It is clear to me that the great twin battle of Imphal & Kohima, which raged from March through to late July 1944, was one of four great turning-point battles in the Second World War, when the tide of war changed irreversibly and dramatically against those who initially held the upper hand.
The first great turning point was arguably at Midway in June 1942 when the US Navy successfully challenged Japanese dominance in the Pacific. The second was at Stalingrad between August 1942 and January 1943 when the seemingly unstoppable German juggernaut in the Soviet Union was finally halted in the winter bloodbath of that city, where only 94,000 of the original 300,000 German, Rumanian and Hungarian troops survived. The third was at El Alamein in October 1942 when the British Commonwealth triumphed against Rommel’s Afrika Korps in North Africa and began the process that led to the German surrender in Tunisia in May 1943. The fourth was this battle, that at Kohima and Imphal between March and July 1944 when the Japanese “March on Delhi” was brought to nothing at a huge cost in human life, and the start of their retreat from Asia began. Adjectives such as “climactic” and “titanic”, struggle to give proper impact to the reality and extent of the terrible war that raged across the jungle-clad hills during these fearsome months.
That the Japanese were contemplating an offensive against India in early 1944 was a surprise to Allied planners, who had given no thought to its possibility. By this time Japan had reached the apogee of its power, having extended the violent reach of its Empire across much of Asia since it launched its first surprise attacks in late 1941. Its initial surge in 1942 into what was briefly to be Japan’s “Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere” was as dramatic as it was rapid and two years further on several millions of peoples across Asia laboured under its heavy yoke. But by early 1944 the tide had turned decisively in the Pacific, the American island-hopping advance reaching steadily but surely towards Japan itself, its humiliated enemies fighting back with desperation, and with every ounce of energy they could muster. They were beginning to prevail in the fight although the struggle on the landmass of Asia was a strategic sideshow in the context of a global conflict: at this time the British and American High Commands were totally occupied with Europe and the Pacific. The British and Americans were preparing for D Day. The Soviets were advancing in Ukraine. There was a stalemate in Italy at Monte Cassino. The Americans were preparing to land in the Philippines. Germany and Japan were both in retreat, but not defeated. In this global context India and Burma appeared strategically peripheral, even inconsequential. Yet in this month, at a time when on every other front the Japanese were on the strategic defensive, Japan launched a vast, audacious offensive deep into India in an attack designed to destroy for ever Britain’s ability to challenge Japan’s hegemony in Burma.
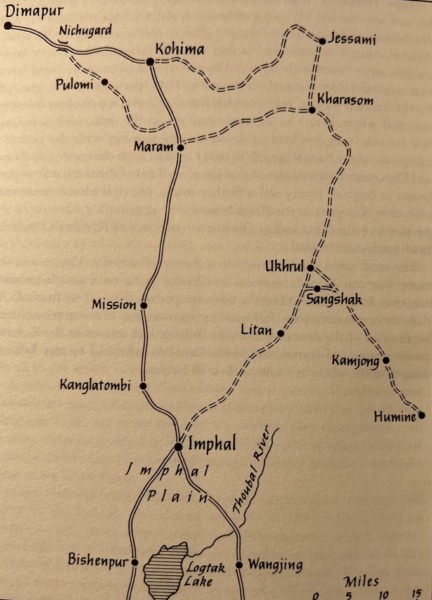
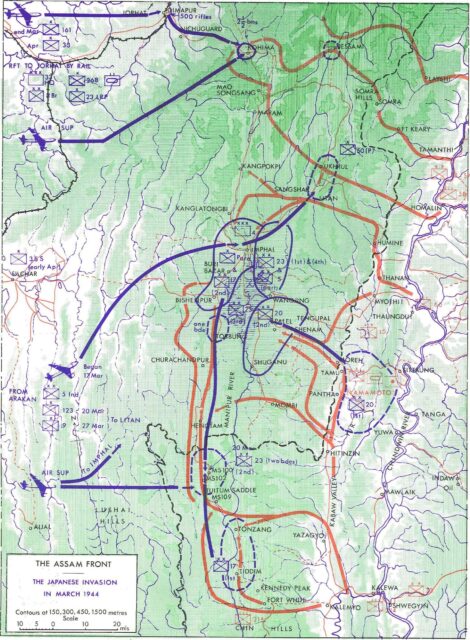
The Japanese commander was General Mutaguchi Renya, a gutsy go-getter who had played a significant role in the collapse of Singapore in February 1942. His evaluation of the British position in northeast India revealed that the three key strategic targets in Assam and Manipur were Imphal; the mountain town of Kohima, and the huge supply base further back on the edge of the Brahmaputra Valley at Dimapur. If Kohima were captured, Imphal would be cut off from the rest of India by land. From the outset Mutaguchi believed that with a good wind Dimapur, in addition to Kohima, could and should be secured. He reasoned that capturing this massive depot would be a devastating, possibly terminal blow to the British ability to defend Imphal, supply the Americans in Northern Burma under Vinegar Joe Stilwell, support the Hump airlift into China and mount an offensive into Burma. It would also enable him to feed his own, conquering army, which would advance across the mountains from the Chindwin on the tightest imaginable supply chain. With Dimapur captured, the Japanese-led Indian National Army under the Bengali nationalist Subhas Chandra Bose could pour into Bengal, initiating the long-awaited anti-British uprising.
(Click to enlarge)
The essence of the battle for India in 1944 can be quickly told. Mutaguchi’s 15th Army advanced in four separate columns into Manipur. The Japanese made determined, even desperate, efforts to seize their objectives: in the north Kohima, with a scratch British and Indian garrison of 1,200 trained fighting soldiers – about two thirds of them Indian – was attacked by an entire division of about 15,000 men in early April. Surrounded and slowly forced back onto a single hill they were supplied by air until relief came on 20 April, although the battle to dislodge the Japanese from Kohima continued bloodily, in appalling weather and battlefield conditions – the annual monsoon was in full spate – through to early June. Further south the Japanese plan entailed attacking Imphal from north, east and south. The plan of the commander of the 14th Army, Lieutenant General Bill Slim, was to withdraw his forces into the hills and there to allow the Japanese to expend themselves fruitlessly against well-supplied and aggressive British bastions, equipped with tanks, artillery and supported by air. The battle for Imphal in Manipur and for Kohima to the north-west in the neighbouring Naga Hills settled down to a bloody hand-to-hand struggle as the Japanese tried to gain the foothold necessary for their survival. They travelled lightly, and reserves soon exhausted themselves and further supplies were almost non-existent. Just as the air situation was becoming critical for Slim through poor weather and shortages of aircraft the relieving division from Kohima – the British 2nd Infantry Division that had last seen action at Dunkirk – began fighting its way towards Imphal, and the four beleaguered divisions began to push out from the Imphal pocket. By 22 June the 2nd Division and the 5th Indian Division met north of Imphal and the road to the plain was open. Four weeks later the Japanese withdrawal to Burma began.
Of all the invading armies of history, it is hard to think of one that was repulsed more decisively, or more ignominiously, than the Japanese 15th Army launched against India in March 1944. Its defeat was not the fault of the Japanese soldiers, who fought courageously, tenaciously and fiercely, but of their commanders, who sacrificed the lives of their troops on the altar of their own hubris. The battle had provided the largest, most prolonged and most intense engagement with a Japanese army yet seen in the war. “It is the most important defeat the Japs have ever suffered in their military career” wrote Mountbatten exultantly to his wife on 22nd June 1944, “because the numbers involved are so much greater than any Pacific Island operation.” The extent of the disaster that befell the 15th Army is captured by a comment by Kase Toshikazu, a member of the wartime Japanese Foreign Office, who lamented: “Most of this force perished in battle or later of starvation. The disaster at Imphal was perhaps the worst of its kind yet chronicled in the annals of war.” The latter might better have included the caveat “Japanese” to avoid charges of exaggeration, but his comment captures something of the enormity of the human disaster that overwhelmed the 15th Army. It might more fairly be described as the greatest Japanese military disaster of all time. The Indian, Gurkha, African and British troops of this remarkably homogeneous organisation had also decisively removed any remaining notions of Japanese superiority on the battlefield.
The importance of this victory was overshadowed at the time, and downplayed for decades afterwards, by the massive victories in 1945 which brought World War II to an end in Europe and the Pacific. But this lack of publicity and of awareness does not remove the fact that, objectively speaking, the battles in India in 1944, epitomized in the fulcrum battle at Kohima, were an epic comparable with Thermopylae, Gallipoli, Stalingrad, and other better known confrontational battles where the arrogant invader became, in time, the ignominious loser.