Perhaps the most fascinating component of [Prof. Thomas] Courchene’s paper is his subtle discussion of what, precisely, equalization is for. Is it meant to render every province in Canada equally well off in general? Or is it meant only to correct inequities introduced by the provinces’ different geographic and natural circumstances? Or is it meant even more narrowly, as a scheme to ensure that the federal government doesn’t accidentally worsen those inequities? Or it is meant merely to discourage culturally harmful labour migration?
There is no official answer to this question, and all the possible answers lead to moral and mathematical absurdities. It’s not just that we don’t know whether equalization works, as Terence Corcoran observed in the Financial Post yesterday. We literally don’t even know what it’s meant to accomplish
Colby Cosh, “Economist plays ethicist”, National Post, 2005-09-01.
September 15, 2025
QotD: Federal equalization payments
July 4, 2025
QotD: US-Canadian conflict before Confederation
Canada has never fought a direct war against the United States. However, before confederation (1867) when Canada became a self-governing dominion, the territories that would later form that dominion, which had been under the control of the British, engaged in a small number of military conflicts with the United States (or as they were known previously, the Thirteen American Colonies). The total is four, if we only count significant engagements which involved organized forces. Economic wars, or trade disputes, are another story. We’ll get there.
The Aroostook War (1838–1839) drew no blood. The conflict concerned the Maine-New Brunswick border and was resolved amicably by the Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1842. A quarter of a century later the Fenian Raids (1866–1871) saw the Irish-American Fenian Brotherhood make multiple non-state sanctioned attacks in British North America in an effort to sway Britain to withdraw forces from Ireland.
The other far more consequential military struggles between the two North American friends and neighbours occurred first in the late eighteenth century, and second in the early nineteenth century. During the American Revolutionary War (1775-1783), which saw limited involvement of areas north of the 49th parallel, British North America thwarted a particularly serious invasion by the Americans in 1775 known as The Battle of Quebec.
It was fought during a snowstorm on December 31, 1775 (one of few battles fought in such miserable conditions during the revolutionary war). The American intention was to conscript the British colony, which today forms the province of Quebec (and also included parts of Ontario) into their struggle against the British. The Patriots of the Thirteen Colonies had earlier that year begun rebelling against British taxation and governance. They surmised that the French-speaking Quebec settlers, disaffected with the imposition of British rule as it was laid out in the 1763 Treaty of Paris (which ended the Seven Years War), would join the American cause. A significant miscalculation, to say the least.
The battle was fought on two fronts against a British garrison of 1800 soldiers led by British commander, Governor Guy Carleton. The combined total of American troops was only 1200. The first front was commanded by Brigadier General Richard Montgomery, who led his troops in an attack of the Lower Town from the south. The second assault occurred from the north and was led by Colonel Benedict Arnold (who would later become an infamous American traitor).
Montgomery and several officers were killed instantly on their initial advance. This sparked a retreat amongst his remaining soldiers. Arnold had slightly more luck. His army penetrated northern defences but were stymied in the narrow streets of Quebec. During fighting Arnold was wounded, after which he handed the command to Daniel Morgan. After hours of fighting, Morgan and his men were forced to surrender. The Americans lost the battle decisively ensuring Quebec would remain a loyalist stronghold.
The second of the two significant conflicts involving British North America and the Thirteen American Colonies was the infamous War of 1812 – a more well-known period of antagonism between proto-Canada and her American neighbours.
Here is a topline summary with some extra history concerning the U.S.-Canada border (the world’s longest undefended border), from Terry Glavin:
The War of 1812 — which the Americans still pretend they won — was officially concluded with the Treaty of Ghent in 1814. Then came the Rush-Bagot Pact of 1817 and the Convention of 1818, which set the border at the 49th parallel.1
The War of 1812 took place during Britain’s struggle against Napoleonic France. The two most famous Canadian battles from this tragic conflict were the Battle of Queenston Heights and the burning of York (now Toronto) – British troops would even the score of the latter by burning Washington D.C.
The war was unpopular. Like today, there were too many bonds between the Americans and proto-Canadians. But also like today, with Canada and the United States once again bickering over trade and various political interests, the disagreements were accompanied by a reluctance to engage in hostilities.
From Pierre Burton’s War of 1812:
At the outset, it was a gentleman’s war. Officers on opposing sides met for parlays under flags of truce, offered hospitality, exchanged cordialities, murmured the hopes that hostilities would quickly end.2
No matter what time period we are examining, we can never forget that Britons, Canadians and Americans are all first cousins. Yes we disagree from time to time, sometimes we even fight. But always over some unfortunate political dispute, and never for each other’s annihilation.
In 1812, for a variety of reasons, the Americans, especially a minority of hawkish elites in Washington, felt they had no other choice but to invade the north. Some of them felt it would be easy. An aggravating factor concerned Britain’s support of Indian tribes in the north west, at a time when the Americans were aggressively expanding into that region. But also, during their imperial contest with France, the British were impressing sailors in the American navy (forcing them to join British forces), because they considered them traitors of the British crown. Further, they blocked key trade ports under Napoleon’s control, disrupting trade between America and France.
Isn’t it curious how trade so often appears as the rift in Canadian-American relations? Further examples include: the Reciprocity Treaty of 1854 which allowed for free trade of natural resources between the American and British colonies. However, the Americans abrogated that treaty in 1866 partly out of frustration at perceived British support of the confederacy after the Civil War. A post-confederation trade war with the Americans ensued after Canada’s first Prime Minister John A. MacDonald adopted the National Policy in 1879, which imposed high tariffs to protect Canadian industry. Triggering the Americans to respond with tariffs of their own.
James Pew, “Canadians and our ties to Americans”, Woke Watch Canada, 2025-03-30.
1. Because of the day that’s in it – by Terry Glavin
2. Pierre Berton’s War of 1812.
July 1, 2025
The Maple Leaf Forever
Columbia Yore
Published 13 Jun 2018The Maple Leaf Forever was written by Alexander Muir in 1867 and served as the unofficial anthem of Canada from 1867-1980.
February 8, 2025
Interprovincial trade barriers in Canada
In the National Post, Jamie Sarkonak pours some icy cold water on the fever dream that we can fix what ails us economically with this one neat trick:
Understand what an interprovincial trade barrier is: it isn’t a simple matter of repealing tariffs, because internal tariffs don’t exist — provinces aren’t allowed to impose them. Instead, barriers take the form of red tape that differs in shade by province; if there are 10 provinces that each regulate, say, what shape of toilet seat is required to be used on a construction site, expect 10 different rules on the matter (Ontario requires a gap at the front of the seat; Alberta doesn’t care).
For Canada’s toilet seat manufacturers, that’s another level of complexity that can complicate production and make it costly to expand to new jurisdictions.
Now repeat the mental exercise for every other provincially regulated product: food, alcohol, pesticides, lumber and so on. And again, with all the other provincially regulated things you can buy but not hold: massage therapy, legal services, hair and aesthetic services, provincially regulated securities.
It adds up to a lot, and that’s by design: in 1867, the Constitution explicitly handed authority over most sectors to provincial governments. Provincial regulations, and by extension, interprovincial trade barriers, are central to provincial autonomy.
Theoretically, rule consolidation is a good deal. It would be far easier to do business in Canada if it worked more like one country with one set of rules, rather than a heterogenous group of 10 micro-states packed into one.
On the taxpayer side, there are savings to be had, too: regulatory bodies use public funds and there are (theoretically) savings to be had by centralizing the offices of 10 different sheriffs into one. Estimates vary, but lifting barriers is thought to add a boost of $80 billion (International Monetary Fund) to $200 billion (Canadian Federation of Independent Business) to the economy.
But standing in the way of free-trade utopia are the practical considerations, the big one being protectionism. Making its case in the Journal de Montreal, William Rousseau put it well: “The abolition of these barriers can even be economically harmful, because for each barrier that blocks a company from the rest of the country, there is a Quebec company that benefits from it and whose business model takes this barrier into account.” The exact same can be said for any province.
This is why I thought well of Pierre Poilievre’s recent trial balloon about ways to coax the provinces into reducing interprovincial trade barriers by … let’s be honest … providing a financial bribe from the federal government. By allowing the individual provinces to “capture” some of that “lost” revenue, it may provide enough incentive to start dismantling at least some of the structural barriers to free trade within Confederation.
January 31, 2025
Canada – sovereign nation or “post-national state” with “no core identity”?
In The Line, Andrew Potter retraces Canada’s history from British colony to self-governing Dominion to proud mover-and-shaker in the postwar world to whatever the heck it is today:
There is a map that shows up on social media from time to time, and it looks like this.
Sometimes it is followed by this one:
And then maybe this one:
What’s the point of these maps? Apart from noting the obvious, which is that Canada is sparsely populated, and much of the population is gathered in cities very close to the border with the United States, they raise important questions about the exercise of political power and its legitimacy, forms of governance, and, ultimately, sovereignty. By what methods did Canada come to be, and by what right does a small and relatively concentrated group of people, most of whom live down by the Great Lakes or along the St. Lawrence River, lay claim to almost ten million square kilometres of the Earth’s landmass?
It is easy to draw lines on maps. Anyone can do it. If you want those lines to represent some sort of generally accepted reality, two things must be true. First, the people inside the lines need to see those lines as legitimate, and be willing to take the necessary steps, up to and including the use of force, to assert them against outsiders. And second, enough outsiders of sufficient global importance also need to recognize those lines.
Any student of Canadian history knows that the borders of Canada are highly contingent. Rewind the tape of the past, and there are any number of moments where things could have turned out differently. In some scenarios, Canada ends up smaller than it currently is; in others, Canada ends up larger, perhaps substantially so. And in some alternative histories, Canada does not exist at all — or if it does, we’re all speaking French.
There’s nothing that is either sinister or celebratory in pointing this out. History is a bunch of stuff that happened, and in some cases, things might have turned out differently. But again, if you know your Canadian history, you know that the process by which Canada went from a French fur trading outpost to a collection of British mercantile colonies to a continent-spanning multinational federation and parliamentary democracy was made possible only through a rough admixture of ambition, cunning, scheming, coercion, violence, strong foreign support, and, between 1812 and 1814, war.
To get to the point: Canada’s sovereignty wasn’t something we just stumbled upon, nor is it something we were happily given. It was a thing we did. We did not do it alone, though; for most of the 19th century, the main ongoing threat to Canada’s sovereignty was the United States, while the ultimate guarantor of that sovereignty was Great Britain.
That dynamic shifted over the first half of the 20th century, when the British Empire went into decline, and the United States became the dominant world power. There was a short period after 1931, while British influence was ebbing and that of the Americans was flowing, in which Canada stood more or less independent and autonomous. This largely ended in 1940; Britain was on the ropes against Nazi Germany, Canada was in Hitler’s sights, and an increasingly anxious Franklin Roosevelt invited Mackenzie King down to Ogdensburg, New York, for a friendly chat about continental security.
January 12, 2025
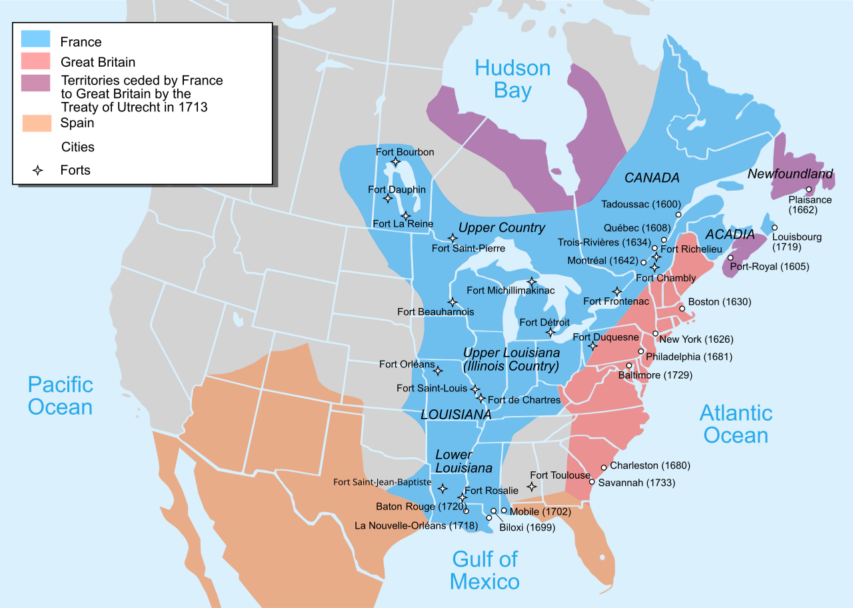
Quebec within the British Empire after 1760
Fortissax, in response to a question about the historical situation of Quebec within Canada, outlines the history from before the Seven Years’ War (aka the “French and Indian War” to Americans) through the American Revolution, the 1837-38 rebellions, the Durham Report, and Confederation:
First and foremost, Canada itself, as a state — an administrative body, if you will — was originally founded by France. Jacques Cartier named the region in 1535, and Samuel de Champlain established the first permanent French settlement in North America in Quebec City in 1608. This settlement would become the largest and most populous administrative hub for the entire territory. Canada was a colony within the broader territory of New France, which stretched from as far north as Tadoussac all the way down to Louisiana. It included multiple hereditary land-owning noblemen of Norman extraction.
During the Seven Years’ War, on 8 September 1760, General Lévis and Pierre de Vaudreuil surrendered the colony of Canada to the British after the capitulation of Montreal. Though the British had effectively won the war, the Conquest’s details still had to be negotiated between Great Britain and France. In the interim, the region was placed under a military regime. As per the Old World’s “rules of war”, Britain assured the 60,000 to 70,000 French inhabitants freedom from deportation and confiscation of property, freedom of religion, the right to migrate to France, and equal treatment in the fur trade. These assurances were formalized in the 55 Articles of the Capitulation of Montreal, which granted most of the French demands, including the rights to practice Roman Catholicism, protections for Seigneurs and clergymen, and amnesty for soldiers. Indigenous allies of the French were also assured that their rights and privileges would be respected.
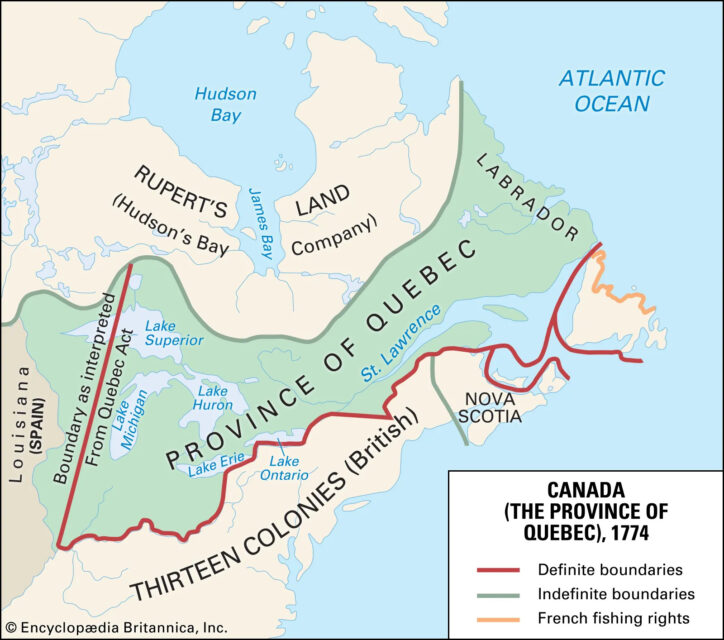
The Treaty of Paris in 1763 officially ended the war and renamed the French colony of “Canada” as “the Province of Quebec”. Initially, its borders included parts of present-day Ontario and Michigan. To address growing tensions between Britain and the Thirteen Colonies and to maintain peace in Quebec, the British Parliament passed the Quebec Act in 1774. This act solidified the French-speaking Catholic population’s rights, such as the free practice of Catholicism, restoration of French civil law, and exemption from oaths referencing Protestant Christianity. These provisions satisfied the Québécois Seigneurs (land-owning nobleman), and clergy by preserving their traditional rights and influence. However, some Anglo settlers in America resented the Act, viewing it as favoring the French Catholic majority. Despite this, the Act helped maintain stability in Quebec, ensuring it remained loyal to Britain during the American Revolutionary War and Quebec was fiercely opposed to liberal French revolutionaries.
British concessions, from the terms of the 1763 Treaty of Paris to the Quebec Act of 1774, safeguarded the cultural and religious identity of Quebec’s French-speaking Catholic population, fostering their loyalty during a period of significant upheaval in North America. Following this period, merchant families such as the Molsons began establishing themselves in Montreal, alongside early Loyalist settlers who trickled into areas now known as the Eastern Townships. These merchant families quickly ingratiated themselves with the local Norman lords and seigneurs.
The Lower Canada Rebellion arose in 1837-1838 due to the Château Clique oligarchy (an alliance of Anglo-Scottish industrialists and French noble landowners), in Quebec refusing to grant legislative power to the French Canadian majority. The rebellion was not solely a French Canadian effort; to the chagrin of both chauvinistic Anglo-Canadians and French Canadians, who in recent years believed it was either a brutal crackdown on French degeneracy, or a heroic class struggle of French peasants against an oppressive Anglo elite. It included figures like Wolfred Nelson, an Anglo-Quebecer who personally led troops into battle.
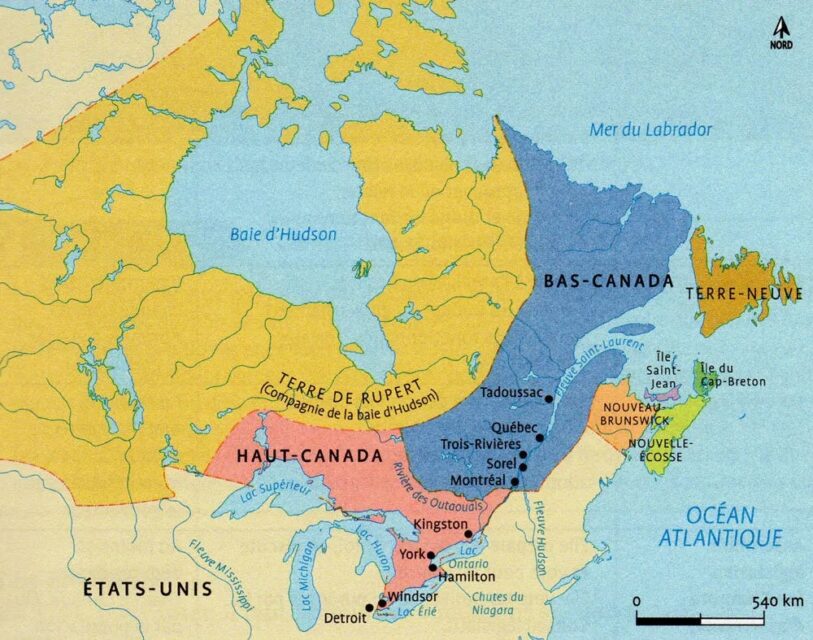
In response to the unrest following the rebellions of 1837-1838, Lord Durham, a British noble, was sent to Canada to investigate and propose solutions. His controversial recommendation, outlined in the Durham Report of 1839, was to abolish the separate legislatures of Upper Canada (Ontario) and Lower Canada (Quebec) and merge them into a single entity: the Province of Canada. This unification aimed to demographically and culturally assimilate the French Canadian population by creating an English-speaking majority.
However, the strategy failed for multiple reasons, and was given up shortly after. Lord Durham, having neither been born nor raised in the New World, underestimated the complexities of Canadian society, which was a unique fusion of Old World ideas in a New World setting. His assumption that French Canadians could be assimilated ignored their strong cultural identity, rooted in large families, which encouraged high birth rates as a means of survival. While Durham hoped unification would erode divisions, the old grievances between the British and French began to dissipate naturally.
Despite Lord Durham’s intentions, French Canadians maintained their dominance in Quebec. Families averaged five children per household for over 230 years, a trend actively encouraged by the Catholic Church’s policy of La Revanche des Berceaux (the Revenge of the Cradles). This strategy aimed to preserve French Canadian culture and identity amidst the British short-lived attempts at assimilation. In Montreal, British industrialists expanded their influence by forging alliances with French landowning nobles through business partnerships and intermarriage. This blending of elites produced a bilingual Anglo-French upper class that became historically influential.
Such alliances drew on long-standing connections established as early as 1763 and later exemplified by the North West Company (NWC). The NWC in particular is interesting as a prominent fur trading enterprise of the late 18th and early 19th centuries, in that it embodied this fusion of cultures. Led primarily by Anglo-Scots, the company’s leaders frequently formed unions or marriages with French Canadian women, fostering vital ties with the French Canadian communities crucial to their trade. Simon McTavish, known as the “father” of the NWC, maintained alliances with French Canadian families, while his nephew, William McGillivray, and other leaders like Duncan McGillivray followed similar paths. Explorers such as Alexander MacKenzie and David Thompson married French women. These unions strengthened familial and cultural bonds, shaping the broader Anglo-French collaboration that defined this period.
This relative harmony between Anglo and French Canadians continued with the formation of the modern Canadian state in 1867 during Confederation. Sir John A. Macdonald deliberately chose George-Étienne Cartier as his second-in-command. This collaboration contributed to the emergence of Canada’s ethnically Anglo-French elite, who have historically been bilingual. This legacy is evident in the backgrounds of many Canadian politicians, such as the Trudeaus, Mulroneys, Martins, Cartiers, and countless others who have both Anglo-Canadian and French-Canadian roots.
In more recent history, this dynamic has been further solidified by the federal government, where higher-paid positions often require bilingual proficiency. Interestingly, about 20% of Canada’s population is bilingual, reflecting the ongoing influence of this historical coexistence.
The last cannon which is shot on this continent in defence of Great Britain will be fired by the hand of a French Canadian.
~ George Etienne Cartier
December 6, 2024
Victoria’s Canada through the eyes of British visitors
In UnHerd, Michael Ledger-Lomas considers what earlier British visitors to Canada after Confederation wrote about their experiences:
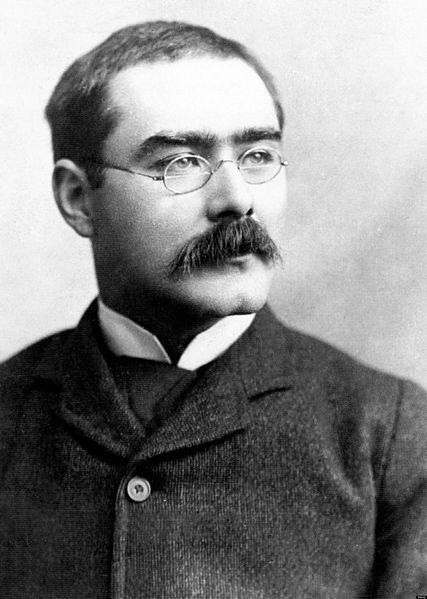

Portrait of Rudyard Kipling from the biography Rudyard Kipling by John Palmer, 1895.
Photo via Wikimedia Commons.
… The re-election of Donald Trump, who has already daydreamed about turning Canada into his 51st state, might even rekindle Tory patriotism. After all, their Victorian ancestors created the dominion of Canada in 1867 to keep British North America from the clutches of the United States.
A longer view shows that Canada has allured but also vexed British observers ever since its creation. The Edwardian era produced an especially rich crop of writings on Canada. In 1887, the year of Queen Victoria’s Golden Jubilee, the first train from Montreal pulled into Vancouver. This completion of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) had persuaded the Crown colony of British Columbia to join in the new federation. In expanding Canada, the CPR also made it easier for British people to see the country. Having crossed from Liverpool to Montreal on a fast liner, they could visit most of its major cities, which were found on or near the railway.
Literary celebrities did so in enviable conditions. The CPR’s bosses loaned the poet Rudyard Kipling his own carriage in 1907, so he could travel in comfort and at his own speed. His impressions, which appeared in newspapers and then as Letters to the Family (1908), make for particularly resonant reading today. Although a man of strong prejudices, he had seen the country up close, rather than merely retweeting allegations about it, and was prepared to be surprised as well as disappointed by it.
Kipling’s contemporaries travelled with heavier and very different ideological baggage than we carry today. It was not wokery that worried them, but irreligion and greed, two poisons that had crept north from America. When the clergyman Hensley Henson steamed into Vancouver, in July 1909, he was horrified to see its beaches plastered with “vulgar advertisements”. The further [East] he travelled, the worse things became. The Anglican clergy were “weaklings” who made no dent on a materialistic society. Winnipeg was given over to “graft”. Young people in Ontario spoke like gum-chewing Yankees. Quebeckers were despoiling their province by setting up hydroelectric dams on its waterfalls.
Kipling did not share Henson’s churchy desire to scold his Canadian hosts. He was a cheerful freethinker who considered materialism a necessary part of nation-building. Canada had “big skies, and the big chances”: he admired its railway workers and lumberjacks for their insouciant and sometimes drunken swagger. Boom towns like Winnipeg excited him: he loved to see office blocks rise and streets flare with natural gas lamps; he lost considerable sums speculating on Vancouver real estate.
What worried him was rather Canada’s fading strategic commitment to the Empire. The modern Right understands Canada as a battleground for the values of “the West”. Kipling, who had married an American and lived for some years in Vermont, naturally believed in and did much to formulate the fervent if vague sense that English-speaking peoples share a civilisation. Yet this did not weaken his overriding concern for the political cohesion of the British Empire. Canada’s failure to join as enthusiastically in Britain’s recent war against the rebellious Dutch Boers of South Africa as he would have liked weighed on him — so much so that he kept calling the prairie the “veldt”. Kipling regarded the scepticism of Liberals and Socialists at home about whether the Empire offered value for money as a “blight”: now this “rot” seemed to be spreading like Bubonic plague, “with every steamer” to Canada.
The way to draw the dominion back to the motherland was to fill it with English settlers who shared his distaste for domestic Socialism. The dilution of English Canada worried Kipling. He allowed the Francophone Catholics of Quebec their differences — he found their basilicas romantic — but the policy of settling the prairies with hardy Slavs from the Habsburg and Russian Empires appalled him. These “beady-eyed, muddy-skinned, aproned women, with handkerchiefs on their heads and Oriental bundles in their hands” could never assimilate to English Canada. Nor did he care that many were fleeing oppression: people who renounce their country have “broken the rules of the game”.
November 24, 2024
How Newfoundland and Labrador lost their independence
Geography By Geoff
Published Jul 16, 2024Did you know that Newfoundland and Labrador were once an independent country in the same manner as Canada was? It’s true! It was called the Dominion of Newfoundland and due to a series of unfortunate events, it had to relinquish its independence. In today’s video, we cover the vast geography of the province, it’s very old history (including Vikings!) and how the country managed to lose its independence when it managed to survive on its own for decades. Oh … and we’ll also talk about why Labrador got included in the name upon confederating with Canada.
(more…)
November 17, 2024
Contrasting origin stories – the 13 Colonies versus the “Peaceful Dominion”
At Postcards From Barsoom, John Carter outlines some of the perceived (and real) differences in the origin stories of the United States and Canada and how they’ve shaped the respective nations’ self-images:

The US had plans to invade Canada that were updated as recently as the 1930s (“War Plan Crimson”, a subset of the larger “War Plan Red” for conflict with the British Empire). Canada also had a plan for conflict with the US, although it fell far short of a full-blooded invasion to conquer the US, designated as “Defence Scheme No. 1”, developed in the early 1920s.
In perennial contrast to its tumultuous southern neighbour, Canada has the reputation of being an extremely boring country.
America’s seeds were planted by grim Puritans seeking a blank slate on which to inscribe the New Jerusalem, and by aristocratic cavaliers who wanted to live the good life while their slaves worked the plantations growing cash crops for the European drug trade. The seeds of America’s hat were planted by fur traders gathering raw materials for funny hats.
America was born in the bloody historical rupture of the Revolutionary War, casting off the yoke of monarchical tyranny in an idealistic struggle for liberty. Canada gained its independence by politely asking mummy dearest if it could be its own country, now, pretty please with some maple syrup on top.
America was split apart in a Civil War that shook the continent, drowning it in an ocean of blood over the question of whether the liberties on which it was founded ought to be extended as a matter of basic principle to the negro. Canada has never had a civil war, just a perennial, passive-aggressive verbal squabble over Quebec sovereignty.1
America’s western expansion was known for its ungovernable violence – cowboys, cattle rustlers, gunslingers, and Indian wars. Canada’s was careful, systematic, and peaceful – disciplined mounties, stout Ukrainian peasants, and equitable Indian treaties.
Once its conquest of the Western frontier was wrapped up, America burst onto the world stage as a vigorous imperial power, snatching islands from the Spanish Empire, crushing Japan and Germany beneath the spurred heel of its cowboy boot, and staring down the Soviet Union in the world’s longest high-stakes game of Texas Hold’Em. Canada, ever dutiful, did some stuff because the British asked nicely, and then they went home to play hockey.
America gave the world jazz music, rock and roll, and hip-hop; Canada contributed Celine Dion and Stan Rogers. America has Hollywood; Canada, the National Film Board and the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. America dressed the world in blue jeans and leather jackets; Canadians, flannel and toques. America fattened the people with McDonald’s; Canada burnt their tongues with Tim Horton’s, eh.2
The national stereotypes and mythologies of the preceding paragraphs aren’t deceptive, per se. Stereotypes are always based in reality; national mythologies, as with any successful mythology, need to be true at some level in order to resonate with the nations that they’re intended to knit together. Of course, national mythologies usually leave a few things out, emphasizing or exaggerating some elements at the expense of others in the interests of telling a good story. Revisionists, malcontents, and subversives love to pick at the little blind spots and inconsistencies that result in order to spin their own anti-narratives, intended as a rule to dissolve rather than fortify national cohesion and will. Howard Zinn’s People’s History of the United States is a good example of this kind of thing, as is Nikole Hannah-Jones’ tendentious 1619 Project.
Probably the most immediately obvious difference between Americans and Canadians is that Americans don’t suffer from a permanent identity crisis. Demographic dilution due to decades of mass immigration notwithstanding, Americans by and large know who they are, implicitly, without having to flagellate themselves with endless introspective navel-gazing about what it means to be an American. The result of this is that most American media isn’t self-consciously “American”; there are exceptions, of course, such as the occasional patriotic war movie, but for the most part the stories Americans tell are just stories about people who happen to be American doing things that happen to be set in America. Except when the characters aren’t American at all, as in a historical epic set in ancient Rome, or aren’t set in America, as in a science fiction or fantasy movie. That basic American self-assurance in their identity means that Americans effortlessly possess the confidence to tell stories that aren’t about America or Americans at all, as a result of which Hollywood quietly swallowed the entire history of the human species … making it all American.
As Rammstein lamented, We’re All Living in Amerika …
Since we’re all living in Amerika, the basic background assumptions of political and cultural reality that we all operate in are American to their very core. Democracy is good, because reasons, and therefore even de facto dictators hold sham elections in order to pretend that they are “presidents” or “prime ministers” and not czars, emperors, kings, or warlords. Insofar as other countries compete with America, it’s by trying to be more American than the Americans: respecting human rights more; having freer markets; making Hollywood movies better than Hollywood can make them; playing heavy metal louder than boys from Houston can play it. It’s America’s world, and we’re all just along for the ride.
America’s hat, by contrast, is absolutely culturally paralyzed by its own self-consciousness … as a paradoxical result of which, its consciousness of itself has been almost obliterated.
Canada’s origin – the origin of Anglo-Canada, that is – was with the United Empire Loyalists who migrated into the harsh country of Upper Canada in the aftermath of the Revolutionary War. As their name implies, they defined themselves by their near-feudal loyalty to the British Crown. Where America was inspired by Enlightenment liberalism, Canada was founded on the basis of tradition and reaction – Canada explicitly rejected liberalism, offering the promise of “peace, order, and good government” in contrast to the American dream of “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness”.
1. Quebec very nearly left the country in a narrow 1995 referendum in which 49.5% of the province’s population voted to separate. It is widely believed in Anglo Canada that had the rest of the country been able to vote on the issue, Quebec would be its own country now.
2. Well actually a Brazilian investment firm has Timmies, but anyhow.
July 2, 2024
April 11, 2024
All the ways A few of the ways Canada is broken
In The Line, Andrew Potter outlines some of the major political and economic pressures that prompted the formation of the Dominion of Canada in 1867, then gets into all the ways some of the myriad ways that Canada is failing badly:
It is useful to remember all this, if only to appreciate the extent to which Canada has drifted from its founding ambitions. Today, there are significant interprovincial barriers to trade in goods and services, which add an estimated average of seven per cent to the cost of goods. Not only does Canada not have a free internal market in any meaningful sense, but the problem is getting worse, not better. This is in part thanks to the Supreme Court of Canada which continues its habit of giving preposterously narrow interpretations to the clear and unambiguous language in the constitution regarding trade so as to favour the provinces and their protectionist instincts.
On the defence and security front, what is there to say that hasn’t been said a thousand times before. From the state of the military to our commitments to NATO to the defence and protection of our coasts and the Arctic to shouldering our burden in the defence of North America, our response has been to shrug and assume that it doesn’t matter, that there’s no threat, or if there is, that someone else will take care of it for us. We live in a fireproof house, far from the flames, fa la la la la. Monday’s announcement was interesting, but even if fully enacted — a huge if — we will still be a long way from a military that can meet both domestic and international obligations, and still a long way from the two per cent target.
As for politics, only the most delusional observer would pretend that this is even remotely a properly functioning federation. Quebec has for many purposes effectively seceded, and Alberta has been patiently taking notes. Saskatchewan is openly defying the law in refusing to pay the federal carbon tax. Parliament is a dysfunctional and largely pointless clown show. No one is happy, and the federal government is in some quarters bordering on illegitimacy.
All of this is going on while the conditions that motivated Confederation in the first place are reasserting themselves. Global free trade is starting to go in reverse, as states shrink back from the openness that marked the great period of liberalization from the early 1990s to the mid 2010s. The international order is becoming less stable and more dangerous, as the norms and institutions that dominated the post-war order in the second half of the 20th century collapse into obsolescence. And it is no longer clear that we will be able to rely upon the old failsafe, the goodwill and indulgence of the United States. Donald Trump has made it clear he doesn’t have much time for Canada’s pieties on either trade or defence, and he’s going to be gunning for us when he is returned to the presidency later this year.
Ottawa’s response to all of this has been to largely pretend it isn’t happening. Instead, it insists on trying to impose itself on areas of provincial jurisdiction, resulting in a number of ineffective programs — dentistry, pharmacare, daycare, and now, apparently, school lunches — that are anything but national, and which will do little more than annoy the provinces while creating more bureaucracy. Meanwhile, the real problems in areas of clear federal jurisdiction just keep piling up, but the money’s all been spent, so, shrug emoji.
What to do? We could just keep going along like this, and follow the slow-mo train wreck that is Canada to its inevitable end. That is is the most likely scenario.
November 20, 2020
Quebec makes Canada’s politics really weird
J.J. McCullough
Published 2 Mar 2019Hypocrisies and blind spots stemming from the role played by French Canadians and the French language in Canada’s politics.
FOLLOW ME:
🇨🇦Support me on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/jjmccullough
🤖Join my Discord! https://discord.gg/xQzjBRE
👾Watch me on Twitch! https://www.twitch.tv/jj_mccullough
🇺🇸Follow me on Instagram! https://www.instagram.com/jjmccullough/
🇨🇦Visit my Canada Website http://thecanadaguide.com
August 12, 2020
June 14, 2020
April 19, 2020
In healthcare matters, Confederation is working as intended
Chris Selley on the viewing-with-alarm concerns that we don’t have a single nation-wide standard of care, and why the Swedish approach to the Wuhan Coronavirus epidemic is worth observing closely:

Front view of Toronto General Hospital in 2005. The new wing, as shown in the photograph, was completed in 2002.
Photo via Wikimedia Commons.
Last week, Maclean’s reported on a group of University of Ottawa researchers who had found, to their consternation, that each province offers different advice to people who think they might be showing coronavirus symptoms. “Even in a cross-Canada pandemic as devastating as this, there is not a single, evidence-based Canadian standard of care simply for self-assessment,” the researchers wrote.
It’s strange how many Canadians seem uncomfortable with the most basic design of their country, which is that of a federation. What the U of O researchers find alarming is not just a matter of Canada operating as it was intended to operate, but also a good example of the benefits. Provinces and territories can shape their responses to the needs of their populations. They can learn from each other what works. It’s a living laboratory.
In the same vein, assuming things don’t go catastrophically wrong, we should be thankful that Sweden is sticking to its guns in avoiding a total lockdown. That, too, will provide very useful data in preparation for COVID-the-next.
It is important to realize that lockdowns take a human toll, sometimes fatal, just like coronaviruses (though probably not on the same scale). Emergency room doctors are worried about their lack of business nowadays, the National Post‘s Richard Warnica reported Friday. “Doctors believe … patients who are afraid of contracting COVID-19 are just waiting (to seek treatment) and getting sicker,” Warnica reported. The head of a Vancouver ER department noted that opioid overdose deaths are up, even as his hospital treats far fewer. Are they overdosing alone, whereas before they might have been saved? When we postmortem this pandemic, we will hear about sexual and domestic assaults, suicides and other isolation-related harms. They will need to be weighed against the risks inherent in a less draconian approach.
Sweden’s strategy has been somewhat caricatured. High schools and universities closed; people aged 70 or older were advised to self-isolate; large gatherings ceased. Easter travel was down a reported 90 per cent. More Swedes have reportedly filed for unemployment benefits than during 2008 crash. Restaurants, pubs and cafés remain open, which seems unfathomable to a Canadian. But “it’s a myth that it’s business as usual,” as Sweden’s deputy prime minister Isabella Lovin told the Financial Times this week.