This vision of the collapse of Roman political authority in the West may seem a bit strange to readers who grew up on the popular narrative which still imagines the “Fall of Rome” as a great tide of “barbarians” sweeping over the empire destroying everything in their wake. It’s a vision that remains dominant in popular culture (indulged, for instance, in games like Total War: Attila; we’ve already talked about how strategy games in particular tend to embrace this a-historical annihilation-and-replacement model of conquest). But actually culture is one of the areas where the “change and continuity” crowd have their strongest arguments: finding evidence for continuity in late Roman culture into the early Middle Ages is almost trivially easy. The collapse of Roman authority did not mark a clean cultural break from the past, but rather another stage in a process of cultural fusion and assimilation which had been in process for some time.
The first thing to remember, as we’ve already discussed, is that the population of the Roman Empire itself was hardly uniform. Rather the Roman empire as it violently expanded, had absorbed numerous peoples – Celtiberians, Iberians, Greeks, Gauls, Syrians, Egyptians, and on and on. Centuries of subsequent Roman rule had led to a process of cultural fusion, whereby those people began to think of themselves as Romani – Romans – as they both adopted previously Roman cultural elements and their Roman counterparts adopted provincial culture elements (like trousers!).
In particular, by the fifth century, the majority of these self-described Romani, including the overwhelming majority of elites, had already adopted a provincial religion: Christianity, which had in turn become the Roman religion and a core marker of Roman identity by the fifth century. Indeed, the word paganus, increasingly used in this period to refer to the remaining non-Christian population, had a root-meaning of something like “country bumpkin”, reflecting the degree to which for Roman elites and indeed many non-elites, the last fading vestiges of the old Greek and Roman religions were seen as out of touch. Of course Christianity itself came from the fringes of the Empire – a strange mystery cult from the troubled frontier province of Judaea in the Levant which had slowly grown until it had become the dominant religion of the empire, receiving official imperial favor and preference.
The arrival of the “barbarians” didn’t wipe away that fusion culture. With the exception of the Angles, Saxons and Jutes who eventually ended up in England, the new-comers almost uniformly learned the language of the Roman west – Latin – such that their descendants living in those lands, in a sense still speak it, in its modern forms: Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, etc. alongside more than a dozen local regional dialects. All are derived from Latin (and not, one might note, from the Germanic languages that the Goths, Vandals, Franks and so on would have been speaking when they crossed the Roman frontier).
They also adopted the Roman religion, Christianity. I suspect sometimes the popular imagination – especially the one that comes with those extraordinarily dumb “Christian dark age” graphs – is that when the “barbarians invade” the Romans were still chilling in their Greco-Roman temples, which the “barbarians” burned down. But quite to the contrary – the Romans were the ones shutting down the old pagan temples at the behest of the now Christian Roman emperors, who busied themselves building beautiful and marvelous churches (a point The Bright Ages makes very well in its first chapter).
The “barbarians” didn’t tear down those churches – they built more of them. There was some conflict here – many of the Germanic peoples who moved into the Roman Empire had been converted to Christianity before they did so (again, the Angles and Saxons are the exception here, converting after arrival), but many of them had been converted through a bishop, Ulfilias, from Constantinople who held to a branch of Christian belief called “Arianism” which was regarded as heretical by the Roman authorities. The “barbarians” were thus, at least initially, the wrong sort of Christian and this did cause friction in the fifth century, but by the end of the sixth century nearly all of these new kingdoms created in the wake of the collapse of Roman authority were not only Christian, but had converted to the officially accepted Roman “Chalcedonian” Christianity. We’ll come back later to the idea of the Church as an institution, but for now as a cultural marker, it was adopted by the “barbarians” with aplomb.
Artwork also sees the clear impact of cultural fusion. Often this transition is, I think, misunderstood by students whose knowledge of artwork essentially “skips” Late Antiquity, instead jumping directly from the veristic Roman artwork of the late republic and the idealizing artwork of the early empire directly to the heavily stylized artwork of Carolingian period and leads some to conclude that the fall of Rome made the artists “bad”. There are two problems: the decline here isn’t in quality and moreover the change didn’t happen with the fall of the Roman Empire but quite a bit earlier. […]
Late Roman artwork shows a clear shift into stylization, the representation of objects in a simplified, conventional way. You are likely familiar with many modern, highly developed stylized art forms; the example I use with my students is anime. Anime makes no effort at direct realism – the lines and shading of characters are intentionally simplified, but also bodies are intentionally drawn at the wrong proportions, with oversized faces and eyes and sometimes exaggerated facial expressions. That doesn’t mean it is bad art – all of that stylization is purposeful and requires considerable skill – the large faces, simple lines and big expressions allow animated characters to convey more emotion (at a minimum of animation budget).
Late Roman artwork moves the same way, shifting from efforts to portray individuals as real-to-life as possible (to the point where one can recognize early emperors by their facial features in sculpture, a task I had to be able to perform in some of my art-and-archaeology graduate courses) to efforts to portray an idealized version of a figure. No longer a specific emperor – though some identifying features might remain – but the idea of an emperor. Imperial bearing rendered into a person. That trend towards stylization continues into religious art in the early Middle Ages for the same reason: the figures – Jesus, Mary, saints, and so on – represent ideas as much as they do actual people and so they are drawn in a stylized way to serve as the pure expressions of their idealized nature. Not a person, but holiness, sainthood, charity, and so on.
And it really only takes a casual glance at the artwork I’ve been sprinkling through this section to see how early medieval artwork, even out through the Carolingians (c. 800 AD) owes a lot to late Roman artwork, but also builds on that artwork, particularly by bringing in artistic themes that seem to come from the new arrivals – the decorative twisting patterns and scroll-work which often display the considerable technical skill of an artist (seriously, try drawing some of that free-hand and you suddenly realize that graceful flowing lines in clear symmetrical patterns are actually really hard to render well).
All of the cultural fusion was effectively unavoidable. While we can’t know their population with any certainty, the “barbarians” migrating into the faltering western Empire who would eventually make up the ruling class of the new kingdoms emerging from its collapse seem fairly clearly to have been minorities in the lands they settled into (with the notable exception, again, of the Angles, Saxons and Jutes – as we’re going to see this pattern again and again, Britain has an unusual and rather more traumatic path through this period than much of the rest of Roman Europe). They were, to a significant degree, as Guy Halsall (op. cit.) notes, melting into a sea of Gallo-Romans, or Italo-Romans, or Ibero-Romans.
Even Bryan Ward-Perkins, one of the most vociferous members of the decline-and-fall camp, in his explosively titled The Fall of Rome and the End of Civilization (2005) – this is a book whose arguments we will come back to in some detail – is forced to concede that “even in Britain the incomers [sic] had not dispossessed everyone” of their land, but rather “the invaders entered the empire in groups that were small enough to leave plenty to share with the locals” (66-7). No vast replacement wave this, instead the new and old ended up side by side. Indeed, Odoacer, seizing control of Italy in 476, we are told, redistributed a third of the land; it’s unclear if this meant the land itself or the tax revenue on it, but in either case clearly the majority of the land remained in the hands of the locals which, by this point in the development of the Roman countryside, will have mostly meant in the hands of the local aristocracy.
Instead, as Ralph Mathisen documents in Roman aristocrats in barbarian Gaul: strategies for survival in an age of transition (1993), most of the old Roman aristocracy seems to have adapted to their changing rulers. As we’ll discuss next week, the vibrant local government of the early Roman empire had already substantially atrophied before the “barbarians” had even arrived, so for local notables who were rich but nevertheless lived below the sort of mega-wealth that could make one a player on the imperial stage, little real voice in government was lost when they traded a distant, unaccountable imperial government for a close-by, unaccountable “barbarian” one. Instead, as Mathisen notes, some of the Gallo-Roman elite retreat into their books and estates, while more are co-opted into the administration of these new breakaway kingdoms, who after all need literate administrators beyond what the “barbarians” can provide. Mathisen notes that in other cases, Gallo-Roman aristocrats with ambitions simply transferred those ambitions from the older imperial hierarchy to the newer ecclesiastical one; we’ll talk more about the church as an institution next week. Distinct in the fifth century, by the end of the sixth century in Gaul, the two aristocracies: the barbarian warrior-aristocracy and the Gallo-Roman civic aristocracy had melded into one, intermarried and sharing the same religion, values and culture.
In this sense there really is a very strong argument to be made that the “Romans” and indeed Roman culture never left Rome’s lost western provinces – the collapse of the political order did not bring with it the collapse of the Roman linguistic or cultural sphere, even if it did fragment it.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Rome: Decline and Fall? Part I: Words”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-01-14.
July 18, 2024
QotD: Culture in the late western Roman Empire
July 9, 2024
What it was like to visit a Medieval Tavern
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 27 Mar 2024Medieval stew with meat, spices, and verjuice, and thickened with egg yolks
City/Region: England
Time Period: 15th CenturySome medieval taverns may have had what is called a perpetual stew bubbling away. The idea is basically what it sounds like: as stew was taken out, more ingredients would be added in so that the stew kept on stewing. In southern France, there was a perpetual stew that was served from the 15th century (around when this recipe was written) all the way up until WWII, when they couldn’t get the right ingredients.
I have opted to not make this stew perpetual, but it is delicious. The medieval flavor of super tender meat with spices and saffron is so interesting, especially with the added acidity and sweetness from the verjuice.
A note on thickening with egg yolks: if you need to reheat your stew after adding the egg yolks, like I did, they may scramble a bit. The stew is still delicious, it’s just the texture that changes a little and it won’t be quite as thick.
Vele, Kede, or Henne in bokenade
Take Vele, Kyde, or Henne, an boyle hem in fayre Water, or ellys in freysshe brothe, and smyte hem in pecys, and pyke hem clene; an than draw the same brothe thorwe a straynoure, an caste there-to Percely, Swag, Ysope, Maces, Clowys, an let boyle tyl the flesshe be y-now; than sette it from the fyre, and alye it up with raw yolkys of eyroun, and caste ther-to pouder Gyngere, Veriows, Safroun, and Salt, and thanne serve it forth for a gode mete.
— Harleian Manuscript 279, 15th Century
June 26, 2024
Lord Balfour
Arthur Lord Balfour, Conservative Prime Minister from 1902 to 1905, is perhaps best known for the Balfour Declaration issued during World War 1 that established the formal goal of an independent homeland for the Jews in the Holy Land. Who was he? Barbara Kay’s essay originally published in the Dorchester Review was recently reposted at Woke Watch Canada:
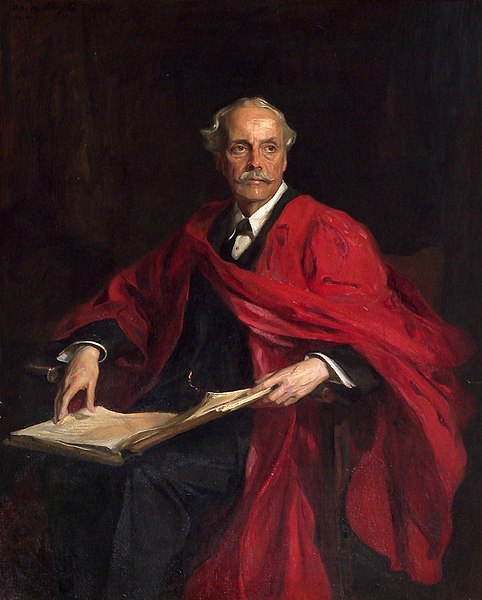

“Arthur James Balfour, 1st Earl of Balfour, KG, OM, PC, Prime Minister and Philosopher” portrait in oil by Philip de László, 1914.
From the Trinity College collection via Wikimedia Commons.
Why was the aristocrat Lord Balfour, the social antithesis of this humble Jew from the Pale of Russia, so taken with Weizmann’s vision that he was willing to expend political capital and exert so much effort to see it realized? Who was Balfour? What was he?
Arthur James Balfour was born at his family seat, Whittingehame, in East Lothian, the “granary of Scotland”. A forebear had made a fortune in India in military materials, so he was financially secure for life, and socially connected at the highest levels.
Having lost his father when he was 7, Balfour was lucky in his mother, a strong-willed and educated woman who, according to Mrs Dugdale, inculcated the idea of duty as “the uncompromising foundation of his character”. He attended Eton and Cambridge, where he was described by a friend as “a man of unusual philosophy and metaphysics”, who could hold his own with the Dons (professors), “some of them men of undoubted genius”. He was devoted to his extended family, and much beloved by his nieces and nephews.
In his essay “Arthur Balfour: a Fatal Charm”1 cultural critic Ferdinand Mount cites “nonchalance” as Balfour’s defining trait. Legendarily indolent, he rarely rose before 11 a.m., claimed never to read newspapers, and disdained the ritual schmoozing of fellow backbenchers expected by his peers in the Members’ Smoking Room. Mount says he was “indifferent to what his colleagues, the public or posterity thought of him or his policies”.
This loftiness — echoed in his unusual physical height — was perceived as admirable or maddening according to the observer and circumstances. Churchill said of him: “He was quite fearless. When they took him to the Front to see the war, he admired the bursting shells blandly through his pince-nez. There was in fact no way of getting to him.”
His self-sufficiency was no act. Sports-mad, he skipped lunch with the Kaiser to watch the Eton and Harrow cricket match, and when in Scotland might play two full rounds of golf a day (his handicap of 10 was better than P. G. Wodehouse and about the same as thriller writer Ian Fleming’s).
Balfour sounds from my description so far as if he was something of a playboy, but that is a very partial portrait. He was also known as “Bloody Balfour” for his readiness to endorse police action and his apparent indifference to their cost.
The Irish loathed him. In 1887 he became personal secretary for Ireland under his uncle, Lord Salisbury, just in time to enforce the Coercion Act against the volatile Irish Land League. Indeed, Balfour’s parliamentary critic William O’Brien saw him as a man who harboured a “lust for slaughter with a eunuchized imagination” who took “a strange pleasure in mere purposeless human suffering, which imparted a delicious excitement to his languid life”.
One hopes this accusation of actual sadism is an exaggeration of Balfour’s indubitable detachment. Yet indifference to human life is certainly not an uncommon charge laid against intellectuals for whom ideas loom larger in their claims to attention than the fate of those beyond their particular tribes.
For balance, we have Barbara Tuchman’s assessment:
Balfour had a capacious and philosophical mind. Words to describe him by contemporaries are often “charm” and “cynicism”. He had a profound and philosophic mind, he was lazy, imperturbable in any fracas, shunned detail, left facts to subordinates, played tennis whenever possible, but pursued his principles of statecraft with every art of politics under the command of a superb intelligence.
Fortunately for his temperament, Balfour’s life circumstances had landed him at the centre of a genuinely intellectual circle. His brothers in-law, for example, were Lord Rayleigh, who became head of the Cambridge Laboratory and won the Nobel Prize for Physics, and Henry Sidgwick, the Cambridge philosopher who with his wife Elaine Balfour founded Newnham College.
Politically, Balfour enjoyed both dramatic success and dramatic failure. He led the Unionist Party longer than anyone before him since Pitt the Younger. And he was a minister longer than anyone else in the 20th century, including Winston Churchill. Balfour was the only Unionist who was invited to join Asquith’s first war cabinet, and continued as foreign secretary after the coup that brought Lloyd George to power.
As Churchill put it: “He passed from one cabinet to the other, from the prime minister who was his champion to the prime minister who had been his most severe critic, like a powerful, graceful cat walking delicately and unsoiled across a rather muddy street”.
One of Balfour’s teachers at Eton described him as “fearless, resolved and negligently great”. On the other hand, Mount tells us, “indecisiveness” was his bane. He would stand paralyzed in the mezzanine of his London home agonizing over which of the matching staircases to descend by. He could love — the great love of his life died after an unreasonably long engagement — but, allegedly too staggered by the loss of his almost-fiancée, he never married.2 He could not be pinned down politically on many issues, a matter of great frustration to his colleagues, and this cost him dearly. As Mount notes, his charm was indisputable, “but more than charm he would not give” and “in the end, the charm is all that remains.”
Balfour fought three general elections as party leader and lost them all. His premiership lasted less than four years and ended in a Liberal landslide in 2006, a great electoral humiliation in making him the only prime minister in the 20th century to lose his own seat. He did not seem greatly to repine at the rejection, though, and it is thanks to the loss that he had time to further his education on the Zionist movement.
1. Mount, Ferdinand, English Voices (2016), pp 358 ff.
2. One suspects that even if May Lyttleton had lived, Balfour would have avoided marrying her on some pretext or other. There is no evidence that Balfour was a closeted homosexual, but he may have been asexual. He enjoyed an “amitié amoureuse” with (married) Mary Elcho for 30 years involving little or nothing in the way of sex, after which she wrote to him, “I’ll give you this much, tho, for although you have only loved me little, yet I must admit you have loved me long”.
May 24, 2024
May 18, 2024
The plight of Greek refugees after the Greco-Turkish War
As part of a larger look at population transfers in the Middle East, Ed West briefly explains the tragic situation after the Turkish defeat of the Greek invasion into the former Ottoman homeland in Anatolia:

“Greek dialects of Asia Minor prior to the 1923 population exchange between Greece and Turkey. Evolution of Greek dialects from the late Byzantine Empire through to the early 20th century leading to Demotic in yellow, Pontic in orange, and Cappadocian in green. Green dots indicate Cappadocian Greek speaking villages in 1910.”
Map created by Ivanchay via Wikimedia Commons.
While I understand why people are upset by the Nakba, and by the conditions of Palestinians since 1948, or particular Israeli acts of violence, I find it harder to understand why people frame it as one of colonial settlement. The counter is not so much that Palestine was 2,000 years ago the historic Jewish homeland – which is, to put it mildly, a weak argument – but that the exodus of Arabs from the Holy Land was matched by a similar number of Jews from neighbouring Arab countries. This completely ignored aspect of the story complicates things in a way in which some westerners, well-trained in particular schools of thought, find almost incomprehensible.
The 20th century was a period of mass exodus, most of it non-voluntary. Across the former Austro-Hungarian, Russian and Ottoman empires the growth in national consciousness and the demands for self-determination resulted in enormous and traumatic population transfers, which in Europe reached its climax at the end of the Second World War.
Although the bulk of this was directed at Germans, the aggressors in the conflict, they were not the only victims – huge numbers of Poles were forcibly moved out of the east of the country to be resettled in what had previously been Germany. The entire Polish community in Lwów, as they called it, was moved to Wrocław, formerly Breslau.
Maps of central and eastern Europe in the 19th century would have shown a confusing array of villages speaking a variety of languages and following different religions, many of whom wouldn’t have been aware of themselves as Poles, Romanians, Serbs or whatever. These communities had uneasily co-existed under imperial rulers until the spread of newspapers and telegraph poles began to form a new national consciousness, usually driven by urban intellectuals LARPing in peasant fantasies.
This lack of national consciousness was especially true of the people who came to be known as Turks; the Balkans in the late 19th century had a huge Muslim population, most of whom were subsequently driven out by nationalists of various kinds. Many not only did not see themselves as Turks but didn’t even speak Turkish; their ancestors had simply been Greeks or Bulgarians who had adopted the religion of the ruling power, as many people do. Crete had been one-third Muslim before they were pushed out by Greek nationalists and came to settle in the Ottoman Empire, which is why there is still today a Greek-speaking Muslim town in Syria.
This population transfer went both ways, and when that long-simmering hatred reached its climax after the First World War, the Greeks came off much worse. Half a million “Turks” moved east, but one million Greek speakers were forced to settle in Greece, causing a huge humanitarian crisis at the time, with many dying of disease or hunger.
That population transfer was skewed simply because Atatürk’s army won the Greco-Turkish War, and Britain was too tired to help its traditional allies and have another crack at Johnny Turk, who – as it turned out at Gallipoli – were pretty good at fighting.
The Greeks who settled in their new country were quite distinctive to those already living there. The Pontic Greeks of eastern Anatolia, who had inhabited the region since the early first millennium BC, had a distinct culture and dialect, as did the Cappadocian Greeks. Anthropologically, one might even have seen them as distinctive ethnic groups altogether, yet they had no choice but to resettle in their new homeland and lose their identity and traditions. The largest number settled in Macedonia, where they formed a slight majority of that region, with many also moving to Athens.
The loss of their ancient homelands was a bitter blow to the Greek psyche, perhaps none more so than the permanent loss of the Queen of Cities itself, Constantinople. This great metropolis, despite four and a half centuries of Ottoman rule, still had a Greek majority until the start of the 20th century but would become ethnically cleansed in the decades following, the last exodus occurring in the 1950s with the Istanbul pogroms. Once a mightily cosmopolitan city, Istanbul today is one of the least diverse major centres in Europe, part of a pattern of growing homogeneity that has been repeated across the Middle East.
But the Greek experience is not unique. Imperial Constantinople was also home to a large Jewish community, many of whom had arrived in the Ottoman Empire following persecution in Spain and other western countries. Many spoke Ladino, or Judeo-Spanish, a Latinate language native to Iberia. Like the Greeks and Armenians, the Jews prospered under the Ottomans and became what Amy Chua called a “market-dominant minority”, the groups who often flourish within empires but who become most vulnerable with the rise of nationalism.
And with the growing Turkish national consciousness and the creation of a Turkish republic from 1923, things got worse for them. Turkish nationalists and their allies murdered vast numbers of Armenians, Greeks and Assyrian Christians in the 1910s, and the atmosphere for Jews became increasingly tense too, with more frequent outbursts of communal violence. After the First World War, many began emigrating to Palestine, now under British control and similarly spiralling towards violence caused by demographic instability.
May 2, 2024
Rome’s Biggest Construction Projects
toldinstone
Published Jan 26, 2024Chapters:
0:00 Introduction
3:06 Domitian’s Temple of Jupiter
4:45 Aura
5:48 The Forum of Trajan
7:16 Nero’s Golden HouseMy new book, Insane Emperors, Sunken Cities, and Earthquake Machines is now available! Check it out here: https://www.amazon.com/Insane-Emperor…
April 30, 2024
DNA and India’s caste system
Earlier this month, Palladium published Razib Khan‘s look at the genetic components of India’s Caste System:
Though the caste system dominates much of Indian life, it does not dominate Indian American life. At slightly over 1% of the U.S. population, only about half of Indian Americans identify as Hindu, the religion from which the broader categories of caste, or varna, emerge. While caste endogamy — marrying within one’s caste — in India remains in the range of 90%, in the U.S. only 65% of American-born Indians even marry other people of subcontinental heritage, and of these, a quick inspection of The New York Times weddings pages shows that inter-caste marriages are the norm. While tensions between the upper-caste minority and middle and lower castes dominate Indian social and political life, 85% of Indian Americans are upper-caste, broadly defined, and only about 1% are truly lower-caste. Ultimately, the minor moral panic over caste discrimination among a small minority of Americans is more a function of our nation’s current neuroses than the reality of caste in the United States.
But this does not mean that caste is not an important phenomenon to understand. In various ways, caste impacts the lives of the more than 1.4 billion citizens of India — 18% of humans alive today — whatever their religion. While the American system of racial slavery is four centuries old at most, India’s caste system was recorded by the Greek diplomat Megasthenes in 300 BC, and is likely far more ancient, perhaps as old as the Indus Valley Civilization more than 4,000 years ago. Indian caste has a deep pedigree as a social technology, and it illustrates the outer boundary of our species’ ability to organize itself into interconnected but discrete subcultures. And unlike many social institutions, caste is imprinted in the very genes of Indians today.
Of Memes and Genes
Beginning about twenty-five years ago, geneticists finally began to look at the variation within the Indian subcontinent, and were shocked by what they found. In small villages in India, Dalits, formerly called “outcastes,” were as genetically distinct from their Brahmin neighbors as Swedes were from Sicilians. In fact, a Brahmin from the far southern state of Tamil Nadu was genetically closer to a Brahmin from the northern state of Punjab then they were to their fellow non-Brahmin Tamils. Dalits from the north were similar to Dalits from the south, while the three upper castes, Brahmins, Kshatriyas and Vaishyas, tended to cluster together against the Sudras.
Some scholars, like Nicholas Dirks, the former chancellor of UC Berkeley, argued for the mobility and dynamism of the caste system in their scholarship. But the genetic evidence seemed to indicate a level of social stratification that echoes through millennia. Across the subcontinent, Dalit castes engaged in menial and unsanitary labor and therefore were considered ritually impure. Meanwhile, Brahmins were the custodians of the Hindu Vedic tradition that ultimately bound the Indic cultures together with other Indo-European traditions, like that of the ancient Iranians or Greeks. Other castes also had their occupations: Kshatriyas were the warriors, while Vaishyas were merchants and other economically productive occupations.
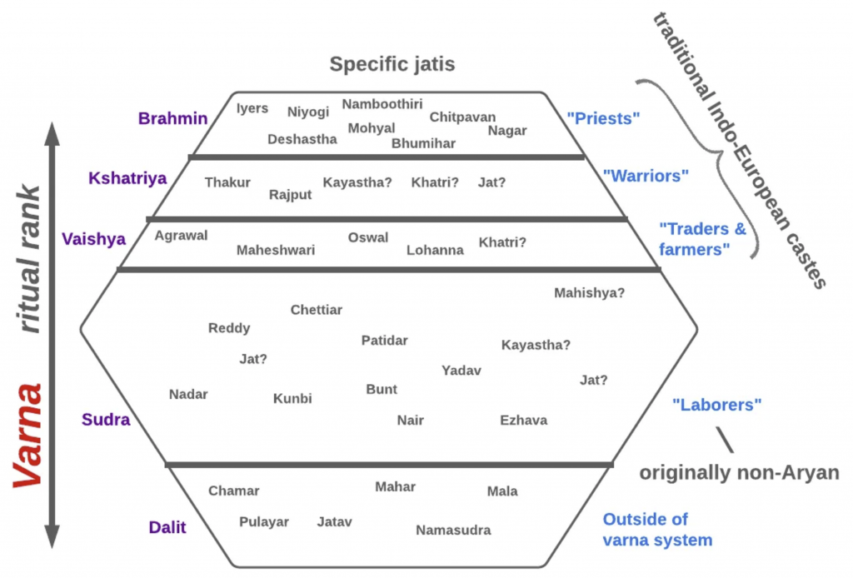
Brahmins, Kshatriyas, and Vaishyas were traditionally the three “twice-born” castes, allowing them to study the Hindu scriptures after an initiatory ritual. The majority of the population were Sudras (or Shudras), India’s peasant and laboring majority. Shudras could not study the scriptures, and might be excluded from some temples and festivals, but they were integrated into the Hindu fold, and served by Brahmin priests. A traditional ethnohistory posits that elite Brahmin priests and Kshatriya rulers combined with Vaishya commoners formed the core of the early Aryan society in the subcontinent, with Shudras integrated into their tribes as indigenous subalterns. Outcastes were tribes and other assorted latecomers who were assimilated at the very bottom of the social system, performing the most degrading and impure tasks.
The caste system as a layered varna system with five classes and numerous integrated jati communities.
Razib KhanThis was the theory. Reality is always more complex. In India, the caste system combines two different social categories: varna and jati. Varna derives from the tripartite Indo-European system, in India represented by Brahmins, Kshatriyas, and Vaishyas. It literally translates as “color”, white for Brahmin purity, red for Kshatriya power, and yellow for Vaishya fertility. But India also has Shudras, black for labor. In contrast to the simplicity of varna, with its four classes, jati is fractured into thousands of localized communities. If varna is connected to the deep history of Indo-Aryans and is freighted with religious significance, jati is the concrete expression of Indian communitarianism in local places and times.
April 17, 2024
QotD: The mid-life crisis, male and female versions
Most men get over the strippers-and-sports-cars overreaction pretty quickly, generally to be replaced by a new outlook on life. The guys who have come through the midlife crisis are generally a lot better people — more focused, more outgoing, far less materialistic — because they’ve taken up, however briefly, the perspective of Eternity. If you’re religious, you wonder if you’ll merit heaven. If you’re not, you wonder how you’ll be remembered. Either way, you start thinking about the kind of world you want to leave behind you, and what you’re going to do to achieve it with whatever time is left to you.
Which is why I’ve found the COVID overreaction so bizarre. Realizing your own mortality changes things. You can always tell, for instance, when it has happened to a younger person — when they come home, combat vets often act like middle-aged men going through a midlife crisis. Readjustment to civilian life is hard. Read the great war narratives, and it’s clear that none of them ever really “got over it”. Robert Graves and Ernst Junger, for instance, both lived to ripe old ages (90 and 103, respectively), and were titans in fields far removed from battle … and yet, the war WAS their lives, in some way we who haven’t been through it will never understand, and it comes through in every line they wrote.
If the Covidians were really freaking out about COVID, then, I’d expect one of two broad types of reaction: Either party-hearty midlife crisis mode, or a new determination to get on with whatever’s left of life. Obviously neither of those are true, and I just can’t grasp it — these might be your last few weeks on Earth, and that’s how you’re going to spend them? Sitting in your apartment like a sheep, wearing a mask and eating takeout, glued to a computer screen?
If you want a measure of just how feminized our society has become, there you go. Call this misogyny if you must, but it’s an easily observed fact of human nature — indeed, it has been observed, in every time, place, and culture of which we have knowledge — that post-menopausal women go a bit batty. Though a man might know for certain that he dies tomorrow, he can still keep plugging away today, because he’s programmed to find real meaning in his “work” — we are, after all, running our snazzy new mental software over kludgy old caveman hardware.
Women aren’t like that. They have one “job”, just one, and when they can’t do it anymore, they get weird. In much the same way high-end sports cars would cease to exist if middle aged men ceased to exist, so there are entire aspects of culture that don’t make sense in any other way except: These are channels for the energies of post-menopausal, and therefore surplus-to-requirements, women. You could go so far as to say that pretty much everything we call culture — traditions, history, customs — exist for that reason. Women go from being the bearers, to being the custodians, of the tribe’s future.
Severian, “Life’s Back Nine”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-05-11.
March 31, 2024
QotD: Sins and “sins”
While true of the puritanical organic lobby, a Supersized ethical position is also advanced by all too many Christians. Indeed, this is where the green-thinkers derive their theology in the first place. Gluttonous McDonald’s visits are on a long list that includes some items mentioned once or twice in scripture such as gay sex, polycotton and women letting their hair down in church and plenty of things from cocaine to coffee which are nowhere to be found in the Bible. The notion is that some things, while pleasurable, will prevent your immortal soul from making it to heaven and that for your own good you must be prevented from enjoying them. That this makes a nonsense of free will, shows precious little faith in the free gift of Grace and that some “sins” are singled out for hysterical attention while most are ignored entirely does not bother puritans historical or contemporary. And the fact most people worship at a different altar altogether does not cross their minds at all.
Ghost of a Flea, “Religion in general”, Ghost of a Flea, 2005-04-13.
March 30, 2024
QotD: Multiculturalism, in theory and practice
The creed of contemporary multiculturalism sought to establish that all societies were roughly equal and that the “other” was but a crude Western fiction. But we were reminded that people like the Taliban who did not vote, treated women as chattel, and whipped and stoned to death dissenters of their primordial world were different folk from citizens of democracy. A chief corollary to such cultural relativism was that Americans have wrongly embraced a belief in the innate humanity of the West largely out of ethnocentric ignorance. But surely the opposite has been proven true: the more Americans after September 11 learned about the world of the madrassas, the six or seven varieties of Islamic female coverings, the Dickensian Pakistani street, and the murderous gangs in Somalia, Sudan, and Afghanistan, then the more not less, they are appalled by societies that are so anti-Western.
Victor Davis Hanson, Ripples of Battle, 2003.
March 9, 2024
The Jewish Avengers Who Hunted Nazi Murderers
World War Two
Published Mar 8, 2024In March 1945, the first Jewish unit in the Allied forces reaches the frontline. Before fighting the Nazis, the men spent years battling against the policies of the British government. After the war, they will take vengeance on the perpetrators of the Holocaust and join the Zionist movement in building and fighting for Israel.
(more…)
March 6, 2024
QotD: Mansa Musa’s disastrous foreign aid to Cairo
Mansa Musa’s good intentions may be the first case in history of failed foreign aid. Known as the “Lord of the Wangara Mines”, Mansa Musa I ruled the Empire of Mali between 1312 and 1337. Trade in gold, salt, copper, and ivory made Mansa Musa the richest man in world history.
As a practicing Muslim, Mansa Musa decided to visit Mecca in 1324. It is estimated that his caravan was composed of 8,000 soldiers and courtiers — others estimate a total of 60,000 — 12,000 slaves with 48,000 pounds of gold and 100 camels with 300 pounds of gold each. For greater spectacle, another 500 servants preceded the caravan, and each carried a gold staff weighing between 6 and 10.5 pounds. When totaling the estimates, he carried from side to side of the African continent approximately 38 tons of the golden metal, the equivalent today of the gold reserves in Malaysia’s central bank — more than countries like Peru, Hungary or Qatar have in their vaults.
On his way, the Mansa of Mali stayed for three months in Cairo. Every day he gave gold bars to the poor, scholars, and local officials. Mansa’s emissaries toured the bazaars paying at a premium with gold. The Arab historian Al-Makrizi (1364-1442) relates that Mansa Musa’s gifts “astonished the eye by their beauty and splendor”. But the joy was short-lived. So much was the flow of golden metal that flooded the streets of Cairo that the value of the local gold dinar fell by 20 percent and it took the city about 12 years to recover from the inflationary pressure that such a devaluation caused.
Orestes R Betancourt Ponce de León, “5 Historic Examples of Foreign Aid Efforts Gone Wrong”, FEE Stories, 2021-06-06.
February 21, 2024
“College attendance is our society’s only meaningful initiation ritual, and it thus assumes an existential importance that renders it near-impossible to replace until an alternative is found”
Johann Kurtz believes the modern university’s survival despite its increasingly irrational and counterproductive actions can be explained as the last modern example of an initiation ritual:
Our understanding of the college system is incomplete. Until we correct this, we won’t be able to fix or replace the system.
First, consider a paradox: college attendance remains near all-time highs [Link], yet the majority of Americans no longer believe it is worth the cost [Link].
The college system seems irrationally resistant to declining value. We must therefore ask: is there an important non-rational reason for college attendance which we have failed to acknowledge?
I believe the answer is “Yes”. College attendance is our society’s only meaningful initiation ritual, and it thus assumes an existential importance that renders it near-impossible to replace until an alternative is found.
Our culture is historically anomalous in lacking explicit initiation rituals.
Mircea Eliade, the great religious historian of the 20th-century, defined initiation rituals as “a body of rites and oral teachings whose purpose is to produce a decisive alteration in the religious and social status of the person to be initiated“.
In philosophical terms, initiation is equivalent to a basic change in existential condition; the novice emerges from his ordeal endowed with a totally different being from that which he possessed before his initiation; he has become another.
— Mircea Eliade, Rites and Symbols of Initiation: The Mysteries of Birth and Rebirth
In Europe, fully expressed initiation rituals were common until the end of the Middle Ages, and in the wider world, until the end of the First World War. Now, they only persist in the West in the sacramental practices of devout Christians (baptism, confirmation, and so forth).
Once, however, these practices were of tremendous importance to us, as Eliade makes clear:
To gain the right to be admitted among adults, the adolescent has to pass through a series of initiatory ordeals: it is by virtue of these rites, and of the revelations that they entail, that he will be recognized as a responsible member of the society. Initiation introduces the candidate into the human community and into the world of spiritual and cultural values. He learns not only the behavior patterns, the techniques, and the institutions of adults but also the sacred myths and traditions of the tribe, the names of the gods and the history of their works …
In the absence of local community rituals, the universities are a natural site for their replacement. These have always been religious sites, although the nature and expression of this religion has transmuted over time.
H/T to Bruce Gudmundsson at Extra Muros for the link and his additional comments:
This hypothesis accords with the argument, made often in this blog, that education and schooling are two very different things. At the same time, it suggests that one of the definitive purposes of Extra Muros, the encouragement of young people to eschew the conventional college experience in favor of a combination of practical pursuits and systematic self-tuition, may be a fool’s errand. After all, if four (or five or six) years of drinking second-rate beer from red plastic cups does for the office-bound folk of North America what fear-filled rites of passage do for members of the bone-in-the-nose set, then I might well be sailing against the wind.
Upon second thought, I find hope in the possibility that the parasite (or, to be more precise, the cancer) promoted by d’Angelo, Kendi, and company will soon deal the coup de grâce to its mortally-wounded host.
The coming-of-age ordeals of warrior tribes demand that boys who would be men prove possession of such martial virtues as courage and self-command. The rites-of-passage of the modern middle classes, however, require that postulants demonstrate a mixture of conformity, conscientiousness, and, to a diminishing degree, intelligence. (Readers familiar with the oeuvre of economist Bryan Caplan will recognize the source of this troika. However, it is worth noting that, while Professor Caplan will occasionally tip his hat in the direction of the campus-based building of basic brain-power, he devotes far more attention to the collegiate cultivation of the two components of Sitzfleisch.)1
The cult of Marx, Mao, and Marcuse demands complete compliance, not only with its basic tenets, but also with any changes in the party line that, from time to time, may occur. (I am old enough to remember the days when campus commies of the caucasian persuasion could don dashikis without facing charges of “cultural appropriation”.) Thus, those who sit at the feet of the acolytes of critical theory learn an art of great value to people who wish to thrive in a large organization, that of discarding the old hat, and putting on the new one, at just the right time. (Think, if you will, of the mid-level employees of the McDonalds Corporation, who, over the course of the last four decades, were obliged to alter their opinion of the McRib sandwich more often than they changed the oil in their cars.)
1. Bryan Caplan, The Case Against Education: Why the Education System is a Waste of Time and Money (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2018), pages 9-21.
February 13, 2024
Step aside, puny humans, here comes “the new Marxist Homo tabularasa“
At Postcards from Barsoom, John Carter considers what might occupy the god-shaped space in the new secular religion of wokeness:

Ryan T. Hancock, via Postcards from Barsoom
It’s trite to observe that the Great Awokening is a fundamentally religious phenomenon, representing a sort of secular Abrahamic heresy mining the latent guilt swirling within the hearts of post-Christian whites and thereby activating the messiah complexes of the Anglosphere’s Protestant populations, who have exhibited other similarly self-destructive enthusiasms throughout their ethnoreligious histories. It’s trite because it’s so obviously apt, but it raises an obvious question: if Woke is a cult, what is its god?
I don’t mean whichever symbols or causes they flock to from one moment to the next. These are merely mortal embodiments of archetypal forms, rising perhaps to the level of heroes or saints should their celebration become widespread enough. George Floyd was not deified but beatified, not because of anything he did in his life (which no one really argues wasn’t a sewer of petty criminality), but because in his death he was filled with a holy spirit of some kind. What spirit was that?
One answer to this question is provided in the title of Lorenzo Warby‘s ongoing series “Worshipping the Future“. As Warby explains in “The Deep Appeal of Marxism“, progressivism is besotted with the transformational future, an imaginary utopia qualitatively different from and superior to the Tartarus of antiquity in every way – an Elysium of peace, stability, equality, wealth, ease, comfort, and bliss, existing in a perpetual state of liberatory ecstasy in which the war, chaos, poverty, strife, suffering, and misery of the past have been permanently eradicated.
As Warby writes, there is no limit to the delights of the transformational future:
As a thing imagined, it can be imagined to be as perfect as one likes. This means politics grounded in an imagined future can be as morally grandiose as one likes, with whatever moral urgency goes with such imaginings.
This is deeply intoxicating.
Grounding one’s politics in an imagined future also provides huge rhetorical advantages, precisely because said future is as perfect as one wants it to be. Anyone who wishes to defend some actually existing thing has the problem that it will be the product of trade-offs and human failings.
An “imagined future” believer, by contrast, can just wish all that away for political purposes while hanging current imperfections on those who wish to defend what exists. In any contest between the actual and the imagined, the imagined sparkles ever so more brightly.
This utopia is of course always at some point just over the horizon. Just one more revolution, bro, and we’ll reach the Promised Land! Just one more gulag, and we’ll get to utopia, I swear! C’mon bro, just one more mass grave, we’re almost there, you gotta believe me!
There is a fatal epistemic flaw at the heart of this faith: no information can be extracted from the future, because information can only be obtained from the past.
Not only does the imagined future have no reality test, it distorts one’s use of the information to which we do have access. The past is profoundly discounted by its distance and difference from the imagined future. It is both morally discounted — a record of sin and depravity — and structurally discounted, because it has not undergone the social transformations that are imagined to change everything.
If the imagined future is a secular heaven, then the past becomes a moral hell from which we must escape. All information from it is tainted as profoundly impure and corrupt: the record of sin.
This means that when policies fail to obtain the desired result, for example erasing ethnic and sexual distinctions through affirmative action and thereby producing the new Marxist Homo tabularasa, no corrective action is possible. Policy failure exists in the past, which is ignored as sinful, and which therefore cannot be learned from. The only permissible answer to failed progress is to progress faster, with the only possible consequence being to fail harder.
January 30, 2024
QotD: Science as religion for the rational
Even now I feel queasy using these religious metaphors and these analogies, because they are so pregnant with horror and oppression and mass death – Muslims screaming “Allahu akbar!” as they detonate suicide bombs, Christians with “Kill them all, God will know his own”. But this Buddha must be faced and killed for the sake of my own sanity. If I do not acknowledge and deal with the ways in which I feel like a religious person, I increase my risk that those emotions will sneak up on my thinking and make it unsane.
So I will say it out loud: science is the functional equivalent of worship for the rational human. In contemplating the wonder and vastness of the universe as it is, I find the equivalent of religious awe before the face of God. In struggling to understand the universe, scientists perform work as dedicated, heartfelt and ecstatic as religious devotion. Humility and self-discipline are even more proper to the scientist than they are to the believer; as the true believer seeks to know God’s will without the obstruction of ego, the true scientist seeks understanding of what is without the obstruction of ego.
Religion makes us the offer that if we believe, it will lift us out of ourselves – perfect us, teach us what is mere transient illusion and what is real and eternal. Science makes almost the same offer; that if we accept the discipline of rationality, we can become better than we are and learn what is really true. These two offers rest on very different ground, and religion’s offer is essentially false while science’s is essentially true – but psychologically, we receive both offers in the same way. They both plug into the same basic human fear of death and the unknown, and the same longing for transcendence.
So maybe science is my religion, after all. The question is definitional. Is it “religion” if it duplicates the emotional constellations of religious feeling without investment in the supernatural, or faith, or revelation, or dogma, or any of the usual content of religious belief?
Eric S. Raymond, “Maybe science is my religion, after all”, Armed and Dangerous, 2011-05-18.