Practical Engineering
Published 21 Oct 2025All the things I love about Niagara Falls
The same thing that makes Niagara Falls impressive for tourists (the big drop) makes it valuable for power and a major challenge for shipping. And out of that comes all kinds of fascinating infrastructure.
Practical Engineering is a YouTube channel about infrastructure and the human-made world around us. It is hosted, written, and produced by Grady Hillhouse. We have new videos posted regularly, so please subscribe for updates. If you enjoyed the video, hit that “like” button, give us a comment, or watch another of our videos!
(more…)
February 26, 2026
The Hidden Engineering of Niagara Falls
January 28, 2026
An ADA unintended consequence in Los Angeles
I’ve heard many people refer to the Americans with Disabilities Act as the worst piece of legislation in US history, and stories like this one make it easy to agree:
Los Angeles’s streets are in notoriously bad shape. Fewer than two-thirds are considered in a state of good repair, according to the city’s Department of Public Works. Broken sidewalks have spawned years of costly litigation, and Los Angeles pays out millions of dollars each year to drivers whose cars are damaged by potholes.
Many cities would see this situation as a mandate for change. And Los Angeles has indeed made a change: last summer, the city quietly stopped repaving its streets. Not slowed. Not fell behind. Stopped completely.
The Bureau of Street Services (StreetsLA) has not repaved a single street since last June, and the city’s latest budget practically zeros out repaving for next fiscal year. StreetLA crews are still doing some road repairs, fixing potholes and patching problem areas. But the most basic form of urban maintenance — full street resurfacing — has all but disappeared in America’s second-largest city.
Why has Los Angeles stopped repaving its streets? The answer, it turns out, has to do with federal disability rules that, paradoxically, have made fixing roads legally riskier than letting them fall apart. Though well-intentioned, L.A.’s shift shows how such policies can unintentionally worsen urban quality of life.
The clearest explanation of the city’s shift comes from L.A.–based housing and transportation advocate Oren Hadar. Digging through budget documents and engineering classifications, Hadar explained in an essay from late last year that the city didn’t necessarily abandon street work so much as reclassify it out of existence.
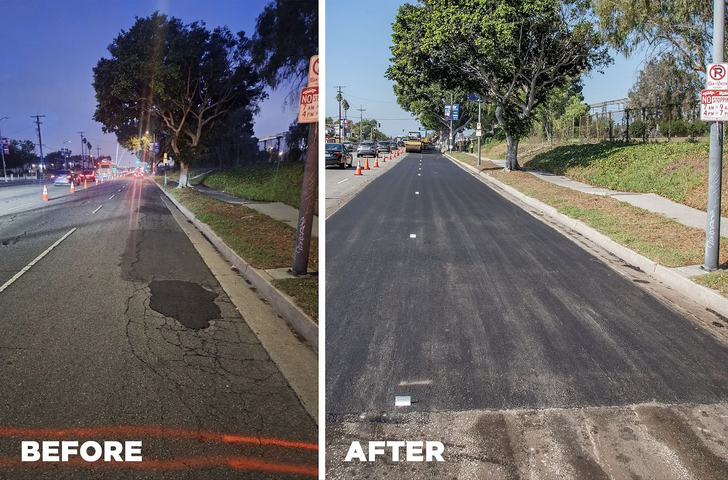
The city seems to have invented a new category of repair specifically designed to avoid triggering costly federal accessibility mandates. Instead of repaving streets, StreetsLA now performs what it calls “large asphalt repairs”. As Hadar explained, these repairs address localized damage — areas larger than a pothole but smaller than full resurfacing. Essentially, the city repaves only part of a street rather than the entire width, as shown below.
A “large asphalt repair” on L.A.’s Century Boulevard. Courtesy: StreetsLA on X
But, as Hadar wrote, “the thing about large asphalt repair is that it’s … not a real thing. It appears to be a term made up by the city some time in the last year.”
Why invent a new classification? The reason lies in federal disability law. Under regulations implementing the Americans with Disabilities Act, when a city alters a street, it must also bring associated pedestrian infrastructure into compliance. That means installing ADA-compliant curb ramps at every intersection along the way.
Repaving is considered an alteration that triggers these requirements. Maintenance activities, such as filling potholes or making minor repairs, are not. The city claims that large asphalt repairs are “pavement maintenance activity” and therefore do not require ADA upgrades.
That distinction carries enormous financial and logistical consequences. Hadar found that each curb ramp costs roughly $50,000, totaling about $200,000 per intersection. With roughly ten intersections per mile, curb ramps alone can add around $2 million per mile to the cost of repaving — a figure that often exceeds the cost of the asphalt itself. Design and construction typically take 9 to 12 months per ramp, and federal rules require the ramps to be completed by the time the street is resurfaced.
Update, 29 January: Welcome, Instapundit readers! Have a look around at some of my other posts you may find of interest. I send out a daily summary of posts here through my Substack – https://substack.com/@nicholasrusson that you can subscribe to if you’d like to be informed of new posts in the future.
January 21, 2026
QotD: White elephant airports
Few things capture modern planning like a multibillion-dollar airport no one’s entirely sure will have any planes. Enter Western Sydney International Airport (WSI), Australia’s shiny $5 billion gamble at Badgerys Creek. It’s a development so hyped it already has merch, an anticipated metro line, and a better skincare routine than most of us, despite rumors it may spend its first year servicing only freight and the occasional confused ibis.
If history teaches us anything, it’s that airports, like wrinkle creams which cost the GDP of a small country but couldn’t iron out a bedsheet, can be wildly overpromised and underdelivered. Western Sydney’s runway might yet join the vainglorious global herd of White Elephant Airports: majestic, expensive, and standing alone in a field wondering where everyone went.
Let’s take a safari.
Mirabel: Montreal’s Monument to Inconvenience
Built in 1975, Mirabel International was meant to replace Montreal’s Dorval Airport and usher in a new aviation era. Instead, it became the architectural embodiment of “We should’ve checked the map”. Located more than 50 kilometers from the city, it was so unpopular that passengers would rather fling themselves onto dogsleds than make the commute.
Eventually, Mirabel stopped pretending to be an airport and transitioned into its second act: a car-racing track and film set. Somewhere in Quebec there’s probably still a baggage carousel being used as a wedding dance floor.
Ciudad Real: A Billion-Euro Garage Sale
Spain saw Mirabel and said, “Hold my sangria”. Ciudad Real International Airport opened in 2009 with a €1.1 billion price tag, dreams of high-speed rail links, and the confidence of a Bachelor contestant in week one. Within three years, it had no flights, no buyers, and no shame.
It was eventually auctioned for €10,000, less than a parking space in Bondi or a bottle of champagne at a Sydney rooftop bar. One imagines the bidding process was just two blokes shrugging in a room and someone whispering, “Ten grand and a paella voucher?”
Berlin Brandenburg: German Efficiency, But Make It Chaos
If you’ve ever wanted to see what happens when a nation famous for precision tries on farce, just pay a visit to Berlin Brandenburg Airport. Construction began in 2006, with an opening scheduled for 2011. By 2015, it was such a national embarrassment that Berliners stopped making jokes about British plumbing to recover emotionally.
In 2020, it finally launched amid the global COVID pandemic, after delays caused by faulty fire systems, suspicious cables, and the ghost of every German engineer pacing in dismay.
Nicole James, “Australia’s New Albino Elephant Sanctuary (Now with Parking)”, The Freeman, 2025-10-16.
January 6, 2026
The “developing world” is not poor because the “rich countries” looted them
On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, Lauren Chen reacts to an emotive claim that the Third World is poor only because of the exploitation of their resources by the First World:
People often say that the developing world is poor because the Western world colonized them and stole their resources.
The truth, however, is that over the past century, the developing world has, for the most part, shown that they are completely incapable of harnessing their own resources. They are not poor because we stole from them. They are poor because they do not know how to run and administer their own countries, resources be damned.
Take Venezuela. The world’s largest oil reserves mean nothing if you have a corrupt communist as your leader. People will actually be starving and trying to eat zoo animals while you sit on trillions of dollars in resources!
Africa is another example. Europeans left behind farmland, trains, roads, and mines in Africa. What happened to it all?
It’s not that all of a sudden, the Africans started running things like anti-colonialist activists had envisioned at the time. No, no.
All the infrastructure fell into disrepair and/or was stripped down and looted. They were literally handed fully functioning, completed supply chains for resource extraction, and basically unlimited wealth, but they couldn’t manage the simple upkeep.
Now, the defense for Africa might be that “The Europeans didn’t teach the Africans how to manage any of this! It’s not the Africans’ fault they couldn’t run it independently! They were never trained!”
But my brother in Christ, the Europeans DID try to train locals for management! Obviously it would have been easier to have at least some locals in administration, rather than having to import an ENTIRE workforce, but efforts to find African talent were largely unsuccessful.
Don’t believe me? Just look at the different outcomes in Hong Kong and Singapore when compared to Africa. In East Asia, Europeans often did work with locals in administrative and management capacities. When colonialism ended, Hong Kong and Singapore were able to manage themselves. Not the case with Africa.
Now, none of this is to say that colonialism is good. People have the right to self-rule and self-determination. However, the idea that colonialism and resources extraction are responsible for the developing world’s ongoing poverty? That is quite simply a crock of shit.
January 2, 2026
How did Ancient Romans build their roads?
Metatron
Published 2 Sept 2025Roman road construction was a marvel of ancient engineering that began in earnest around 312 BC with the famous Appian Way. The Romans developed a systematic approach that would serve their empire for centuries, creating over 250,000 miles of roads by 200 AD.
Their construction process started with careful surveying using tools called groma and chorobates to ensure straight lines and proper gradients. Roman engineers would then excavate a roadbed typically 14 to 16 feet wide, digging down 3 to 5 feet deep depending on local conditions and expected traffic. The foundation layer, called the statumen, consisted of large flat stones carefully fitted together. Above this came the rudus, a layer of crushed stone and mortar about 9 inches thick, followed by the nucleus, a finer mixture of gravel and mortar. The top surface, known as the summum dorsum, was made of large polygonal stone blocks called silex, fitted so precisely that no mortar was needed between them. These roads were built with a slight crown in the center to promote drainage, and ditches were dug alongside to carry away rainwater.
Roman construction crews, often composed of soldiers, would work in organized teams with specialized roles for quarrying stone, mixing mortar, laying foundations, and fitting the surface blocks. The entire process could take months or even years for major routes, but the result was a road surface so durable that many Roman roads remained in use well into the medieval period and beyond. Quality control was maintained through strict military discipline and the personal responsibility of engineers who literally put their names on milestone markers. By 117 AD, at the height of the empire, this road network connected Britain to the Middle East and North Africa to the Rhine frontier, facilitating trade, communication, and military movement across the known world.
#romanempire #ancientrome #romanroads
November 29, 2025
“There comes a point where government waste stops looking like incompetence and starts looking like treason”
Canadians must be literally the most passive and forgiving people on Earth. It’s the only thing that can account for how we are governed by incompetents or idiots, yet keep re-electing them despite all the clear signs of failure and opportunistic crony looting of the public purse:
There comes a point where government waste stops looking like incompetence and starts looking like treason. Canada has long passed that point. What we are witnessing now is not mere mismanagement or bureaucratic drift — it is the systemic looting of a nation by the people meant to serve it. Billions vanish with no oversight, no accountability, and no shame. The numbers have grown so grotesque that one struggles not to call this what it is: organized theft.
Take Stellantis. Ottawa handed the automaker $15 billion — the largest corporate subsidy in Canadian history — and the industry minister didn’t even read the contract before approving it. This, despite Stellantis shifting Jeep production to the U.S., delaying its employment targets at the Windsor battery plant, and refusing to appear before Parliamentary Committee hearings. Honda received a major subsidy without full Treasury Board review. Volkswagen hid its cost estimates. Northvolt was showered with subsidies and then slipped into insolvency. Each scandal blurs into the next until you realize the pattern is not incompetence but a business model.
Then there’s the LNG project in British Columbia. The main industrial partner is an American firm. The terminal will be built overseas, floated to Nisga’a land, and subsidised by Canadian taxpayers. In other words: Canadians take the risk while the profits flow abroad and the jobs go to Korea or Japan.
Or consider Telesat. They received $2.14 billion to connect rural Canadians to high-speed internet — with no obligation to connect a single home, no penalties for failure, no clawbacks if the project collapses, and no enforced timelines. Three years later, the network still does not exist. Meanwhile, Starlink already worked, already served rural communities, could have done it for half the cost, and offered immediate deployment — but was rejected because Elon Musk is “polarizing”.
ArriveCAN? $54 million spent on an app worth $80,000, much of it funnelled to GC Strategies, a boutique firm that admitted it didn’t actually build anything. Then the Sustainable Development Fund — the so-called green slush fund — where $400 million flowed into Liberal-friendly firms.
The State tells us its creed is “responsible governance”. Yet almost every act defies that claim. What we have instead is a system run by well-dressed operators who treat the public purse as their own. Canada is now a nation run by criminals, for criminals.
November 18, 2025
Canada’s major projects announcements are an economic “hostage release” program
On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, David Knight Legg vents about Dear Leader Carney’s penchant for even-more-Trudeauesque-than-Justin performative governing. Far more emphasis is put on the PR value of an announcement than on the common sense practicality of the thing being announced. And Carney is also starting to re-announce already announced “projects” as if speaking it aloud will magically manifest it into reality:
Canada’s major projects announcements are a national embarrassment — an economic “hostage release” program — that tells the world just how uninvestible Canada has become under the Liberal party.
1970s central planning Liberal govt arrogance is at an all time GDP destroying high.
Try naming another OECD nation (we’re at the bottom now) where the press waits with bated breath for a “dear leader” politician who has never built anything in his life to fly in to grant a bureaucratic benediction on a few projects his bureaucrats will allow past the gate of the caps, taxes, green rules and red tape his govt imposes on everything.
Idea: set up the Major Dumb Redtape office in Calgary instead and get rid of the 10 anti-business rules written into law by the Montreal green alarmist fringe that’s holding Canadian energy, ag, forestry, and manufacturing back while other nations grow …
But PM Carney seems to like his bureaucratic power over what used to be a leading free market economy. Even while our GDP grinds down to the worst in the OECD.
The arrogance is breathtaking.
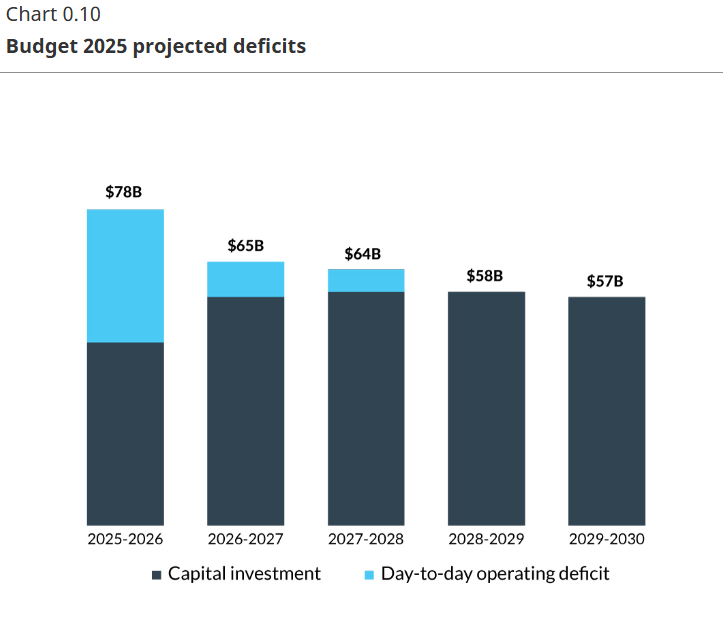
So is the ineptitude. This same central planning genius just punched a record new $78billiom hole through our public finances because he can’t manage basic public service delivery without more crushing debt.
The budget is a train wreck solidifying the final year of a Liberal decade steeply eroding purchasing power, national wealth, personal security and living standards and public services.
The irony is that this has driven Canada to ever-greater 51st state economic dependency. Donald Trump didn’t do that. They did.
But he’s been a too-convenient way to con the elderly with “elbows up” PR.
But should the next generation really be forced to lend this govt another $78bn in addition to the 1 trillion they’ve already taken to fund their failed decade of central planning, green slush funds and EV mandates while real infrastructure projects wait years for the Liberal party to bless them?
It’s not going to last.
Fitch just questioned the sustainability of all this. Unlike our lacklustre press they aren’t buying “net debt” or “operating/investment” Liberal financial illiteracy.
I had high hopes PM Carney would return fiscal sanity to Canada after openly borrowing Conservative policies to get elected by cutting the carbon and cap gains taxes.
But this budget, this major projects farce and his inability to kill a dozen economy killing rules of his own govt is showing the work how uninvestible Canada has become — and it’s accelerating national economic decline.
2026 is the end of the Liberal lost decade. First recession. Then debt downgrade. Then an election. And Carney can go back offshore to his assets and all the other global investors who like him don’t invest in Canada under Liberal mismanagement.
@SteveSaretsky thx for the brilliant line chart as usual.
A day later, after his post got significant attention on the social media site formerly known as Twitter, he posted this follow-up:
This angry post I wrote a day ago got 300,000 views.
Canadians are tired of the fake “major projects” PR by the same people who prevented those projects for a decade with their green taxes and prohibitions.
Announcing the release of 7 hostage projects is a joke. Some of these projects aren’t major and most aren’t new. None needed the govt to do anything but get out of the way from the beginning.
All the several hundred major projects still in purgatory need is for this govt to reverse their anti-job and anti-infrastructure tanker ban, industrial carbon tax, emissions cap, and electricity regs.
Oh — and also clarify by law that in Canada property rights are not overridden by leftist judges and UN wishful thinking.
Then get out of the way so a couple trillion dollars can flow in, major projects can get built and the govt revenue will flow to better public services — and to pay down that debt they just added $78bn to.
November 12, 2025
Bike lanes are only the start
Spaceman Spiff explains how aspirational schemes proposed by our technocratic governments at all levels seem to quickly and effortlessly shift from a nice non-intrusive improvement in life to an overbearing imposition of ever tighter controls on our lives:
The adoption of cultural novelties follows a predictable path. Some bright idea is proposed and there is nominal support or at least not widespread opposition.
Soon after implementation begins its opposite is condemned. This is the first warning the lunatics have taken over the asylum. We move from a positive, optimistic drive to condemning a perceived negative. By then the intolerant are amassing, attracted to a secular pulpit with which to lecture the rest of us.
More time passes and condemnation of the opposite is not enough. We are commanded to behave in ways more pleasing to our public servants. We learn a key aspect of our future has been decided by a shadowy committee we have never heard of. A well-meaning experiment has become an imperative used to control us.
This absurd sequence is more common than it should be.
A common example in Britain is the creation of bike lanes.
The idea sounds benign. Let’s build cycle lanes to encourage exercise. It is broadly popular, a kind of inoffensive fad to encourage better health despite the weather being an impediment for most.
Few people actively object which is taken to mean they endorse these projects.
It is not long before support for helping cyclists degenerates into discouraging cars since people should be cycling more anyway. The initiative lends moral weight to an otherwise fringe view. The construction of the bike lanes accelerates these ideas as roads are narrowed and traffic slows, frustrating many. There are too many vehicles on the road we are told, all the more reason to get on your bike.
Soon suggestions are made to ban cars completely. The new idea proposed is to shut down the congested roads and replace them with even more bike lanes and pedestrian zones.
Some even openly discuss intentionally making driving awkward and expensive as an explicit goal. The technocratic mind often forgets its charges are people not slaves.
Before long everything shifts, then we wonder how we got to the point our own paid employees can openly gloat we will soon be banned from travelling in ways they dislike as if they are our controllers.
An idea appealing to a minority is imposed on all. Acquiescence to novelties becomes weaponized and subsumed into the ambitions of others. No one ever votes for these things. They seem to just appear.
The end result is often the destruction of goodwill as popular initiatives are rammed down our throats and used to berate us for failing to live up to the standards our public servants impose upon us.
We then tire of the lectures. We wonder where these lunatics come from.
A moment of complacency means unwanted bike lanes but before long it is banned cars, government-controlled IDs and digital currencies. Those who pay attention to the activist world often sense they’d build concentration camps if they could get away with it and all thanks to some benign-sounding scheme we didn’t object to.
November 10, 2025
November 6, 2025
Reactions to Tuesday’s budget announcement
Mark Carney’s government finally got around to releasing their 2025 budget and lots of folks have thoughts and concerns about what is in it and what isn’t in it. After all, it could be the best possible budget, but it would still not satisfy all concerns … and nobody is pretending that this is anything close to “best possible” territory. Sylvain Charlebois says that the budget ignores the food insecurity issues and grocery prices for ordinary Canadians:
For a government that often talks about food affordability and insecurity, Budget 2025 offers surprisingly little that directly addresses either. There’s no bold food strategy, no affordability roadmap, and no new incentives for domestic food production. Yet, in between the lines, Ottawa has quietly set the stage for some indirect relief — not through grocery subsidies or consumer-facing policies, but through infrastructure, trade, and administrative reforms that could make the food system work a little more efficiently.
The largest signal comes from the government’s $115 billion infrastructure plan, one of its so-called “generational investments”. The new Trade Diversification Corridors Fund aims to modernize ports, railways, and airports — all chronic weak points in Canada’s food supply chain. When bottlenecks ease, goods move faster, and perishable products arrive fresher and cheaper. While no one in Ottawa framed this as a food-price measure, logistics efficiency has long been one of the most effective — and least visible — forms of price control.
[…]
Still, the absence of a broader vision for food affordability stands out. After years of grocery price volatility and public debate about “greedflation”, Canadians might have expected a more direct focus on food resilience — investments in innovation, local processing, or retail transparency. Instead, the government seems to have opted for a quieter, systemic approach: strengthen the arteries of trade and logistics, and trust that efficiency will trickle down to the dinner table.
The budget forecasts a $78.3 billion deficit for the 2025-26 fiscal year, which is significantly higher than notorious spendthrift Justin Trudeau’s last budget number. This adds to an already staggering $1.27 trillion debt load, which is nearly double what it was just before the pandemic. In the lead-up to the budget release Mark Carney had hinted at major sacrifices to be made, and while there wasn’t a lot in the document directly corresponding to sacrifice, the need to service that long-term debt will do the job quite adequately.
In the National Post, John Robson says that the budget is “elbows up, IQs down”:
Since I was last propelled years ago into the purgatory known as “the lockup”, where journalists spend budget day, have either process or contents improved? No. Instead they now insert a false stolen-land “acknowledgement” before even getting to the same old same old labeled bold and new. Which is especially troubling at this supposedly critical juncture.
The document is the familiar brick, 406 paper pages and 493 digitally with no explanation for the discrepancy and no excuse for the length. (Or for being called “Canada Strong” with an inexplicable picture of a ship.) Especially as the Finance Minister gabbled “This is a budget that talks to everyday Canadians,” and its purpose is to state plainly how much the government intends to spend, where it hopes to get the money and how far short it already knows it will fall, you shouldn’t have to wade through 248 pages of sludge to find out.
As P.J. O’Rourke said, “beyond a certain point, complexity is fraud”. Though we “privileged” insiders search “Summary Statement of Transactions” and voila, submerged on p. 249 (all references digital) is a $78.3 billion deficit next year if all goes well, and the national debt increasing $80.5 billion so it already didn’t.
Much commentary, and special-interest attention, focuses on trivial fiddles. But what matters is that Leviathan is in hock up to its horns, with interest payments projected at $55.6 billion next year, soaring to $76.1 billion by 2029-30. If the Lord is willing and the creek don’t rise, both forlorn hopes. NDP MP Leah Gazan, who would jail you for “downplaying” residential schools, snarled about not supporting an “austerity budget” but she won’t get the chance.
Some may bleat that times are tough. Indeed the finance minister’s campaign-speech “Foreword, Budget” gasses “The world is changing, profoundly and in real time; we are no longer living in an era of calm, but of significant change”.
The projected deficits are clearly hallucinatory, as the Liberals never seem to get deficit spending to go down, running deficits every year since 2015:
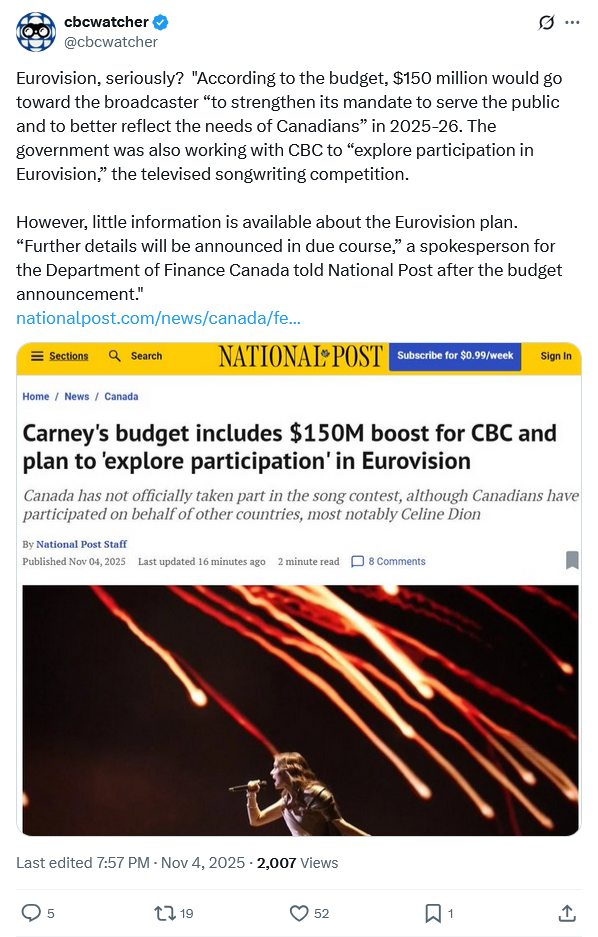
However, on the ludicrous side, the feds want to spend money to “investigate” Canada taking part in the freaking Eurovision contest:
On the slightly less ludicrous side, Noah considers the military aspects of the budget:
Budget 2025 outlines the government’s generational investment to quote, “defend Canada’s people and values, secure its sovereignty, and position the nation as a strong, reliable partner to its allies“. This starts by initiating a process of rebuilding, rearming, and reinvesting in the DND, CCG, and CAF to provide everyone with the necessary tools and equipment to protect sovereignty and bolster security.
Budget 2025 starts by outlining the government’s previous commitment to accelerate investments to meet NATO’s 2 per cent defence-spending target this year, which is five years ahead of schedule.
Budget 2025 goes a step further by setting Canada on a path to meet NATO’s 5 per cent Defence Investment Pledge by 2035. This will be broken down into two categories, 3.5 per cent of GDP by 2035 in core military needs, including supporting the CAF, modernising equipment and technology, and building up defence industries, and 1.5 per cent on security-related infrastructure and investments.
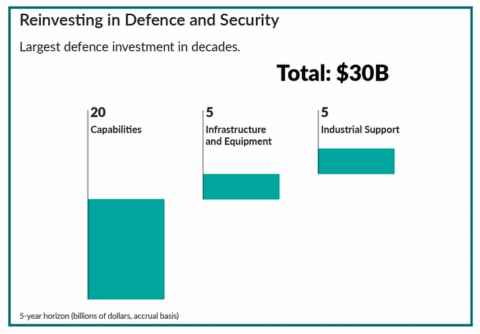
This reinvestment in defence and security is the largest in decades, totaling $30 billion over a five-year horizon on an accrual basis. This funding is allocated across three main pillars: $20 billion for capabilities, $5 billion for infrastructure and equipment, and $5 billion for industrial support.
On a cash basis, Budget 2025 proposes to provide $81.8 billion over five years, starting in 2025-26, to rebuild, rearm, and reinvest in the CAF. This figure includes over $9 billion in 2025-26 that was previously announced in June 2025. This is the funding previously set out for Canada to reach the 2 per cent NATO target.
Key investments from this $81.8 billion fund include $20.4 billion over five years to recruit and retain a strong fighting force, which incorporates the previously announced updates to pay and support for CAF health care.
An additional $19.0 billion over five years is allocated to repair and sustain CAF capabilities and invest in defence infrastructure, including the expansion of ammunition and training infrastructure. Upgrades to digital infrastructure for the Department of National Defence, CAF, and the Communications Security Establishment, particularly for cyber defence, are funded with $10.5 billion over five years.
Finally, $17.9 billion over five years is designated to expand Canada’s military capabilities, with investments in logistics, utility, and armoured vehicles, as well as counter-drone, long-range precision strike capabilities, and domestic ammunition production.
This is a serious chunk of change, although sadly, and as you will see, we don’t get a major breakdown of what this looks like. What we are left with are general piles of money, which isn’t always a bad thing. It’s also expected. The budget is set for a timeline before many critical capabilities will be delivered, so they won’t be included. Almost everything comes after 2030.
September 27, 2025
NATO – the alliance of paper tigers?
In UnHerd, Edward Luttwak suggests that despite President Trump calling the Russians “paper tigers”, the non-US members of the NATO alliance could more appropriately be described that way:

It’s been an open secret for decades that Canada’s NATO contributions are more rhetoric than reality, but it’s true of many of the European NATO allies, too.
… simply raising defence spending will not turn Europe’s states into genuinely effective military powers. For one thing, the GDP criterion is much too vague to mean much. Finland, for instance, spends only 2.4% of its GDP on defence and yet can mobilise some 250,000 determined soldiers. Other Nato members, which spend much more than the Finns, obtain far less for their money.
Moreover, focusing on GDP instead of force requirements — so many battalions, artillery regiments, fighter squadrons — is nothing but an invitation to cheat, an opportunity lustily taken up across the continent. The latest Spanish submarine, for instance, is not imported for €1 billion or so from Thyssen-Krupp, which supplies navies around the world with competent, well-proven submarines. Instead, it was proudly designed and built at the Navantia state-owned Spanish shipyard: for €3.8 billion, roughly the cost of a much bigger French nuclear-powered submarine. As a feeble justification for that absurdly high cost, Spain’s defence minister cited a supposedly advanced air-recirculation system — so greatly advanced, in fact, that it is not actually ready, and will not be installed even in the submarine’s next iteration.
Soon, though, Italy will outdo Spain’s platinum submarine: by including a new bridge to Sicily, set to cost some €13.5 billion, into its 2% of GDP Nato spending quota. The government’s excuse is that some 3,000 Italian troops may need to cross the Strait of Messina were the Italian army ever to be fully mobilised. But it would be much cheaper to fly them individually, each trooper in his own luxurious private jet. Even without the bridge, meanwhile, Italy’s cheating on the 2% target is bad enough. Most notably, much of the Italian Navy’s spending goes towards warships made by Italy’s state-owned Fincantieri shipyard. But there is not enough money for the fuel and maintenance expenses to operate more than half of them, meaning another industrial subsidy is camouflaged as defence spending. All the while, Italy refuses to increase its defence budget beyond the very modest target of 2% — which it has yet to meet.
As for Germany, three and half years since the start of the Ukraine war, with ever more ambitious rearmament plans loudly promised, the total number of personnel in uniform has actually slightly decreased. And, aside from beginning a multi-billion euro purchase on an Israeli missile-defence system, nothing much has happened. Despite its high demand in Ukraine, even the battle tank, that German specialty, is being produced in very, very small numbers: so low that the annual output could be lost in a morning of combat. In May 2023, indeed, a meagre 18 Leopard tanks were ordered to replace older models lost in Ukraine. The expected delivery date? Between 2025 and 2026! Then, in July, Germany purchased a further 105 advanced Leopard 2A8s. That is the number needed to equip a single brigade, the German force stationed in Lithuania — and they are expected to arrive in 2030!
The sad truth, then, is that Germany has yet to start working in earnest to correct the extreme neglect inflicted on its armed forces during the long Merkel premiership, when she kept saying that “even if we had the money we would not know how to spend it”. All the while, German helicopters lacked rotors and tanks lacked engines. The exceedingly slow recovery of the German army is especially frustrating because Nato is not actually short of air or naval forces. What it lacks are ground forces, soldiers more simply, or rather soldiers actually willing to fight. Having added Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania to the alliance, tiny countries with outsized defence needs, the alliance faces a severe troop deficit across the entire Baltic sector. The troops so far sent by Nato allies, such as visiting Alpini battalions from Italy, cannot improve the maths.
Update, 30 September: Welcome, Instapundit readers! Please do have a look around at some of my other posts you may find of interest. I send out a daily summary of posts here through my Substack – https://substack.com/@nicholasrusson that you can subscribe to if you’d like to be informed of new posts in the future.
September 13, 2025
“It was about control before green policy became popular, and it is about control now”
In the National Post, Carson Jerema identifies the common thread among all of Prime Minister Mark Carney’s efforts since becoming Liberal party leader:

Then-Governor of the Bank of Canada Mark Carney at the 2012 Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland.
WEF photo via Wikimedia Commons.
Prime Minister Mark Carney may not be as obnoxiously progressive as Justin Trudeau, but that doesn’t mean he isn’t stubbornly left wing in his own right, though he has managed to convince many critics otherwise.
Over the past decade, the Liberals were particularly self-righteous over climate policy, so much so that the deviations made by Carney since assuming office have been met with praise — or, on the left, with scorn — that he is somehow pro-business and represents the return of the centre-right Liberals. Some even think he’s a conservative. Others have suggested that Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre is now entirely redundant.
This narrative is just more proof of how utterly captured the media is in this country by the Liberal party. It is true that Carney gives the appearance that he is abandoning many of the government’s environmental policies. He set the carbon tax rate to zero, paused the EV mandate and, on Thursday, he refused to endorse his government’s own carbon-emissions targets.
None of this, however, should be taken as evidence that Carney represents some sort of rightward or pro-business shift in the Liberal party. He is not proposing to let markets determine what infrastructure projects get built. Nor is he proposing to minimize regulations to attract investment.
Instead, Carney wants to command the economy by himself, laying bare the reality that what attracts left-wing politicians to climate policy is not saving the planet from carbon, but using environmental objectives to manage the economy. It was about control before green policy became popular, and it is about control now. For Carney specifically, before he entered politics, “decarbonizing” markets was quite remunerative in his various banking roles.
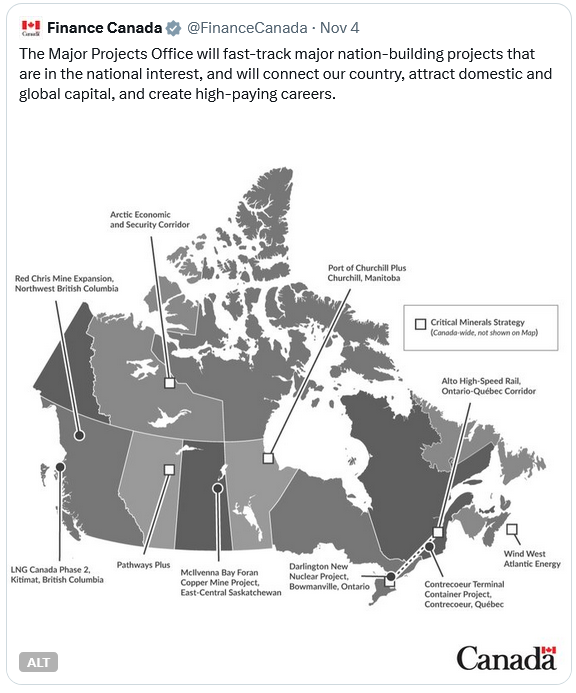
Noticeably absent from the five infrastructure projects that the prime minister said on Thursday would be fast-tracked under the Major Projects Office was an oil and gas pipeline. Also noticeable was the fact that all five of the projects had already been approved, but the government tried to pass them off as something new anyway.
Even if the projects had been all brand new, the lack of a pipeline would still be of no surprise, as what private investor would be willing to back a pipeline when the Liberals’ Impact Assessment Act, tanker ban and emissions cap all exist to conspire against energy projects of any kind?
One thing that became incredibly obvious early in Justin Trudeau’s premiership was that the prime minister — and his ministers in general — really did seem to believe that talking about doing something was as effective in solving problems as actually doing the thing. Many had hoped that Mark Carney would be different … but as Dan Knight points out, he may actually be worse:
From there, [Poilievre] broadened the attack. He spoke of an entire generation priced out of homeownership, of immigration growing “three times faster than housing and jobs”, of crime rising, and of what he called “the worst economy in the G7”. And then he turned squarely on Carney: “Mr. Carney is actually more irresponsible than even Justin Trudeau was“, citing an 8% increase in government spending, 37% more for consultants, and 62 billion dollars in lost investment — the largest outflow in Canadian history, according to the National Bank.
The message was simple: Liberals talk, Conservatives build. Poilievre painted Carney as a man of speeches and promises, not results. “The mistake the media is making is they’re judging him by his words rather than his deeds“, he said.
It was an opening statement designed less to introduce policy — those details came later — and more to frame the battle. For Poilievre, Carney isn’t just Trudeau’s replacement. He’s Trudeau’s sequel, and in some ways worse.
[…]
Pierre Poilievre didn’t hold back when asked about Mark Carney’s record. His words: “Mr. Carney is actually more irresponsible than even Justin Trudeau was“. That’s not a throwaway line, he backed it with numbers.
According to Poilievre, Carney inherited what he called a “morbidly obese government” from Trudeau and made it worse: 8% bigger overall, 37% more for consultants, and 6% more bureaucracy. He says Carney’s deficit is set to be even larger than Trudeau’s.
Then the jobs number: 86,000 more unemployed people under Carney than under Trudeau. That, Poilievre argued, is the real measure, not the polished speeches Carney gives. His line: “The mistake the media is making is they’re judging him by his words rather than his deeds“.
August 20, 2025
California’s ever-receding High Speed Rail dream
Chris Bray provides an on-the-ground update of California’s ultra-expensive high speed rail project which still has yet to deliver a single passenger from one station to another after nearly 20 years of funding:
Start with a description: “In 2008, California voters approved $9.95 billion of state bond funding as seed money to build an 800-mile high-speed rail (HSR) network connecting Los Angeles and San Francisco, and the Central Valley to coastal cities, at speeds of up to 220 miles per hour, with an expected completion date of 2020.”
Construction started in 2015. Pause for a moment and really notice the date.
Ten years later, the project has consumed $18 billion, and an effort to connect Los Angeles and San Francisco has turned into a much more modest “Phase One” plan to connect the cities of the Central Valley, well east of the coast. The modest declared cost of the proposed LA-to-SF bullet train now looks like this for the much shorter line: “a cost range of $89 billion to $128 billion.” The Trump administration has declined to provide more federal funding for the project, but California is suing to try to keep the federal spigot open.
[…]
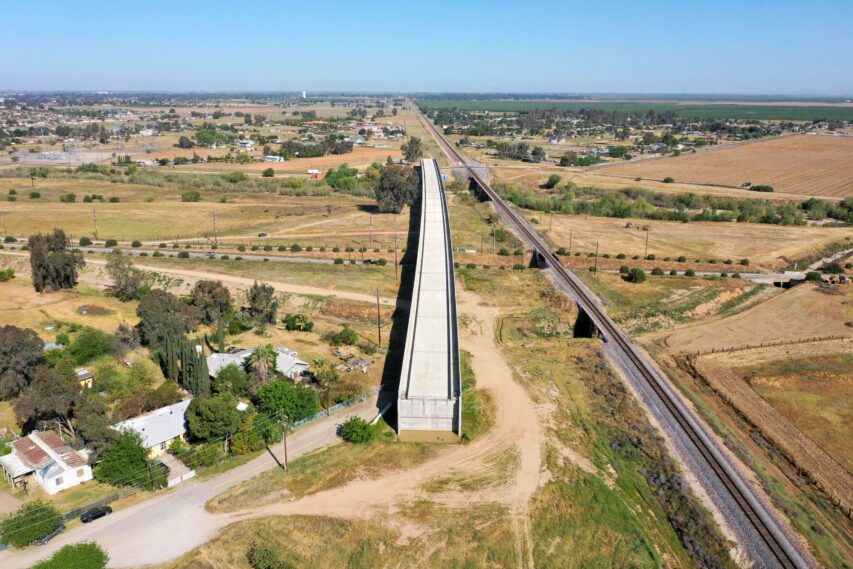
Famously, the California High-Speed Rail Authority has been posting pictures of its huge construction successes on social media:
See, that’s … almost a whole rail line for a bullet train. Obviously!
So!
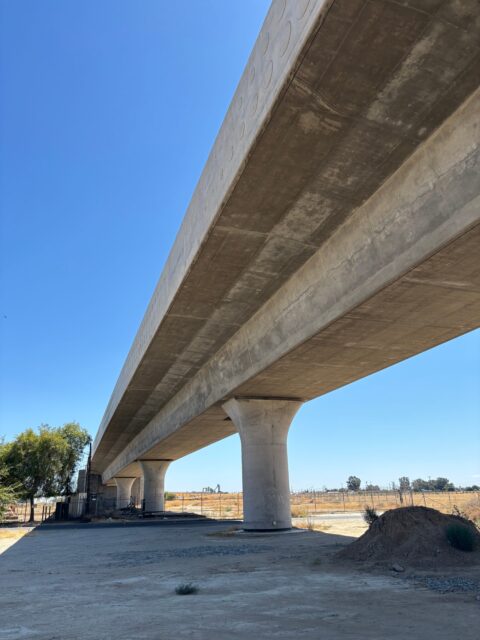
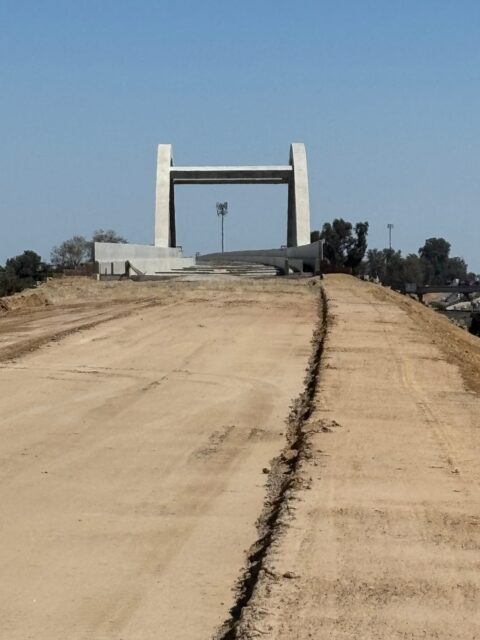
If you ever find yourself in Fresno, and I sincerely hope you don’t, the structures that have been built for “high-speed rail” are surprisingly easy to access. There are several places where those structures aren’t fenced in or guarded. At all. […] So when you see this:
…it’s not that hard to just head up onto the thing. It’s also very dangerous, legally dubious, and something you definitely shouldn’t do. Since it’s an elevated construction site, there are a lot of places without guardrails where you can just fall off the thing, and it’s a long way down.
Everyone see this part: Don’t go up there. It’s dangerous. You can fall and die. […] But if you were to climb up onto the thing, which you absolutely should never do, you would see a whole bunch of this:
That’s a section at the northern end of Fresno, looking south.
Of course, California isn’t the only jurisdiction struggling to complete big infrastructure projects: Toronto’s long-awaited Crosstown LRT project got started in 2007 and still has no confirmed completion date, although a faint possibility exists that a portion of the line may open later in 2025.
May 19, 2025
The Roman Empire and climate change
Sebastian Wang considers “what we all know” about the rise and fall of the Roman Empire in the light of more recent research (not all of it politically motivated) into climate change:
Before we get into climate, and for those who tend to the wholly ignorant spectrum of my readers, we need a quick sketch of Roman history. The Empire officially began in 27 BC, when Octavian — better known as Augustus — became the first emperor. It ended in the west in AD 476, when the last western emperor was kicked out. As said, the eastern half, based in Constantinople, carried on for another thousand years.
Broadly, we can divide Roman history as follows:
- 27 BC – AD 180: The golden age. Augustus and his successors took over and further expanded a huge empire. There was peace (mostly), trade flourished, and cities grew. People call it the “Pax Romana“.
- AD 180 – 284: Everything starts to fall apart. This is called the Crisis of the Third Century. Civil wars, foreign invasions, plagues, and economic collapse all hit at once.
- AD 284 – 395: The empire pulls itself together. Emperors like Diocletian and Constantine bring in reforms. But the empire is now divided for administrative convenience — east and west.
- AD 395 – 476: The west goes under. It’s invaded. It’s conquered and broken up. Very quickly, it disappears. Though, once again, a parochial view of history, we call this the Fall of the Roman Empire.
The standard histories still blame bad rulers or too many wars. That’s fair enough. There were some very bad rulers, and the wars without number. But if you look at the climate data — tree rings, ice cores, sediment levels — you start to see another pattern underneath what may be called the political and economic superstructure of Roman history.
When Rome came to greatness, the climate was unusually good. From around 200 BC to AD 150, there was a long phase of stable, warm, and mostly wet conditions. Scientists call this the Roman Climate Optimum. In Egypt, the Nile flooded regularly and well. That meant lots of grain. In the Alps, glaciers shrank. In northern Europe, people were growing grapes in places too cold for vineyards today. In the Middle East, the Dead Sea stayed high, showing good rainfall.
This kind of weather made everything easier. Crops were reliable. Surpluses could be taxed. Cities could be fed. Roads and aqueducts could be built and maintained. And because the army was well supplied, the Empire was protected, and could even continue a modest expansion. But, as McCormick and his team point out, the high phase of Nile flooding correlates exactly with the high point of Roman prosperity — and once those floods became less predictable, problems followed.
The good times came to an end. By the mid-second century, a wave of volcanic eruptions thew great masses of dust into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight. Solar activity dropped. The climate became less stable. Then came the Antonine Plague in AD 166. It probably started in the east and spread quickly. Some think it was smallpox. Whatever it was in terms of microbiology, it was almost certainly brought on by changes in the climate. It may have killed a third of the Empire’s population.
Worse was coming. By AD 200, climate records show more erratic rainfall and cooling. In Gaul and the Balkans, harvests became less predictable. Glaciers began to advance again. Speleothem data from Austrian caves shows sharp shifts in rainfall patterns.
At the same time, the empire started to shake. Between 235 and 284, Rome had over twenty emperors. Most were generals who seized power, then got killed. Civil wars broke out. Trade declined. Foreign tribes pushed harder at the frontiers. Coin hoards — money buried for safety — increased in number. That’s usually a sign of fear and instability. Cities shrank. The economy shrivelled.
Was this all because of climate? No — not wholly. A good definition of historical crank is someone who tries to explain everything in terms of one cause or set of causes. But as McCormick et al. argue, bad weather made everything worse. It weakened agriculture, strained supplies, and made people more likely to panic or rebel. In a world without modern logistics, you couldn’t afford bad harvests two or three years in a row.
The empire buckled in the third century, but didn’t collapse. And its survival probably was an effect of human agency. A line of competent Emperors rose from the army and stabilised the frontiers. This line culminated in the reigns of Diocletian and Constantine, who restructured the Empire. They fixed taxes. They reorganised the army. Constantine built his new capital in the east. His successors found Constantinople safer and more strategically useful than Rome.
This being said, around AD 290, climate records suggest a small rebound. Warmer temperatures and better rainfall returned — especially in the east. That helped the eastern provinces recover faster. They had stronger governments and better infrastructure. But climate helped. Dead Sea levels remained relatively high, which meant steady rain in the Levant.
The west wasn’t so lucky. Italy and parts of Gaul stayed unstable. In Britain, pollen records show that farmland was being abandoned. The archaeology matches this, with fewer building projects and shrinking urban centres. The killing shock for the west came in the fifth century. In Central Asia, a long drought began around AD 370. Steppe tribes like the Huns were hit hard. They migrated west, pushing other tribes like the Goths ahead of them. In AD 376, the Goths crossed the Danube into Roman territory. Two years later, they crushed a Roman army at Adrianople. This all happened in the eastern half. But greater wealth and better leadership allowed the government in Constantinople to push the barbarians west. Over the next century, the western empire was hit again and again.
Meanwhile, the weather got worse. Europe cooled. Rainfall patterns shifted. Flooding and crop failures increased. Volcanic sulphur levels spike in the ice core record from Greenland.
Rome was sacked in AD 410. Again in 455. Finally, in 476, the last western emperor was deposed. That was it. The western Roman Empire was gone.
The east survived. But was hardly untroubled. In AD 536, a huge volcanic eruption darkened skies around the world. The sun barely shone. Crops failed. Famines spread.
A few years later, the Plague of Justinian broke out. It probably started in Egypt and spread through trade routes. Some say it killed half the population in affected areas.
Climate and disease worked together. Hunger weakened people. Infection finished them off. As McCormick et al. put it, the event of 536 and the plague that followed created one of the worst demographic shocks in recorded history.
May 12, 2025
The rise of the Hansa
At Works in Progress, Agree Ahmed describes the conditions in northern Europe in the Middle Ages that helped create the Hanseatic League:
Today, we typically think of coalitions in the context of modern electoral politics. So it might be surprising that one of the greatest case studies in the history of coalitions is a community of medieval German merchants known as the Hansa.
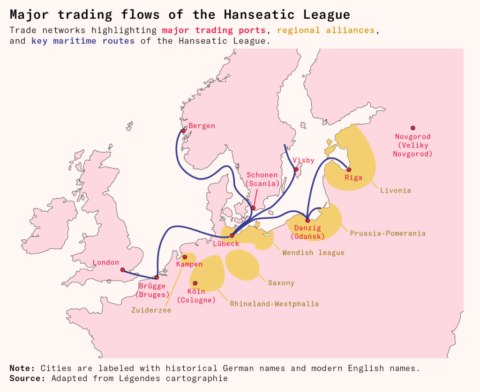
Starting as individual traveling traders, the Hansa built up coalitions for collective bargaining, collective action, and collective security. Through this process, they formed Northern Europe’s first ever long-distance trade network.
Without corporate structures, they built supply chains that distributed goods between Northern Europe’s major ports, with capillaries that spread into each city’s hinterlands. Without formal territory, their laws governed trading hubs spanning thousands of miles, from London all the way to Western Russia. And, despite being composed of hundreds of member cities, the Hanseatic League had no head of state. Yet the Hansa still managed to sign treaty after treaty with foreign rulers and, a few times, even fought (and won!) wars.
[…]
Better climate, more arable land, and better farming techniques lifted Europe’s crop yields to above subsistence levels for the first time since the Roman period. After several centuries of decline, Europe’s population grew from 18 million in the 600s to over 70 million by the 1300s – nearly triple the population of the Roman period. The nutritional surplus allowed for Europe’s first significant artisan class since the Roman empire. Each town had common craftsmen like blacksmiths, leatherworkers, and carpenters. But local skills and resources allowed for the emergence of specialized crafts, which were unique to specific regions and could therefore be traded.
Tax-hungry lords across Europe began to set up permanent marketplaces for their growing communities. And so hundreds of towns formed in Europe, filled with workers who had flocked from countryside manors. These towns were the first substantial permanent markets in Northern Europe’s history.
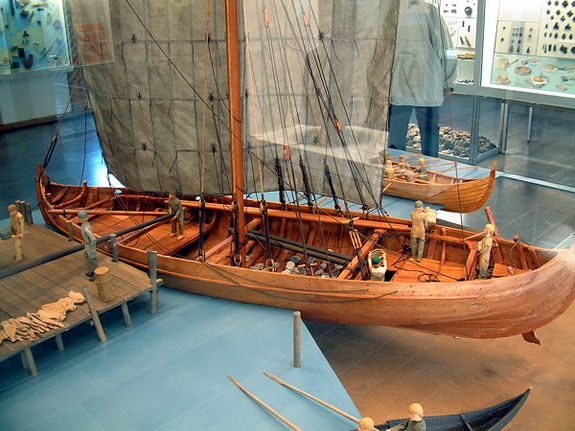
As production accelerated, so did shipping. The warmer climate meant waterways in the North and Baltic Seas were navigable for longer stretches of the year. Meanwhile innovations in boatmaking dramatically improved shipping capacity. Excavations of the few surviving ships from this era show that, in the span of a few centuries, vessels tripled their average tonnage from 10 to 30 while dropping the number of rowers required by a factor of four.
The breakthrough in tonnage starting in 900 can be credited to the knarr, a Viking-style ship that was shorter and wider than the longboat that preceded it, allowing it to load substantially more cargo with a smaller crew. Prior to the knarr, trade convoys had to carry cargo on longboats, which were agile but could only carry small fractions of what the knarr could.
When Northern Europe’s first long-haul merchants set off on their voyages, they faced a world that had not yet been ordered for trade. Sailors had to worry about pirates in the Baltic and shipwrecks at icelocked winter ports.
Riverways gave merchants access to inland communities, where they could find products at lower prices to then sell for a profit in major port cities. But riverside towns were more interested in their own engineering projects or grinding their grain and so would block rivers with dams and water mills, and they would redirect water to irrigate fields.
And even if a river were clear of obstructive mills or dams, it might be heavily punctuated by toll stations. The Rhine River, a key shipping artery that connected inland Germany with the Baltic coast, had tolls approximately every five kilometers.
Under the laws of the Holy Roman Empire, the right to collect tolls on the Rhine could only be granted by the Emperor. But unauthorized tolling stations, or tolls levied in excess of what was authorized, were so rampant that the malpractice had a name: the lonia iniusta (Latin for “unjust tolls”). Some local authorities enforced toll collections along rivers by running chains from bank to bank, making it impossible for a boat to pass without paying. Others would patrol the river on their own boats and deny vessels passage until they paid up.
In the first four years of the Great Interregnum Period (1250–73), when the Empire had no emperor, the number of toll stations on the Rhine doubled to 20. This is the origin of the term “robber baron”: local barons, operating out of riverside castles, would set up illicit toll stations and demand significant shares of merchant cargo in order to pass.
The journey on land wasn’t much easier. Toll booths were similarly common. Nominally, these were to pay the landowner for the maintenance of the roads and bridges but in reality they were usually left dilapidated. Merchants voyaging on land had to load their wares on the backs of mules and horses (which were about a third the speed of ships). The narrow widths of medieval roads meant these caravans stretched out in long lines, leaving animals and cargo physically exposed. These vulnerable, slow moving, value-dense caravans attracted bandits who roamed the isolated roads between towns. It was nearly guaranteed a caravan would face an attempted robbery – either illegally by bandits or (somewhat) legally in the form of a toll shakedown – over the course of a sufficiently long trip.
As a matter of safety, Northern European merchants learned to move together in armed groups. These traveling merchant bands were called hansas, a Lower German word meaning “company” or “troop”. When a hansa formed for a trip, they elected an alderman (literally “elder man”) who would speak on behalf of the group to the various authorities – lords, princes, bishops, and other rulers – they might encounter along the way.
Once they completed the arduous journey, the merchants had to deal with the local governments of their destination cities, each of which had different and constantly changing laws. To protect the local merchants and craftsmen within their city walls from competition, princes might demand exorbitant taxes from foreign merchants or deny them access to the city altogether. Merchant bands had to negotiate collectively to secure the right to trade within each city in which they wished to conduct business. And if they made it into the city walls, they might not make it out: capricious lords might suddenly imprison foreign merchants (as happened to German merchants in England in 1468 and Novgorod in 1494), raid their offices, or seize their merchandise.
Local laws threatened foreign merchants more than they protected them. Most town courts, themselves newly formed, had minimal experience adjudicating long distance commercial disputes. When such disputes did arise, courts could take weeks or months to arbitrate them, and were heavily biased towards locals over foreign traders. Without sovereign states, merchants were left dealing with a fractured landscape of town courts, where each market had its own idiosyncratic laws. And because foreign traders could evade punishment by fleeing overseas, courts in England, France, Italy, and the Holy Roman Empire often collectively punished foreign merchant communities for the unpaid debts of their countrymen.
The lack of early medieval records makes it difficult to quantify just how much Northern European commerce grew as a result of continuous long distance trade. Before the late medieval period, Northern Europe’s archaeological record of trade shows just several dozen sites known as emporiums: small, temporary settlements outside of towns where foreign merchants traded with locals. But starting in the late medieval period (1300 to 1500), Lower German merchants began to change this.
H/T to Niccolo Soldo for the link.