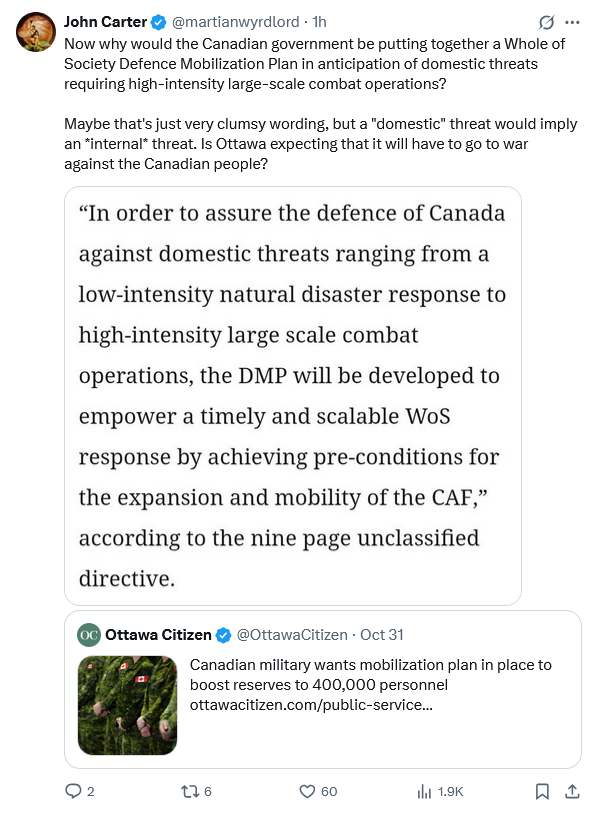
Mark Carney’s government finally got around to releasing their 2025 budget and lots of folks have thoughts and concerns about what is in it and what isn’t in it. After all, it could be the best possible budget, but it would still not satisfy all concerns … and nobody is pretending that this is anything close to “best possible” territory. Sylvain Charlebois says that the budget ignores the food insecurity issues and grocery prices for ordinary Canadians:

Graphic stolen from Small Dead Animals.
For a government that often talks about food affordability and insecurity, Budget 2025 offers surprisingly little that directly addresses either. There’s no bold food strategy, no affordability roadmap, and no new incentives for domestic food production. Yet, in between the lines, Ottawa has quietly set the stage for some indirect relief — not through grocery subsidies or consumer-facing policies, but through infrastructure, trade, and administrative reforms that could make the food system work a little more efficiently.
The largest signal comes from the government’s $115 billion infrastructure plan, one of its so-called “generational investments”. The new Trade Diversification Corridors Fund aims to modernize ports, railways, and airports — all chronic weak points in Canada’s food supply chain. When bottlenecks ease, goods move faster, and perishable products arrive fresher and cheaper. While no one in Ottawa framed this as a food-price measure, logistics efficiency has long been one of the most effective — and least visible — forms of price control.
[…]
Still, the absence of a broader vision for food affordability stands out. After years of grocery price volatility and public debate about “greedflation”, Canadians might have expected a more direct focus on food resilience — investments in innovation, local processing, or retail transparency. Instead, the government seems to have opted for a quieter, systemic approach: strengthen the arteries of trade and logistics, and trust that efficiency will trickle down to the dinner table.
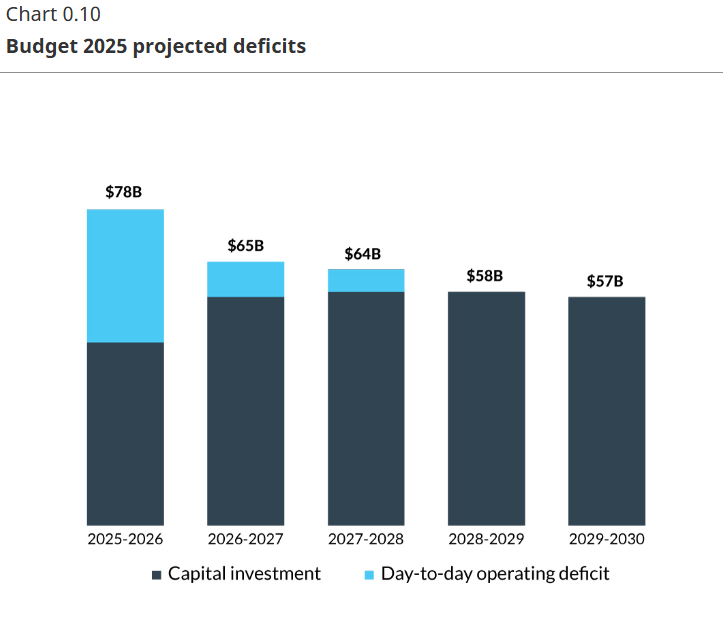
The budget forecasts a $78.3 billion deficit for the 2025-26 fiscal year, which is significantly higher than notorious spendthrift Justin Trudeau’s last budget number. This adds to an already staggering $1.27 trillion debt load, which is nearly double what it was just before the pandemic. In the lead-up to the budget release Mark Carney had hinted at major sacrifices to be made, and while there wasn’t a lot in the document directly corresponding to sacrifice, the need to service that long-term debt will do the job quite adequately.
In the National Post, John Robson says that the budget is “elbows up, IQs down”:
Since I was last propelled years ago into the purgatory known as “the lockup”, where journalists spend budget day, have either process or contents improved? No. Instead they now insert a false stolen-land “acknowledgement” before even getting to the same old same old labeled bold and new. Which is especially troubling at this supposedly critical juncture.
The document is the familiar brick, 406 paper pages and 493 digitally with no explanation for the discrepancy and no excuse for the length. (Or for being called “Canada Strong” with an inexplicable picture of a ship.) Especially as the Finance Minister gabbled “This is a budget that talks to everyday Canadians,” and its purpose is to state plainly how much the government intends to spend, where it hopes to get the money and how far short it already knows it will fall, you shouldn’t have to wade through 248 pages of sludge to find out.
As P.J. O’Rourke said, “beyond a certain point, complexity is fraud”. Though we “privileged” insiders search “Summary Statement of Transactions” and voila, submerged on p. 249 (all references digital) is a $78.3 billion deficit next year if all goes well, and the national debt increasing $80.5 billion so it already didn’t.
Much commentary, and special-interest attention, focuses on trivial fiddles. But what matters is that Leviathan is in hock up to its horns, with interest payments projected at $55.6 billion next year, soaring to $76.1 billion by 2029-30. If the Lord is willing and the creek don’t rise, both forlorn hopes. NDP MP Leah Gazan, who would jail you for “downplaying” residential schools, snarled about not supporting an “austerity budget” but she won’t get the chance.
Some may bleat that times are tough. Indeed the finance minister’s campaign-speech “Foreword, Budget” gasses “The world is changing, profoundly and in real time; we are no longer living in an era of calm, but of significant change”.
The projected deficits are clearly hallucinatory, as the Liberals never seem to get deficit spending to go down, running deficits every year since 2015:
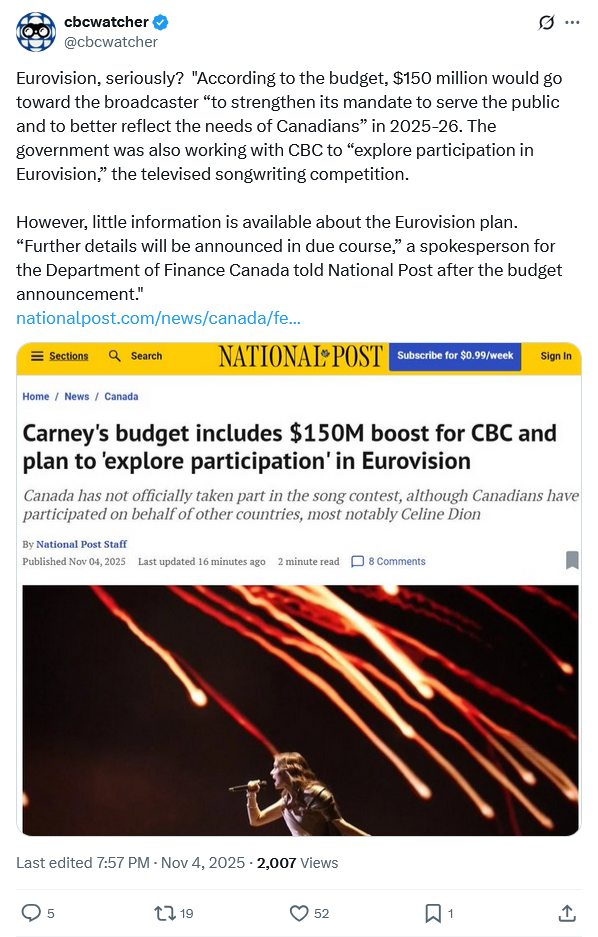
However, on the ludicrous side, the feds want to spend money to “investigate” Canada taking part in the freaking Eurovision contest:
On the slightly less ludicrous side, Noah considers the military aspects of the budget:
Budget 2025 outlines the government’s generational investment to quote, “defend Canada’s people and values, secure its sovereignty, and position the nation as a strong, reliable partner to its allies“. This starts by initiating a process of rebuilding, rearming, and reinvesting in the DND, CCG, and CAF to provide everyone with the necessary tools and equipment to protect sovereignty and bolster security.
Budget 2025 starts by outlining the government’s previous commitment to accelerate investments to meet NATO’s 2 per cent defence-spending target this year, which is five years ahead of schedule.
Budget 2025 goes a step further by setting Canada on a path to meet NATO’s 5 per cent Defence Investment Pledge by 2035. This will be broken down into two categories, 3.5 per cent of GDP by 2035 in core military needs, including supporting the CAF, modernising equipment and technology, and building up defence industries, and 1.5 per cent on security-related infrastructure and investments.
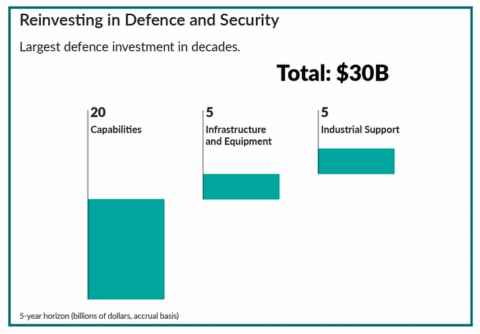
This reinvestment in defence and security is the largest in decades, totaling $30 billion over a five-year horizon on an accrual basis. This funding is allocated across three main pillars: $20 billion for capabilities, $5 billion for infrastructure and equipment, and $5 billion for industrial support.
On a cash basis, Budget 2025 proposes to provide $81.8 billion over five years, starting in 2025-26, to rebuild, rearm, and reinvest in the CAF. This figure includes over $9 billion in 2025-26 that was previously announced in June 2025. This is the funding previously set out for Canada to reach the 2 per cent NATO target.
Key investments from this $81.8 billion fund include $20.4 billion over five years to recruit and retain a strong fighting force, which incorporates the previously announced updates to pay and support for CAF health care.
An additional $19.0 billion over five years is allocated to repair and sustain CAF capabilities and invest in defence infrastructure, including the expansion of ammunition and training infrastructure. Upgrades to digital infrastructure for the Department of National Defence, CAF, and the Communications Security Establishment, particularly for cyber defence, are funded with $10.5 billion over five years.
Finally, $17.9 billion over five years is designated to expand Canada’s military capabilities, with investments in logistics, utility, and armoured vehicles, as well as counter-drone, long-range precision strike capabilities, and domestic ammunition production.
This is a serious chunk of change, although sadly, and as you will see, we don’t get a major breakdown of what this looks like. What we are left with are general piles of money, which isn’t always a bad thing. It’s also expected. The budget is set for a timeline before many critical capabilities will be delivered, so they won’t be included. Almost everything comes after 2030.