Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 13 Mar 2024Absolutely fantastic tomato and meat sauce served over spaghetti tossed with butter and parmesan
City/Region: Cleveland, Ohio
Time Period: 1930sChef Boyardee was not born in Cleveland (sorry, 30 Rock), but in Borganovo, just outside of Piacenza in Italy. And his name was not Hector Boyardee, but Ettore Boiardi (boy-AR-dee). He opened an Italian restaurant in Cleveland in 1924, where the food was so popular that he frequently sent patrons home with bottles of his spaghetti sauce.
We can’t know exactly what that original sauce was, but this is from a family recipe and is probably pretty close. And it’s phenomenal. It’s fairly simple, but so good. You get a lot of the fresh basil, and the creaminess from mixing the butter and parmesan directly with the pasta is delicious. I don’t often make dishes from the show again, but I can see myself making this any day of the week.
(more…)
June 23, 2024
The Original Chef Boyardee Spaghetti Dinner
QotD: Shoes
Mismatched shoes are also nicely subversive. There is somewhere in the clothing code a notion that holds over from the Elizabethan era that says a person’s shoes must show that they are in the Elizabethan lingo, unconcussable. Shoes, especially the shoes of the male and the young, are meant to show that the wearer is, all apologies, grounded. (High heel shoes take their semotic precisely from the way they break this rule. The wearer, a female, demonstrates her vulnerability, her fragility, her elegance, her powers of evocation by showing herself not at all grounded.)
Grant McCracken, “Cotton, Converse and co-creation”, This Blog Sits at the, 2005-07-27.
June 22, 2024
The End of Everything
In First Things, Francis X. Maier reviews Victor Davis Hanson’s recent work The End of Everything: How Wars Descend into Annihilation:
A senior fellow in military history and classics at Stanford University’s Hoover Institution, Hanson is a specialist on the human dimension and costs of war. His focus in The End of Everything is, as usual, on the past; specifically, the destruction of four great civilizations: ancient Thebes, Carthage, Constantinople, and the Aztec Empire. In each case, an otherwise enduring civilization was not merely conquered, but “annihilated” — in other words, completely erased and replaced. How such catastrophes could happen is the substance of Hanson’s book. And the lessons therein are worth noting.
In every case, the defeated suffered from fatal delusions. Each civilization overestimated its own strength or skill; each misread the willingness of allies to support it; and each underestimated the determination, strength, and ferocity of its enemy.
Thebes had a superb military heritage, but the Thebans’ tactics were outdated and their leadership no match for Macedon’s Alexander the Great. The city was razed and its surviving population scattered. Carthage — a thriving commercial center of 500,000 even after two military defeats by Rome — misread the greed, jealousy, and hatred of Rome, and Roman willingness to violate its own favorable treaty terms to extinguish its former enemy. The long Roman siege of the Third Punic War saw the killing or starvation of 450,000 Carthaginians, the survivors sold into slavery, the city leveled, and the land rendered uninhabitable for a century.
The Byzantine Empire, Rome’s successor in the East, survived for a millennium on superior military technology, genius diplomacy, impregnable fortifications, and confidence in the protection of heaven. By 1453, a shrunken and sclerotic Byzantine state could rely on none of these advantages, nor on any real help from the Christian West. But it nonetheless clung to a belief in the mantle of heaven and its own ability to withstand a determined Ottoman siege. The result was not merely defeat, but the erasure of any significant Greek and Christian presence in Constantinople. As for the Aztecs, they fatally misread Spanish intentions, ruthlessness, and duplicity, as well as the hatred of their conquered “allies” who switched sides and fought alongside the conquistadors.
The industrial-scale nature of human sacrifice and sacred cannibalism practiced by the Aztecs — more than 20,000 captives were ritually butchered each year — horrified the Spanish. It reinforced their fury and worked to justify their own ferocious violence, just as the Carthaginian practice of infant sacrifice had enraged the Romans. In the end, despite the seemingly massive strength of Aztec armies, a small group of Spanish adventurers utterly destroyed Tenochtitlán, the beautiful and architecturally elaborate Aztec capital, and wiped out an entire culture.
History never repeats itself, but patterns of human thought and behavior repeat themselves all the time. We humans are capable of astonishing acts of virtue, unselfish service, and heroism. We’re also capable of obscene, unimaginable violence. Anyone doubting the latter need only check the record of the last century. Or last year’s October 7 savagery, courtesy of Hamas.
The takeaway from Hanson’s book might be summarized in passages like this one:
Modern civilization faces a toxic paradox. The more that technologically advanced mankind develops the ability to wipe out wartime enemies, the more it develops a postmodern conceit that total war is an obsolete exercise, [assuming, mistakenly] that disagreements among civilized people will always be arbitrated by the cooler, more sophisticated, and more diplomatically minded. The same hubris that posits that complex tools of mass destruction can be created but never used, also fuels the fatal vanity that war itself is an anachronism and no longer an existential concern—at least in comparison to the supposedly greater threats of naturally occurring pandemics, meteoric impacts, man-made climate change, or overpopulation.
Or this one:
The gullibility, and indeed ignorance, of contemporary governments and leaders about the intent, hatred, ruthlessness, and capability of their enemies are not surprising. The retreat to comfortable nonchalance and credulousness, often the cargo of affluence and leisure, is predictable given unchanging human nature, despite the pretensions of a postmodern technologically advanced global village.
I suppose the lesson is this: There’s nothing sacred about the Pax Americana. Nothing guarantees its survival, legitimacy, comforts, power, or wealth. A sardonic observer like the Roman poet Juvenal — were he alive — might even observe that today’s America seems less like the “city on a hill” of Scripture, and more like a Carthaginian tophet, or the ritual site of child sacrifice. Of course, that would be unfair. A biblical leaven remains in the American experiment, and many good people still believe in its best ideals.
The Curious Case of Hitler’s Corpse – War Against Humanity 136
World War Two
Published 21 Jun 2024Joseph Stalin claims that Adolf Hitler managed to escape Berlin and is now living somewhere in hiding. It’s complete nonsense of course. But it raises some interesting questions. What remains do we have of Hitler? How do we know they belong to the Fuhrer? And, why is Stalin spreading these far-fetched lies?
(more…)
“We can learn a lot about our betters from looking at each exception to their rules”
Julie Burchill isn’t a soccer fan, but she points out that the “exceptions” to the usual “rules” that the kakistocrats allow during international soccer tournaments tell us a lot about them:
Patriotism is not the only “bad” thing we’re suddenly “allowed” to do in the weeks when the national team plays on the world stage. The BBC in particular reminds men that they can disregard the finger-wagging for a few brief weeks. In EastEnders, male characters cringingly ask their mates to “get the beers in for the game”. Alcohol would generally be condemned as a public-health menace by Auntie, but during “The Game”, one more “cheeky” tipple apparently won’t hurt you.
We can learn a lot about our betters from looking at each exception to their rules. Don’t be racist – except against Jews. Believe all women about sexual assault – unless they’re Israeli. Oh, and be careful not to “culturally appropriate” the slightest thing from any other nationality, even to the point of never wearing a sombrero in a Mexican restaurant – but it’s fine to be a cross-dressing man culturally appropriating my sex. Meanwhile, if you’re a woman, be a good little Transmaid and stand by smiling, even if you call yourself a feminist.
Like most other places in the West in these dog days of civilisation, England feels like a nation devoid of hope and pride. Even so, being allowed to take pride in some overpaid ball-kickers, but not in the fact that this country contributed massively to ending slavery – lest we be called out as White Saviours – is a somewhat surreal situation to find ourselves in, after all those centuries of blood, sweat and struggle.
Flying the flag for the duration of the Euros is like being a eunuch who’s permitted to have his nuts back for a couple of weeks – for old times’ sake – and wear them as earrings. But those who indulge must be sure to tear their St George’s down sharpish once the festivities are over, lest they be fingered as a fascist for liking their own flag more than others. Remember, the only flag that can be flown constantly now is the Pride flag. This must be saluted respectfully wherever it pops up – failure to do so may identify you as an unworthy citizen of Soft Play Pit Nation.
Why and when did the Romans start wearing different clothing and armor?
Maiorianus
Published Mar 5, 2024
QotD: The rise of post-modernism
Culture, like politics, is not immune to these billowing waves of combat. And we can look to the past to see that cultural repercussions usually follow from battles. The catalysts for modernism were Verdun, the Somme, and the general carnage of the First World War trenches. Out of those infernos spread the belief that the old foundations of staid manners, traditional genres of art and literature, unquestioning patriotism — dulce et decorum est pro patria moria — and national politics had somehow led to Europe’s millions being gassed and blown apart for years in the mud of the French countryside without either victory or defeat.
Perhaps the present brand of postmodernism was born primarily in France as well. After the humiliating drive of the Panzers through the Ardennes in May, 1940, the collapse of Europe’s largest army in six weeks, and the rescue by the Americans and the British in August, 1944, theories were easier to accept than facts. For a few elite but stunned postwar Frenchmen, fiction was more palatable than reality, text and discourse a refuge from a truth as unacceptable as it was bothersome.
Victor Davis Hanson, Ripples of Battle, 2003.
June 21, 2024
From “invention” to “tradition”
At Astral Codex Ten, Scott Alexander considers some “traditions” which were clearly invented much more recently than participants might believe:

Two NYC synagogues, one in Moorish Revival style and the other is some form of modernism (you can tell it’s not Brutalism because it’s not all decaying concrete). Like Scott, I vastly prefer the one on the left even if it isn’t totally faithful to the Moroccan original design.
A: I like Indian food.
B: Oh, so you like a few bites of flavorless rice daily? Because India is a very poor country, and that’s a more realistic depiction of what the average Indian person eats. And India has poor food safety laws – do you like eating in unsanitary restaurants full of rats? And are you condoning Narendra Modi’s fascist policies?
A: I just like paneer tikka.
This is how most arguments about being “trad” sound to me. Someone points out that they like some feature of the past. Then other people object that this feature is idealized, the past wasn’t universally like that, and the past had many other bad things.
But “of the past” is just meant to be a pointer! “Indian food” is a good pointer to paneer tikka even if it’s an idealized view of how Indians actually eat, even if India has lots of other problems!
In the same way, when people say they like Moorish Revival architecture or the 1950s family structure or whatever, I think of these as pointers. It’s fine if the Moors also had some bad buildings, or not all 1950s families were really like that. Everyone knows what they mean!
But there’s another anti-tradition argument which goes deeper than this. It’s something like “ah, but you’re a hypocrite, because the people of the past weren’t trying to return to some idealized history. They just did what made sense in their present environment.”
There were hints of this in Sam Kriss’ otherwise-excellent article about a fertility festival in Hastings, England. A celebrant dressed up as a green agricultural deity figure, paraded through the street, and then got ritually murdered. Then everyone drank and partied and had a good time.
Most of the people involved assumed it derived from the Druids or something. It was popular not just as a good party, but because it felt like a connection to primeval days of magic and mystery. But actually, the Hastings festival dates from 1983. If you really stretch things, it’s loosely based on similar rituals from the 1790s. There’s no connection to anything older than that.
Kriss wrote:
I don’t think the Jack in the Green is worse because it’s not really an ancient fertility rite, but I do think it’s a little worse because it pretends to be … tradition pretends to be a respect for the past, but it refuses to let the past inhabit its own particular time: it turns the past into eternity. The opposite of tradition is invention.
Tradition is fake, and invention is real. Most of the human activity of the past consists of people just doing stuff … they didn’t need a reason. It didn’t need to be part of anything ancient. They were having fun.
I’ve been thinking a lot about [a seagull float in the Hastings parade] … in the procession, the shape of the seagull became totemic. It had the intensity of a symbol, without needing to symbolise anything in particular. Another word for a symbol that burns through any referent is a god. I wasn’t kidding when I said I felt the faint urge to worship it. I don’t think it would be any more meaningful if someone had dug up some thousand-year-old seagull fetishes from a nearby field. It’s powerful simply because of what it is. Invention, just doing stuff, is the nebula that nurses newborn gods.
I’m nervous to ever disagree with Sam Kriss about ancient history, but this strikes me as totally false.
Modern traditionalists look back fondly on Victorian times. But the Victorians didn’t get their culture by just doing stuff without ever thinking of the past. They were writing pseudo-Arthurian poetry, building neo-Gothic palaces, and painting pre-Raphaelite art hearkening back to the early Renaissance. And the Renaissance itself was based on the idea of a re-naissance of Greco-Roman culture. And the Roman Empire at its peak spent half of its cultural energy obsessing over restoring the virtue of the ancient days of the Roman Republic:
Then none was for a party;
Then all were for the state;
Then the great man helped the poor,
And the poor man loved the great:
Then lands were fairly portioned;
Then spoils were fairly sold:
The Romans were like brothers
In the brave days of old.Now Roman is to Roman
More hateful than a foe,
And the Tribunes beard the high,
And the Fathers grind the low.
As we wax hot in faction,
In battle we wax cold:
Wherefore men fight not as they fought
In the brave days of old.(of course, this isn’t from a real Imperial Roman poem — it’s by a Victorian Brit pretending to be a later Roman yearning for the grand old days of Republican Rome. And it’s still better than any poem of the last fifty years, fight me.)
As for the ancient Roman Republic, they spoke fondly of a Golden Age when they were ruled by the god Saturn. As far as anyone knows, Saturn is a wholly mythical figure. But if he did exist, there are good odds he inspired his people (supposedly the fauns and nymphs) through stories of some even Goldener Age that came before.
“Neoliberal ideology is antidemocratic at its very core. Its aim is to give free-reign over our societies to corporations, not citizens”
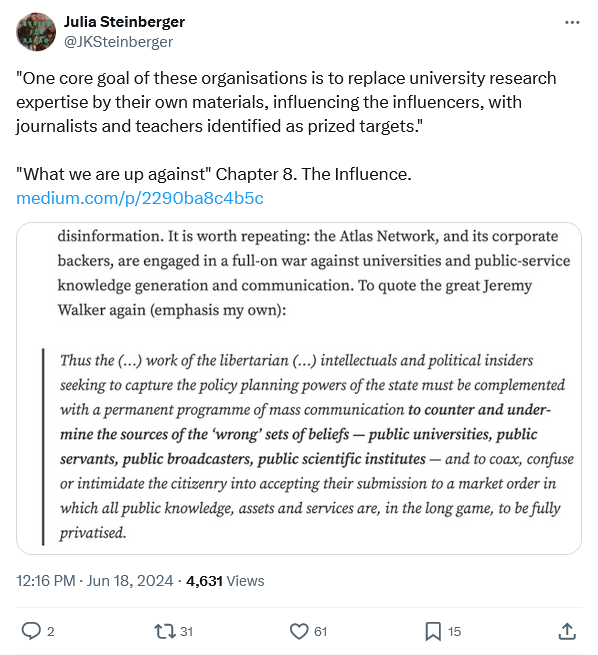
Tim Worstall responds to a recent Medium essay by Julia Steinberger which illustrates that “neoliberal” has joined “fascist” as a generic term to indicate strong disapproval of a person, organization, or idea:
The idea that an adult woman can believe these things is just amazeballs. But here we are. A tweet from Julia Steinberger leads to her Medium essay about what’s wrong with the world.
An upheaval in 10 chapters:
1. The cause. We know the climate crisis is brought to us by highly unequal and undemocratic economic systems.
Err, no? Emissions are emissions. 100 people emitting one tonne each is exactly the same as 1 person emitting 100 tonnes. Sure, it’s true that a more unequal society will have more people emitting those 100 tonne personal amounts. But a more equal society will have more people able to emit another 1 tonne each. For, more equality is by definition the movement of some of those assets of the richer to those poorer — the economic assets which either allow or do the emitting. Sure, Jim Ratcliffe’s £50,000 private jet flight emits more than my £100 Easyjet one. But if we take the £50k off Jim and give it to 500 folk like me then all 500 of us might spend the marginal income on an Easyjet flight each — which would be more emissions than Jim’s spending of the money.
It simply is not true that economic inequality is the heart, the core or the cause of climate change. It’s idiocy to think it is too.
Of course, we know what’s happening here. Climate Change is Bad, M’Kay? Which it is, obviously. Economic inequality is Bad, M’Kay? Well, there the evidence is a great deal more mixed but whatever. But in the minds of the stupid all bad things have the same cause. So, if inequality is bad, climate change is bad, then they must be the same thing because they’re Bad, M’Kay?
2. The rise. The recent history of these economic systems, in the Americas and Eurasia, is dominated by the ascendance of neoliberal ideology.
Oh, that is good. Given that I am a neoliberal — a fully paid up one, Senior Fellow at the Adam Smith Institute and all — that’s very good. Given HS2, looming wealth taxation, the increased bite of idiot regulation and all that I can’t say that I see neoliberalism as winning right now but that might depend upon your starting point. If you’re a socialist — or an idiot but I repeat myself — you might well regard the plenitude of bananas in the supermarket as neoliberal. After all, that is something that socialism never did achieve.
3. The threat. Neoliberal ideology is antidemocratic at its very core. Its aim is to give free-reign over our societies to corporations, not citizens.
And, well, you know, bollocks. The very beating heart of neoliberalism is that corporations need to be controlled and they’re best controlled by the citizens. In the form of free markets rather than voting on which bureaucrats get the gold plated pension, true. But neoliberals are between indifferent and actually against capitalist power. The whole nub of the idea is that markets do the job of controlling capitalists better than bureaucrats, politicians or, obviously, capitalists.
There’s not really any way for her thesis to survive after getting so much of the basics wrong, is there?
But just one more tidbit:
Hayek and his neoliberal colleagues now needed another, antidemocratic way, to organise society. They didn’t want democracy, but they wanted some kind of self-maintaining organisation — by which they meant hierarchy. Organisation was supposed to be supplied by the market, and hierarchy by competition within markets. (It’s worth noting that neoliberals in the 1950s did not, although they should have, predict that unfettered markets lead to concentrations in monopolies or cartels. They would arguably disapprove of the vast corporations running our current economies, even though their market-above-democracy policies predictably brought them into being.)
Well, that wasn’t actually the last tidbit. But the idea that Friedman, Mises, Menger, Hayek and the rest didn’t worry about monopolies? Jesu C is really bouncin’ on that pogo stick right now. And then the idea that democracy will be better bulwark against monopolies than markets? Can you actually do backflips on a pogo stick?
All Of The Saws One Video
Wood By Wright How To
Published Mar 7, 2024There are a lot of saws. we may call them all hand saws but there are many names and types of saws.
(more…)
June 20, 2024
The “Idiot Nephew Theory” of show business management
Ted Gioia recalls his hopes of getting into the entertainment industry after graduation:
The story of how I became a strategy consultant is shameful.
I was a student at Stanford’s Graduate School of Business, and needed a job after graduation. I wanted to work in the music or entertainment industries — but I soon learned this was an impossible dream.
They didn’t want me. And they didn’t want my classmates either.
Hundreds of companies came to our business school to recruit talent, and they included most of the leading US corporations. So I talked with everybody — Coca Cola, Morgan Stanley, Atari, Procter & Gamble, you name it.
But no record label or movie studio ever showed up. They didn’t even send job listings.
Can you guess why?
I asked around on campus and was told the following (off the record):
Come on, Ted. You will never see the entertainment business recruit here. Those folks are not looking for business talent.
They give the choice jobs to their family members — the idiot nephew gets hired, not an MBA. Even better if it’s an idiot son.
And if there are other openings? Well … You’ve heard about the casting couch, haven’t you? Let me give you a hint — that couch isn’t just for auditioning the cast.
But you wouldn’t want a job there even if they gave you one. When time comes for a promotion, the drooling idiot nephew moves up — not you.
I’ve never shared that story before — because I know how people inside the music business hate hearing it.
And maybe it’s not a fair story.
All I can say is that I found this advice very helpful. I stopped planning on a career in the music business. And I also developed a very useful theory to explain why record labels are so bad at making strategic decisions.
I call it the “Idiot Nephew Theory”:
THE IDIOT NEPHEW THEORY: Whenever a record label makes a strategic decision, it picks the option that the boss’s idiot nephew thinks is best.
And what does the idiot nephew decide? That’s easy — they always do whatever the company lawyer recommends.
Maybe this theory is wrong. All I can say is that it helps me predict events in the entertainment industry with a surprising degree of accuracy.
I always operate on the assumption that there’s no business strategy in the music or movie business — only legal maneuvering.
Years later, when the music business got totally reamed by tech companies — a phase we’re still living through, by the way — I wasn’t surprised in the least. The record labels respond to every new music technology by litigating, but whenever they encounter a company with more legal clout than them (Apple or Google/YouTube, for example), they simply gave up.
In the future, you can test this theory yourself. You will see that it possesses great explanatory power.
The birth of para-rescue
At The War Room, Dr. Robert Lyman discusses an air crash in 1943 and the innovative and daring rescue of the survivors using parachutes:
The birth of para-rescue can be placed in operations across the Hump airlift in 1942 and 1943. The story of the crash of Flight 12420 was a central part of the story.
The story itself is extraordinary. In 1943 a Soviet spy inside the predecessor organization to the CIA and a proud descendant of the famous Southern leader General Robert E Lee, on his way to China to meet General Dai Li, the mysterious and secretive Kuomintang intelligence chief; a celebrated American journalist sent by President Roosevelt to ascertain the “truth about China”; and General “Vinegar Joe” Stilwell’s political adviser; together with eighteen others — American and Chinese — survived a C46 air crash on the mountainous and remote border between India and Burma. It was, and remains, the largest evacuation of an aircraft by parachute, and, given the fact that even the crew had never been trained in the technique, it was a miracle that so many survived. But they fell with their crippled plane from the frying pan into the fire. On disentangling themselves from their parachutes, the twenty shocked survivors soon found that they had arrived in wild country dominated by a tribe that had an especial reason to hate white men. The Nagas of the Patkoi Hills on their remote and unsurveyed land were notorious headhunters, who continued — despite the feeble wrath of distant British imperial authority — to practice both slavery and human sacrifice. Their specialty was the removal of the heads of their enemies — often women and children — achieved with a swipe of ugly, razor-sharp daos. On two occasions in recent years their village, or parts of it, had been burned to the ground and their warriors killed in running battles with sepoys sent to teach the villagers a lesson and to exert the authority of the Raj.
Nevertheless, and against all the odds, all but one of the twenty-one passengers and crew on the doomed aircraft survived. The story of the extraordinary adventure of those men among the Nagas of Pangsha and of their rescue by the young representative of the distant imperial power, the British deputy commissioner who arrived wearing “Bombay bloomers” and stout leather walking shoes, carrying a bamboo cane, and leading an armed party of “friendly” Nagas, is told in my book Among the Headhunters. In their meeting in some of the world’s most inaccessible and previously unmapped terrain, three very different worlds collided. The young, exuberant apostles of the vast industrial democracy of the United States came face-to-face with members of an ancient mongoloid race, uncomprehending of the extent of modernity that existed beyond the remote hills in which they lived and determined to preserve their local power, based on ancient head-hunting and slaving prerogatives. Both groups met — not for the first time for the Nagas, whose village had been burned twice, in 1936 and 1939, because of persistent head-hunting — the vestiges of British authority in India, disintegrating as the Japanese tsunami washed up at its gate.
One of the reasons for the survival of the men whose aircraft fell to earth that tumultuous day was the quick thinking, rapid action and spontaneous sacrifice of a group of US servicemen at the airbase from whence the aircraft departed that morning, Chabua. One in particular needs calling out, thirty-six-year-old ATC wing surgeon Lieutenant Colonel Don Flickinger. He had been duty medical officer at Pearl Harbor during the Japanese attack on December 7, 1941 and in 1943 found himself stationed in the upper reaches of Assam as part of the mammoth Hump airlift to China.
On the day the C46 went down over the rugged Paktoi ranges, the dividing line between astern India and Burma in the first leg of the journey to China, a C47 sent up to see if it could find the wreckage, and found the survivors waving from a remote village high in the hills. Using ground signalling panels the C47 dropped to the survivors they indicated that at least one of the party was badly injured. When the C47 returned to Chabua with the news that survivors were seen in the sprawling village and its location pinpointed on the map, the British deputy commissioner gave the Americans the grave news that the men were likely to be in grave danger. The villagers were, unknown to the survivors, the most practised headhunters of the region, a powerful and unruly tribe who were notorious for their violence. It was unlikely that the men would survive the encounter.
“Surely the only way to defeat racism and homophobia is to treat ethnic and sexual minorities as incapable of high achievement and in need of a leg up from their betters?”
Andrew Doyle on a radical new approach to hiring that might just catch on:
With the inexorable spread of DEI – Diversity, Equity and Inclusion – across the western world, it’s refreshing to see at least one major company resist the decrees of this new religion. This is precisely what happened this week when Scale, an Artificial Intelligence company based in San Francisco, launched a new policy to ensure that its employees were hired on the basis of – wait for it – being the most talented and best qualified for the job.
This innovation, which sees race, gender and sexuality as irrelevant when it comes to hiring practices, should hardly be considered revolutionary. And yet in a world in which the content of one’s character is less important than the colour of one’s skin, to treat everyone equally irrespective of these immutable characteristics is suddenly deemed radical.
Scale’s CEO, Alexandr Wang, explained that rather than adopt DEI policies, the company would henceforth favour MEI, which stands for Merit, Excellence, and Intelligence. He explained the thinking behind the new scheme in a post on X.
There is a mistaken belief that meritocracy somehow conflicts with diversity. I strongly disagree. No group has a monopoly on excellence. A hiring process based on merit will naturally yield a variety of backgrounds, perspectives, and ideas. Achieving this requires casting a wide net for talent and then objectively selecting the best, without bias in any direction. We will not pick winners and losers based on someone being the “right” or “wrong” race, gender, and so on. It should be needless to say, and yet it needs saying: doing so would be racist and sexist, not to mention illegal. Upholding meritocracy is good for business and is the right thing to do.
One can already hear the likes of Robin DiAngelo and Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez screaming in fury at this blatant implementation of good old-fashioned liberal values. Surely the only way to defeat racism and homophobia is to treat ethnic and sexual minorities as incapable of high achievement and in need of a leg up from their betters?
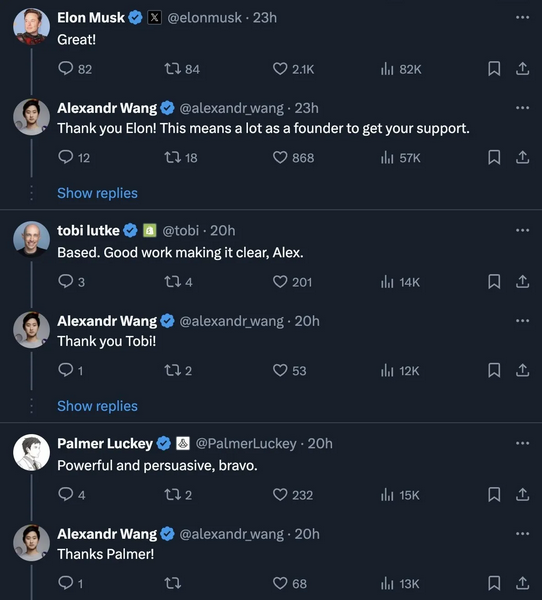
It is instructive to compare reactions from the Twittersphere (now X) and Instagram, as one X user has done. If nothing else, the comparison reveals how the divide in the culture war is playing out on social media since Elon Musk’s takeover. On X, major figures in the corporate world such as Tobias Lütke (CEO of Shopify), Palmer Luckey (founder of Oculus VR) and Musk himself have congratulated Wang on his new initiative.
By contrast, here are some of the responses on Instagram:
You’re ‘disrupting’ current hard-fought standards you don’t like, by reverting to a system rooted in bias and inequality that asks less of you as a hiring manager and as a leader
– Dan Couch (He/Him)Curious to see how hiring processes can effectively (and objectively) measure one’s ‘merit’, ‘excellence’, and ‘intelligence’, all of which are very subjective terms
– Cole Gawin (He/Him)What is merit and how do we measure it?
– Rio Cruz Morales (They/Them)This sounds a lot like excuse making for casting off DEI principles
– R.C. Rondero De Mosier (He/Him)The pronouns, of course, signify membership of the cult, and so we should not be surprised to see the sentiments of its minions mirroring each other so closely. What Wang is proposing of course builds equality into the hiring system and, contrary to these complaints, it is entirely possible to measure merit objectively. This, after all, is the entire point of academic assessment. The arguments against merit can only be sustained if one presupposes that systemic inequalities are ingrained within society, that all of these relate to the concept of group identity, and that adjustments have to be made accordingly to guarantee equality of outcome.