World War Two
Published 10 Nov 2022Hitler commemorates the twentieth anniversary of the failed Beer Hall Putsch, in Auschwitz 50 men are shot in celebration, and Arthur Liebehenschel replaces Rudolf Höss as commandant.
(more…)
November 14, 2022
The Auschwitz Business Model – War Against Humanity 086
Two Variants of the French RSC 1917 Semiauto WW1 Rifle
Forgotten Weapons
Published 2 Apr 2017The RSC 1917, aka FSA1917, has the distinction of being the only true semiautomatic service rifle to see significant frontline infantry use during World War One. It was introduced in 1917 as a long rifle, and about 75,000 were made in that configuration. An improved carbine model was developed in in 1918 right at the end of the war, with only a few thousand of those made. However, what we are looking at today are a pair of 1917 rifles which show a couple of differences.
One of these is a standard RSC 1917 as originally produced, and the other has been updated to a 1918 standard in two ways: the bolt handle/disassembly and the bolt holdopen mechanism. I do not know if these changes were actually implemented during the war, or in the years afterward, but they make the rifles substantially easier to field strip.
If you know of details relevant to these changes, please let me know in the comments!
(more…)
QotD: The first modern revolution
The first modern revolution was neither French nor American, but English. Long before Louis XVI went to the guillotine, or Washington crossed the Delaware, the country which later became renowned for stiff upper lips and proper tea went to war with itself, killed its king, replaced its monarchy with a republican government and unleashed a religious revolution which sought to scorch away the old world in God’s purifying fire.
One of the dark little secrets of my past is my teenage membership of the English Civil War Society. I spent weekends dressed in 17th-century costumes and oversized helmets, lined up in fields or on medieval streets, re-enacting battles from the 1640s. I still have my old breeches in the loft, and the pewter tankard I would drink beer from afterwards with a load of large, bearded men who, just for a day or two, had allowed themselves to be transported back in time.
I was a pikeman in John Bright’s Regiment of Foote, a genuine regiment in the parliamentary army. We were a Leveller regiment, which is to say that this part of the army was politically radical. For the Levellers, the end of the monarchy was to be just the beginning. They aimed to “sett all things straight, and rayse a parity and community in the kingdom”. Among their varied demands were universal suffrage, religious freedom and something approaching modern parliamentary democracy.
The Levellers were far from alone in their ambitions to remake the former Kingdom. Ranters, Seekers, Diggers, Fifth Monarchists, Quakers, Muggletonians: suddenly the country was blooming with radical sects offering idealistic visions of utopian Christian brotherhood. In his classic study of the English Revolution, The World Turned Upside Down, historian Christopher Hill quotes Lawrence Clarkson, leader of the Ranters, who offered a radical interpretation of the Christian Gospel. There was no afterlife, said Clarkson; only the present mattered, and in the present all people should be equal, as they were in the eyes of God:
“Swearing i’th light, gloriously”, and “wanton kisses”, may help to liberate us from the repressive ethic which our masters are trying to impose on us — a regime in which property is more important than life, marriage than love, faith in a wicked God than the charity which the Christ in us teaches.
Modernise Clarkson’s language and he could have been speaking in the Sixties rather than the 1640s. Needless to say, his vision of free love and free religion, like the Leveller vision of universal equality, was neither shared nor enacted by those at the apex of the social pyramid. But though Cromwell’s Protectorate, and later the restored monarchy, attempted to maintain the social order, forces had been unleashed which would change England and the wider world entirely. Some celebrated this fact, others feared it, but in their hearts everyone could sense the truth that Gerard Winstanley, leader of the Diggers, was prepared to openly declare: “The old world … is running up like parchment in the fire”.
Paul Kingsnorth, “The West needs to grow up”, UnHerd, 2022-07-29.
November 13, 2022
Carrying on about the Carry On movies
In The Critic, Alexander Larman looks back at one of the longest-running film series beginning with 1958’s Carry On Sergeant (not to be confused with the earlier — and reputedly terrible — interwar Canadian film of the same name) and continuing with many more until the filmic disaster of Carry On Emmanuelle in 1978 (there was also a 1992 attempt to revive the franchise, which failed):
In Alan Bennett’s The History Boys, it is decreed by the contrarian history master, Irwin, that “if George Orwell had lived, nothing is more certain than that he would have written an essay on the Carry On films”.
We are invited to take Irwin’s instructions that the Carry On films represent a valuable insight into British social history with suitable detachment. (The precise, suitably pompous quote is that “while they have no intrinsic merit, they acquire some of the permanence of art simply by persisting, and acquire an incremental significance if only as social history”.)
Yet Irwin (or Bennett) was almost certainly right that, had Orwell survived into the Sixties and Seventies, he would have found the Carry On film series both repellent and fascinating. It is literature’s, and history’s, loss that we do not have an account of Orwell’s thoughts on the antics of Charles Hawtrey, Kenneth Williams, Barbara Windsor et al.
In 1941, Orwell wrote of postcards by the cheerfully lowbrow artist Donald McGill that “your first impression is one of overpowering vulgarity” and that “what you are really looking at is something as traditional as Greek tragedy, a sort of sub-world of smacked bottoms and scrawny mothers-in-law which is a part of Western European consciousness”. He goes on to say that “jokes barely different from McGill’s could casually be uttered between the murders in Shakespeare’s tragedies”.
[…]
The joy of watching the Carry On films, then, is twofold. On the one hand, the hackneyed stories, two-dimensional characterisation and laboured puns and innuendo can be enjoyable, on a purely basic level, but hardly threaten to aspire to the levels of great art.
Yet on the other, the cheerfully Rabelaisian sentiments of the pictures — in which all men and women are defined purely in sexual and scatological terms — exist on a level of reductio ad absurdum.
It is no coincidence that the best Carry On films contain a vein of social satire in their mocking of great British institutions, whether it be the NHS, MI5, the army or the Raj, and the final set piece of Carry On Up The Khyber — in which the stiff-upper-lip British occupiers ignore the Afghan invaders while taking formal dinner in black tie — rises to a level of surrealist genius that would have made Buñuel proud.
There is occasional talk of making another Carry On film, but with all the principal cast (save the ever-sprightly Dale) now dead and with the world a very different place, it is impossible to imagine that we will ever see, say, Carry On Tweeting or the like.
There is every possibility that a really top-notch cast could be assembled, if there was any serious intent behind it — I would love to see Andrew Scott, for instance, offer a more dynamic take on the kind of roles that Williams essayed, because he would do so brilliantly, and if the script could be written by the award-winning likes of Patrick Marber or Richard Bean, it could be a thing of innuendo-heavy beauty.
But then the Carry On series never was a thing of beauty. In its grim and hilarious way, it took every British national stereotype, pulled its trousers down, and gave it a hearty slap on its bare buttocks. Some might find this offensive; others might mourn its loss from public life.
In either case, we shall not look upon its like again. Dr Nookey, Francis Bigger, Professor Inigo Tinkle, Vic Flange: your services are no longer required. To which unkind cut we must solemnly say: “Ooh, matron.”
Kiev Liberated! Celebrations in Moscow! – WW2 – 220 – November 12, 1943
World War Two
Published 12 Nov 2022The Red Army has driven the Axis forces out of Kiev, the third largest city in the USSR. The Allies are also advancing, albeit slowly and at great cost, in Italy, but in the South Pacific, they launch a massive air strike against Rabaul … and what is the result?
(more…)
Corruption in US politics? Where’s the fainting couch?
Elizabeth Nickson looks at several recent books covering political corruption in US politics:
Whitney Webb’s One Nation under Blackmail published late last month, explains in exhaustive detail how the American government was taken over by well-dressed thieves. Webb writes from the left, but she is dispassionate. In 1,000 pages, she explains the history of the turning of democracy, starting post WW2 with the heinous Dulles brothers, moving through Reagan with country club thugs calling themselves The Enterprise, to Jeffrey Epstein’s seduction of Bill and Hillary Clinton. Promising riches beyond their imaginings, the seduction led the couple, by increments, to sell out the country to China and Wall Street.
Webb explains how Epstein set up the Clinton and Gates Foundations promising a new iteration in “charity”, one that made profits, and pushed forward the founders as Saviours. Clinton in her years as Sec State, flew around the world eating brownies and demanding tithes for herself, in return for every beneficence she gave courtesy of the American taxpayer. The ’08 crisis was brought to us by the same crooks, and the same methods, chipping away at regulation. The head Fannie and Freddie Mae bureaucrat, James A Johnson walked away with $100 million leaving the world in crisis. Tens of millions lost everything.
Add this to [Profiles in Corruption] Peter Schweizer’s extraordinary detailing of how Pelosi etc. made their hundreds of millions using taxpayer money, pinpointed deregulation and insider trading.
Schweizer describes how the mega-criminal dealing of the Bidens with China and the Ukraine has walked us into a potential nuclear conflict with both Russia and China. The Lords of Easy Money shows how Wall Street and all the pension funds, all the index funds, have been rolling over corporate debt and taking profits, then borrowing more, selling, borrowing more, selling, and repeat. Which means that every American enterprise that is traded and somehow functional, is laden with corporate debt it cannot possibly pay the interest on, as interest rates rise. Jay Powell made his $50 million that way.
Webb shows how Epstein coached Gates through invading and then purchasing public health both at home and through the UN. Add in the Covid mess, and another bunch of corporate and government thieves walked away with $3 Trillion, in the US alone.
Do you really think they’d allow the endless prosecutions they deserve? Do you really think they want to give back the money they stole?
Are dollar store tools any good? Saving money in financially strapped times
Steve Ramsey – Woodworking for Mere Mortals
Published 8 Jul 2022Dollar Store vs. Home Depot vs. Amazon. Saving money in financially strapped times.
(more…)
QotD: Your “true self”
When someone above the age of young adulthood says that he is searching for himself, it is almost always because he has been behaving badly or has had reversals in life. No one goes off in search of himself whose life is satisfactory. The assumption is that, once found, the true self will be charming, successful, and, above all, good. This is because man is born good, though — paradoxically — everywhere is bad. Finding yourself is a panacea, and you will live happily ever after.
Unfortunately, the search for the true self has a tendency to go on for years or even for decades. I used to ask my patients who said that they were in search of themselves how they would know when they had found it. The true self, after all, is not like a mislaid pair of cuff links. They said that their unhappiness would fall away when they found it, presumably like the outer mold of a casting. But they had no real idea of what a better life than the one they were leading would be like. Mostly they thought of the better life as one of luxury and more consumption, bathing in ass’ milk rather than in mere water. When I suggested that they needed to lose rather than to find themselves, they asked how one lost oneself.
“By being interested in something outside of and other than oneself,” I said.
“How do you do that?” I asked.
Here the weakness of my advice became apparent to me. I have been interested in many different things in my life, usually in succession, and my library is a testimony to my tendency to serial monomania; but I have never been interested in nothing, and therefore have no idea how people develop the capacity to be interested in something (that is to say, in anything) ex nihilo, so to speak, nor do I have any recollection of how I did so myself. I suspect (though I cannot prove) that modern education, which lays emphasis on the relevance of what is taught to children’s present lives rather than, as it should be, on its irrelevance, is partly to blame for the very large numbers of people who cannot lose themselves, and therefore are left to the vagaries of entertainment provided for them under our current regime of bread and circuses. The unassuageable thirst for entertainment is both a manifestation and a symptom of a profound boredom with the world. Indeed, entertainment is also one of the greatest causes of boredom in the world, inasmuch as everyday reality can now rarely compete in raw sensation with entertainment. But since dealing with everyday reality remains a necessity for most people, it results in boredom because it is compared with entertainment. Only a deeper engagement with the world can avoid or overcome this problem.
Theodore Dalrymple, “Lose Yourself”, Taki’s Magazine, 2018-11-10.
November 12, 2022
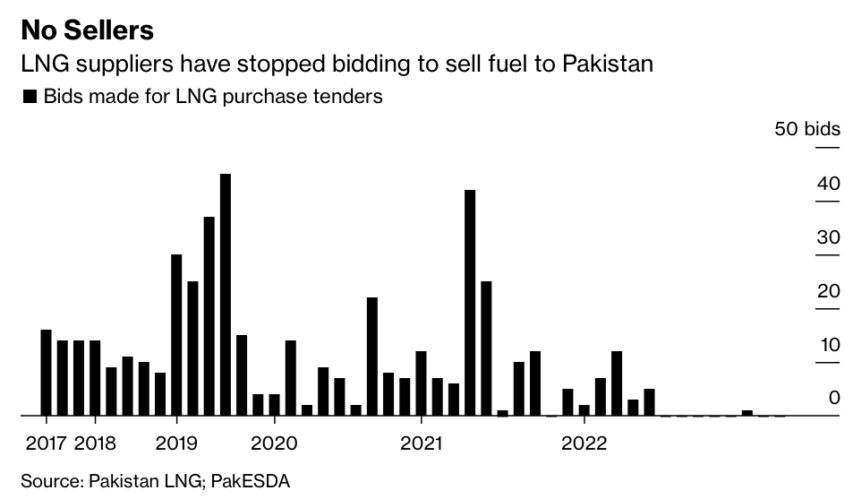
Climate imperialism
Michael Shellenberger on the breathtaking hypocrisy of first world nations’ rhetoric toward developing countries’ attempts to improve their domestic energy production:
What’s worse, global elites are demanding that poor nations in the global south forgo fossil fuels, including natural gas, the cleanest fossil fuel, at a time of the worst energy crisis in modern history. None of this has stopped European nations from seeking natural gas to import from Africa for their own use.
Rich nations have for years demanded that India and Pakistan not burn coal. But now, Europe is bidding up the global price of liquified natural gas (LNG), leaving Pakistan forced to ration limited natural gas supplies this winter because Europeans — the same ones demanding Pakistan not burn coal — have bid up the price of natural gas, making it unaffordable.
At last year’s climate talks, 20 nations promised to stop all funding for fossil fuel projects abroad. Germany paid South Africa $800 million to promise not to burn coal. Since then, Germany’s imports of coal have increased eight-fold. As for India, it will need to build 10 to 20 full-sized (28 gigawatts) coal-fired power plants over the next eight years to meet a doubling of electricity demand.
This is climate imperialism. Rich nations are only agreeing to help poor nations so long as they use energy sources that cannot lift themselves out of poverty.
Consider the case of Norway, Europe’s second-largest gas supplier after Russia. Last year it agreed to increase natural gas exports by 2 billion cubic meters, in order to alleviate energy shortages. At the same time, Norway is working to prevent the world’s poorest nations from producing their own natural gas by lobbying the World Bank to end its financing of natural gas projects in Africa.
The IMF wants to hold hostage $50 billion as part of a “Resilience and Sustainability Trust” that will demand nations give up fossil fuels and thus their chance at developing. Such efforts are working. On Thursday, South Africa received $600 million in “climate loans” from French and German development banks that can only be used for renewables. The Europeans hope to shift the $7.6 billion currently being invested by South Africa in electricity infrastructure away from coal and into renewables.
Celebrities and global leaders say they care about the poor. In 2019, the Duchess of Sussex, Meghan Markle, Prince Harry’s wife, told a group of African women, “I am here with you, and I am here FOR you … as a woman of color.” Why, then, are they demanding climate action on their backs?
The Final Bloody Chapter of Operation Reinhard – War Against Humanity 085
World War Two
Published 9 Nov 2022The genocide of the Jews of Eastern Europe concludes with Operation Harvest Festival — Aktion Erntefest when 42,000 are murdered in the Lublin district.
(more…)
Long distance communication in the pre-modern era
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes considers why the telegraph took so long to be invented and describes some of the precursors that filled that niche over the centuries:
… I’ve also long wondered the same about telegraphs — not the electric ones, but all the other long-distance signalling systems that used mechanical arms, waved flags, and flashed lights, which suddenly only began to really take off in the eighteenth century, and especially in the 1790s.
What makes the non-electric telegraph all the more interesting is that in its most basic forms it actually was used all over the world since ancient times. Yet the more sophisticated versions kept on being invented and then forgotten. It’s an interesting case because it shows just how many of the budding systems of the 1790s really were long behind their time — many had actually already been invented before.
The oldest and most widely-used telegraph system for transmitting over very long distances was akin to Gondor’s lighting of the beacons, capable only of communicating a single, pre-agreed message (with flames often more visible at night, and smoke during the day). Such chains of beacons were known to the Mari kingdom of modern-day Syria in the eighteenth century BC, and to the Neo-Assyrian emperor Ashurbanipal in the seventh century BC. They feature in the Old Testament and the works of Herodotus, Aeschylus, and Thucydides, with archaeological finds hinting at even more. They remained popular well beyond the middle ages, for example being used in England in 1588 to warn of the arrival of the Spanish Armada. And they were seemingly invented independently all over the world. Throughout the sixteenth century, Spanish conquistadors again and again reported simple smoke signals being used by the peoples they invaded throughout the Americas.
But what we’re really interested in here are systems that could transmit more complex messages, some of which may have already been in use by as early as the fifth century BC. During the Peloponnesian War, a garrison at Plataea apparently managed to confuse the torch signals of the attacking Thebans by waving torches of their own — strongly suggesting that the Thebans were doing more than just sending single pre-agreed messages.
About a century later, Aeneas Tacticus also wrote of how ordinary fire signals could be augmented by using identical water clocks — essentially just pots with taps at the bottom — which would lose their water at the same rate and would have different messages assigned to different water levels. By waving torches to signal when to start and stop the water clocks (Ready? Yes. Now start … stop!), the communicator could choose from a variety of messages rather than being limited to one. A very similar system was reportedly used by the Carthaginians during their conquests of Sicily, to send messages all the way back to North Africa requesting different kinds of supplies and reinforcement, choosing from a range of predetermined signals like “transports”, “warships”, “money”.
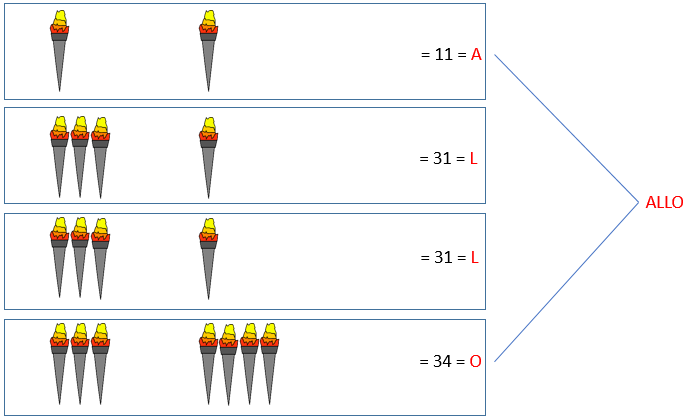
Diagram of a fire signal using the Polybius cipher.
Created by Jonathan Martineau via Wikimedia Commons.By the second century BC, a new method had appeared. We only know about it via Polybius, who claimed to have improved on an even older method that he attributed to a Cleoxenus and a Democleitus. The system that Polybius described allowed for the spelling out of more specific, detailed messages. It used ten torches, with five on the left and five on the right. The number of torches raised on the left indicated which row to consult on a pre-agreed tablet of letters, while the number of torches raised on the right indicated the column. The method used a lot of torches, which would have to be quite spread out to remain distinct over very long distances. So it must have been quite labour-intensive. But, crucially, it allowed for messages to be spelled out letter by letter, and quickly.
Three centuries later, the Romans were seemingly still using a much faster and simpler version of Polybius’s system, almost verging on a Morse-like code. The signalling area now had a left, right, and middle. But instead of signalling a letter by showing a certain number of torches in each field all at once, the senders waved the torches a certain number of times — up to eight times in each field, thereby dividing the alphabet into three chunks. One wave on the left thus signalled an A, twice on the left a B, once in the middle an I, twice in the middle a K, and so on.
By the height of the Roman Empire, fire signals had thus been adapted to rapidly transmit complex messages over long distances. But in the centuries that followed, these more sophisticated techniques seem to have disappeared. The technology appears to have regressed.
SUPERCUT – Every Window Cameo in Batman (1966-1968)
Tommy Westphall’s Snowglobe
Published 14 Jan 2020The dynamic duo’s show of the 60s was fond of celebrity cameos. Here is a Supercut of every single one of them.
In order of appearance:
1. Jerry Lewis
2. George Cisar (from the 1966 film)
3. Dick Clark
4. Van Williams and Bruce Lee as The Green Hornet and Kato from The Green Hornet
5. Sammy Davis Jr.
6. Bill Dana as José Jiménez
7. Howard Duff as of Sam Stone from Felony Squad
8. Werner Klemperer as Colonel Klink from Hogan’s Heroes
9. Ted Cassidy as Lurch from The Addams Family
10. Don Ho
11. Santa Claus
12. Art Linkletter
13. Edward G. Robinson
14. Suzy Knickerbocker
15. The Carpet King
(more…)
QotD: The short careers of secret police chiefs
The first thing you learn on even the most cursory look at any secret police is: they aren’t. Secret, that is. Otherwise they wouldn’t be effective. Oh, they’d probably be a lot better at gathering certain kinds of intel, but intelligence gathering is really only their secondary function. Their primary function, of course, is intimidation. That’s why every Hans and Franz on the street in Nazi Germany could tell you exactly where the nearest Gestapo office was.
(The Romanian Securitate had public intimidation down to an art form. They’d follow random guys around using big, obvious details, the better to prove to the proletariat that everyone was suspect. It is to them, not Mafia dons or aspiring rappers, that we owe the now-standard Eurotrash track suit look).
Secret police goons suffer from two serious structural problems, though, that not even the guys in Stove’s book [The Unsleeping Eye] really ever solved. The first is the obvious one, that guys who know where the bodies are buried are always at risk of using that knowledge. Napoleon’s guy Joseph Fourche, and FDR’s main man J. Edgar, lived out their natural lives (as did Elizabeth’s spymaster Sir Francis Walsingham), but of them, only Fourche lived in anything approaching what we would call an ideologized society, and that was small beer.
The rest of those guys died in harness, because of course they did. Adolf Hitler was an especially stupid dictator, and Heinrich Himmler an especially servile little freak, but I have no doubt that if the Reich had gone on much longer [Himmler] would’ve shanked [Hitler]. If Heydrich hadn’t gotten perforated in Prague, he no doubt would’ve gone after [Himmler] even sooner. Lenin and especially Stalin burned through secret police chiefs on the regular, because they pretty much had to.
I don’t know about the goons in the Chinese etc. secret police, but I’d be shocked to find anyone with more than a few years’ tenure, because purges are simply a way of life in totally ideologized societies. For every Khrushchev who manages to hang on – n.b. he was a Red Army commissar during the war, i.e. a not-so-secret police goon — there are fifty guys who live fast and die hard, because that’s just how totalitarians rule.
The stoyaknik, of course, is well served to consider the current scene as if he were watching the Politburo of an exceptionally deluded Commie regime, one made up almost entirely of ruthless yet clueless retards … who still believe, for the most part, in Communism.
That was always the problem for Kremlinologists in evaluating the USSR — whatever the Boss of the moment decided would, of course, immediately be retconned into the Scriptures by the Academicians, but what did the Big Guy himself think about it? That constrained his choices. Stalin and Khrushchev were true Communists, there’s no question about that, but they came up in the school of the hardest possible knocks — if they needed to do something directly contrary to Leninism in order to hang on to power, then Comrade Ilych can suck it.
For anything short of mortal, though, they’d more often than not behave as stereotypical Commies, so the first thing any Kremlinologist had to do was determine the seriousness of the situation from the Politburo’s perspective. Not an easy task, as you might imagine, and what made it worse was: as the USSR gained stability and Communism matured, the old school hardasses all died off and were replaced by True Believers. Mikhail Gorbachev, for instance, didn’t start making his mark until after Stalin’s death, and he wasn’t a real up-and-comer until after Khrushchev — that is, he started rising through the ranks only after the hard boys were gone.
Thus, while Khrushchev was a true Commie, he still had some hard reality to constrain him. Gorby didn’t. He really believed all that Marxist-Leninist horseshit about democracy and etc.; he was far more doctrinaire than the earlier generation could possibly be. Thus Kremlinologists were forever baffled when he did stupid things that made no sense from the Realpolitik perspective, but were perfectly in keeping with the Scriptures. They thought Perestroika was some big 4D chess feint, for instance, instead of just a soft boy doing something noodle-headed.
Severian, “Book Review: The Unsleeping Eye by R.J. Stove”, Founding Questions, 2022-08-09.
November 11, 2022
Mark Knopfler – “Remembrance Day”
Bob Oldfield
Published on 3 Nov 2011A Remembrance Day slideshow using Mark Knopfler’s wonderful “Remembrance Day” song from the album Get Lucky (2009). The early part of the song conveys many British images, but I have added some very Canadian images also which fit with many of the lyrics. The theme and message is universal… “we will remember them”.
In memoriam
A simple recognition of some of our family members who served in the First and Second World Wars:
The Great War
 Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
(Elizabeth’s great uncle)- Private Archibald Turner Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, mortally wounded 25 September, 1915 at Loos, age 27
(Elizabeth’s great uncle) - Private David Buller, Highland Light Infantry, died 21 October, 1915 at Loos, age 35
(Elizabeth’s great grandfather) - Private Harold Edgar Brand, East Yorkshire Regiment. died 4 June, 1917 at Tournai.
(My first cousin, three times removed) - Private Walter Porteous, Durham Light Infantry, died 4 October, 1917 at Passchendaele, age 18
(my great uncle) - Corporal John Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, wounded 2 September, 1914 (shortly before the First Battle of the Aisne), wounded again 29 June, 1918, lived through the war.
(Elizabeth’s great uncle)
The Second World War
- Flying Officer Richard Porteous, Royal Air Force, survived the defeat in Malaya, was evacuated to India and lived through the war
(my great uncle) - Able Seaman John Penman, Royal Navy, served in the Defensively Equipped Merchant fleet on the Atlantic convoys, the Murmansk Run (he may have been on a ship in convoy PQ-17, as we know he spent a winter in Russia) and other convoy routes, was involved in firefighting and rescue efforts during the Bombay Docks explosion in 1944, lived through the war
(Elizabeth’s father) - Private Archie Black (commissioned after the war and retired as a Major), Gordon Highlanders, captured during the fall of Singapore (aged 15) and survived a Japanese POW camp (he had begun to write an autobiography shortly before he died)
(Elizabeth’s uncle) - Elizabeth Buller, “Lumberjill” in the Women’s Timber Corps, an offshoot of the Women’s Land Army in Scotland through the war.
(Elizabeth’s mother) - Trooper Leslie Taplan Russon, 3rd Royal Tank Regiment, died at Tobruk, 19 December, 1942 (aged 23).
Leslie was my father’s first cousin, once removed (and therefore my first cousin, twice removed).
My maternal grandfather, Matthew Kendrew Thornton, was in a reserved occupation during the war as a plater working at Smith’s Docks in Middlesbrough. The original design for the famous Flower-class corvettes came from Smith’s Docks and 16 (including four intended for the French Marine National) of the 196 built in the UK during the war (more were built in Canada).
For the curious, the Commonwealth War Graves Commission the Royal British Legion, and the Library and Archives Canada WW1 and WW2 records site provide search engines you can use to look up your family name. The RBL’s Every One Remembered site shows you everyone who died in the Great War in British or Empire service (Canadians, Australians, New Zealanders, South Africans and other Imperial countries). The CWGC site also includes those who died in the Second World War. Library and Archives Canada allows searches of the Canadian Expeditionary Force and the Royal Newfoundland Regiment for all who served during WW1, and including those who volunteered for the CEF but were not accepted.
In Flanders fields the poppies blow
Between the crosses row on row,
That mark our place; and in the sky
The larks, still bravely singing, fly
Scarce heard amid the guns below.We are the Dead. Short days ago
We lived, felt dawn, saw sunset glow,
Loved and were loved, and now we lie
In Flanders fields.Take up our quarrel with the foe:
To you from failing hands we throw
The torch; be yours to hold it high.
If ye break faith with us who die
We shall not sleep, though poppies grow
In Flanders fields.Lieutenant Colonel John McCrae, MD Canadian Army Medical Corps (1872-1918)