Niccolo Soldo continues his in-depth look at the situation in Spain leading up to the outbreak of the civil war in 1936. It’s clear that bloodshed was in the immediate future — so much so that it’s almost surprising that it took as long as it did for the war to start in earnest:

Flag of Spain during the Second Spanish Republic (1931-1939).
Image by SanchoPanzaXXI via Wikimedia Commons.
In 1930, almost half of all Spaniards over the age of 10 were illiterate. The country was still overwhelmingly agrarian, with a small number of very wealthy landowners owning about 2/3rds of all the arable land in Andalusia alone, employing almost a million landless campesinos at barely subsistence-level wages. Industry was almost entirely found only in the north and northeast. Industrialization was beginning to pick up pace by the turn of the century, but was still very far behind the rest of Western Europe by the time the Second Spanish Republic came into being in 1931.
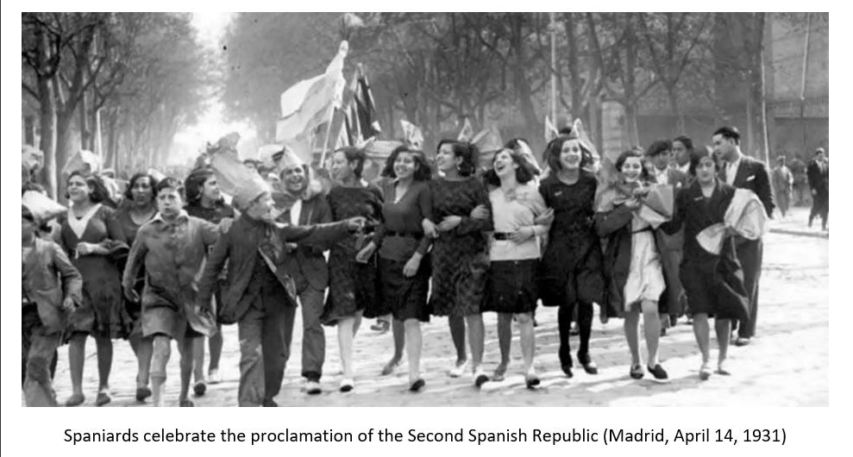
Despite Spain having one foot in the past, its other foot was in the present, a present that was rapidly changing and very unstable politically. The loss of confidence in King Alfonso XIII on the part of the middle and upper classes led to his abdication which opened the door to the establishment of the Second Republic, a democracy in a time when democracy itself was under attack throughout Europe, having already lost in Russia and Italy, and on its way to disappearing in other countries, most notably Germany.
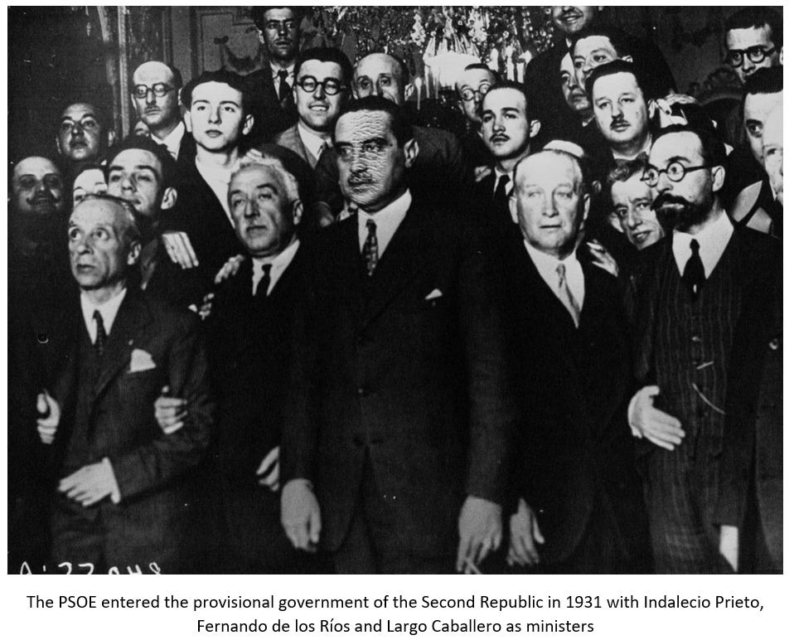
The end of the monarchy was celebrated throughout the country (with some exceptions), but not always for the same reason. Yes, anti-monarchist forces viewed the monarchy as retrograde and out of step with the modern era, but only the liberals and various republican parties were committed to democracy and parliamentary politics. The Socialists (PSOE) for example, were riven by factionalism and a generational divide whereby there were those who sought to use power in office to both settle scores with their old enemies in the military, the landowning class, and especially the Catholic Church, and to actually launch a revolution along Marxist lines. For them, the Second Republic was a vehicle for a larger goal, and not an end goal in and of itself. Anarchists celebrated the end of the monarchy, but they were opposed to any and all government on principle. For Anarchists, the Second Republic was also a path towards revolution as well. For Catalan separatists, the Spanish Second Republic was a stepping-stone towards independence, or at least towards as much political and economic autonomy as possible.
Conservatives were in a state of disarray upon the establishment of the Second Republic. Despite this condition, all the factions that could be grouped as “conservatives” largely supported the new regime … at least at the outset. Once the agenda of the first government of the Second Republic was made public, opposition began to harden.
Rather than trying to generate a grand consensus among the various factions that dominated Spanish politics, economics, and society in 1931, the liberals, republicans, and socialists who led the country from 1931-33 instead chose to attack the core interests of their political rivals to the right. The military was to be slashed via the retirement of a large number of its officer class, land was to be seized from wealthy landowners in order to redistribute it to the poor and landless, and the Catholic Church was to be stripped of its role in educating young Spaniards, with the Jesuits expelled from the country altogether, and many churches, convents, monasteries, episcopal residences, parish houses, seminaries, etc. expropriated by the Spanish state. Private Catholic schools were also expropriated and turned into government-run ones instead. The Church was also forced to pay taxes and was banned from all industry and trade, “… enforced with strict police severity and widespread mob violence”.
These attacks on the Catholic Church (which also saw the torching of churches, monasteries, and convents in 1931 as we saw in the previous entry in this series) resulted in the release of a Papal Encyclical by Pope Pius XI on June 5, 1933 entitled “Dilectissima Nobis“. In this encyclical, Pius XI decries the persecution of the Church in Spain, and asks Spanish Catholics to defend themselves and the Church from attacks by the government. He describes the attacks as “… [an] offense not only to Religion and the Church, but also to those declared principles of civil liberty on which the new Spanish regime declares it bases itself”. As we already saw previously, then-Minister of War in the Spanish cabinet, Manuel Azaña, famously declared that “All the convents in Spain are not worth a single Republican life“.
There was no attempt to build a solid democratic foundation for the Second Republic whatsoever. Instead, a cultural revolution was quickly ushered in, and an agrarian revolution was threatened, but only implemented half-heartedly. The first government of the Second Spanish Republic managed to alienate the military, the landowning class, conservatives, and the Catholic Church overnight.
On the other side of the political divide, the centrists were attacked from the left for not going far enough, fast enough. Campesinos and small landowners demanded immediate expropriation of latifundia estates to be redistributed to them. The youth wing of the PSOE urged the nationalization of all industry, which led to factionalism within the socialist groupings. Less radical socialists pointed to the extension of voting rights to women, to the enshrining of the eight hour workday in law, and to the increase in wages for industry workers as the biggest successes of the first two years of the Second Republic. These radical factions were not content with these incremental gains, and demanded “more, now!”
This radicalism culminated in the “Casas Viejas Incident”, which I described in the previous entry:
Staying true to form, the anarchists were restless and, as is their nature, opposed the present government in Spain as they opposed all governments, viewing them as inherently oppressive. Their massive labour union, CNT, led by the vanguard of FAI, began demonstrations in various locations across the country, with the greatest actions taking place in Andalusia. Political violence ensued, with two Civil Guards wounded. The Assault Guards, set up by the new Constitutional authorities in the Republic to provide a new force to purportedly protect those who lacked protection under the Monarchy, raided the village of Casas Viejas near Cadiz. They encountered a group of anarchists locked in a house and set fire to it (while disarming others in the village who were armed), and then executed them.
This act of state violence was committed not by fascists, nationalists, royalists, or even conservatives. It was committed by a liberal-socialist regime and its purposely-created security force, against anarchists. All the parties involved in this incident would find themselves on the same side in the not-too-distant Spanish Civil War.