Forgotten Weapons
Published Jun 28, 2024Was the 1911 an emotional support totem or a viable combat weapon? Or both? American soldiers had a bit different take on handguns than soldiers of many other armies, and I think it stems from the American identity with the frontier — the Wild West was well within memory for many people when World War Two broke out. So today, let’s look at the American take on handguns during that war …
https://utreon.com/c/forgottenweapons/
http://www.floatplane.com/channel/For…Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.forgottenweapons.com
October 7, 2024
Handguns in the US Army in World War Two
October 5, 2024
Did South Korea Provoke the Korean War?
The Korean War by Indy Neidell
Published 4 Oct 2024Was South Korea on the verge of invading North Korea in 1949? Today Indy looks at the bloody fighting across the Korean border in the years leading up to war. Then he asks the question, why did Kim finally decide to invade South Korea in the early months of 1950?
(more…)
October 4, 2024
Gustloff VG1-5 Nazi Last Ditch Rifles
Forgotten Weapons
Published Nov 20, 2015The Volkssturmgewehr Gustloff, more commonly (albeit incorrectly) known as the VG1-5, was one of the few semiautomatic Volkssturm weapons produced at the end of WWII. I have discussed these rifles before, but wanted to take advantage of the opportunity to take a close look at two more examples of the type.
Mechanically the Gustloff uses a system quite unusual in rifles — gas delayed blowback. Chambered for the 8×33 Kurz cartridge, there are 4 small gas vent holes in the front half of the barrel which vent gas into a chamber in the front muzzle plug. Pressure in this chamber acts to keep the slide closed, thus delayed the opening of the action. A nearly identical system is used in the much later Steyr GB pistol.
One of these in particular still has its original sling, which is a neat feature (the other clearly was issued with a sling but has lost it). In total 10,000 of these were manufactured, but they were not able to make a significant impact to prolong Germany’s war effort.
QotD: Farmers and slaves in ancient Mesopotamia
In one of my favorite parts of the book [Against The Grain], Scott discusses how this shaped the character of early Near Eastern warfare. Read a typical Near Eastern victory stele, and it looks something like “Hail the glorious king Eksamplu, who campaigned against Examplestan and took 10,000 prisoners of war back to the capital”. Territorial conquest, if it happened at all, was an afterthought; what these kings really wanted was prisoners. Why? Because they didn’t even have enough subjects to farm the land they had; they were short of labor. Prisoners of war would be resettled on some arable land, given one or another legal status that basically equated to slave laborers, and so end up little different from the native-born population. The most extreme example was the massive deportation campaigns of Assyria (eg the Ten Lost Tribes of Israel), but everybody did it because everybody knew their current subjects were a time-limited resources, available only until they gradually drained out into the wilderness.
Scott Alexander, “Book Review: Against The Grain“, Slate Star Codex, 2019-10-15.
October 3, 2024
Middle East situation – “There are really two international delusions we are seeing in play”
CDR Salamander on the situation in the Middle East as we come up on the one-year anniversary of the Hamas terrorist attacks on Israeli civilians on the border between Israel and Gaza:

“Israeli flag, Tel Aviv, Star of David” by Tim Pearce, Los Gatos is licensed under CC BY 2.0 .
Less than a week since the invasion of Israel from Gaza and the resulting pogrom that witnessed the largest one day murder, rape, kidnapping and tortures of Jews since World War Two — it is clear that Israel has decided that it was finally time to reset and repair the damage from decades of bad international theory and delusion.
There are really two international delusions we are seeing in play, one Israel has more control over, one has yet to be fully revealed to be the folly it is.
You can see the threads heading back decades earlier, but the first delusion hit its peak during the Clinton Administration in the 1990s, the withdrawal from the Southern Lebanon security zone in 2000, and finished its summit with Israel’s withdrawal from Gaza in 2005.
The delusion was that The Smartest People in the Room™ in DC, New York, Brussels, and Tel Aviv could, if they talked enough, wished enough, and said nice things to each other enough, would find a way to get the various Palestinian. Hope, wishes, and a mistaken trust in international organizations convinced Israel to give peace a chance.
Peace had a chance, and it culminated on October 7th, 2023.
Now, it appears, Israel will take the world as it is, not as it and others wished it to be. The key part of “this world” that some schools of international security affairs for decades have refused to recognize is the common, evil thread connecting them all: The Islamic Republic of Iran.
Gaza
Hamas was always a proxy for Iran. It could not have been able to be the threat it was without two things: 1) Iran; 2) UN. There can be no returning to the world of October 6th, 2023.
Whatever status Gaza winds up having in the future, it will not be like the past. While there remains much hard work to be done in Gaza, the hardest military part is done. It will be pacified thoroughly, and then the really hard part — what will happen to the population and territory of Gaza — will have to be worked out.
Egypt wants nothing to do with it. The Arab nations have already let it be known they don’t want that radicalized population, and Israel cannot let another Hamas like governance take over that strip of land that points in to Israel like a dagger.
It appears that Israel is following a variation of my COA-A I posted four days after last year’s attacks. The bitter fruit of a half-century of bad theory will have to be fixed, somehow.
Lebanon
From its birth as a Shia militia boosted by Iran, Hezbollah has, even more than Hamas, been a proxy for Iran. Only vaguely connected to the Palestinian cause, it has simply become an advanced military force for Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps.
For a year, well over 60,000 Israeli citizens have been internally displaced from their homes in Northern Israel due to unending rocket attack from Hezbollah in Southern Lebanon. As they rightfully focused on the war in Gaza, (as President Lincoln advised, “One war at a time“), Israel took the blows with minimal response until the last few weeks.
The formerly Christian led government of Lebanon cannot police their own nation, and have not been able to for decades, and the UN is more of a problem than a solution, Israel will have to take steps to secure her own safety.
Like the Gaza situation, this will create problems down the road because the hostile population is not going anywhere. That is an issue for later. For now, the rockets must stop.
D-Day 80th Anniversary Special, Part 2: Landings with firearms expert Jonathan Ferguson
Royal Armouries
Published Jun 12, 2024This year marks the 80th anniversary of D-Day, the Allied invasion of France which took place on 6th June 1944. From landing on the beaches of Normandy, the Allies would push the Nazi war machine and breach Hitler’s Atlantic Wall.
To commemorate this, we’re collaborating with IWM to release a special two-part episode as Jonathan will look at some of the weapons that influenced and shaped this historic moment in history.
Part 2 is all about the pivotal landings, including allied efforts to aid in its success.
0:00 Intro
0:25 Twin Vickers K Gun
2:03 Pointe du Hoc
2:45 Water off a DUKW’s back?
3:50 Magazines x3
4:07 Usage & History
5:50 Bring up the PIAT!
7:00 Dispelling (Or Projecting via Spigot) Myths
7:55 PIAT Firing Process
9:50 PIAT Details
10:31 Usage in D-Day
13:19 Pegasus Bridge
15:05 MG 42
15:41 Defensive Machine Gun
16:37 1200 RPM
17:35 Replaceable Barrel
19:08 Usage in D-Day
21:37 Sexton Self-Propelled Gun
21:33 Artillery in D-Day
22:15 Run-In Shoot
22:40 The Need for Mobile Artillery
23:25 Usage in D-Day
24:21 17-Pounder Gun
25:11 Function & Usage
26:05 Usage in D-Day
28:00 IWM at HMS Belfast
30:27 Outro
(more…)
October 2, 2024
The Korean War 015 – The Liberation of Seoul – October 1, 1950
The Korean War by Indy Neidell
Published 1 Oct 2024My, how the tide has turned. Less than two weeks ago, US X Corps landed at Incheon, far behind enemy lines, and already this week they take Seoul, the South Korean capital. Not without a fight, however, and the result is serious tension in US High Command. There are more UN advances in the field, though, and troops of US 8th Army advance north, and link up with those of X Corps, making a solid, united front, trapping many thousands of North Korean soldiers in South Korea.
(more…)
October 1, 2024
ZH-29 Semiauto Rifle
Forgotten Weapons
Published Apr 16, 2015The ZH-29 was the brainchild of noted Czech arms designer Emmanuel Holek in the late 1920s. It was one of the earliest practical and reliable semiauto rifles available, although Holek and the Brno factory were unable to secure any large orders for it (the three known orders total about 500 rifles, for China, Lithuania, and Ethiopia). Several other countries tested the rifle (including the United States), but none adopted it. The ZH29 was a long-stroke gas piston operated rifle with a tilting bolt which actually pivoted sideways into the left side of the receiver to lock. This design choice led to some unusual geometry to the gun, as the barrel is mounted at an angle to the receiver, so as to be perpendicular to the breech face when the bolt is in its locked position. Manufacturing quality was excellent on these rifles, and they all display a very pretty plum patina today. This particular example has no magazine with it, but my understanding is that ZB26 LMG magazines are a perfect fit.
QotD: Napoleon Bonaparte and Tsar Alexander I
Jane: … The most affecting episode in the whole book [Napoleon the Great by Andrew Roberts], to my mind — even more than his slow rotting away on St. Helena — is Napoleon’s conferences with Alexander I at Tilsit. Here are these two emperors meeting on their glorious raft in the middle of the river, with poor Frederick William of Prussia banished from the cool kids’ table, and Napoleon thinks he’s found a peer, a kindred soul, they’re going to stay up all night talking about greatness and leadership and literature … And the whole time the Tsar is silently fuming at the audacity of this upstart and biding his time until he can crush him. The whole buildup to the invasion has a horror movie quality to it — no, don’t go investigate that noise, just get out of
the houseRussia! — but even without knowing how horribly that turns out, you feel sorry for the guy. Napoleon thinks they have something important in common, and Alexander thinks Napoleon’s very existence is the enemy of the entire old world of authority and tradition and monarchy that he represents.Good thing the Russian Empire never gets decadent and unknowingly harbors the seeds of its own destruction!
John: Yeah, I think you’ve got the correct two finalists, but there’s one episode in particular on St. Helena that edges out his time bro-ing out with Tsar Alexander on the raft. It’s the supremely unlikely scene where old, beaten, obese, dying Napoleon strikes up a bizarre friendship with a young English girl. It all begins when she trolls him successfully over his army freezing to death in the smoldering ruins of Moscow, and after a moment of anger he takes an instant liking to her and starts pouring out his heart to her, teaching her all he knows about military strategy, and playing games in her parents’ yard where the two of them pretend to conquer Europe. Call me weird, but I think this above all really showcases Napoleon’s greatness of soul. That little girl later published her memoirs, btw, and I really want to read them someday.
Jane and John Psmith, “JOINT REVIEW: Napoleon the Great, by Andrew Roberts”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2023-01-21.
September 30, 2024
Sulla, civil war, and dictatorship
Adrian Goldsworthy. Historian and Novelist
Published Jun 5, 2024The latest instalment of the Conquered and the Proud looks at the first few decades of the first century BC. We deal with the final days of Marius, the rise of Sulla, the escalating spiral of civil wars and massacres as Rome’s traditional political system starts breaking down.
Primary Sources – Plutarch, Marius, Sulla, Pompey, Crassus, Cicero and Caesar. Appian Civil Wars and Mithridatic Wars.
Secondary (a small selection) –
P. Brunt, Social Conflicts in the Roman Republic & The Fall of The Roman Republic
A. Keaveney, Sulla – the last Republican
R. Seager, Pompey the Great: A political Biography
September 29, 2024
Yankee Go Home!
There’s a major war in continental Europe that might further embroil the NATO alliance in hot combat, so it’s the perfect time for … pulling the US military out of Europe and letting the European NATO allies handle their own defence needs, right?

“Finland flag raising at NATO Headquarters 4 April 2023” by UK Government Picture by Rory Arnold / No 10 Downing Street is licensed under CC BY 2.0 .
For decades, U.S. policy toward Europe stayed the same: Washington anchored itself to the continent via NATO and acted as the region’s main security provider while the European members of NATO accepted U.S. leadership. Today, however, much of the Republican Party has departed from this consensus, opting instead for a policy summed up by Donald Trump’s comments on “delinquent” NATO countries: “If they’re not going to pay, we’re not going to protect.” In other words, the United States may remain committed to Europe, but only if European states pay up. Democrats, for their part, have dug in deeper in response to this shift. President Joe Biden has affirmed the “sacred” Democratic commitment to European defense and trumpeted the admission of Finland and Sweden to NATO as a great achievement of his administration. Kamala Harris has signaled no departure from Biden’s position as the presumptive Democratic presidential nominee.
A debate about the U.S. role in Europe is long overdue, but both sides have wrongly defined the issues and interests at play. In fact, the United States has the same cardinal interest in Europe today that it has had since at least the early 1900s: keeping the continent’s economic and military power divided. In practice, pursuing this goal has meant preventing the emergence of a European hegemon. Unlike the continent in the mid-twentieth century, however, Europe today lacks a candidate for hegemony and, thanks in part to the success of U.S. efforts after 1945 to rebuild and restore prosperity to Western Europe, another hegemonic threat is unlikely to emerge.
The United States should recognize that it has achieved its main goal in Europe. Having successfully ensured that no country can dominate the continent, it should embrace a new approach to the region. Under a revised strategy, the United States would reduce its military presence on the continent, Europeanize NATO, and hand principal responsibility for European security back to its rightful owners: the Europeans.
A Fine Balance
For more than 100 years, the United States has had one enduring national interest in Europe: keeping the continent’s economic and military power split among multiple states by preventing the emergence of a European hegemon that sought to consolidate that power for itself.
In World War I and World War II, Washington went to war to stop Germany from dominating Europe. NATO, founded in 1949, was designed to foreclose the possibility that a single country could take over the continent. As Secretary of State Dean Acheson remarked that year, the two world wars “taught us that the control of Europe by a single aggressive, unfriendly power would constitute an intolerable threat to the national security of the United States.”
U.S. support for NATO was a reasonable move at a time when the Soviet Union was threatening to overrun the continent, wartime memories were fresh, and Germany’s future was unclear. Yet even back then, Washington’s goal was not to take permanent responsibility for European security. Instead, NATO was intended as a temporary expedient to protect Western European states as they recovered from World War II, facilitate Western European efforts to balance Soviet power, and integrate West Germany into a counter-Soviet coalition that would also help civilize German power. In 1951, as the supreme Allied commander in Europe, Dwight Eisenhower noted, “If in ten years, all American troops stationed in Europe for national defense purposes have not been returned to the United States, then this whole project will have failed.”
To that end, Presidents Harry Truman and Eisenhower tried to pull together a “Third Force” of European power by encouraging France, the United Kingdom, West Germany, and other Western European states to combine their political, economic, and military resources against the Soviet Union. Once formed, this Third Force would relieve the United States of the duty to serve as Europe’s first line of defense. Only as it became clear in the late 1950s and early 1960s that Western European states worried as much about Germany as they worried about the Soviet Union did the United States reluctantly accept a more enduring role in the alliance.
QotD: Pyrrhus, King of Epirus
Last time, we sought to assess some of the assumed weaknesses of the Hellenistic phalanx in facing rough terrain and horse archer-centered armies and concluded, fundamentally, that the Hellenistic military system was one that fundamentally worked in a wide variety of environments and against a wide range of opponents.
This week, we’re going to look at Rome’s first experience of that military system, delivered at the hands of Pyrrhus, King of Epirus (r. 297-272). The Pyrrhic Wars (280-275) are always a sticking point in these discussions, because they fit so incongruously with the rest. From 214 to 148, Rome will fight four “Macedonian Wars” and one “Syrian War” and utterly demolish every major Hellenistic army it encounters, winning every single major pitched battle and most of them profoundly lopsidedly. Yet Pyrrhus, fighting the Romans some 65 years earlier manages to defeat Roman armies twice and fight a third to a messy draw, a remarkably better battle record than any other Hellenistic monarch will come anywhere close to achieving. At the same time, Pyrrhus, quite famously, fails to get anywhere with his victories, taking losses he can ill-afford each time (thus the notion of a “Pyrrhic victory”), while the Roman armies he fights are never entirely destroyed either.
So we’re going to take a more in-depth look at the Pyrrhic Wars, going year-by-year through the campaigns and the three major battles at Heraclea (280), Ausculum (279) and Beneventum (275) and try to see both how Pyrrhus gets a much better result than effectively everyone else with a Hellenistic army and also why it isn’t enough to actually defeat the Romans (or the Carthaginians, who he also fights). As I noted last time, I am going to lean a bit in this reconstruction on P.A. Kent, A History of the Pyrrhic War (2020), which does an admirable job of untangling our deeply tangled and honestly quite rubbish sources for this important conflict.
Believe it or not, we are actually going to believe Plutarch in a fair bit of this. So, you know, brace yourself for that.
Now, Pyrrhus’ campaigns wouldn’t have been possible, as we’ll note, without financial support from Ptolemy II Philadelphus, Antigonus II Gonatus and Ptolemy Keraunos. So, as always, if you want to help me raise an Epirote army to invade Italy (NATO really complicates this plan, as compared to the third century, I’ll admit), you can support this project on Patreon.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Phalanx’s Twilight, Legion’s Triumph, Part IIIb: Pyrrhus”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2024-03-08.
September 28, 2024
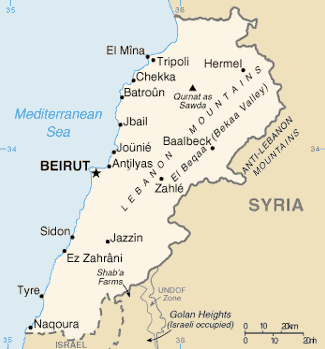
Lebanon is no longer a nation … it’s a parasitized husk operated by Iran’s proxies
In UnHerd, Tom McTague explains why there can be no “settlement” of the South Lebanon problem, because Lebanon ceased functioning as an independent state and is now largely controlled by Hezbollah, which means it’s indirectly controlled by Iran:
[…] A similar assessment was made about Lebanon, a country without a functioning state or economy and at the mercy of Iran’s colonial army, Hezbollah. This, also, was a situation that was thought to be containable — even as Iran exploited the anarchic chaos of Iraq and Syria to supply its proxy with enough weapons to devastate Israel.
The central conceit of the Abraham Accords was that, irrespective of Hamas, Hezbollah and the occupation of the West Bank, once the Israel-Saudi axis was formed, Iran could be pushed back and contained without direct American involvement. But, then, the depth of Hamas’s murderous brutality on 7 October shattered that assumption, leaving not only a traumatised and vulnerable Israel, but also a traumatised and vulnerable Western order forced to confront the stark realities of the Middle East.
Today, Lebanon is a dead state, eaten alive by Hezbollah’s parasitic power. The scale of the catastrophe in the country is hard to comprehend, much of it caused by the disruptive nature of Syria’s civil war. Since its neighbour’s descent into anarchic hell, some 1.5 million Syrians have sought refuge in Lebanon — a tiny country with a population of just 5 million. But, more fundamentally, with Hezbollah fighting to protect Bashar al Assad, the opposing countries — led by Saudi Arabia — began withdrawing funds from Lebanese banks. This sparked a financial crisis that left Lebanon with no money for fuel.
By spring 2020, the country had defaulted on its debts, sending it into a downward spiral which the World Bank in 2021 described as among “the top 10, possibly top three, most severe crises globally since the mid-nineteenth century”. Lebanon’s GDP plummeted by around a third, with poverty doubling from 42% to 82% in two years. At the same time, the country’s capital, Beirut, was hit by an extraordinary explosion at its port, leaving more than 300,000 homeless. By 2023 the IMF described the situation as “very dangerous” and the US was warning that the collapse of the Lebanese state was “a real possibility”.
With Iranian support, however, Hezbollah created a shadow economy almost entirely separate from this wider collapse. It could escape the energy shortages, while creating its own banks, supermarkets and electricity network. Hezbollah isn’t just a terrorist group. It is a state within a state, complete with a far more advanced army. “They may have plunged Lebanon into complete chaos, but they themselves are not chaotic at all,” as Carmit Valensi, from the Institute for National Security Studies at Tel Aviv University, told the Jerusalem Post.
Then came 7 October, after which Hezbollah tied its fate to that of the Palestinians, promising to bombard Israel with rockets until the war in Gaza was brought to a close. We have witnessed the frightening scale of its power over the past year, its bombardment forcing some 100,000 Israelis from their homes in Galilee to the safety of the Israeli heartlands around Tel Aviv. For the first time since modern Israel’s creation, the land where Jews are able to live in their own state has shrunk; the rockets are a daily reminder of the country’s extraordinary vulnerability, threatened on all sides by states who actively want it removed from the map — even from history itself. The pretence that the Palestinian and Lebanese questions could be contained, ignored or bypassed as part of a wider grand strategy to contain Iran has been shattered.
September 27, 2024
Evolution of the Karabiner 98k, From Prewar to Kriegsmodell
Forgotten Weapons
Published 7 Nov 2018The Mauser Karabiner 98k began production as an excellent quality rifle, with every nuance of fine fit and finish one would have expected from the Mauser company. World War Two had barely begun by the time a few compromises began to be made to maintain production, however — and by the end of the war the K98k was a mere shadow of its former self. As with the similar deterioration in quality with Japanese Arisaka rifles, the critical mechanical elements of the K98k were just as safe and functional at the very end as the were at the beginning — but the ancillary aspects came crashing down. One might argue that these changes should have been made from the beginning; that issuing an infantry rifle made to the same finish as a fine commercial sporting arm is a silly waste of resources …
(more…)