to be placed on the list of speakers for the citizen comment period starting at 8:00 a.m. on the Saturday immediately preceding the School Board meeting at which the citizen wishes to speak. Requests received prior to 8:00 a.m. on the Saturday immediately preceding the School Board meeting will not be honored. Speakers will be signed up on a first-come, first-served basis, ending at noon on the day of the meeting. The sign-up list will close once the number of total speakers who have signed up reaches twenty and there will be no sign-up thereafter, nor at the meeting.
That last sentence will become important: twenty commenters are signed up in advance, in the order in which they apply, and then the list for public comment is closed, the end. Can you see where this is going?
Before we get there, I’ll just note that a more detailed board policy on comments, available here, adds that the board chairman can end a public comment session, and ask school district security to remove speakers, if a commenter wanders into “inappropriate topics” or a tone the board regards as uncivil. You can feel the spontaneity and openness being drained.