Biographics
Published 19 Mar 2021Dive into Discworld.
September 12, 2021
Terry Pratchett: Discworld And Beyond
September 7, 2021
How William Fairbairn Created the Modern SWAT Team in Warlord Era Shanghai
Forgotten Weapons
Published 1 Jun 2021William E. Fairbairn is best known for his work with Eric Sykes and their “Commando” knife design during World War Two. However, Fairbairn spent some 33 years in the Shanghai Municipal Police, working his way up from a beat constable to Assistant Commissioner. There he was responsible for the SMPD adopting truly forward-thinking fighting methods, and he essentially invented the modern SWAT team (the “Reserve Unit”, which Fairbairn led for 10 years). He combined expertise in formal marksmanship, instinctive practical shooting, and hand-to-hand combat schools (including jiu-jitsu and judo) into a comprehensive training program like no other on earth at the time.
Book references:
The World’s First SWAT Team, by Leroy Thompson:
https://amzn.to/2TrYiNvGentleman & Warrior, by Peter Robins:
https://amzn.to/3vuODn9http://www.patreon.com/ForgottenWeapons
https://www.floatplane.com/channel/Fo…
Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.forgottenweapons.com
Contact:
Forgotten Weapons
6281 N. Oracle 36270
Tucson, AZ 85740
August 31, 2021
Isambard Kingdom Brunel: The Genius of the Industrial Revolution
Biographics
Published 23 Mar 2020Check out Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/biographics
Check out Business Blaze: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYY5…
This video is #sponsored by Brilliant.
TopTenz Properties
Our companion website for more: http://biographics.org
Our sister channel TopTenz: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCQ-h…
Our Newest Channel about Interesting Places: https://studio.youtube.com/channel/UC…Credits:
Host – Simon Whistler
Author – Morris M.
Producer – Jennifer Da Silva
Executive Producer – Shell HarrisBusiness inquiries to biographics.email@gmail.com
Source/Further reading:
Oxford National Dictionary of Biography: https://www.oxforddnb.com/view/10.109…
Interesting podcast on his life: https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/b04n…
Britannica: https://www.britannica.com/biography/…
History Today: https://www.historytoday.com/archive/…
The Thames Tunnel: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/histor…
The atmospheric railway: https://www.theguardian.com/science/t…
SS Great Britain accident: https://www.ssgreatbritain.org/about-…
August 27, 2021
On Which Side is Brazil? – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 26 Aug 2021Brazilian President, Getúlio Vargas, has led his country as dictator since the 1930s. He has embraced European fascist ideas and fostered close ties with Germany and Italy. Yet, he also maintains a close relationship with the United States. After skilfully playing both sides, he must now choose Axis or Allies.
(more…)
August 8, 2021
Presidential biographies
As I’m not an American, I haven’t read many biographies of US Presidents (just Jefferson, Jackson, Lincoln, Grant, and Coolidge if I remember correctly), so I can’t really comment on this project by a man who read and ranked 240 of them:
In 2012, an investment banker and avid history reader named Stephen Floyd began making his way through the American presidents, one biography at a time. It was a way to fill time while commuting to Hong Kong on twelve-hour flights. “I got tired of drinking free wine and watching cheap movies,” he says. Starting with George Washington, he read 240 titles (123,000 pages) in six years or, to be precise, 2,243 days, bringing him up to Obama. (Floyd is not alone in this pursuit: as the Washington Post reports, reading biographies of all the presidents is a thing).
Along the way, Floyd blogged about the books he read at bestpresidentialbios.com where fellow enthusiasts commented on his reviews, sometimes challenged his opinions, and suggested additional biographies to read. His blog posts improved to the point where he became a reliable and knowledgeable reviewer, as good as most professionals. When Stephen Floyd says David McCullough’s much-celebrated biography of John Adams is the second-best biography of John Adams, you need to listen. He can back it up.
Floyd, who continues to review biographies he overlooked in his initial journey, as well as new releases, has covered a dozen volumes on George Washington alone, including all four volumes and 1,800 pages of James Flexner. He rates Ron Chernow’s Washington: A Life the best of the bunch, by far. Chernow is the only biography of the 270-some Floyd has reviewed to earn a five-star rating. Only sixteen authors have 4.5 stars or better. (In case you’re wondering, Floyd gave Hoover one of the worst reviews it got anywhere, but still placed it among the dozen or so biographies with 4.25 stars, and seeing as it’s keeping company with Edmund Morris’s magnificent Theodore Roosevelt series, I won’t complain.)
Of course, one can quibble with Floyd’s judgments, as with those of any reviewer. He has 4.5 stars for Doris Kearns Goodwin’s The Fitzgeralds and the Kennedys, notwithstanding the padding and the plagiarism (it has been taken out of print by its publisher). He found a lot more to like in Peggy Noonan’s Reagan biography than I did. Also in H. Wayne Morgan’s McKinley, which is nowhere near as fine as Margaret Leech’s lower-rated effort. But Floyd knows what he likes and why.
Going back to the Adams biographies, he celebrates Ferling for his judicious details and careful opinions. “The author’s descriptive capability is on consistent display and he sets the context in most scenes magnificently.” He appreciates that Ferling finds Adams’ relationship with his wife, Abigail, more complicated than the perfect romance portrayed in other biographies.
Floyd is less charmed by McCullough’s “enormously sympathetic” biography of Adams. It is “incontrovertibly excellent,” and firmly rooted in the abundant Adams source material, but the author’s tendency to end every scene with a remark favorable to the subject irks after a while. McCullough comes across as “a mother doting on a favorite child.”
It’s a fair point, and Ferling gets the higher mark.
Bestpresidentialbios.com has all of Floyd’s reviews, and summaries of his reviews broken down by president. It’s a great resource and, as mentioned, he’s still adding to it.
August 6, 2021
Shostakovich: Stalin’s Composer? – WW2 Biography Special
World War Two
Published 5 Aug 2021Leningrad’s Dmitri Shostakovich has risen from a child prodigy to be one of the Soviet Union’s most celebrated composers, having rescued his career from Stalin’s interference along the way. Desperate to defend Russia after the German invasion, he fights back, not with a rifle, but with music.
(more…)
July 19, 2021
July 13, 2021
“Samuel Beckett was one of the twentieth century’s very greatest conmen and his dupes continue to relish being parted from their cash”
In The Critic, J.S. Barnes digs up the bones of Samuel Beckett for a thorough kicking:
A good conman needs three key attributes to succeed: swagger, plausibility and commitment to the perpetuation of the con. A great conman, meanwhile, needs one additional factor: the discovery and nurturing of victims who are not only willing to be gulled but who come to actively enjoy that sensation.
Samuel Beckett was one of the twentieth century’s very greatest conmen and even now, decades after his death, his dupes continue to relish being parted from their cash.
That he was plausible in his claims is clear from the fact that his plays are still performed all around the world. His swagger may be witnessed in the endless succession of black and white photographs which accompany most editions of his work: the old fraud gazing grimly out at the reader from his home in France, like some weathered statue come dolefully to life, looking as though he is considering the fundamental inequities of existence or, perhaps, rumours of a forthcoming croissant shortage.
As for his commitment to the long con, he had form. In 1930, he gave a lecture at Trinity College, Dublin, about a poet (Jean du Chas) and an artistic movement (Le Concentrisme) which he had entirely invented, both fooling and riling up the dons. He learnt well from this, one suspects, never again to allow the mask to slip.
Following his early, glumly unreadable novels, much indebted to James Joyce, the real foundation of Beckett’s reputation is his 1953 play Waiting for Godot. The set-up is vivid and intriguing: in a rural wasteland sit two ravaged, witty tramps, Vladimir and Estragon, who trade barbs and banter while waiting for the arrival of a third individual who, we soon suspect, will never show up. And then, of course, nothing of any consequence happens.
Two additional characters wander on and off stage. The tramps talk and bicker some more. Godot never puts in an appearance. As one of the characters remarks: “Nothing happens. Nobody comes, nobody goes. It’s awful.”
There is no progression or change in the characters, no shift in their situation. Any clear-eyed audience member who has gone into the theatre meaning to judge the thing in as objective a fashion as possible will soon find themselves restless, then bored, then on the cusp of feigning some sort of medical emergency simply to get out of the stalls without causing too much of a fuss.
At this, avid Beckettians are no doubt sprawling on their chaise longues, sucking ferociously on a Gauloise and muttering to themselves that this lack of narrative progression, this absence of change, is the very crux of old Sam’s oeuvre. Confronted with the horrors of the twentieth-century, they say, pointlessness and circularity are the only things which make sense. Laughter in the ruins is all that’s left.
July 9, 2021
Alexander Larman on George MacDonald Fraser’s Flashman novels
I happened upon a copy of the first Flashman in my teens and was totally taken in by the assertion that the book was about “a real historical figure involved in most of the Victorian era’s most notorious episodes and that his papers were discovered during a sale of household furniture at Ashby, Leicestershire in 1965.” I’d watched the TV adaptation of Tom Brown’s Schooldays, so I had some awareness about the character Flashman, which only helped keep the cover story going for me. I absolutely loved the book and while it eventually became clear that it was fiction, I haunted the bookshops for years afterwards searching for more from Fraser. In The Critic, Alexander Larman looks at the author and his works — which almost certainly could never have been published in this neo-Victorian age:
When Flashy first entered the scene in bestselling form in 1969, there was confusion as to whether the tales were fanciful fiction or eyebrow-raising fact. This was due to MacDonald Fraser’s straight-faced claim that his protagonist was a real historical figure involved in most of the Victorian era’s most notorious episodes and that his papers were discovered during a sale of household furniture at Ashby, Leicestershire in 1965.
MacDonald Fraser presented himself as an impartial editor. He wrote, “I have no reason to doubt that it is a completely truthful account; where Flashman touches on historical fact he is almost invariably accurate, and readers can judge whether he is to be believed or not on more personal matters.”
The subterfuge succeeded. A third of the initial reviews treated it as a serious work of non-fiction, rather than a brilliantly conceived and superbly written counter-factual piece.
Not bad for the continued exploits of a minor character in the sanctimonious Victorian novel Tom Brown’s Schooldays, whose major achievement is to bully the protagonist and his friend Harry “Scud” East, before being expelled for drunkenness. It set its creator on a hugely lucrative path, and established him as one of the great comic novelists of his day.
MacDonald Fraser was a contradictory figure. A patriotic right-winger who had a deep respect for other cultures and peoples; one of Hollywood’s most in-demand screenwriters who happily lived on the Isle of Man in a self-conscious recreation of “the good old days”; a fully paid-up reactionary who wished to reintroduce corporal and capital punishment, but who loathed British incursions abroad.
Above all, he despised cant and hypocrisy. He described Tony Blair as “not just the worst prime minister we’ve ever had, but by far the worst prime minister we’ve ever had” and angrily added, “it makes my blood boil to think of the British soldiers who’ve died for that little liar.”
Christopher Hitchens, who may not have agreed with his views on foreign expeditions, but knew a thing or two about the value of being able to hold one’s drink, was a friend of MacDonald Fraser’s. When Hitchens telephoned him on his eightieth birthday to offer his regards, he was stoutly informed that he shared the company of “Charlemagne, Casanova, Hans Christian Andersen and Kenneth Tynan” on that date.
Their politics may have differed — Christopher acknowledged MacDonald Fraser’s “robust Toryism” — but Hitchens respected the older writer’s enduring affection for his Zulu, Sikh and Afghan characters, as well as the dutiful admiration he showed towards both American culture and its presidents.
July 5, 2021
General George H. Thomas (1816-1870)
One of the references for the latest Atun-Shei Films “Checkmate Lincolnites!” video was an older article in the Smithsonian Magazine outlining the career of one of the best — yet least known — Union generals in the American Civil War:
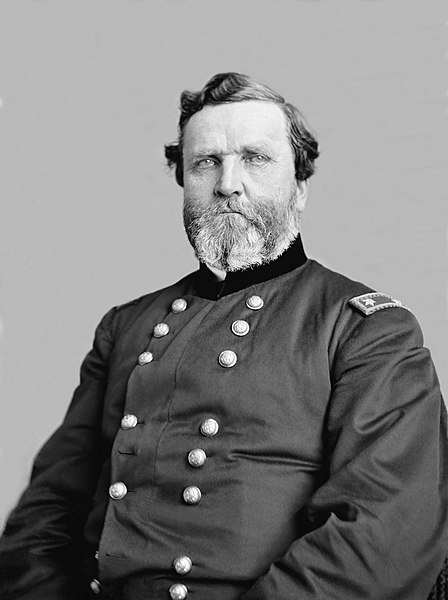

George Henry Thomas (July 31, 1816 – March 28, 1870), the “Rock of Chickamauga”, was a career U.S. Army officer and a Union general during the American Civil War, one of the principal commanders in the Western Theatre.
Image from the Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division via Wikimedia Commons.
… for Thomas, every battlefield success seemed to stir controversy or the jealousy of ambitious rivals. Unlike other noted generals, he had no home-state politicians to lobby on his behalf in Washington. Ulysses S. Grant, for example, was championed by Illinois congressman Elihu Washburne, and Sherman by his brother, Ohio senator John Sherman. For Thomas, every step upward depended solely on his performance in the field.
In one of the war’s first skirmishes, he led a brigade in the Shenandoah Valley that bested Confederates under Stonewall Jackson. When the dashing Rebel J.E.B. Stuart heard that Thomas was commanding Union cavalry, he wrote to his wife that “I would like to hang him as a traitor to his native state.” Even after that, there was lingering doubt among some Unionists, including Lincoln. Unlike Grant, Sherman, George McClellan and some other ranking Union officers who had broken their military service with years as civilians, Thomas had been a soldier since the day he entered West Point. Yet when his name came up for promotion, the president, restrained by Northern radicals and surrounded in the Federal bureaucracy by Southerners, said, “let the Virginian wait.” But Sherman among others vouched for Thomas, and soon the Virginian was elevated to brigadier general and ordered to organize troops away from Virginia, beyond the Appalachians.
[…]
As Thomas rose, he proved to his men that his addiction to detail and his insistence on preparation saved lives and won battles. His generalship behind the front, before the battle, was generations ahead of his peers. He organized a professional headquarters that made other generals’ staff work seem haphazard. His mess and hospital services, his maps and his scouting network were all models of efficiency; he was never surprised as Grant had been at Shiloh. He anticipated modern warfare with his emphasis on logistics, rapidly repairing his railroad supply lines and teaching his soldiers that a battle could turn on the broken linchpin of a cannon. He demanded by-the-book discipline, but taught it by example. He made no ringing pronouncements to the press. His troops came to understand his fatherly concern for their welfare, and when they met the enemy they had faith in his orders.
In late summer, Rosecrans moved against the Rebel stronghold of Chattanooga, a crucial gateway between the eastern and western theaters of war. Confederate general Bragg pulled out of the town onto the dominating nearby mountains, waiting for Maj. Gen. James Longstreet to bring reinforcements from Virginia. When they came, Bragg threw everything into an assault on Union lines along Chickamauga Creek, just inside Georgia. Thomas’ corps was dug in on the Union left. On the second day of furious fighting, a misunderstood order opened a wide gap on his right. Longstreet’s Rebels crashed through; with the always aggressive John Bell Hood’s division leading, they bent the Union line into a horseshoe.
Rosecrans, certain the battle was lost, retreated into Chattanooga with five other generals and thousands of blue-uniformed soldiers. But Thomas inspired his men to stand fast, and only their determined resistance saved his army from destruction. They held all that afternoon against repeated Confederate assaults, withdrawing into Chattanooga after nightfall. It was the greatest of all battles in the West, and since that day, Thomas has been known to history as the Rock of Chickamauga.
[…]
On December 15, Thomas, unaware that Grant intended to fire him, roared out of his works against Hood. In two days his troops crushed the Rebel army. His infantry, including two brigades of U.S. Colored Troops, smashed into Hood’s troops while the Union cavalry, dismounted with its fast-firing Spencers, curled around and behind the Rebel left. Almost a century later, historian Bruce Catton summed up the battle in two words: “Everything worked.”
Thomas “comes down in history…as the great defensive fighter, the man who could never be driven away but who was not much on the offensive. That may be a correct appraisal,” wrote Catton, an admirer and biographer of Grant. “Yet it may also be worth making note that just twice in all the war was a major Confederate army driven away from a prepared position in complete rout — at Chattanooga and at Nashville. Each time the blow that finally routed it was launched by Thomas.”
Nashville was the only engagement in which one army virtually annihilated another. Thomas B. Buell, a student of Civil War generalship, wrote that in Tennessee, Thomas performed the war’s “unsurpassed masterpiece of theater command and control….So modern in concept, so sweeping in scope, it would become a model for strategic maneuver in 20th-century warfare.” After it, there was no more large-scale fighting west of the Blue Ridge.
QotD: Robert Walpole, the first Prime Minister
This month marks exactly 300 years since the Whig statesman Robert Walpole officially became our first prime minister. Not only was the country squire and landowner the first politician to occupy 10 Downing Street, he has also served the longest time at the top: an unbroken 20-year reign dubbed the “Robinocracy”.
Most historians rate Walpole as one of our more successful prime ministers: he stabilised the nation’s finances, saw off Jacobite sedition, and kept the country out of foreign wars, proudly boasting: “There are 50,000 slain in Europe this year and not one Englishman.” But inevitably, there was a downside to Walpole: he was charged by his enemies with corruption.
In fact, considering the spectacular eighteenth-century standards of sleaze, Walpole was — to borrow a phrase coined by Tony Blair — “a pretty straight kind of guy”. True, he spent six months in the Tower of London accused by his political foes of all sorts of malpractice; but he was eventually cleared. True, too, that he built a magnificent mansion, Houghton Hall, in his native Norfolk — but he had legitimately made a fortune in the South Sea Bubble financial crash that ruined so many others (by buying shares when they were low and selling them when they were high). Nevertheless, Walpole was not above sailing close to the wind of propriety, cynically remarking: “Every man has his price.”
Nigel Jones, “Scandal, corruption and collusion: 300 years of British prime ministers”, The Critic, 2021-04-03.
June 24, 2021
The Founder | Based on a True Story
The Cynical Historian
Published 27 Jul 2017This one is a contender for best historical film of 2016. The Founder is an amazing movie about the beginning of the McDonald’s food chain. Seriously, more films should take cues from this.
————————————————————
references:
http://www.historyvshollywood.com/ree…http://time.com/money/4602541/the-fou…
http://content.time.com/time/magazine…
https://www.bustle.com/p/how-accurate…
https://www.washingtonpost.com/entert…
https://www.theatlantic.com/entertain…
https://www.nytimes.com/2016/05/20/bu…
http://www.abc.net.au/news/2016-11-24…
http://www.cbsnews.com/news/the-real-…
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ray_Kroc
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Richard…
————————————————————
contribute to my Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/CynicalHistorianLET’S CONNECT:
https://twitter.com/Cynical_History
————————————————————
Wiki:
The Founder is a 2016 American biographical drama film directed by John Lee Hancock and written by Robert Siegel. The film stars Michael Keaton as businessman Ray Kroc, and portrays the story of his creation of the McDonald’s fast food chain. Nick Offerman and John Carroll Lynch co-star as McDonald’s founders Richard and Maurice McDonald.The film premiered at Arclight Hollywood on December 7, 2016 and was released in the United States on January 20, 2017, by The Weinstein Company. It grossed $23 million worldwide and received generally positive reviews from critics, with praise for Keaton’s performance.
————————————————————
Hashtags: #History #TheFounder #McDonalds #Review #BasedOnATrueStory #RayKroc
June 21, 2021
QotD: The young Richard Nixon
As a schoolboy he hadn’t a single close friend, preferring to cloister himself up in the former church’s bell tower, reading, hating to ride the school bus because he thought the other children smelled bad. At Whittier, a fine Quaker college of regional reputation unknown anywhere else, he embarked upon what might have been his most humiliating job of all: learning to be a backslapping hail-fellow-well-met. (“I had the impression he would even practice his inflection when he said ‘hello'”, a reporter later observed.) The seventeen-year-old blossomed when he realized himself no longer alone in his outsiderdom: the student body was run, socially, by a circle of swells who called themselves the Franklins, and the remainder of the student body, a historian noted, “seemed resigned to its exclusion.” So this most unfraternal of youth organized the remnant into a fraternity of his own. Franklins were well-rounded, graceful, moved smoothly, talked slickly. Nixon’s new club, the Orthogonians, was for the strivers, those not to the manner born, the commuter students like him. He persuaded his fellows that reveling in one’s unpolish was a nobility of its own. Franklins were never photographed save in black tie. Orthogonians wore shirtsleeves. “Beans, brains, and brawn” was their motto. He told them *orthogonian* — basically, “at right angles” — meant “upright,” “straight shooter.” Also, their enemies might have added, all elbows.
The Orthogonians’ base was among Whittier’s athletes. On the surface, jocks seem natural Franklins, the Big Men on Campus. But Nixon always had a gift for looking under social surfaces to see and exploit the subterranean truths that roiled underneath. It was an eminently Nixonian insight: that on every sports team there are only a couple of stars, and that if you want to win the loyalty of the team for yourself, the surest, if least glamorous, strategy is to concentrate on the nonspectacular — silent — majority. The ones who labor quietly, sometimes resentfully, in the quarterback’s shadow: the linemen, the guards, the punter. Nixon himself was exemplarily nonspectacular: the 150-pounder was the team’s tackle dummy, kept on squad by a loving, tough, and fatherly coach who appreciated Nixon’s unceasing grit and team spirit — nursing hurt players, cheering on the listless, even organizing his own team dinners, entertaining the guests on the piano, perhaps favoring them with the Orthogonian theme song. It was his own composition.
Nixon beat a Franklin for student body president. Looking back later, acquaintances marveled at the feat of this awkward, skinny kid the yearbook called “a rather quiet chap about campus,” dour and brooding, who couldn’t even win a girlfriend, who attracted enemies, who seemed, a schoolmate recalled, “the man least likely to succeed in politics.” They hadn’t learned what Nixon was learning. Being hated by the right people was no impediment to political success. The unpolished, after all, were everywhere in the majority.
Rick Perlstein, Nixonland: The Rise of a President and the Fracturing of America, 2008.
June 17, 2021
Encouraging innovation by … rejigging the honours system
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes considers how one man’s efforts to encourage and reward innovation in the United Kingdom eventually led to “mere inventors” receiving honours that once were dedicated to military paladins and political giants:
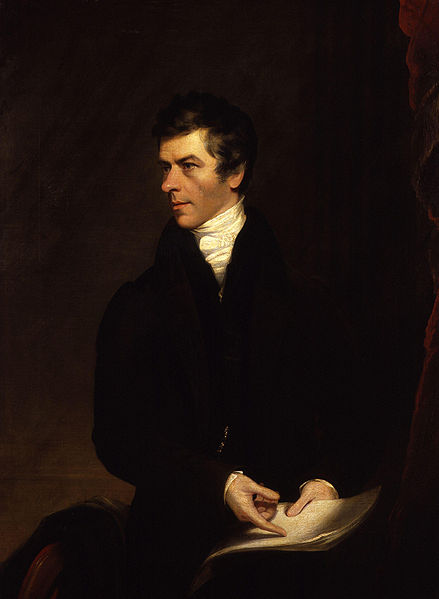

Henry Brougham, 1st Baron Brougham and Vaux, by James Lonsdale (died 1839), given to the National Portrait Gallery, London in 1873.
Image from the National Portrait Gallery via Wikimedia Commons.
One of my all-time favourite innovation evangelists is the nineteenth-century barrister, journalist, and politician Henry Brougham. He was an innovator himself, in the late 1830s designing a form of horse-drawn carriage, and as a teenager even managed to get his experiments on light published in the Royal Society’s prestigious Transactions. But his main achievements were as an organiser. Clever, dashing, and articulate, the son of minor gentry, he was an evangelist extraordinaire. In the 1820s he helped George Birkbeck to found the London Mechanics’ Institute (which survives today as Birkbeck, University of London), was instrumental in the creation of University College London (to provide a university in England where you didn’t have to swear an oath to the Church of England), and founded the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (to print reference works and textbooks cheaply and in bulk). They were all organisations intended to widen access to education, spreading science to the masses.
He also presided at the opening of many more worker-run mechanics’ institutions, libraries, and scientific societies. As a Member of Parliament who went out of his way to support workers’ efforts at self-education, even though none of them could vote, Brougham thus became something of a celebrity to working-class inventors. John Condie, born in Gorbals, Glasgow, to poor parents, and apprenticed to a cabinet maker, would become a prolific and successful improver of iron-making, locomotive springs, and photography, as well as an inspiring lecturer on scientific subjects in his own right — his students at the Eaglesham Mechanics’ Institution were reportedly so engrossed that they would attend his evening classes until midnight. Having once exhibited a model steam engine at the opening of the Carlisle Mechanics’ Institution, however, Condie was reportedly “not a little proud” that Brougham — who had presided at the opening — recalled the model over thirty years later. The detail comes from Condie’s obituary notice in the local papers; I like to think that it was a story upon which he frequently dined out.
Brougham’s celebrity, I suspect, made him appreciate the usefulness of status and prestige, and his influence only grew when in 1830 he was made a lord and appointed Lord High Chancellor — a high-ranking ministerial position, which he held for four years. Brougham was soon behind many efforts to increase the visibility of inventive role-models. The nineteenth-century mania for putting up statues — to people like Johannes Gutenberg, Isaac Newton, and James Watt — often had Brougham or his political allies behind them. Brougham even hoped that while the “temples of the pagans had been adorned by statues of warriors, who had dealt desolation … ours shall be graced with the statues of those who have contributed to the triumph of humanity and science”.
His hero-making extended to print, too, when in the 1840s his Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge embarked on publishing a comprehensive biographical dictionary — an early forerunner to the Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, but with the extraordinary aim of covering notable individuals from all over the world. It managed to print seven volumes covering the letter “A” before financial considerations forced the whole society to cease, but in 1845 Brougham published Lives of Men of Letters and Science who Flourished in the Time of George III, in which he showcased a handful of eighteenth-century literati and scientists from whom readers were to draw inspiration.
And Brougham tried to raise the status of inventors who were still living. This was done by co-opting a Hanoverian order of chivalry, the Royal Guelphic Order (by this stage the kings of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland were also simultaneously the kings of Hanover). The order was generally used to recognise soldiers, but an interesting precedent had been set when the astronomer Frederick William Herschel, the discoverer of Uranus, had been made a knight of the order in 1816. So when Brougham rose to power in the 1830s, he envisaged using it more widely, to recognise inventors, scientists, and medical pioneers, as well as literary scholars like museum curators, archivists, antiquarians, historians, heralds, and linguists. Thanks to Brougham’s machinations, the knighthood of the order was offered to the mathematician James Ivory, the scientist and inventor David Brewster, and the neurologist Charles Bell (after whom Bell’s Palsy is named). It was later also awarded to serial inventors like John Robison, who improved the accuracy of metal screws, experimented with cast iron canal locks and the water resistance of boats, and applied pneumatic presses to cheesemaking.
One problem, however, was that the Royal Guelphic Order was considered second-rate. It was technically a foreign order, and did not actually entitle one to be called “Sir” in the UK. The mathematician and computing pioneer Charles Babbage was apparently insulted to have been fobbed off with the offer of a Guelphic knighthood instead of a British one. Although William Herschel had accidentally been called “Sir” during his lifetime, this was soon realised to be a mistake in protocol. When his son John — a scientific pioneer in his own right — was also made a knight of the order, he was also quietly knighted normally a few days later so that the rest of the family would be none the wiser. And regardless, the whole scheme came to an end with the accession of Queen Victoria in 1837 — as a woman, she did not inherit the throne of Hanover, and so appointments to the Guelphic order simply passed out of British control.
June 16, 2021
QotD: The Shah of Iran
The Shah that emerges from these pages would be almost a tragic figure, if they gave us a better feel for him as a person, that is to say as a living being rather than a mere policy-maker. He was by nature a vacillator, thrust by inheritance and a destiny beyond his control into a position in which vacillation would eventually prove fatal. In addition to self-doubt, however, he was also inclined to vainglory, oscillating between the two, retreating from crises and ostentatiously parading himself, and boasting, when things seemed to be going well. He thought that he had both the right and the duty, genuinely for the sake of his country, to rule rather than reign, but while he had the ideas of an autocrat, he also had those of an ordinary decent person who baulked at the shedding of much blood, the only way, in the end, that he could have preserved his throne (and possibly not even then).
He was intelligent and wily, and his achievements were not negligible. He managed to wrest control of Iran’s oil first from the British and then from the international oil consortium that succeeded them. He played the oil market with great skill. He instituted an important land reform that genuinely benefitted the peasantry, expanded education, and had a full understanding of the importance of technology in the modernization of Iran necessary if it were to be anything other than a dependent state. His foreign policy was flexible, pragmatic, and shrewd. He needed the Americans but did not trust them (or anybody else, for that matter), realising that in politics there were no friendships, only common interests. This was to be borne out in the most terrible and tragic way during his last few years of exile, with which this book does not deal. Where there is no friendship, there is no gratitude for services rendered.
His failures were at least as great as his successes, and in the end more important from the point of view of his personal destiny. He so hollowed out political life in Iran, in order to exercise power as a true autocrat, that it came to have two poles: sycophancy and plotting against him. Sycophancy is a terribly addictive drug, no doubt a permanent temptation of the powerful (and therefore a good reason to restrict political terms of office); you can never have enough of it, nor can it ever be outrageous enough.
Unfortunately for the Shah, no one is sycophantic from principle, indeed sycophants tend (rightly) to despise themselves, fully aware that they are acting from the most naked of self-interest. There is no rat that leaves a sinking ship faster than a sycophant deserting a lost cause. A sycophant will take a risk to preserve his skin, but not to preserve his master.
Theodore Dalrymple, “Downfall of the House of Pahlavi”, The Iconoclast, 2021-03-03.