Jago Hazzard
Published 26 Jul 2023The future is slightly dingy.
(more…)
November 15, 2023
The Future of Railways (circa 1961)
November 14, 2023
The deep cognitive dissonance of “Queers for Palestine”
In Quillette, Armin Navabi points out the utter absurdity of a group of self-identified queers actively supporting the terror organization running the Gaza Strip, which would execute as many of them as came within its power:
Leftists in English-speaking nations tend to see Palestinians (including Hamas) as an oppressed, brown victim class, whose freedom-fighting “resistance” against their oppressive, white, US-backed colonizers in Israel is a righteous cause with which to stand in solidarity. This facile view of the long-standing conflict in the Middle East leads to confused and contradictory thinking, as seen in the incoherent slogan (and now meme) “Queers for Palestine“, emblazoned on banners brandished at anti-Israel rallies.
“Queers for Palestine” attempts to meld LGBT advocacy with Palestinian liberation, a juxtaposition that has precipitated a whirlwind of criticism and ridicule, since LGBT rights scarcely exist within the Muslim world; and the Palestinian territories are no exception. The slogan has been widely satirized. Variations like “Chickens for KFC” and “Blacks for the KKK” highlight its proponents’ basic lack of awareness of just how incompatible the values of the Western left are with those of the Islamic right they so readily champion.
The reality of the situation could not be starker. Though there is room for improvement in Israeli attitudes towards these issues, Israel is at the forefront of LGBT rights in the Middle East. In Israel, LGBT people are visible members of society with legal protections and civil rights, and are accepted by a plurality of its citizens.
Palestine is quite a different story. A 2021 report on LGBT acceptance by UCLA’s Williams Institute rated Israel 44th out of the 175 countries/territories they examined. Palestine came in at number 130, behind Russia, Saudi Arabia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Georgetown University likewise placed Palestine 160th out of 170 countries on their women’s peace and security index, in company with most of the countries in that region. Amnesty International‘s 2020 report on human rights highlights the fact that, in Gaza, male same-sex relationships are punishable by up to 10 years’ imprisonment and points out the conspicuous absence of legal protections against anti-LGBT discrimination and harassment. This lack of civil rights has led hundreds of gay and bisexual Palestinians to flee to Israel to escape persecution. One such refugee, Ahmad Abu Marhia, a 25-year-old gay Palestinian man, was living under asylum in Israel when, in 2022, he was kidnapped and beheaded in the West Bank city of Hebron. His murderers uploaded footage of the killing to social media.
Every time these disparities are mentioned, critics are quick to lob accusations of “pinkwashing” — a concept invented to frame any discussion of Israel’s progressive stance on LGBT issues as a distraction from their mistreatment of Palestinians. But the fact remains that these “Queers for Palestine” could march in Pride parades in Israel if they wanted to. In Palestine, they’d be killed.
Another disconcerting element of “Queers for Palestine” is that the slogan popped up in prominent left-wing anti-Israel/pro-Palestine rallies in the immediate aftermath of Hamas’s terrorist attacks, before Israel had even had the chance to respond. There is no way to interpret this slogan and the surrounding leftist fervor except as a signal of support not merely for Palestine, but specifically for Hamas, a jihadist movement with the explicit aim of eradicating the state of Israel. It’s imperative to understand that Hamas, as detailed in its 1988 Covenant, is propelled by a fundamentalist Islamist ideology whose goal is not only to eliminate all Jews but to conquer the world — just like ISIS. Senior Hamas official Mahmoud al-Zahar has stated on record, “The entire planet will be under our law, there will be no more Jews or Christian traitors”.
Western support for Hamas, under the guise of support for Palestinian liberation, betrays an ignorance of the deep-seated radical Islamist ethos driving that organization, which, if left unchecked, would jeopardize the very freedoms cherished by LGBT people across the developed world. Anyone who doubts this should try being gay, bi, or trans in most of the Middle East and North Africa’s (MENA) Muslim-majority countries. Almost all these nations have laws that criminalize both homosexuality and transsexuality, some of which carry the death penalty. Human Rights Watch’s report “Everyone Wants Me Dead” succinctly encapsulates in its title alone the perilous environment faced by LGBT individuals in these regions.
“Like all Luttwak stories, this is probably false but totally believable”
In the latest book review from Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, John Psmith considers Edward Luttwak’s fascinating and controversial The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, a book I quite enjoyed reading although I think his much later The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire one of his best books.
In one of the dozens of notorious interviews of Edward Luttwak that float around the internet, he’s asked how he chose the topic for his PhD dissertation. His answer is that one day at university he had a humiliating social encounter. Immediately afterwards, somebody pounced on him and asked what his dissertation was about anyway. He hadn’t even started thinking about what his topic would be, but he obviously couldn’t say that, and so instead he puffed himself up and made something up on the spot, and he did so by saying the most grandiloquent series of words one at a time like a large language model feverishly choosing the next token to maximize self importance: “The … GRAND … Strategy … … OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE!!” His interlocutor was sufficiently awed and impressed, but then he had to write the damn thing. Like all Luttwak stories, this is probably false but totally believable.1
But I’m very glad he wrote that thesis, because it was later turned into the wonderful book I’m reviewing. Now, one of the ways that the Psmiths subvert traditional gender roles is that it’s Jane, not I, who thinks about the Roman Empire every day. But this is only pretending to be a book about the Roman Empire. It’s really a book about “grand strategy” — how states can efficiently allocate scarce military, diplomatic, and financial resources to counter a variety of internal and external threats. It’s true that the examples are mainly drawn from four centuries of Roman history — starting with the Julio-Claudian dynasty and ending with the Empire losing control of Italy and Western Europe — but the analysis, and the lessons, are abstract enough that they transcend that particular context.
Luttwak believes that the state is a kind of machine for turning arable land into military power via taxation and conscription. A state that wants to maximize its survival odds can do so in three ways: (1) it can increase its “inputs”, by bringing a larger quantity of arable land under its control (so long as it avoids a commensurate increase in the threats it faces); (2) It can increase the efficiency of the machine, by extracting more grain and more labor from the people it rules, or by undertaking internal reforms to reduce the amount of potential that’s bled away by corruption and decadence; or (3) It can use its military as effectively as possible, doing more with less, killing many birds with one stone or setting up situations where a small allocation of force can tie down much larger opponents.
This third option is more or less what Luttwak means by “grand strategy,” and I think it may be the key that ties together all of Luttwak’s writing and thought. What do a book about the ancient world and a book about Cold War era coups have in common? They’re both about doing more with less, economizing force by wielding it with overwhelming brutality and efficiency. Luttwak’s coldly arithmetic view of the state is reminiscent of nothing so much as James C. Scott’s view of the world,2 but Luttwak is on the opposite team. Scott is an anarchist, Luttwak is a hard-boiled realist, and moreover he’s one with a deep aesthetic appreciation for power and violence, especially when used elegantly, like a scalpel, such that they have effects far out of proportion with their quantity.3
The history of Rome that Luttwak wants to tell is not the history of its cultural or civilizational achievements, but rather the history of how these people were so incredibly good at economizing on violence that they were able to waste a huge portion of their military and economic potential on civil wars, but still keep the lights on and the barbarians at bay. “Grand strategy” is how they accomplished that, but the strategy changed as the threats evolved and as the internal condition of the empire deteriorated. Luttwak delineates three distinct epochs — the founding of the empire under the Julio-Claudian dynasty, the rationalization of frontiers under the Antonine emperors, and the Crisis of the Third Century — and argues that each of the three featured a fundamentally different overall strategic posture on the part of Rome.
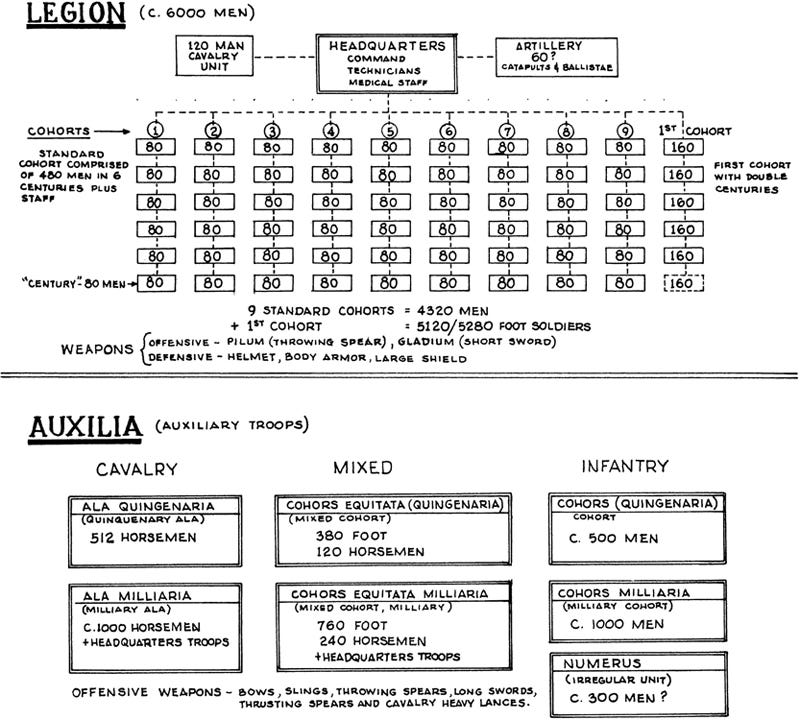
But before we get into all of that, I suppose we ought to talk about the legions. When people think of Roman military power, they usually think of the heavily-armed guys with red cloaks and horsehair plumes on their helmets. But of course they only made up a small fraction of the Roman military. We know that this has to be true because ancient armies, as much as modern armies, relied on combined-arms for their success. A legionary was a very scary kind of soldier, combining the roles of heavy infantry and combat engineer, but an army made up entirely of heavy infantry would be shredded by an opposing force of horse archers, for instance. So the Romans brought many other kinds of troops to bear: skirmishers, slingers, archers, light infantry, cavalry of their own (including mounted archers, light cavalry, and lancers with primitive barding that are a clear precursor of Medieval knights). And … almost to a man, all of these other forces were non-Roman.4 They were either mercenaries, or allied barbarians, or auxiliaries. As a kid in ancient history class I just accepted this as a fact, but reflect on it for a second and it seems very weird. This whole arrangement caused the Romans no end of trouble, so why did they do it that way?
Take the Luttwak pill and it all becomes clear: the Romans went all-in on legionaries as a way of economizing on force. The only people Rome could absolutely rely on were her citizens. The definition of a “real” Roman changed over time — at first it was only inhabitants of the city of Rome itself, later it was expanded to the surrounding countryside, and finally to all of Italy. But at every point it was a tiny fraction of the total population of the empire. Of that tiny fraction, some even smaller fraction are available to be trained as soldiers and to bear arms. What do you want those guys to be doing? The Roman answer is that you want them to be legionaries, because legionaries are not general-purpose soldiers, they’re specialists, and their specialties are: (1) besieging enemy cities, and (2) battles of attrition and annihilation.
1. Evidence that it’s false, he tells a completely different story in a different interview!
“I chose the subject because no theme in contemporary strategy was anywhere as interesting as the simple question of how Rome defended its territories (and added to them, now and then). Also, I did not want to waste my days reading the stultified & chaotically duplicative literature of ‘political science’ in which Strategy is imprisoned, when I could read instead in the often elegant, multi-lingual literature of Roman imperial studies.”
2. The zoomed-out, autistic alien robot anthropologist nature of this analysis also reminds me a bit of Vaclav Smil.
3. Wouldn’t the most elegant use of power be its deployment in such a way that it doesn’t really have to be used at all? In fact this is the main theme of Luttwak’s most recent book, The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire, a sort of sequel to this one. In the same interview as in the first footnote, Luttwak summarizes the argument of that book: Byzantine strategy was based on:
“a single, paradoxical, principle: do everything possible to raise, equip and train the best possible army and navy, and then … do everything possible to use them as little as possible … every alternative was to be tried to avoid, or at least minimize the destructive ‘attrition’ combat of main forces. Instead, potential enemies were to be dissuaded, bribed, subverted, weakened by getting others to attack them, sidetracked into other ventures; if enemy forces attacked nonetheless, they were to be contained and delayed by skirmishing, feints and demonstrations while the search went on for other powers near or far willing to attack or at least threaten the enemy power; if enemy attacks persisted nonetheless, they were to be met by countering maneuvers designed to exhaust them rather than the destructive combat of main forces, the very last resort. It was not only the precious trained manpower of the empire that this strategy wanted to conserve, but also the enemy’s … because today’s enemy could become tomorrow’s ally.
4. This isn’t quite true in every period. For instance during the Punic Wars, the Romans fielded “equites“, native Roman cavalry of their own, but it fell out of fashion pretty quickly thereafter.
Australian voters rejected “The Voice”, fearing “they were being sold a pig in a poke”
Theodore Dalrymple on the recent failure of the Austrialian government to install a nebulous and ill-defined advisory body for Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander representation to Parliament:

Uluru Dialogue co-chair Pat Anderson in an early ad for “The Voice” referendum.
Screen capture from YouTube.
Among my wife’s family papers dating from the Occupation of France are a couple of certificates of aryanité issued to her forebears, that they might continue to be employed and not deported. In Australia, people apply for certificates of aboriginality, in order that they might receive various advantages, subventions, etc.
The former is bad racism, the latter good, at least for those who believe in positive racial discrimination. Unfortunately, it is logically impossible to believe in positive racial discrimination without also believing in the negative kind, irrespective of one’s supposed good intentions.
Australia recently held a referendum on a proposed race-based amendment to the constitution. The amendment proposed something called “The Voice” to be inscribed in the constitution: an advisory body composed of Aborigines who would advise parliament on matters specifically affecting Aborigines. The details of the proposed body — how it was to be chosen or appointed, its purpose, its powers, its duties, its emoluments — were not specified, and those in favour of it, up to and including the Prime Minister, Anthony Albanese, were either unwilling or unable to specify further, relying entirely on the Australian emotional equivalent of Noel Coward’s famous song, “Don’t Let’s Be Beastly to the Germans”. The latter was not much of a policy.
Australian voters, initially favourable to the proposal, rejected it by a large majority, suspecting, rightly in my view, that they were being sold a pig in a poke. They also suspected, I surmise, that what was being proposed was a corrupt and corrupting bureaucratic pork barrel that would reward a small class of Aboriginal Al Sharptons. Far from improving the situation of Australian Aborigines, which is sometimes but not always tragic, the Voice would permanently raise the ideological temperature and prevent measured debate about practical improvements. Benefits would be received without gratitude and, would never, virtually by definition, be sufficient. And of course, the Voice would be the end of the ideal of racial equality. Australia would join the old South Africa in its inscription of race in its constitution.
The abysmal intellectual level of the proponents of the Voice was very well instantiated in an article by Thomas Keneally, the famous Australian novelist, in the Guardian newspaper. It began as follows:
Last Sunday, many in Australia profoundly mourned the loss of the Indigenous voice to parliament referendum, the greatest kindly Amendment ever to be proposed for the Australian constitution, those dreary old articles of association by which our states and territories rub along together in far-flung federation.
I will overlook the use of the word profoundly in this context: I think the words superficially, self-satisfactorily, and exhibitionistically would have been better. But note that, even if the loss were deeply mourned, only the grossest of sentimentalists would claim that such mourning would have any bearing on the rightness or otherwise of the loss that was mourned. Many Nazis and many communists mourned the loss of Nazi Germany and Soviet Russia far more deeply than any Australian mourned the loss of the referendum, but no one, I think, would sympathise with them because of the depth of their sorrow.
Inside T-72: A Commander’s Perspective | Tank Chats Reloaded
The Tank Museum
Published 21 Jul 2023A fast tank with a low profile and a big gun, the T-72 is a classic Soviet designed Main Battle Tank, in use all over the world. In this video, we talk to Dag Patchett, a former T-72 commander and get his impressions of a tank built in the Cold War era but still very much in service.
(more…)
QotD: Don’t bother trying to reason someone out of a position they never reasoned themselves into
Forget political philosophy; that stuff is way down the line. The first thing to do is to counter Leftism’s emotional appeal. For as much as we all recognize that the Left runs on nothing but spite and envy, it’s remarkable how few people really acknowledge this. Trying to reason a fanatic out of his fanaticism is like asking your cat to factor quadratics — not only can’t he do it, he’s not even able to comprehend that you’re asking him to do something. It doesn’t compute.
We’re dealing with emotion, kameraden. Think of your last big fight with your girlfriend, and let me know how well your unassailable facts, your airtight logic, worked out for you.
That’s the reason the old Right (back when that term meant something) lost every fight with the Left. Even when they saw it, they didn’t really grasp it. For instance, there’s a reason I’ve never read a single other word by Henry Hazlitt, though he was a big league public intellectual in his day — he saw, but he didn’t know:
The whole gospel of Karl Marx can be summed up in a single sentence: Hate the man who is better off than you are. Never under any circumstances admit that his success may be due to his own efforts, to the productive contribution he has made to the whole community. Always attribute his success to the exploitation, the cheating, the more or less open robbery of others. Never under any circumstances admit that your own failure may be owing to your own weakness, or that the failure of anyone else may be due to his own defects – his laziness, incompetence, improvidence, or stupidity.
That’s the best definition of “Leftism” ever penned. It describes Social Justice Warriors perfectly, though it was written in 1946. And still Hazlitt, like all his brethren on the Right, still kept trying to reason Leftists out of their Leftism.
Severian, “Crossing the Bar”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-04-06.
November 13, 2023
Lessons for Canada from the Australian referendum on “The Voice”
Conrad Black contrasts the experiences of First Nations in Australia and Canada after contact with European explorers and settlers and the recent attempt to create a formal role for Aboriginal representation in the Australian Parliament.

Uluru Dialogue co-chair Pat Anderson in an early ad for “The Voice” referendum.
Screen capture from YouTube.
Canadians should perhaps pay more attention than we have to the referendum in Australia on Oct. 14 on the subject of the Aboriginal peoples. There are just under one million designated Aboriginals in Australia, slightly below four per cent of Australia’s 25 million people. The roughly corresponding figures in Canada are that Indigenous Canadians, including in both countries a good number of mixed ancestry, are slightly under five per cent — just, at under two million in a population of 40 million. The issue in the referendum was a proposed amendment to the Australian Constitution by which a federal advisory body comprised of native people would be set up which would have only a consultative role. How this body would be selected and its recommendations presented would be dealt with later. The idea was just to give Aboriginal people, in the wording of the referendum, a “voice” in the politics of the country.
The history of the white settlers of Australia and the natives whom they encountered there is fairly parallel to the Canadian experience. Initial contact was friendly enough, but there was a native vulnerability to certain diseases to which the Australian natives had had no occasion to develop an immunity. Their lands were gradually encroached upon although the inconvenience to them was for a time not as great as it was in Canada where the conversion of huge tracts of arable land on the prairies into immensely productive grain producing farms made it steadily more difficult for our native people to maintain that part of their diet based on the buffalo. Australian Aboriginals had less difficulty, at least for some time, retreating to places that did not especially attract the settlers, and where it was comparatively possible to maintain a traditional life.
However, there was soon inevitably interaction, some of it successful intermarriage, and some of it outright racial friction with not infrequent outbursts of violence, though nothing on the scale of the Riel rebellions in this country, let alone the outright warfare of the American Indian Wars. But eventually, reservations were created for some Australian Aboriginals. In contrast to this country, there was practically no attempt to help formally educate them or to assist them in integrating into the larger Australian society. They were gradually pushed to the nether regions of the immense country, almost as large as Canada and with a greater habitable area, and the provision of health and education services to the natives was greatly less generous in the amounts of money and numbers of personnel involved than the corresponding efforts in Canada.
Gradually the theory developed and took hold in Australia that perhaps the early settlers and the autonomous government of Australia created by the British in 1901, could have been more generous and thoughtful. As these matters tend to do, the issue gnawed somewhat at the conscience of white Australia and finally in 2008, the government of Australia passed through both houses of its Parliament an apology and expression of regret for past injustices. There was nothing remotely like the orgy of self-defamatory penitence backed by stupefying amounts of money that has flowed in this country like the Niagara River onto the native people.
Shortly after the new Labor government in Australia was elected in 2022, it proceeded with its declared intention to hold a referendum on the issue of giving the Aboriginal peoples a “voice”. And soon after this campaign began, it became clear that the proposed measure was going to have a rocky ride with the country. The predominant opinion among Australians above the age of 45 was that the native had the opportunity to participate fully in Australian life and that there were some substantial gestures of assistance made to them that the more purposeful native people took up.
Winners and losers of the “sexual revolution”
Janice Fiamengo missed her trip to London this week due to illness, so she also missed a panel discussion at the ARC (Alliance for Responsible Citizenship) Conference that raised her ire:
On the subject of widespread sexual promiscuity, family breakdown, and fatherless homes, pundits Jordan Peterson, Louise Perry, Mary Harrington, and Stephen Blackwood carefully ignored the hulking feminist elephant in the room, arguing that the primary victims of the sexual revolution have been women (and children as well, as something of an afterthought). The primary beneficiaries have been a few psychopathic men who have left a trail of broken hearts and rudderless children in their wake. It’s a convenient thesis in a culture terminally averse to criticizing women, but it avoids some important facts.
The whole discussion, actually, begins from a false premise. If there was ever a sexual revolution in which we all simply consented to do what we wanted sexually, as Louise Perry claimed, that revolution ended over 30 years ago when Anita Hill complained before a Senate Judiciary Committee that Clarence Thomas, former chair of the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, should not be confirmed as a Supreme Court Justice because he had once joked to her about a pubic hair floating on his Coke. At that point, the alleged sexual vulnerability of women, whose sensitive ears must not be subject to comments by male colleagues about pornography or penis size — and the need for legislation to protect and accommodate them at the expense of male freedom of expression — reasserted itself with a vengeance. The feminist claim that women merely wanted equal rights and an end to sexual double standards was exposed as a feeble lie.
Sexual harassment legislation soon made it a potential firing offence for a man to make a female workmate uncomfortable, whether by standing too close, looking too intently, or making the wrong joke or comment. Later, the #MeToo movement proclaimed it righteous that any man who had ever been sexual with any woman (or even just any man, who didn’t even have to know the woman smearing his name) could be accused of sexual misconduct, fired from his job, and permanently disgraced (the DAMN Handbook contains an extraordinary list of celebrity men destroyed by allegations in 2017 alone; see pp. 8-17). Free love, if it ever existed, has been dead for a long time, and some of the same women who cheered on the idea of sexual freedom were the ones who killed it.
But #MeToo, false allegations, the ever-expanding territory of sexual misconduct, and the anti-male tenor of nearly every public discussion about sex—these were emphatically not the focus of the ARC panel, which zeroed in on female sexual victimization. The goals that countless women have proclaimed necessary—sexual freedom, abundant birth control, single motherhood—were criticized as harms for women. We heard that the medium to long-term well-being of women and children has been sacrificed to the short-term gratification of a minority of men; and that these men also tend to be, according to Peterson, possessed of psychopathic, Machiavellian, narcissistic, and sadistic tendencies. Amongst the fallout are the 50% of British children raised in homes without fathers.
It was stirring stuff, certainly, though not exactly a new proposition. Radical feminists like Sheila Jeffries have long argued (in her book Anticlimax: A Feminist Perspective on the Sexual Revolution and elsewhere) that the sexual revolution merely affirmed and updated the victimization of women by men while conservative non-feminists like Phyllis Schlafly pointed out how feminist policies and laws have disadvantaged women.
Yet even those of us without doctorates in psychology might wonder how it could be true that so many women have been the innocent and unwitting victims of men even when they themselves chose those men. Are there not women who engage in abundant casual sex with as much blithe indifference as the men; some of them too psychopathic, narcissistic, Machiavellian and cruel? Why have so many women over the years championed the loosening of sexual mores — including the availability of abortion, never mentioned by any of the panelists — if it was not in their own best interests to do so?
Or are these panelists saying that women cannot be trusted to know their own best interests and those of their children? Why do so many women continue to embrace sexual hedonism, abortion, and divorce? In reality, the epidemic of fatherlessness, as nobody on the panel was interested in exploring, is not the result of the sexual revolution per se, but was made possible specifically by the rise of no-fault divorce and child support laws that, in feminist-compliant family courts, made it highly attractive for women to discard their husbands while still living off his earnings (divorce is today initiated by women in about 70% of cases, and is one of the major reasons so many young men today are averse to marriage). It may well be that nobody’s long-term well being is served by this reality, but it is what women have been choosing with their eyes wide open for many years, and it is a bit rich now to pretend it was something done to them without their consent.
Carefully trained and shaped hollow people
At Ricochet, David Foster talks about how today’s university students have become … hollow:
I’ve been writing for years about the rise of toxic ideologies on America’s college campuses – totalitarian, anti-Israel, outright anti-Semitic – but still have been surprised by what has happened in these places since October 7. We need to discuss the reasons why it’s gotten so bad.
A few days ago, someone republished an essay, written in 2016, by a professor who has taught at several “elite” colleges. Excerpt:
My students are know-nothings. They are exceedingly nice, pleasant, trustworthy, mostly honest, well-intentioned, and utterly decent. But their brains are largely empty, devoid of any substantial knowledge that might be the fruits of an education in an inheritance and a gift of a previous generation. They are the culmination of western civilization, a civilization that has forgotten nearly everything about itself, and as a result, has achieved near-perfect indifference to its own culture. It’s difficult to gain admissions to the schools where I’ve taught – Princeton, Georgetown, and now Notre Dame. Students at these institutions have done what has been demanded of them: they are superb test-takers, they know exactly what is needed to get an A in every class (meaning that they rarely allow themselves to become passionate and invested in any one subject); they build superb resumes. They are respectful and cordial to their elders, though easy-going if crude with their peers. They respect diversity (without having the slightest clue what diversity is) and they are experts in the arts of non-judgmentalism (at least publically). They are the cream of their generation, the masters of the universe, a generation-in-waiting to run America and the world.
And when someone has devoted the first 18 years of their lives in large part to jumping through hoops in hopes of making a good impression on some future college admissions officers … and then, in many cases, having to get good ratings from professors whose criteria are largely subjective … that someone is unlikely to develop into a person with a strong internal gyroscope. Quite likely, they are likely to be subject to social pressures and mass movements.
Someone at X said that the Cornell student arrested for making threats against Jewish students was probably just trying too hard to fit in and win approval of his peers and took it a step too far. My view is that there’s no just about it … the desire to fit in and win approval is very often the reason why people commit evil acts. I’m reminded of something CS Lewis said: “Of all the passions, the passion for the Inner Ring is most skillful in making a man who is not yet a very bad man do very bad things“.
The above sentence is from a talk that Lewis gave at King’s College in 1944. Also from that address:
And the prophecy I make is this. To nine out of ten of you the choice which could lead to scoundrelism will come, when it does come, in no very dramatic colours. Obviously bad men, obviously threatening or bribing, will almost certainly not appear. Over a drink, or a cup of coffee, disguised as triviality and sandwiched between two jokes, from the lips of a man, or woman, whom you have recently been getting to know rather better and whom you hope to know better still — just at the moment when you are most anxious not to appear crude, or naïf or a prig — the hint will come. It will be the hint of something which the public, the ignorant, romantic public, would never understand: something which even the outsiders in your own profession are apt to make a fuss about: but something, says your new friend, which “we” — and at the word “we” you try not to blush for mere pleasure — something “we always do”.
And you will be drawn in, if you are drawn in, not by desire for gain or ease, but simply because at that moment, when the cup was so near your lips, you cannot bear to be thrust back again into the cold outer world. It would be so terrible to see the other man’s face — that genial, confidential, delightfully sophisticated face — turn suddenly cold and contemptuous, to know that you had been tried for the Inner Ring and rejected. And then, if you are drawn in, next week it will be something a little further from the rules, and next year something further still, but all in the jolliest, friendliest spirit. It may end in a crash, a scandal, and penal servitude; it may end in millions, a peerage and giving the prizes at your old school. But you will be a scoundrel.
So yes, the passion for approval has always existed. But I feel sure it is much stronger, or at least has fewer countervailing forces, among people who experience today’s college admissions race and its eventual fulfillment.
The students about whom the professor wrote in the essay linked above have not only been encouraged to devote their time to hoop-jumping, they have also been told again and again that their country and their society are evil – that their ancestors were evil, and their parents are probably evil as well. And that practically all aspects of culture more than five years old, whether traditional songs and folktales or classic movies, are harmful and certainly unworthy of study except for purposes of deconstructing their bad examples. And, of course, relatively few of these students are influenced by or have seriously studied any traditional religion.
Krešimir: Croatia’s Truly Insane Grenade Launcher
Forgotten Weapons
Published 17 Jul 2023The Krešimir is honestly the most bonkers weapon I have come across in a long while. Made by IM Metall in Croatia at the beginning of the Croatian Homeland War circa 1991, this is a semiautomatic grenade launcher. Most grenade launchers fire a big cartridge with an explosive warhead, but not this thing. Instead, it uses a 5-round magazine of M50 hand grenades with percussion fuses. A second magazine holds 7.62x39mm grenade-launching blank cartridges. Pulling the trigger drops two strikers in succession; one to ignite the hand grenade fuse, and then one to fire the launching cartridge. What could possibly go wrong?
When you do fire, the recoil cycles the whole barrel and bolt backwards like a long recoil action, although it appears to be blowback and not locked. This loads a fresh grenade in the barrel and leaves it ready to fire again with the next trigger pull. We don’t know how many of these insane creations were actually made, but I have multiple reports of their actual wartime use from veterans of the conflict.
Thanks to the Sisak Municipal Museum for giving me access to film this!
(more…)
QotD: The “queering-the-museum” movement
The so-called queering-the-museum movement, which was launched in Amsterdam in 2016, is all about contemporary identity politics. It rests on the assumption that museum curation is too “heteronormative”. By queering museum collections, activist curators claim they are including and representing gay and gender non-conforming people.
That at least is the objective. But the actual result is an exercise in narcissism. It turns the past into little more than a mirror reflecting the identitarian obsessions of the present back at us. It tells us less than nothing.
And no wonder. Understanding the past through a “queer” prism is profoundly ahistorical. In the 1500s, “queer” didn’t mean what it does today. It meant “strange, peculiar, odd or eccentric“, and had nothing to do with sexual or gender identity at all. Queer only started to be used as a term for gay men at the turn of the 20th century. And “queer studies” was not named as such until the mid-1990s. Viewing the Mary Rose collection through a “queer” lens is to obscure its historical specificity.
It’s not just the Mary Rose Museum that has succumbed to the cult of queer theory, either. Even more bizarrely, the British Library claimed during Pride month this year that the animal world can be viewed through a queer lens. And so Britain’s national centre of knowledge and learning staged events “celebrat[ing] nature in all its queerness”. In particular, it focussed on animals whose sexual behaviour breaks free from standard “gender roles”, from bisexual penguins and lesbian albatrosses to gender-bending fish. “[Researchers’] discoveries”, stated a press release, “show that animal sexuality is far more diverse than we once thought and has been limited by narrow human stereotypes of heterosexuality, monogamy and gender roles”.
This is obviously absurd. Animals do not experience or possess a sense of identity, sexuality or gender. For a fish to “bend” gender it would need to understand what gender is and how to subvert it – quite an achievement for a creature with a five-second memory recall.
Applying “queer” models to the animal world in this way does a disservice not just to our knowledge of animals, but also to our understanding of humans. Non-human animals aim to remain alive and comfortable and propagate their species. Human sex and sexual identity goes far beyond mere survival and comfort. While there may be many interesting reasons why two female penguins pair off, we can be certain that a sense of lesbian self-identity is not one of them.
As the cases of the Mary Rose Museum and the British Library show, queer methodology does not help us to understand history or nature. This is hardly a surprise. Applying a queer lens to species or epochs where it has no place simply exposes the banality of queer theory. It sees nothing but its own reflection. This narcissistic endeavour is now posing a threat to knowledge itself.
Ann Furedi, “The narcissism of queer theory”, Spiked, 2023-08-12.
November 12, 2023
The Futile Fight in Hurtgen Forest – WW2 – Week 272 – November 11, 1944
World War Two
Published 11 Nov 2023The struggle for Hurtgen forest, one tiny piece at a time, continues. The Allies have, however, secured Walcheren Island, and also launch Operation Queen to try and reach and cross the Roer River, and further south even launch a new offensive aiming for Metz. Things are not going well for the Americans on Leyte, though, but they’re even worse for the Chinese as both Guilin and Liuzhou fall to the Japanese. As for the Soviets, they are busy making big plans for a gigantic offensive to drive in to Germany when the new year comes.
(more…)
The most dangerous man in the world?
Elizabeth Nickson on Daniel Jupp’s new biography of Bill Gates, Gates of Hell: Why Bill Gates is the Most Dangerous Man in the World:
A new book, Gates of Hell: Why Bill Gates Is the Most Dangerous Man in the World by Daniel Jupp, manages to dissect all of Gates’s activities since September 2011 and has he ever been a busy psychopath. Jupp is one of the several gifted polemicists called forth by the gnarly times we live in. He soared to recognition with witty, but somehow soothing Facebook blasts that combined PJ O’Rourke with Jonathan Swift with Steve Bannon. Everyone passed around his posts exulting. Jupp, if that is his real name, hails from working class England, Essex to be precise-ish, and edits or writes for Country Squire Magazine. Whatever, he is of the time and do we ever need him.
Jupp in Gates of Hell is careful. He does not risk libel, not even a whiff of it. And in contrast to his usual oxygen-rich posts, he is measured, calm, working with a surgeon’s focus, as he peels back the PR, the methodology, the results, the hiding of the malign results, the cantering on to the next heady task as the ultimate white Saviour. Unfortunately, as Jupp describes, Gates is not quite as simple as that. He also changes law, dictates policy in far too many countries where he does not belong, buys all the media, and every politician he can. When he calls, the Great and the Good come to sit in his Presence and be lectured to in that stickily sentimental tone about his noble purpose. When he makes a mistake, and almost everything he does is a mistake, he spends several hundred million dollars buying desperate legacy media and every functional PR firm to cover it up.
Gates’s life changed when his practice of turning competitors to scorched earth, thereby crippling innovation in the digital world, resulted in an embarrassing court case. The sullen, nit-picking slug on trial, radiating contempt is, I suspect, the real Gates, or his shadow self, very much like Gollum in LOTR defending his Precious. Jupp skates by the many charges of sexual abuse, but points out that he formally left Microsoft after one of them became too big to ignore.
Gates then constructed his new self. He married, not a babe, but a substantive character, and had three children in quick succession. He hired the most expensive fixers and PR, and built himself an avuncular sweater-clad persona. He was going to give away his massive fortune, give back to the people from his incredible privilege.
In the ensuing years, that fortune doubled and then doubled again.
That’s because he met Jeffrey Epstein. While Epstein’s sexual activities have received 90% of the attention, his activities during the last years of the Clinton administration are the more significant. First of all, Epstein was running an entrapment scheme for various covert agencies, which made his insinuation into government easy. At the same time, he taught high-level government officials, cabinet ministers, heads of agencies, and the great larcenous dame herself, Hillary Clinton, how to steal. It was a pincer movement. Having second thoughts? Here’s a video of your encounter with a fourteen year old.
I’ll make it super simple: he taught these people, and they weren’t all Democrats, how to stand up a policy meant to benefit the least advantaged, like for instance access to the housing ladder, and then profit off it. Since then every government initiative has carved out for its progenitor, a fortune. His first, of course, was Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae and James Johnson who ran these agencies into deep bankruptcy, collapsed the ’08 economy, nevertheless walked away with $100 million from a government job. Wall Street Journal reporter, Gretchen Morgenson’s Reckless Endangerment covers the waterfront here.
“When I use a word … it means just what I choose it to mean”
Andrew Sullivan on how our “elites” now live in a world that the renowned Oxford academic Charles Lutwidge Dodgson1 predicted in his writings a century and a half ago:

“Israeli flag, Tel Aviv, Star of David” by Tim Pearce, Los Gatos is licensed under CC BY 2.0 .
The word “genocide” may be the one rendered most meaningless in our discourse. It has some steep competition, of course. “White supremacy” now means asking someone to show up on time. “Trauma” means being referred to with the wrong pronoun. And “genocide” can, among other things, mean debating experimental sex reassignment procedures for children. (Go look up #transgenocide on Twitter and weep.)
But the supporters of Hamas and of the Palestinians have seized the g-word with particular zeal. And who can blame them? There’s a real, adolescent frisson in accusing the victims of the worst genocide in modern history of being genocidal themselves. “Israel, we charge you with genocide” is a common chant in many of the pro-Palestinian protests. “Genocide Joe” has been trending on Twitter. Eight hundred artists signed an open letter calling the Israeli counteract in Gaza “a genocide”. Yale professor Zareena Grewal channeled much of the “decolonizing” left: “Israeli [sic] is a murderous, genocidal settler state and Palestinians have every right to resist through armed struggle”.
It’s not just the activists. Congresswoman Tlaib has accused Biden of “funding Netanyahu’s genocide”, and said “We are literally watching people commit genocide” — referring to the blast next to a Gaza hospital caused by a Hamas rocket. Congresswoman Omar retweeted a photo of dead kids with the caption “CHILD GENOCIDE IN PALESTINE” — but the photo was from a 2013 chemical weapons attack in Syria. A State Department official tweeted that Biden is “complicit in genocide”. A UN official just quit his post, adding:
In just 4 weeks, Israel with US backing has cut off food, water, power & then brutally exterminated more than 10,000 imprisoned civilian men, women & children in Gaza, destroyed their homes, churches, mosques, schools & hospitals because they are Palestinians. Name it? #Genocide.
The devastation in Gaza is horrifying to watch, worse than horrifying. Anyone who isn’t deeply troubled by the mass death has lost humanity. But the UN official, and all those echoing him, are full of it. The basic definition of “genocide” provided by the State Department is “the deliberate killing of a large number of people from a particular nation or ethnic group with the aim of destroying that nation or group.”
The key, defining thing here is the aim. Horrifying massacres may or may not be genocidal, depending on the intention. The Hiroshima bomb, for example, was devastating, but it was aimed at ending the war, not obliterating the Japanese people as a race. And if Israel were interested in the “genocide” of Palestinian Arabs, it has had the means to accomplish it for a very long time. And yet, for some reason, the Arab population of Israel and the occupied territories has exploded since 1948, and the Arabs in Israel proper have voting rights, and a key presence in the Knesset.
This is not to exonerate Israel entirely. I’ve had strong words for the Netanyahu governments over the years. And Israeli politicians, on the far right, have used foul rhetoric and deemed the Palestinians subhuman in some respects. Bibi swiftly suspended a rogue minister for saying a nuke could be dropped on Gaza. There are anti-Arab maniacs among the West Bank settlers and in Bibi’s cabinet. But a policy of Arab genocide? Please.
The only people actively and proudly engaged in genocide are Hamas. The marchers on the streets this weekend will not be opposing genocide; they will be defending its perpetrators. It’s right there in the Hamas founding charter:
[All of Israel, Gaza and the West Bank is] consecrated for future Moslem generations until Judgement Day. It, or any part of it, should not be squandered: it, or any part of it, should not be given up. … The Day of Judgement will not come about until Moslems fight the Jews (killing the Jews), when the Jew will hide behind stones and trees. The stones and trees will say O Moslems, O Abdulla, there is a Jew behind me, come and kill him.
This is not mere rhetoric. On October 7, we saw what genocide is in practice. Hamas didn’t kill civilians as a tragic consequence of attacks on military targets. Its torture and murder of Jewish civilians was its core mission. And if Hamas had the capacity, they would gladly enact a second Holocaust, and they have proudly said so, with even more sadism than the Nazis. They would kill every Jew they could.
1. Lewis Carroll, “an English author, poet, mathematician and photographer. His most notable works are Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland (1865) and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass (1871). He was noted for his facility with word play, logic, and fantasy. His poems ‘Jabberwocky’ (1871) and ‘The Hunting of the Snark’ (1876) are classified in the genre of literary nonsense.” (Wiki)