Lindybeige
Published Jul 10, 2024A poem with an excellent popularity-to-title-length ratio.
The timeless classic. A father talks to his son about how to be a good man. If any son ever lived up to all the virtues described, he would certainly be impressive.
If you can keep your head when all about you
Are losing theirs and blaming it on you,
If you can trust yourself when all men doubt you,
But make allowance for their doubting too;
If you can wait and not be tired by waiting,
Or being lied about, don’t deal in lies,
Or being hated, don’t give way to hating,
And yet don’t look too good, nor talk too wise:If you can dream — and not make dreams your master;
If you can think — and not make thoughts your aim;
If you can meet with Triumph and Disaster
And treat those two impostors just the same;
If you can bear to hear the truth you’ve spoken
Twisted by knaves to make a trap for fools,
Or watch the things you gave your life to, broken,
And stoop and build ’em up with worn-out tools:If you can make one heap of all your winnings
And risk it on one turn of pitch-and-toss,
And lose, and start again at your beginnings
And never breathe a word about your loss;
If you can force your heart and nerve and sinew
To serve your turn long after they are gone,
And so hold on when there is nothing in you
Except the Will which says to them: “Hold on!”If you can talk with crowds and keep your virtue,
Or walk with Kings — nor lose the common touch,
If neither foes nor loving friends can hurt you,
If all men count with you, but none too much;
If you can fill the unforgiving minute
With sixty seconds’ worth of distance run,
Yours is the Earth and everything that’s in it,
And—which is more — you’ll be a Man, my son!
July 11, 2024
“If -“, by Rudyard Kipling
On immigration, progressives are following Brecht’s advice to “dissolve the people and elect another”
In the US, Canada, Britain, and most of western Europe the tide of immigration (legal and illegal) never seems to ebb, despite clear indications from the electorates that they’ve had enough. But perhaps progressives in each country are merely taking Bertolt Brecht’s advice for times when the people have forfeited the government’s confidence:
The problem extends far, far beyond merely glutting the labor market and lowering our wage scale, however. See, I’ve explained above why many Republicans go along with the Amnesty Express. But what about the Democrats? What’s in it for them, especially since Big Labor – whose members stand to lose a great deal because of the depression of wage levels – makes up such a prominent part of the Democrat coalition?
What the Democrats stand to win is permanent political power.
See, unlike previous waves of immigration, we are making no effort whatsoever to assimilate current immigrants to our culture and society. Instead, immigrants tend to cluster in indigestible lumps, maintaining their own cultures, languages, and ways from “the old country”. This is doubly true of illegal immigrants, who have managed to turn large swathes of many of our cities into small-scale replicas of Mexico and Morocco. This is even more troublesome because practically all of these immigrants come from places whose histories and traditions are grossly incompatible with our own. These folks don’t know about the idea of protecting life, liberty, and property through a rule of law system, so consequently they don’t CARE about such a system. They’re just here to get jobs or get welfare, for the most part.
In essence, when you import millions of people from socialistic and/or primitive Global South countries, you will end up with a socialistic, primitive Global South country of your own. And that’s what the Democrats are counting on. This is essentially what has been happening with the millions of people coming across our southern border from all over the world.
If the Democrats can get all of the 30-60 million illegals in America amnestied so that they can stay here and start their “path to citizenship”, and can bring in millions more through the various visa processes, then the Democrats are setting themselves up to be able to gain total control in about two decades – which is how long it will take for the children of all these immigrants to join the pool of voters with their parents. Further, they don’t seem to even want to have to wait that long, considering how they are opposing a bill currently before the Congress that would crack down on voting by illegal immigrants. Essentially, the Democrats – who have been unable to convince the current set of American voters to consistently elect them – want to replace us with a new set of voters, one which will vote overwhelmingly for the Democrats every election, up until we reach the point where there aren’t any more elections.
This is why I say that immigration is more important even than abortion or these other issues that people on the Right are so concerned about. Think about it. With 100 million newly-minted Democrat voters, the Democrats will be able to gain permanent control of all branches of government, at all levels, in nearly all of the states. What that means is that they will get to push through their policies at will. That means no more pro-life restrictions on infanticide. No more gun rights. No more religious liberty. No more rollback of the gay agenda. No more tax cuts or spending rollbacks. No more economic liberty. Kiss private property goodbye. THAT’S what the Democrats want – and the only way for them to get it to convince enough idiots in this country to give it to them via immigration, both legal and illegal.
So while conservatives are clawing each other’s eyes out because one candidate or the other isn’t as pro-life as they want them to be, the Democrats are setting up the playing field to replace the current American electorate with a new one from the Third World, complete with all the third world values of corruption and socialism that come with them.
Of course, for “Democrats”, read “Liberals” in Canada, “Labour” in the UK, and so on. The party labels change, but the basic beliefs are remarkably consistent across the western world (and Rishi Sunak’s just-ousted Conservatives were just as committed to open borders and mass immigration as Keir Starmer’s new Labour government).
Wittmann’s Tiger Rampage | Villers-Bocage, June 1944
The Tank Museum
Published Mar 30, 2024In the space of 15 minutes, Michael Wittmann took a single Tiger tank and stopped a major British advance, destroying 10 tanks, 10 halftracks, 8 Bren carriers, 1 scout car and a six-pounder anti-tank gun in the process. An eye-catching achievement … But was this a victory handed on a plate?
John Delaney outlines Wittmann’s audacious and decisive action at Villers Bocage against the British Desert Rats, examining its military significance. It’s become the stuff of legend. It was a gift to Nazi propagandists, who wasted no time in championing the achievements of their “tank ace”. For the British, it was an embarrassing blow to military prestige.
Wittmann got lucky. But luck runs out eventually …
00:00 | Introduction
00:42 | Arrival into Villers-Bocage
03:08 | Wittmann’s Rampage Begins
04:51 | Rampaging Through the Village
11:56 | Wittmann’s Luck Runs Out
14:09 | Was Wittmann Really a Tank Ace?
16:54 | ConclusionThis video features archive footage courtesy of British Pathé.
#tankmuseum #tankactions #johndelaney #michaelwittmann #tigertank
July 10, 2024
The Korean War – Never Fear, MacArthur’s Here! – Week 003 – July 9, 1950
The Korean War by Indy Neidell
Published 9 Jul 2024American troops have arrived in Korea and engage the KPA — the forces of the North — in the field this week for the first time. It does not go well for them. In fact, it’s hard to imagine it going worse. The Americans are outnumbered and outgunned and are routed. In fact, the KPA are advancing all over the country, though they are taking heavy casualties themselves.
(more…)
After 1177 B.C.
Jane Psmith reviews the follow-on book from Eric Kline’s bestseller about the Bronze Age Collapse, After 1177 B.C.: The Survival of Civilizations:
Sometime around 1150 BC, the dense network of politically, economically, and culturally interdependent states around the eastern Mediterranean collapsed. In 2014, GWU archaeologist Eric Cline wrote a book about it. And then, surprisingly, it became a bestseller.
Okay, maybe it’s not that much of a surprise: most people can recognize an obvious historical analogy when it hits them over the head, and the globalized1 state system of the Late Bronze Age has extremely clear parallels to the modern day. An interconnected and cosmopolitan world? Centralized state bureaucracy? High-level diplomacy between ruling elites? A technologically complex civilization enabled by extensive international trade along lengthy and elaborate supply chains? Well, gosh, that seems remarkably familiar. An audience that had just weathered a global financial crisis (and, later, a global pandemic) was perfectly poised to appreciate Cline’s exploration of the fragility of complex systems. No wonder it sold! (A copy entered the Psmith household in early 2020 for, uh, obvious reasons.)
Cline’s basic argument in the book was that the Collapse was due not to any single cause but to a “perfect storm” of calamities: drought and accompanying famine, earthquake, internal rebellion, external invasion. These were all problems that the civilizations of the Bronze Age Mediterranean had faced and survived in the past, but under their combined onslaught the most fragile parts of the system at last began buckle. When one society disintegrated, its sudden absence from the interconnected global economy became a new stressor on its surviving neighbors — until at last, domino-like, the whole thing came down.2 It would be decades, or in some places centuries, before the standard of living returned to anything like its previous level, and it would be nearly five hundred years before an international system as complex and sophisticated as the world of the Late Bronze Age emerged.
Now, a decade after his original book, Cline has a sequel exploring what happened after the Collapse. Which civilizations were able to rebound to something approaching their former glory, which barely managed to limp along into the Iron Age, and which vanished into the sands of time? And, more importantly, why?
This is a much more difficult story to tell. The original 1177 B.C. spent much of its page count on the zenith of Bronze Age civilization, the 15th through 13th centuries BC, to explain what it was that did the collapsing. It’s a sweeping tale, full of wonderful stories and fascinating digressions into the historicity of the Trojan War (yes) and the Exodus (not archeologically substantiated) as well as being a compelling portrait of a complicated set of societies. Cline’s narrative darts from Egypt to Assyria to the Aegean to the Hittites, treating each in turn as he moves forward through time towards what we all know is coming.
But chronological framing is impossible for the sequel. There is, definitionally — there can be — no grand narrative of regional divergence after the fall of a “world-system“. The fate of Mesopotamia is no longer linked to that of Greece; there are no more Cretan envoys in New Kingdom tomb reliefs, no more battles between the Hittite Great King and the wanax of a Mycenaean palatial center, no more Uzbek tin shipwrecked off the coast of Anatolia. Once the ties are cut, each story must stand alone, and accordingly Cline gives each region its own chapter.
Alas, this is a lot less fun to read.
1. For sufficiently small values of “globe”. But larger than you might expect!
2. The revised 2021 edition apparently gives a larger role to climate factors, especially the 3.2kya megadrought, but that’s not the one I read and anyway the other elements were still present.
Two World Wars: Finnish C96 “Ukko-Mauser”
Forgotten Weapons
Published Mar 27, 2024A decent number of C96 Mauser pistols were present in Finland’s civil war, many of them coming into the country with the Finnish Jaegers, and others from a variety of sources, commercial and Russian. They were used by both the Reds and the Whites, and in both 9x19mm and 7.63x25mm. After the end of the civil war, when the military was standardizing, the C96s were handed over to the Civil Guard, where they generally remained until recalled to army inventories in 1939. They once again saw service in the Winter War and Continuation War, and went into military stores afterwards until eventually being surplussed as obsolete.
One of the interesting aspects of Finnish C96s is that many of them come from the so-called “Scandinavian Contract” batch (for which no contract has actually turned up). These appear to be guns made in 7.63mm that were numbered as part of the early production in the Prussian “Red 9” series, probably for delivery to specific German units or partner forces during World War One.
(more…)
July 9, 2024
What it was like to visit a Medieval Tavern
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 27 Mar 2024Medieval stew with meat, spices, and verjuice, and thickened with egg yolks
City/Region: England
Time Period: 15th CenturySome medieval taverns may have had what is called a perpetual stew bubbling away. The idea is basically what it sounds like: as stew was taken out, more ingredients would be added in so that the stew kept on stewing. In southern France, there was a perpetual stew that was served from the 15th century (around when this recipe was written) all the way up until WWII, when they couldn’t get the right ingredients.
I have opted to not make this stew perpetual, but it is delicious. The medieval flavor of super tender meat with spices and saffron is so interesting, especially with the added acidity and sweetness from the verjuice.
A note on thickening with egg yolks: if you need to reheat your stew after adding the egg yolks, like I did, they may scramble a bit. The stew is still delicious, it’s just the texture that changes a little and it won’t be quite as thick.
Vele, Kede, or Henne in bokenade
Take Vele, Kyde, or Henne, an boyle hem in fayre Water, or ellys in freysshe brothe, and smyte hem in pecys, and pyke hem clene; an than draw the same brothe thorwe a straynoure, an caste there-to Percely, Swag, Ysope, Maces, Clowys, an let boyle tyl the flesshe be y-now; than sette it from the fyre, and alye it up with raw yolkys of eyroun, and caste ther-to pouder Gyngere, Veriows, Safroun, and Salt, and thanne serve it forth for a gode mete.
— Harleian Manuscript 279, 15th Century
July 8, 2024
Train & Public Transport in London (1941)
Charlie Dean Archives
Published Sep 24, 2013According to tfl.gov.uk: “Not only did the Tube help 200,000 inner-city children escape to the country, it was also used to shelter hundreds of thousands of civilians every night during the Blitz. On 27 September 1940 a census found that a staggering 177,500 Londoners were sleeping in Tube train stations. With so many people seeking shelter in the Tube, London Underground sprang into action and installed 22,000 bunk beds, washroom facilities and even ran trains that supplied seven tonnes of food and 2,400 gallons of tea and cocoa every night. Before long there were even special stations with libraries, evening classes, movies and musical evenings.”
The film states that 10 million people used public transport in London. Today, that figure stands at around 8.6 million. The opening title cards state that this film began filming just as the London Blitz began, yet there is very little visual reference to this.
(more…)
July 7, 2024
More on the British general election results
At Postcards from Barsoom, John Carter has some further thoughts on the Sunak implosion on the 4th of July:

Sir Keir Starmer speaking to the media outside Number 10 Downing Street, 5 July, 2024.
Picture by Kirsty O’Connor/ No 10 Downing Street via Wikimedia Commons.
The Conservative wipeout was disappointingly not the annihilation that early polls predicted. The Tories were successful in scaring a critical mass of boomers in a last minute get-out-the-vote effort. At the same time, I suspect that some incidents late in the election that were used to paint Reform as raving Nazis were successful in driving down the Reform vote. One such incident involved a marginal Reform candidate caught on microphone being extraordinarily vulgar, who later turned out to be an actor that specialized in playing precisely the sort of character he was portraying for the media, which is of course all rather suspicious.
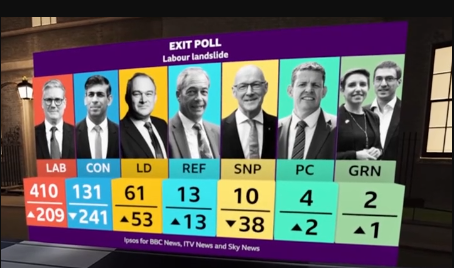
As a result, Reform only got 4 seats. This was less than the 13 that were predicted by the BBC based on exit polling, which prediction was revised to the 4 that Reform in fact won partway through counting, as the models’ Bayesian priors were updated accordingly, no doubt. That said, among those 4 seats is Nigel Farage, who is now a sitting member of Parliament.
That Parliament is now, in all likelihood, in the hands of the weakest massive majority government in its history, and if that’s not true (British history in its entirety being rather extensive), certainly close to it.
Keir Starmer’s Labour has 412 seats of Parliament’s total 650, giving it an unassailable majority. This is not because of a sudden surge in their popularity: their share of the popular vote didn’t budge, from around a third of the population. Turnout was moreover unenthusiastic, about 59% of the population I think, which while not as wince-inducing as the nearly 50% participation that the BBC was claiming throughout most of the counting period, is still nothing to write home about. The total number of people who voted for Labour decreased by 600,000. Labour cannot claim any sort of popular mandate, and they know it.
Not that Labour — or any western political party elected under these circumstances — could be expected to take it into consideration. From their point of view, all that matters is the seats in the House of Commons, and they’ve got them in spades.
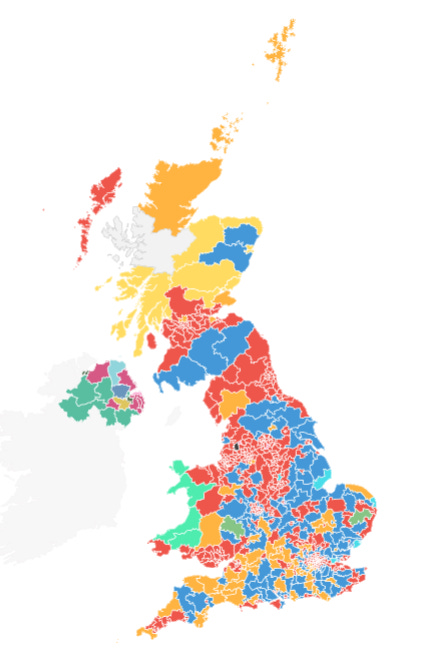
Reform and the Lib Dems were not the only beneficiaries of the Conservative collapse. This can be seen immediately in the crazy quilt of the electoral map, which despite Labour’s two-thirds majority, is planted with the flags of all sorts of weird political tribes.
My favourite part is Northern Ireland, where Sinn Fein held its 7 seats (making it the fifth-largest party after the SNP), and the rest of it is split up in an impenetrable jumble of splinter parties vaguely associated with different reasons for remaining part of the UK and/or the EU. Wales has been painted bright green by Plaid Cymru, the Party of Wales, who doubled their presence in parliament to 4. This is the same number of seats as Reform got, despite Plaid Cymru having gotten just under 200,000 votes, as compared to Reform’s 4.1 million, yet another perversity of first-past-the-post.
To everyone’s disappointment, first-past-the-post did not deliver a seat into the hands of the Monster Raving Loony Party, who received only 5,814 votes, a dismal 0.02% of the total 28.4 million votes cast. I do not know what kind of person votes for the Monster Raving Loony Party, but I bet they are absolutely fascinating. They should consider moving to one of Britain’s remote underpopulated islands, the Orkneys perhaps, where they might just be able to take over a seat. Having a strong, concentrated regional presence seems to be the best way to get members into Parliament in a first-past-the-post system, and having a sitting member for the Monster Raving Loonies would be even funnier than having Nigel in there.
First-past-the-post gets a lot of hate, and I’ve been ripping on it here, but it actually seems well-suited to an island which is shared by a bunch of squabbling ancient tribes. While it tends to produce majorities quite easily due to the winner-take-all nature of the contest within each riding, this also allows areas with strong regional identities to assert a disproportionate presence in parliament, despite getting a measly percentage of the vote. Not that that especially matters, given the aforementioned tendency for the system to hand out crushing jackpot majorities to the dominant players, as it has indeed done once again.
With the sole exception of Reform, there has not been any wave of enthusiasm for any of the parties in parliament. Large numbers of voters simply stayed home, whether tuning it all out or punishing their home parties while failing to see anything they wanted to vote for. It is as though the tide has gone out, exposing the sand and rocks of the sea shore. Whether this is a regular tide, which will gently slosh back in again in time, or a tsunami, remains to be seen. Certainly it feels that the water has receded very far indeed, exposing more of the seafloor’s surface than one normally sees. Say, is that Doggerland over there?
Electrolux Charlton: Washing Machine Company Converts Bolt Action to Semiauto
Forgotten Weapons
Published Mar 25, 2024The Charlton was a conversion of a bolt action Lee rifle into a light machine gun, designed by New Zealander Phillip Charlton. Some 1500 were made in New Zealand, but a bit later it appears that there was an effort to also produce the gun in Australia. The Electrolux company (the same one that makes washing machines and other home appliances today) made a few prototypes.
The Electrolux version is different from the original in a couple ways. While the basic conversion mechanism is the same, the Electrolux is more refined, with a shorter gas system and a fairly clean action cover over the working parts. It is also semiautomatic only, intended to be a shoulder-fired rifle where the original was made for the LMG role. Electrolux also used standard No1 MkIII rifles as its base, where the originals were made from a variety of mostly worn out Lee Metfords and Long Lees.
The Electrolux contract was cancelled in June 1944, and only a few prototypes were made. This example is in the British Royal Armouries collection, to whom I am grateful for the access and the trust to take it apart for you!
My video on the standard production Charlton:
https://forgottenweapons.vhx.tv/video…
(more…)
July 6, 2024
Canada, NATO’s most egregious freeloader
In The Line, Eugene Lang and Vincent Rigby explain why our NATO allies are less and less willing to listen to Canadian virtue-signalling and posturing when we continue to refuse to live up to our commitments on the Canadian Armed Forces and contributing our full share toward NATO operations:
Next week’s NATO Summit in Washington marks the 75th anniversary of the trans-Atlantic Alliance. Yet despite being one of the original 12 founding members, Canada’s credibility within the alliance will be at an all-time low.
There is no question Canada has a proud history with NATO. Canadian statesmen — including Lester B. Pearson, Louis St. Laurent, Hume Wrong and Escott Reid — were architects of the alliance in the late 1940s, and helped author Article Two of the North Atlantic Treaty calling for political and economic collaboration among member-states, the so-called “Canadian Article”.
Over the decades, the Canadian military has made significant contributions to NATO missions in western Europe, the Balkans and Afghanistan. But that was then and this is now, and two years ago, Michel Miraillet, France’s ambassador to Canada, put things bluntly: “You are riding a first-class carriage with a third-class ticket. If you want to remain in the first-class seat, you need to train and expand (the military) and to go somewhere.”
Sentiments like these have been fuelled by Canada’s stubborn refusal to meet NATO’s defence spending target of two per cent of gross domestic product (GDP) — a commitment Ottawa has signed onto twice in the past ten years but is far from achieving. Last year, NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg expressed frustration over this recalcitrance: “Canada has not conveyed a precise date but I expect (it) to deliver on the pledge to invest two per cent of GDP on defence, because this is a promise we all made”.
Stoltenberg’s comments evidently had little impact in Ottawa. While Canada’s recent Defence Policy Update (DPU) placed greater emphasis on the Arctic (NATO’s northern flank) and promised new defence investments, its pledge to increase defence spending to 1.76 per cent of GDP by 2030 fell well short of the NATO target. Canada, currently spending 1.37 per cent of its GDP on defence, remains among only a handful of NATO members which have failed to reach the two per cent threshold and have no plan to do so.
The Defence Policy Update’s silence on this issue did not go unnoticed among allies. Criticism of Canada’s NATO posture reached new heights last month when 23 U.S. senators wrote to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, stating “we are concerned and profoundly disappointed that Canada’s most recent projection indicated that it will not reach its two percent commitment this decade”. Canadians can be forgiven for failing to recall the last time nearly a quarter of the U.S. Senate wrote to the Canadian government on anything.
It’s well known that Justin Trudeau has no time for military issues, but it’s surprising that he hasn’t done a few things that wouldn’t increase the actual spending on the CAF, but would be “bookkeeping” changes that would shift some existing government spending into the military category, like militarizing the Canadian Coast Guard. (That is, moving the CCG from the Fisheries and Oceans portfolio into the National Defence portfolio, not actually putting armaments on CCG vessels. Something similar could be done with the RCMP, switching it from Public Safety to National Defence with no other funding or operational changes.) That Trudeau hasn’t chosen to make even these symbolic changes shows that he actively opposes fulfilling the commitment his government has made twice in the last ten years for reasons of his own.
Labour’s “landslide”
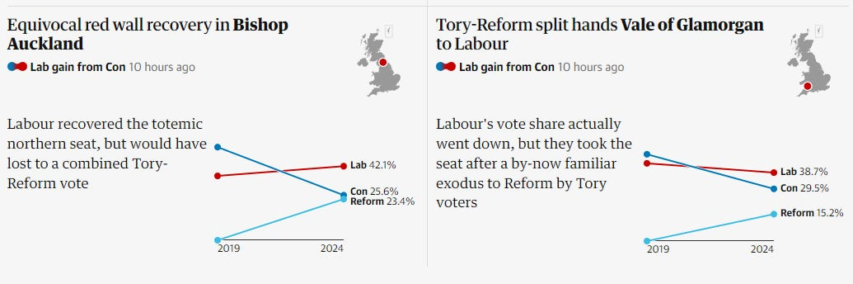
I put the scare quotes around the word “landslide” because Labour’s eye-popping total of seats in Parliament was won on a remarkably narrow share of the actual votes cast in the British general election on Thursday (less than Jeremy Corbyn’s Labour party won in 2019). Fratricide on the right allowed a lot of Labour candidates to squeak in the win as the combined Tory/Reform votes would have been more than enough to top Labour.
Labour has won a landslide and the largest swing in British history without even increasing its vote share in England, and winning perhaps only 35% nationally. Its only significant gains in proportional terms were in Scotland, largely at the expense of the SNP, who have suffered catastrophic losses, meaning they are only 1 seat ahead of Sinn Fein, now the largest party in Northern Ireland — who are in turn 3 seats ahead of Reform, the third largest party in Britain by vote.
But these Reform MPs are — as I write — outnumbered by the five pro-Gaza independents, who won seats in Yorkshire, Lancashire, the Midlands and London in reaction to Keir Starmer’s position on Israel. Labour are down an average of 18 points in seats where the Muslim population is 20%, and in seats where that figure is above 25%, they are down 23 percentage points. While Labour lost a huge share of the Muslim vote, what is more worrying is the atmosphere in which this has taken place.
In Birmingham Yardley Jess Phillips held on by 700 votes, and in a remarkably unpleasant – I might even say upsetting, although I’ve only had three hours’ sleep — count she lamented that “This election has been the worst election I have ever stood in”, as she was booed.
“I understand that a strong woman standing up to you is met with such reticence”, she told her antagonists, and described how opponents had filmed a Labour activist in the streets and slashed her tyres, while another was screamed at by a man. She told how Jo Cox’s family had wanted to come and campaign but she couldn’t let them endure it. “Can you throw them out?” she asked the authorities of her hecklers.
There were similar scenes in Birmingham Ladywood as Shabana Mahmood was heckled as she gave her speech, the returning officer pleading with the supporters of independent Ahkmed Yakoob to stop.
Yakoob was described by the Sunday Times‘s Will Lloyd as “the one man in Britain who embodies the way our politics have changed”. He described “a 36-year-old defence solicitor who wears black Prada trainers, a glittering diamond watch, tinted gold-framed sunglasses and Gareth Southgate-like waistcoats. He has 195,000 followers on TikTok, a platform he understands more intuitively than 99 per cent of the politicians in this country. He speaks in clipped, brutal epigrams that sound like they are only ever a few” and “The word ‘genocide’ is never far from his mouth with ‘For Gaza’ printed on his leaflets.”
Labour hung on in Ladywood, a historic constituency in England’s second city where in 1924 Neville Chamberlain very narrowly beat a rising star of the Labour Party called Oswald Mosley.
Gaza independents also narrowly lost Birmingham Hodge Hill by just 1000 votes, and Ilford North, the constituency of Wes Streeting by just 528 votes.
While the media focus was largely engaged in catching out the musing of some of Reform’s less intellectually capable candidates, this other populist revolt has been carried out in an atmosphere of anger and intimidation perhaps not seen in English elections since the days of Rotten Boroughs.
There was police intervention in Oldham last month, Naz Shah MP was abused as a “dirty, dirty Zionist … paid by Friends of Israel”.
Fellow Canadian observer Damian Penny refuses to apologize for his headline “The Sunak Sets over the British Empire” (and I don’t blame him in the slightest):
Canadian readers, stop me if you’ve heard this before: an historically unpopular center-right Tory government heads into an election under a hapless leader running a catastrophically poor campaign and finds that even its traditional support is being badly eroded by an upstart right-wing populist party called Reform.
What happened in Britain on July 4 (weirdly symbolic, that) is not exactly what we experienced in Canada in 1993 – the Tories suffered the worst election result in their history, but they’re left with 119 more seats than the venerable Progressive Conservative party under Twitter-troll-in-waiting Kim Campbell, and at least the outgoing PM managed to hold on to his own seat — but it’s kind of nice to see the Mother Country adopting our traditions for once.
Honestly, 121 seats for Rishi Sunak’s Conservative Party is much better than I’d expected at the start of this campaign. And had it not been for Nigel Farage’s Reform Party, they might have managed a much less embarrassing defeat, because this kind of thing happened many times over last night:
Not everyone who voted Reform defected from the Conservatives – had Farage’s protest party not been on the ballot, many of its supporters would have stayed home or cast their votes for fringe parties and independent candidates — but it might have made the difference between a bad night for the Tories and the worst election in the Tories’ history.
Reform won four seats outright – less than a hyperbolic exit poll predicted, but four more than most observers expected at the start of the campaign. They can’t really affect much at the national level, especially with Keir Starmer’s Labour Party holding an absolutely massive majority of seats in Parliament, but they will make things very difficult for the Conservatives.
Helen Dale summarized the British general election result in a modified Gary Larson image:
Andrew Doyle points at the disproportional share of the vote won by Nigel Farage’s new Reform UK party compared to the tiny number of seats as a condemnation of the first-past-the-post system (also used here in Canada):
Keir Starmer surely cannot believe his luck. He has achieved a landslide victory by doing very little. He received fewer votes than Jeremy Corbyn in 2019, and yet has ended up with a whopping 412 seats in parliament. The rise of Nigel Farage’s Reform Party has split the right-wing vote and ushered the Conservatives along to their worst ever election result, plunging them to even greater depths than the disastrous election of 1906 under Arthur Balfour.
This was very much a Conservative loss rather than a Labour victory. There is no great enthusiasm for Starmer, and his majority is an indictment of the “First Past The Post” system which, as I have argued previously, should be abandoned in favour of Proportional Representation. It is unsurprising that upon his victory in Clacton-on-Sea, one of Farage’s first public statements has been a commitment to campaign for electoral reform. His party received over 4 million votes and has returned only 5 seats. So that’s 1% of the seats for 14% of the votes. Compare that with the Liberal Democrats, who have 11% of the seats for only 12% of the votes. Most of us will see that there is a problem here, irrespective of our political affiliations.
Worse still, Labour’s victory will empower the culture warriors, those identity-obsessed activists who have accrued so much power already in our major institutions. While the Tory party claimed to be fighting a “war on woke”, all the while enabling the ideology of Critical Social Justice to flourish, leading Labour politicians have cheered on the culture warriors while pretending that they were nothing more than a right-wing fantasy. We have seen some pushback over the past two years in regards to the worst excesses of this movement, but all of this may soon be undone. Now that the identitarians have their political wing in power, we should expect a few years of regression.
In Spiked, Brendan O’Neill thinks the real lesson to be learned from this election is that populism is here to stay:
To see the true quake, you need to look beyond Labour’s mirage-like landslide. As is now becoming clear, Labour has not been swept to power on anything like a wave of public enthusiasm. On the contrary, it won its 412 seats on the second lowest electoral turnout since 1885, and more as a result of people’s exhaustion with the Tories than their love for Sir Keir. No, it is those who refused to vote Labour who have brilliantly unsettled British politics. It is those who took a punt on Nigel Farage’s Reform party who have planted a bomb in the political landscape that will not be easily defused.
For me, the most fascinating stat of the election is the share of the vote received by Labour and the Tories. Labour won around 34 per cent of vote, the Tories around 24 per cent. Let’s leave to one side what a lame landslide it is if only 34 per cent of the people who could be bothered to vote put an X in your box. More striking is the fact that the combined vote share of Labour and the Tories, the parties that have dominated British politics for a century, was 58 per cent. That is staggeringly – and, if you will allow me, hilariously – low.
To put it in historical context: at the last General Election, in 2019, their combined vote share was 75.8 per cent. In 2017 it was even higher: 82.4 per cent. In the elections of the 2000s it hovered around 70 per cent. Why has it now dropped to less than 60 per cent, giving rise to the possibility that in the next few years the two parties that have run this country for decades might see their combined vote drop to less than half of all votes cast? Largely, because of Reform. And a few independents, too. Reform’s vote share is around 14 per cent, enough to shatter the Labour / Tory duopoly and to unravel the two big parties’ arrogant belief that they and they alone have a right to rule.
The speedy turnaround of the Reform revolt was extraordinary. It was only a few weeks ago that Farage ditched his plans to go to America to assist the Trump campaign and instead decided to become leader of Reform. He has now been elected MP for Clacton. Reform has won four seats in total. What’s shocking is that the Liberal Democrats won 71 seats despite getting fewer votes than Reform. The Lib Dems got around 12 per cent of the vote, to Reform’s 14 per cent. That the democratically less popular party of the two will wield far greater power in the Commons is a testament to how busted our first-past-the-post electoral system is. This is unsustainable. It is outright undemocratic.
And yet, even without the parliamentary representation their vote share deserves, Reform has struck a blow for democracy. Their voters, in thinking for themselves and rejecting both the Labour and Tory variety of technocracy, have forcefully created a new opening in political life. They have burst a few of the buckles on the political straitjacket that is our two-party system. The last time this happened was with Farage’s UK Independence Party, in the 2015 General Election, when it won 12.6 per cent of the vote, reducing the Tory / Labour vote share to 67.3 per cent. But where UKIP was mostly a one-issue party, dedicated to getting Britain out of the EU, Reform has broader policy goals. The millions of working-class people who voted for it are saying something very clear indeed: “We want something different”.
“Western media resembles … the consumer landscape of the Soviet bloc. We find the same product on offer everywhere in all leading publications”
eugyppius invites us to contemplate the “awesome, terrifying power of the press”, and not for its useful role in keeping us proles informed about the goings-on of our governments and the doings of the great and the good, but its utterly cynical co-ordinated manipulation of “the narrative”:
Take a moment to contemplate the awesome and terrifying power of the press.
Since 2020, the United States have had a geriatric president who suffers from serious mental deficits. The media discounted this awkward state of affairs as a conspiracy theory or as Trumpist propaganda for years, substantially blunting the political impact of Biden’s dementia. Then, after the president’s terrible debate performance on 27 June, the press made Biden’s incapacity the centre of their coverage, finally welcoming this fact into official regime-sanctioned reality and bringing Biden’s candidacy into crisis. All of this happened within just hours. As I write this, Biden has no more than even odds of securing his party’s nomination, and the press are working overtime to rehabilitate Kamala Harris. Journalists who spent years quietly mocking the vice president for her abrasive personality and her bizarre speaking gaffes are now making the latter a cornerstone of her candidacy. Are you coconutpilled, dear reader?
The Biden Affair is nothing new. So overwhelming is the influence of the press over our politics, that many have described liberal democracies as media-steered regimes, wherein politicians adopt positions and enact policies calculated above all to secure favourable coverage from journalists.
As I mentioned the other day, a healthy media would provide a range of opinions wider than our current spectrum of centre-left/left/hard-left/totally woke. That they do not, despite that spectrum not covering the majority of beliefs among the general public, shows just how monolithic and partisan the surviving mainstream media outlets have become.
Imagine, for a moment, that you wanted to found your own periodical. Maybe you hope to run a weekly magazine or a daily newspaper, maybe you have ambitions of amassing an enormous audience of millions, or maybe you’re content to collect primarily regional readers. Whatever the details, you want to cover national politics in some way. The most rational approach – before you even rent office space or begin to hire staff – would be to study what existing publications are saying and what they’re reporting on, and plan to offer something different. Unless you provide content that your readers can’t get anywhere else, after all, you’ll have trouble convincing anyone to read you.
You’d think, therefore, that the media landscape would be a richly differentiated thing – especially when it comes to big, national stories. Variation like this is present everywhere else in the consumer economy. There are a near-infinite variety of headphones, energy drinks, shoes and coffee makers. Newspapers should be just as varied in their coverage, focus and analysis as all of these other things.
But of course, it is the opposite. Western media resembles much more the consumer landscape of the Soviet bloc. We find the same product on offer everywhere in all leading publications. As in the communist East, variety is confined to a kind of black market – that is to say an array of blogs, social media accounts and alternative (mostly online) publications that you’re not supposed to read and that the official discourse wholly ignores. This anomaly is easy enough to see if you spend multiple hours every day reading news stories. The average consumer of political reporting, however, has a much more casual and sporadic relationship to press discourse, and he’s apt to think that the convergence is entirely natural. The New York Times, the Süddeutsche Zeitung, and Le Monde report the very same things in the very same way at the very same time, often under extremely similar headlines, because they’re just reporting on the way the world is.
In hard authoritarian regimes, like National Socialist Germany, regime propaganda was an open, blunt instrument. Everybody who read the Völkischer Beobachter knew very well that the paper propagated the official Nazi Party line. The soft authoritarianism of the liberal West, in contrast, manages the information and opinions available to the public in a much more effective manner, namely by pretending not to. Millions of people open their newspapers every day in the belief that they contain accurate accounts of the goings-on in the world, and they form their beliefs and political preferences within this highly convincing illusion.
The distributed propaganda network maintained by our establishment press is very expensive. Especially the opportunity costs are very high. In a healthy, uncoordinated media environment, it would be impossible for somebody like me to make a living blogging about the insanity of German politics. I’d have very stiff competition from a multitude of professional, well-funded journalists who would be fighting at every moment to take my readers away from me by writing the kinds of things I do, only more effectively, more frequently and with fewer typographical errors. Of course I am a very small player in the broader ecosystem of alternative media; the audience for this content is hundreds of millions strong. It consists of all those people who have been written off by the establishment press, as the necessary price of exercising narrative control.
Among the forces that conspire to keep legacy media on-message is their aforementioned collaboration with the political establishment. This collaboration includes a tacit understanding that leading politicians and bureaucrats will only provide interviews and information to regime-adjacent journalists, granting them an effective monopoly on political news.
Why Germany Lost the Battle of Verdun
The Great War
Published Mar 8, 2024The Battle of Verdun represents the worst of trench warfare and the suffering of the soldiers in the minds of millions – and for many, the cruel futility of the First World War. But why did Germany decide to attack Verdun in the first place and why didn’t they stop after their initial attack failed?
(more…)
QotD: The Roman Republic at war … many wars … many simultaneous wars
With the end of the Third Samnite War in 290 and the Pyrrhic War in 275, Rome’s dominance of Italy and the alliance system it constructed was effectively complete. This was terribly important because the century that would follow, stretching from the start of the First Punic War in 264 to the end of the Third Macedonian War in 168 (one could argue perhaps even to the fall of Numantia in 133) put the Roman military system and the alliance that underpinned it to a long series of sore tests. This isn’t the place for a detailed recounting of the wars of this period, but in brief, Rome would fight major wars with three of the four other Mediterranean great powers: Carthage (264-241, 218-201, 149-146), Antigonid Macedon (214-205, 200-196, 172-168, 150-148) and the Seleucid Empire (192-188), while at the same time engaged in a long series of often quite serious wars against non-state peoples in Cisalpine Gaul (modern north Italy) and Spain, among others. It was a century of iron and blood that tested the Roman system to the breaking point.
It certainly cannot be said of this period that the Romans always won the battles (though they won more than their fair share, they also lost some very major ones quite badly) or that they always had the best generals (though, again, they tended to fare better than average in this department). Things did not always go their way; whole armies were lost in disastrous battles, whole fleets dashed apart in storms. Rome came very close at points to defeat; in 242, the Roman treasury was bankrupt and their last fleet financed privately for lack of funds (Plb. 1.59.6-7). During the Second Punic War, at one point the Roman censors checked the census records of every Roman citizen liable for conscription and found only 2,000 men of prime military age (out of perhaps 200,000 or so; Taylor (2020), 27-41 has a discussion of the various reconstructions of Roman census figures here) who hadn’t served in just the previous four years (Liv. 24.18.8-9). In essence the Romans had drafted everyone who could be drafted (and the 2,000 remainders were stripped of citizenship on the almost certainly correct assumption that the only way to not have been drafted in those four years but also not have a recorded exemption was intentional draft-dodging).
And the military demands made on Roman armies and resources were exceptional. Roman forces operated as far east as Anatolia and as far west as Spain at the same time. Livy, who records the disposition of Roman forces on a year-for-year basis during much of this period (we are uncommonly well informed about the back half of the period because those books of Livy mostly survive), presents some truly preposterous Roman dispositions. Brunt (Italian Manpower (1971), 422) figures that the Romans must have had something like 225,000 men under arms (Romans and socii) each year between 214 and 212, immediately following a series of three crushing defeats in which the Romans probably lost close to 80,000 men. I want to put that figure in perspective for a moment: Alexander the Great invaded the entire Persian Empire with an army of 43,000 infantry and 5,500 cavalry. The Romans, having lost close to Alexander’s entire invasion force twice over, immediately raised more than four times as many men and kept fighting.
These armies were split between a bewildering array of fronts (e.g. Liv 24.10 or 25.3): multiple armies in southern Italy (against Hannibal and rebellious socii now supporting him), northern Italy (against the Cisalpine Gauls, who also backed Hannibal) and Sicily (where Syracuse threatened revolt) and Spain (a Carthaginian possession) and Illyria (fighting the Antigonids) and with fleets active in both the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian Sea supporting those operations. And of course a force defending Rome itself because did I mention Hannibal was in Italy?
If you will pardon me embellishing a Babylon 5 quote, “Only an idiot fights a war on two fronts. Only the heir to the throne of the kingdom of idiots would fight a war on twelve fronts.” And apparently, only the Romans would then win that war anyway.
(I should note that, for those interested in reading up on this, the state-of-the-art account of Rome’s ability to marshal these truly incredible amounts of resources and especially men is the aforementioned, M. Taylor, Soldiers & Silver (2020), which presents the consensus position of scholars better than anything else out there. I’d be remiss if I didn’t note that my own book project takes aim at this consensus and hopes to overturn parts of it, but seeing as how my book isn’t done, for now Taylor holds the field (also it’s a good book which is why I recommended it)).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Queen’s Latin or Who Were the Romans, Part II: Citizens and Allies”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-06-25.