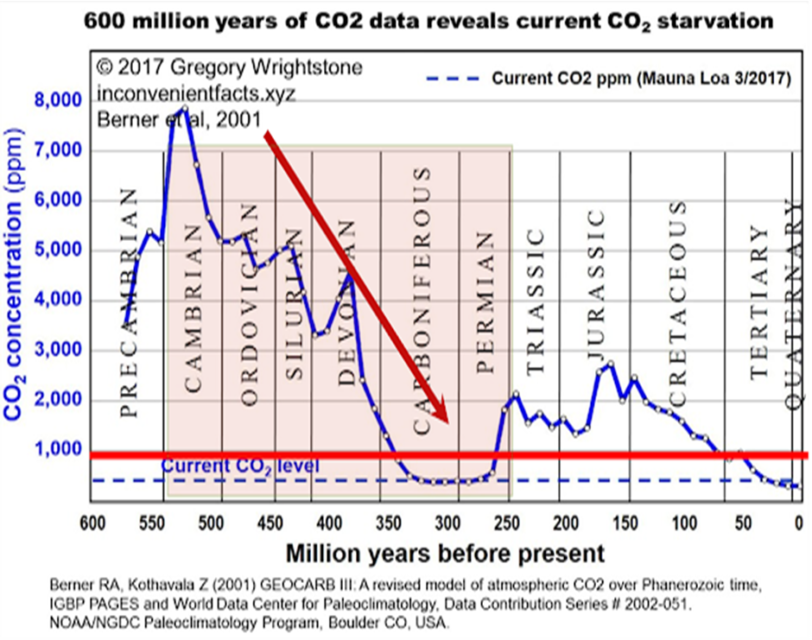
Tim Worstall really, really enjoys kicking the stuffing out of strawman arguments, especially when they touch on something he’s very well informed about:
Some environmental claims are not just perfectly valid they’re essential for the continuation of life at any level above E. Coli. None of us would want the Thames to return to the state of 1950 when there was nothing living in it other than a collection of that E. Coli reflecting the interesting genetic and origin mix of the population of London. Sure, the arguments from Feargal and the like that a river running through 8 million people must be clean enough to swim in at all times is a bit extreme the other way around. One recent estimate has it that to perform that task for England would cost £260 billion — a few swimming baths sounds like a more sensible use of resources than getting all the rivers sparkling all the time.
Some are more arguable — violent and immediate climate change would be a bad idea, losing Lowestoft below the waves (possibly Dartford too) in 2500 AD might be something we can all live with. Arguable perhaps.
But some of these claims are wholly and entirely doolally. So much so that it’s difficult to imagine that grown adults take them seriously. But, sadly, they do and they do so on our money too.
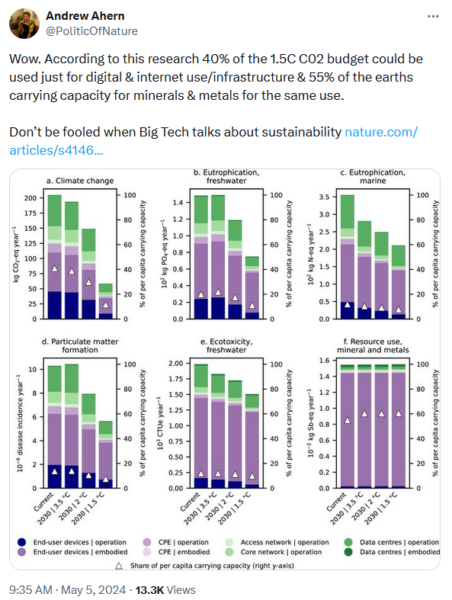
Wow. According to this research 40% of the 1.5C C02 budget could be used just for digital & internet use/infrastructure & 55% of the earths carrying capacity for minerals & metals for the same use.
The internet alone could use 55% of the Earth’s carrying capacity of metals and minerals? Well, to take that seriously is insane. That is not mere hyperbolic insult, that actually is insane. I write as someone who has written an entire book on this very subject (available here, for free, save your money to buy a subscription to this excellent Substack instead). There is no metal or mineral that we’re even going to run short of — in the technical, not economic, sense that is — for tens of millions of years yet. As the average lifetime of a species is perhaps 2 million years that should see us out.
So, clearly, they’re using some odd definition of how many minerals and metals we’ve got that we can use. I thought they’d do the usual Club of Rome thing (no, read the book to find out), confuse mineral reserves with what’s available and thus insist we all died last Tuesday afternoon. Rather to my surprise, no, they didn’t. They went further into raging lunacy.
It’s not wholly obvious as they don’t really quite announce their assumption, it’s necessary to track back a bit — and that’s a problem in itself. A top tip about scientific papers — if they say “As Bloggs said” then what that really means is that many people accept what Bloggs said as being true and also useful. You do not have to reprove Einstein every time you do physics, you can just say “As is known”. You’ve only got to reprove Al if that’s what you’re really trying to do.
Thus, if a definition is a referral back to something else, elsewhere, then you can be sure that the definition is a building block being used by others in their own papers. It’s a generalised insanity, not a specific one.
So, what is that limit?
Here we quantify the environmental impacts of digital content consumption encompassing all the necessary infrastructure linked to the consumption patterns of an average user. By applying the standardised life cycle assessment (LCA) methodology, we evaluate these impacts in relation to the per capita share of the Earth’s carrying capacity using 16 indicators related to climate change, nutrients flows, air pollution, toxicity, and resources use, for which explicit thresholds that should never be exceeded were defined
Now this is in Nature Communications. So it’s science. Even, it’s Science. It’s also lunatic. For, tracking back to try to find what those “resources use” are that will be 55% used up by the internet. It’s possible to think that maybe we’re going to use too much germanium in the glass in the fibreoptic cables say, or erbium in the repeaters, or … specific elements might be in short supply? As the book wot I wrote above points out, that’s nonsense. So, what is the claim?
Tracking back we get to this:
Resource use, mineral and metals MRD kg Sb eq Abiotic resource depletion (ADP ultimate reserves) 2.19E+08 3.18E-02 JRC calculation based on factor 2 concept Bringezu (2015); Buczko et al. (2016) Resource use
That’s from Table 3.
Which takes us one stage further back. This paper here is talking about Planetary Boundaries and as with the building block idea. PBs — I assume — make the assumption that Bringzeu, and Biczlo et al have given us a useful guide to what those PBs are. Which is why they just use their method, not invent a new one. But that, in turn, also means that other people working on PBs are likely to be using that same definition.
[…]
Note what they’re doing. Humans should not take out of that environment more than nature puts back into it each year. That’s some pretty dumb thinking there, as we don’t, when we use a metal or mineral — except in very rare circumstances — take it off planet. We move it around a bit, no more. But the claim really is that we should abstract, for use, no more than is naturally added back each year.
So, the correct limitation on our minerals use is how much magma volcanoes add each year.
No, really, humanity can use no more earth than gets thrown out of a volcano each year. That’s it. To use more would mean that we are depleting the stock and that’s not sustainable, see?