Mark Felton Productions
Published 18 Apr 2020The last time the Parachute Regiment dropped into combat was during the 1956 Suez Crisis when 3 PARA landed on El Gamil Airfield outside Port Said, Egypt.
(more…)
September 2, 2022
The Paras Last Drop – Gamil Airfield 1956
June 23, 2022
1177 B.C.: When Civilization Collapsed | Eric Cline
Long Now Foundation
Published 19 Apr 2020Consider this, optimists. All the societies in the world can collapse simultaneously. It has happened before.
In the 12th century BCE the great Bronze Age civilizations of the Mediterranean — all of them — suddenly fell apart. Their empires evaporated, their cities emptied out, their technologies disappeared, and famine ruled. Mycenae, Minos, Assyria, Hittites, Canaan, Cyprus — all gone. Even Egypt fell into a steep decline. The Bronze Age was over.
The event should live in history as one of the great cautionary tales, but it hasn’t because its causes were considered a mystery. How can we know what to be cautious of? Eric Cline has taken on on the mystery. An archaeologist-historian at George Washington University, he is the author of 1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed. The failure, he suggests, was systemic. The highly complex, richly interconnected system of the world tipped all at once into chaos.
“1177 B.C.: When Civilization Collapsed” was given on January 11, 2016 as part of Long Now’s Seminar series. The series was started in 2003 to build a compelling body of ideas about long-term thinking from some of the world’s leading thinkers. The Seminars take place in San Francisco and are curated and hosted by Stewart Brand. To follow the talks, you can:
Subscribe to our podcasts: http://longnow.org/seminars/podcast
Explore the full series: http://longnow.org/seminars
More ideas on long-term thinking: http://blog.longnow.orgThe Long Now Foundation is a non-profit dedicated to fostering long-term thinking and responsibility. Our projects include a 10,000 Year Clock, endangered language preservation, thousand year+ data storage, and Long Bets, an arena for accountable predictions.
Become a Long Now member to support this series, join our community, and connect with our ongoing work to explore and deepen long-term thinking: http://longnow.org/membership
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/longnow
Subscribe to our channel: https://www.youtube.com/longnow
June 12, 2022
History Re-Summarized: Egypt
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 18 Feb 2022I for one was shocked to learn the Egyptians actually buried their kings in a giant Millennium Puzzle.
We’ve covered Egypt on this channel in previous videos, but this History Re-Summarized is the Definitive Edition, redone from the ground up to present the best possible account — starting at the beginning for a full chronology of Ancient Egypt, from the very first Pharaohs to the Muslim Conquest.
(Observant Egyptologists and D&D players might note the Pyramids are actually D-*Fives*, but technically they’re D-*Nines* since each face is actually two right triangles at a slight angle to each other and not a single flat isosceles triangle, so shhh, we can pretend it’s a D4.)
Sources & Further Reading: The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt & Ancient Egypt: A Very Short Introduction by Ian Shaw, World History Encyclopedia entries on “Ancient Egypt”, “Old Kingdom of Egypt”, “First Intermediate Period of Egypt”, “Middle Kingdom of Egypt”, “Second Intermediate Period of Egypt”, “New Kingdom of Egypt” https://www.worldhistory.org/egypt/, The Great Courses’ lecture series “History of Ancient Egypt” by Bob Brier. Additionally, I have an undergraduate degree in classical studies (re: Persia, Ptolemies and Rome). Extra special thanks to our OSP Discord server moderator & Egyptology connoisseur Billy, for his assistance and guidance for this video!
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
PODCAST: https://overlysarcasticpodcast.transi…
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/osp
MERCH LINKS: http://rdbl.co/osp
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
June 10, 2022
The Early Roman Emperors – Part 1: Augustus
seangabb
Published 26 Sep 2021The Roman Empire was the last and the greatest of the ancient empires. It is the origin from which springs the history of Western Europe and those nations that descend from the Western Roman Empire. It is the political entity within which the Christian faith was born, and the growth of the Church within the Empire, and its eventual establishment as the sole faith of the Empire, have left an indelible impression on all modern denominations. Its history, together with that of the ancient Greeks and the Jews, is our history. To understand how the Empire emerged from a great though finally dysfunctional republic, and how it was consolidated by its early rulers, is partly how we understand ourselves.
Here is a series of lectures given by Sean Gabb in late 2021, in which he discusses and tries to explain the achievement of the early Emperors. For reasons of politeness and data protection, all student contributions have been removed.
More by Sean Gabb on the Ancient World: https://www.classicstuition.co.uk/
Learn Latin or Greek or both with him: https://www.udemy.com/user/sean-gabb/
His historical novels (under the pen name “Richard Blake”): https://www.amazon.co.uk/Richard-Blak…
June 3, 2022
The Crusades: Part 10 – The End of the Crusader Kingdoms
seangabb
Published 27 Mar 2021The Crusades are the defining event of the Middle Ages. They brought the very different civilisations of Western Europe, Byzantium and Islam into an extended period of both conflict and peaceful co-existence. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this long encounter with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
May 23, 2022
QotD: The adoption of Astrology by the Greeks and Romans
Perhaps the most influential form of divination to arrive in the Roman world from the East was astrology. Systems for divining the will of the gods and the course of the future emerged in both Egypt and Mesopotamia c. 2000 B.C. and were thus both very ancient when Alexander the Great conquered both in the late fourth century. From there, astrology, practiced by professional experts, moved into the Greek and then Roman world, though Roman elites were often deeply ambivalent about this foreign method of divination; both Cato and Cicero express doubts (of course, the Roman practice of haruspicy was also foreign in that it was Etruscan, but this adoption had been sanctified by long use in Roman tradition and was thus mostly beyond reproach). Nevertheless, it is clear that this form of divination become common, with the writer, geographer and astronomer Ptolemy (c. 100-170 A.D.) even producing a long explication of the practice of astrology in his Tetrabiblos.
This portability is not restricted merely to divination. Herodotus’ suspicion that quite a bit of Greek religion might have come from somewhere else has merit, though Anatolia, not Egypt, appears to be the main source (see: M.L. West, The East Face of Helicon (1999); and for the person already writing this comment, yes I am aware of Bernal’s Black Athena and no I am not convinced, nor are many specialists in the field). The Romans were open about importing gods from Greece and make a clear distinction between gods worshiped in traditional Roman manner and those imported from Greece (a quite small number) and thus whose rituals followed ritus graecus – rituals in Greek fashion.
In other cases, the foreign practice was modified to fit the culture it arrived in. The Romans adopted the cult of Cybele, an Anatolian goddess, during the dark days of the Second Punic War (the Senate made that decision based on a consultation with the Sibylline books, a written source of oracular prophecy we can talk about another day). Cybele was called Magna Mater (“Great Mother”) in Rome, and it seems made some modifications to her rituals, in particular possibly limiting the role of the Galli (eunuch priests) whose rituals and style seemed decidedly “unRoman” (though I should note that the scholarship here is contested and the issue and evidence complex).
The normal technical term for this kind of religious borrowing is syncretism, and it is a sort of interweaving of religious traditions that polytheisms both ancient and modern are exceptionally capable of. It is simply not hard to add one more god or one more ritual into a religious system that already assumes the existence of innumerable gods.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Practical Polytheism, Part III: Polling the Gods”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-11-08.
May 14, 2022
QotD: The farming cycle in pre-modern Mediterranean cultures
As you might imagine, time in agriculture is governed by the seasons. Crops must be planted at particular times, harvested at particular times. In most ancient societies, the keeping of the calendar was a religious obligation, a job for educated priests (either a professional priestly class as in the Near East, or local notables serving as amateurs, as in Greece and Rome).
The seasonal patterns vary a bit depending on the conditions and the sort of wheat being sown. In much of the Mediterranean, where the main concern was preserving a full year’s moisture for the crop, planting was done in autumn (November or October) and the crop was harvested in early summer (typically July or August). In contrast, the Han agricultural calendar for wheat planted in the spring, weeded over the summer and harvested in fall. The Romans generally kept to the autumn-planting schedule, except our sources note that on land which was rich enough (and wet enough) to be continuously cropped year after year (without a fallow), the crop was sown in spring; this might also be done in desperation if the autumn crop had failed. In Egypt, sowing was done as the Nile’s flood waters subsided at the beginning of Peret (in January), with the harvest taking place in Shemu (summer or early fall).
(As an aside on the seasons: we think in terms of four seasons, but many Mediterranean peoples thought in terms of three, presumably because Mediterranean winters are so mild. Thus the Greeks have three goddesses of the seasons initially, the Horae (spring, summer and fall) and Demeter’s grief divides the year into thirds not fourths in the Homeric Hymn to Demeter. In ancient Egypt, there were three seasons: Akhet (Flood); Peret (Emergence [of fertile lands as the waters recede]) and Shemu (Low Water). The perception of the seasons depended on local climate and local cycles of agriculture.)
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Bread, How Did They Make It? Part I: Farmers!”, A collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-07-24.
April 19, 2022
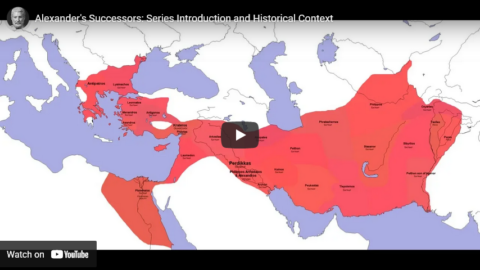
Alexander’s Successors (the Diadochi): Series Introduction and Historical Context
Thersites the Historian
Published 24 Nov 2018This video introduces my series on Alexander’s Successors by talking about what the series will be like and by going through the historical context that the viewer might need to understand the age of the Successors.
Patreon link: https://www.patreon.com/thersites
PayPal link: paypal.me/thersites
Twitter link: https://twitter.com/ThersitesAthens
Minds.com link: https://www.minds.com/ThersitestheHis…
Steemit/dtube link: https://steemit.com/@thersites/feed
Backup Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUrD…
April 11, 2022
Republic to Empire: The Ides of March to Actium
seangabb
Published 13 Mar 2021In 120 BC, Rome was a republic with touches of democracy. A century later, it was a divine right military dictatorship. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this transformation with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
April 7, 2022
Republic to Empire: The Triumph of Caesar
seangabb
Published 5 Mar 2021In 120 BC, Rome was a republic with touches of democracy. A century later, it was a divine right military dictatorship. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this transformation with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
April 2, 2022
QotD: The pre-modern farming household
Looking at our peasant household, what we generally have are large families on small farms. The households in these farms were not generally nuclear households, but extended ones. Pre-Han Chinese documents assume a household to include three generations: two elderly parents, their son, his wife, and their four children (eight individuals total). Ptolemaic and Roman census data reveal a bewildering array of composite families, including multi-generational homes, but also households composed of multiple nuclear families of siblings (so a man, his wife, his brother and then brother’s wife and their children, for instance), and so on. Normal family units tended to be around eight individuals, but with wide variation (for comparison, the average household size in the United States for a family is 3.14).
At the same time that households were large (by modern standards), the farms they tilled were, by modern standards, very small. The normal size of a Roman household small farm is generally estimated between 5 and 8 iugera (a Roman measurement of land, roughly 3 to 5 acres); in pre-Han Northern China (where wheat and millet, not rice, were the staple crops), the figure was “one hundred mu (4.764 acres)” – essentially the same. In Languedoc, a study of Saint-Thibery in 1460 showed 118 households (out of 189) on farms of less than 20 setérée (12 acres or so; the setérée appears to be an inexact unit of measurement); 96 of them were on less than 10 setérée (about 6 acres). So while there is a lot of variation, by and large it seems like the largest cluster of household farms tend to be around 3 to 8 acres or so; 5 acre farms are a good “average” small farm.
This coincidence of normal farm size and family size is not an accident, but essentially represents multi-generational family units occupying the smallest possible farms which could support them. The pressures that produce this result are not hard to grasp: families with multiple children and a farm large enough to split between them might do so, while families without enough land to split are likely to cluster around the farm they have. Pre-modern societies typically have only limited opportunities for wage labor (which are often lower status and worse in conditions than peasant farming!), so if the extended family unit can cluster on a single farm too small to split up, it will (with exception for the occasional adventurous type who sets off for high-risk occupations like soldier or bandit).
Now to be clear that doesn’t mean the farm sizes are uniform, because they aren’t. There is tremendous variation and obviously the difference between a 10 acre small farm and a 5 acre small farm is half of the farm. Moreover, in most of the communities you will have significant gaps between the poor peasants (whose farms are often very small, even by these measures), the average peasant farmer, and “rich peasants” who might have a somewhat (but often not massively so) larger farm and access to more farming capital (particularly draft animals). […] Nevertheless, what I want to stress is that these fairly small – 3-8 acres of so – farms with an extended family unit on it make up the vast majority of farming households and most of the rural population, even if they do not control most of the land (for instance in that Languedoc village, more than half of the land was held by households with more than 20 setérée a piece, so a handful of those “rich peasants” with larger accumulations effectively dominated the village’s landholding […]).
This is our workforce and we’re going to spend this entire essay talking about them. Why? Because these folks – these farmers – make up the majority of the population of basically all agrarian societies in the pre-modern period. And when I say “the majority” I mean the vast majority, on the order of 80-90% in many cases.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Bread, How Did They Make It? Part I: Farmers!”, A collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-07-24.
March 1, 2022
What was lost when the Library of Alexandria burned?
Kings and Generals
Published 18 Nov 2021⚔️Myth of Empires is out in Early Access on Steam, check it out and make sure to wishlist it https://click.fan/KingsGenerals-MoE
Kings and Generals’ historical animated documentary series on the history of Ancient Civilizations and Ancient Greece continue with a video on the Library of Alexandria, as we ask what was lost when the library burned.
Support us on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/KingsandGenerals or Paypal: http://paypal.me/kingsandgenerals … We are grateful to our patrons and sponsors, who made this video possible: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1o…
The video was made by animator Waily Romero and illustrator Simone González, while the script was researched and written by David Muncan. This video was narrated by Officially Devin (https://www.youtube.com/user/OfficiallyDevin).
✔ Merch store ► teespring.com/stores/kingsandgenerals
✔ Podcast ► Google Play: http://bit.ly/2QDF7y0 iTunes: https://apple.co/2QTuMNG
✔ Twitter ► https://twitter.com/KingsGenerals
✔ Instagram ► http://www.instagram.com/Kings_GeneralsProduction Music courtesy of EpidemicSound
#Documentary #AncientGreece #Alexandria
QotD: The Great Library of Alexandria
… we don’t know exactly who founded the Library and we aren’t clear on precisely when. What is clear is that it was quite early in the history of what was to become the great city of Alexandria and that its establishment made the city a centre of learning for centuries to come. What should also be made clear, however, is that it was not actually a “library” that was established at all. The “Great Library” that we refer to was a collection of books associated with a religious shrine – the Musaeum or Mouseion. This institution was, as the name implies, dedicated to the Nine Muses: Clio (history), Urania (astronomy), Calliope (epic poetry and song), Euterpe (lyric song), Polyhymnia (sacred song), Erato (erotic song), Melpomene (tragedy), Thalia (comedy) and Terpsichore (dance). The temple to the Muses had a dedicated priest appointed by the Ptolemaic kings and was the centre of a complex that included an exhedra, or hall, with recesses and seats for lectures and private study. According to the only and rather brief surviving description, given by Strabo in the early first century AD, it also included a communal dining hall with kitchens, a dormitory and other residential apartments, extensive gardens decorated with statues and a shaded walk. What we call the “Great Library” was a collection of books gathered to service the scholars who were housed and worked in the Mouseion and it was stored partially in the complex itself and, later, on other sites including at least three “daughter libraries”. The popular image of the Great Library as an echoing hall lined with shelves of scrolls with desks and tables for scholars is almost certainly inaccurate. That kind of library, which is still the model for many traditionally-styled libraries today, was developed much later by the Romans and the Mouseion would instead have had “a colonnade with a line-up of rooms behind … the rooms would serve for shelving the holdings and the colonnade provide space for the readers.” (Lionel Casson, Libraries of the Ancient World, Yale University Press, 2001, p. 34)
The Mouseion at Alexandria was far from the only shrine to the Muses in the ancient world, nor was it the only one with an associated centre of study. Pythogoras had recommended the establishment of a shrine to the Muses for the promotion of learning on his first arrival on Croton, for example and the Seleucid kings built one at Antioch in the late second century BC, with an attendant centre for study and a library. The fact that the Great Library was actually associated with a religious shrine is something that is ignored or glossed over in many modern accounts. [Carl] Sagan […] mentions about how one of the “daughter libraries” was the Serapeum, which was the temple of Serapis, but he skips around this in a rather gingerly manner. He says the Serapeum was “once a temple, but was later reconsecrated to knowledge”. This is nonsense. The Serapeum was always a temple and was not “reconsecrated” to anything. Libraries were often established as adjuncts to temples but it seems Sagan was attempting to distance the “annex” of the Great Library from the temple in which it sat because this did not quite fit his theme of secular knowledge’s superiority to “mysticism”. Like the Serapeum, the Mouseion was a temple with a research institution and a book collection associated with it.
This aside, the Mouseion really was primarily a research institution and its associated book collection – which we will continue to refer to by the shorthand expression the “Great Library” – was clearly one of if not the most extensive in the ancient world (more on that below). Many famous ancient scholars worked in the Mouseion, including Eratosthenes and probably Ptolemy. But several who are often claimed as working there (or even as being “librarians” of the Great Library, no less) clearly did not. Sagan’s hymn of praise says that Hipparchus studied there, but he seems to have only used some of the books from the collection and there is no evidence he ever even visited from his home on Rhodes. Likewise Sagan says Archimedes worked there, but there is no clear evidence for this and what little we know of Archimedes’ life indicates he spent it in Syracuse. Of the others Sagan mentions, Euclid and Herophilos may have studied there, depending on when the Mouseion was established and Dionysius of Thrace is another maybe, though more likely. On the whole, Sagan’s roll call of great scholars is mainly hyperbole and speculation rather than historical fact. The other figure who is regularly invoked as being associated with the Great Library, and even presented as its “last librarian”, is (again) Hypatia. This is despite the fact that both the Great Library and its daughter library in the Serapeum had ceased to exist by her time.
Tim O’Neill, “The Great Myths 5: The Destruction Of The Great Library Of Alexandria”, History for Atheists, 2017-07-02.
January 7, 2022
Desert War – Dysentery, Disease, and Dehydration – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 6 Jan 2022North Africa. The Axis and Allies are fighting each other but even more, they’re fighting the desert itself. The men of the desert burn during the day and freeze at night. They do most of their fighting on a litre of water and a packet of army biscuits. What is life in such a hostile environment?
(more…)
January 3, 2022
How did the Greeks and Romans count Years?
toldinstone
Published 31 Dec 2021The AD/CE system we use to date the year was introduced — more or less by accident — during the Middle Ages. Before its invention, the classical world used a wide range of dating systems.
Please consider supporting this channel on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/toldinstoneIf you liked this video, you might also enjoy my book Naked Statues, Fat Gladiators, and War Elephants: Frequently Asked Questions about the Ancient Greeks and Romans:
https://www.amazon.com/Naked-Statues-…
If you’re so inclined, you can follow me elsewhere on the web:
https://www.reddit.com/r/AskHistorian…
https://www.instagram.com/toldinstone/
https://www.goodreads.com/author/show…Chapters:
0:00 Introduction
0:51 Ancient Greek Calendars
1:42 Counting by Olympiads
2:22 The Seleucid Era
2:56 Consular Dating
3:26 Ab Urbe Condita
4:28 Indictions
4:56 Christian Chronology
5:40 Anno Domini
7:00 Conclusion