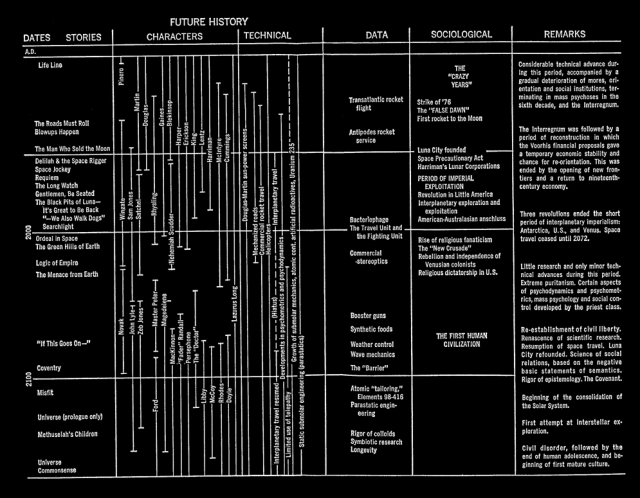
In Robert Heinlein’s famed “Future History” he constructed an elaborate timeline of thing to come, to provide a structure for his short stories.
Looking forward from the year 1940, when the timeline was first formed, it was reasonable, even conservative, guesswork to predict the moon landing by the 1980’s, forty years later, since the first powered flight by the Wright Brothers had been forty years earlier. Heinlein’s Luna City founded in 1990 a decade or so later, with colonies on Mars and Venus by 2000. Compare: a submersible ironclad was written up as a science romance by Jules Verne in 1869, based on the steam-powered “diving boat” of Robert Fulton, developed in 1801. In 1954 the first atomic-powered submarines — all three boats were named Nautilus — put to sea. The gap between Verne’s dream and Rickover’s reality was eight decades, about the time separating Heinlein’s writing of “Menace from Earth” and its projected date.
Looking back from the year 2010, however the dates seem remarkably optimistic and compressed. We have not even mounted a manned expedition to Mars as yet, and no return manned trips to the Moon are on the drawing boards.
One prediction that was remarkably prescient, however, was the advent of “The Crazy Years” described as “Considerable technical advance during this period, accompanied by a gradual deterioration of mores, orientation, and social institutions, terminating in mass psychoses in the sixth decade, and the interregnum.”
He optimistically predicts a recovery from the Crazy Years, the opening of a new frontier in space, and a return to nineteenth-century economy. Full maturity of the human race is achieved by a science of social relations “based on the negative basic statements of semantics.” Those of you who are A.E. van Vogt fans will recognize our old friends, general semantics and Null-A logic cropping up here. Van Vogt, like Heinlein, told tales of a future time when the Non-Aristotlean logic or “Null-A” training would give rise to a race of supermen, fully integrated and fully mature human beings, free of barbarism and neuroses.
Here is the chart [full size version here]. Note the REMARKS column to the right.
What Heinlein failed to predict was that the Crazy Years would simply continue up through 2010, with no sign of slackening. Ladies and gentlemen, we live in the Crazy Years.
John C. Wright, “The Crazy Years and their Empty Moral Vocabulary”, John C. Wright, 2019-02-18.
October 31, 2021
QotD: We’re still trapped in Heinlein’s “Crazy Years”
October 30, 2021
Look at Life — Turning Blades (1962)
PauliosVids
Published 20 Nov 2018The world of the helicopter in 1962; from the Belvedere to the experimental Rotodyne VTOL craft.
October 27, 2021
Alouette and The Ionospheric Satellites; A Beginners Guide To The Early Canadian Space Program
Polyus Studios
Published 22 Aug 2109Don’t forget to like the video and subscribe to my channel!
Support me on Patreon – https://www.patreon.com/polyusstudiosIn the early 1960s Canada was among the early pioneers of space technology and research. Scientists and engineers took advantage of then cutting edge technologies like the transistor and solar panels, to produce the Alouette and ISIS series of satellites. It was an immense engineering challenge that represented the high water mark of a tradition of ionospheric research that began back before the establishment of Canada as a nation. The Alouette and ISIS series of satellites produced more than 1200 research papers exploring all aspects of the Earth’s ionosphere, the aurora, and other phenomena. They also demonstrated to the world that Canada was a world leader in peaceful space technology.
0:00 Intro
0:29 Arctic exploration and early magnetic field research
2:40 New technologies promote new questions
5:35 Birth of the Canadian Space Program
9:25 Testing and Launch of Alouette
13:04 ISIS series of satellites
17:12 Legacy and ConclusionMusic:
“Denmark” – Portland Cello ProjectResearch sources:
https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/space…
https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/i…
http://www.friendsofcrc.ca/Projects/I…
https://www.ieee.ca/millennium/alouet…
https://www.ieee.ca/millennium/isis/i…
http://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/satellit…
http://friendsofcrc.ca/Projects/ISIS/…
https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/space…
http://acuriousguy.blogspot.com/2017/…
https://photostories.ca/explore/photo…
http://www.ieee.dreamhosters.com/digl…
https://www.ieee.ca/millennium/alouet…#Spacecraft #PolyusStudios #CanadianAerospace
October 23, 2021
The English Statute of Monopolies gets far more credit than it actually deserves
The Statute of Monopolies (1624) is often said to have been critical in helping to start England on the road to the Industrial Revolution, but in the latest Age of Invention newsletter Anton Howes argues it is far more complicated than it seems:
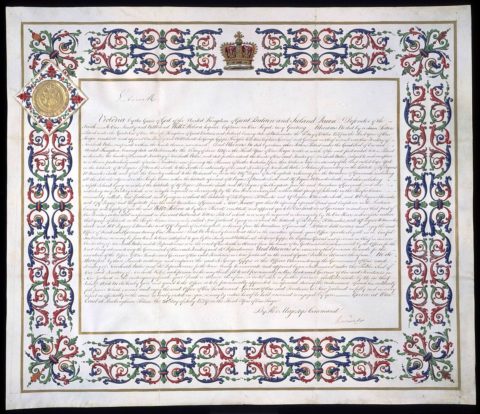

Letters Patent Issued by Queen Victoria, 1839. On 15 June 1839 Captain William Hobson was officially appointed by Queen Victoria to be Lieutenant Governor General of New Zealand. Hobson (1792 – 1842) was thus the first Governor of New Zealand.
Constitutional Records group of Archives NZ via Wikimedia Commons.
One of the most frequently mentioned landmarks in the history of intellectual property is the Statute of Monopolies, passed by the English parliament in 1624. I’ve often seen it lauded as the beginning of the system of patents for invention, or the first patent law. I remember giving a talk a few years ago where I downplayed the role of formal institutions in encouraging the Industrial Revolution, prompting an outraged economist in the audience to point to the law as a sort of gotcha — “here’s a better explanation: with patents you incentivise invention, and the Brits had just invented patents”.
Which is all to illustrate that the Statute of Monopolies is often fundamentally misunderstood. So what, exactly, did it actually do? It’s a tale of opportunism, corruption, and court intrigue, with some actual innovation inbetween. The whole saga ended Francis Bacon’s political career, led to a major constitutional crisis, and set the scene for how inventors were to behave and act for well over a century. In this first part, I’ll give the context you’ll need to really appreciate what was going on, and I’ll publish the rest in the weeks to come.
First off, the Statute of Monopolies was certainly not the first patent law. Venice’s senate had enacted a law on monopolies for invention as early as 1474. But even then, we shouldn’t be looking for statutes at all. The history of patents does not begin in 1474, but much earlier, with plenty of monopolies over new inventions having already been granted by the ruling grand council of Venice, and by the authorities of other Italian cities like Florence. The key thing to recognise about early patents is that they were not a creation of parliaments or their statutes, but of those in charge. They were the creation of sovereigns, a creature of kings and queens (or in the case of republics like Venice, of governing councils).
As regular readers of this newsletter might remember, patent monopolies for invention had already had long history in England, well before 1624. Patents in general were a very ordinary tool of English monarchs, used to communicate their will. By issuing letters patent, monarchs essentially issued public orders, open for everyone to see. (Think “patently”, as in clearly or obvious, which comes from the same root.) Monarchs used letters patent to grant titles and lands, appoint or remove people as officials, extend royal protections to foreign immigrants, incorporate cities, guilds, even theatre troupes — in general, just to rule.
And, eventually, English monarchs copied the Venetians by issuing letters patent to grant temporary monopolies to particular people, to encourage them to make discoveries, publish books, or introduce new industries or inventions to the realm. It’s only over the passage of centuries that we’ve come to refer to patents for invention — a mere subset of letters patent, and really even a mere subset of patent monopolies for all sorts of other creative work — as simply patents. Intellectual property was thus a ruler-granted privilege, created in the same way that a town gains the official status of a city, or a commoner becomes a knight. English monarchs began granting monopolies for discovering new territories and trade routes from 1496, for printing certain books from 1512, and for introducing new industries or inventions from 1552 (with one weird isolated exception from as early as 1449).
October 22, 2021
The Vehicle That Will Win World War Two – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 21 Oct 2021The Higgins Landing Craft, Higgins Boat, Landing Craft, or whatever you would like to call it, is one of the most important vehicles of the Second World War — perhaps just as much as tanks, planes, and warships. In a war full of amphibious invasions, landing on beaches in a safer and more efficient way is crucial to victory. So let’s find out the history of this war machine and its use by the World War Two allies.
(more…)
October 19, 2021
Places – Lost in Time: The Crystal Palace
Ruairidh MacVeigh
Published 1 Jun 2020This is a reupload of my original Crystal Palace video, which I had to take down and do some amendments to in order to fix some technical issues.
Hello! 😀
Not to change the format so early in it’s conception, but here I present an idea I’ve had for several years now, but am proud to finally bring to fruition.
For as long as I can remember I have been fascinated by places that have either been abandoned or destroyed, not so much out of interest for how they were lost, but more the microcosm of society that revolved around them — how people interacted with them and made them more human. Specifically, places which existed in living memory or photographic record are the ones that have captured my imagination the most, as you can see how people did interact with these wondrous locations and almost put yourself in their shoes.
Therefore, without further ado, I present Episode 1 of Places — Lost in Time, with my first feature being the lavish and opulent Crystal Palace in London. This video follows the history of the two structures to share this iconic name, and how both were created through Victorian engineering feats, how they became icons of British culture, and how they eventually met their end.
All video content and images in this production have been provided with permission wherever possible. While I endeavour to ensure that all accreditations properly name the original creator, some of my sources do not list them as they are usually provided by other, unrelated YouTubers. Therefore, if I have mistakenly put the accreditation of “Unknown”, and you are aware of the original creator, please send me a personal message at my Gmail (this is more effective than comments as I am often unable to read all of them): rorymacveigh@gmail.com
The views and opinions expressed in this video are my personal appraisal and are not the views and opinions of any of these individuals or bodies who have kindly supplied me with footage and images.
If you enjoyed this video, why not leave a like, and consider subscribing for more great content coming soon.
Thanks again, everyone, and enjoy! 😀
References:
– British Library (and their respective references)
– Victoria and Albert Museum (and their respective references)
– Wikipedia (and its respective references)Music – YouTube Audio Library
October 14, 2021
October 1, 2021
September 24, 2021
Battle of the Hampton Roads – The Fury of Iron and Steam
Drachinifel
Published 20 Feb 2019The first ironclad vs ironclad battle is reviewed, along with the origins of the ships and some of the myths and legends about this historic battle.
Want to support the channel? – https://www.patreon.com/Drachinifel
Want to talk about ships? https://discord.gg/TYu88mt
September 23, 2021
QotD: The problem with “free” tech stuff
… I’m baffled by this idea — seemingly everywhere in modern marketing — that they can somehow annoy you into buying their products. Music streaming services like Spotify are all but unlistenable because of it — not only do you get four ads every three songs, but three of the four ads ask “Want a break from the ads? Join premium!!” Or … you know … I could just go back to listening to tunes the old fashioned way. Humanity’s Greatest Genius, when he lays off that shtick for a minute, actually has some good riffs on this. We all must learn to deprogram ourselves from the Cult of Free. If they’re giving away the product, then you are the product. Much like a college degree, “free” tech is actually negative equity — you’re actually worse off for doing it.
It has gotten so bad lately that they don’t just barrage you with ads, they’re now starting to force-feed you content. I used to have Amazon Music — the free one, of course — because it was a good way to listen to The Z Man’s podcasts and my classical library during my commute. I’d download albums to my phone, switch to “offline” mode, and listen that way. Which Amazon obviously considers no good, because they pushed out some “car mode” bullshit that now automatically turns your wifi on, then starts blasting hip hop at you. And that’s not all! A few weeks back, while trying to figure out a way to turn the damn thing off, I noticed that it now has a “your playlist” feature, based on “your” music … which is, of course, the same force-fed rap shit I’ve been trying so desperately to avoid. It has decided that not only shall I listen to Young Jeezy, Big Weezy, and MC Funetik Spelyn, I will also like it, to such a degree that they will start force-feeding me other shit based on my “likes”.
Yeah. Uninstalled. Fuck you, Bezos. I’ve got a CD player. And when Microsoft decides that I’m not listening to the right music on that, and uninstalls the driver, I’ve got a tape deck. And when that breaks, I will sing to myself as I go down the highway. 99 bottles of beer on the wall, motherfucker, just like bus trips back in Boy Scouts. Enough is enough.
Severian, “Mailbag / Grab Bag”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-06-18.
September 22, 2021
The Extremely Bizarre Engineering Rituals of Canada (And the Fascinating Way They Came to Be)
Today I Found Out
Published 31 Jul 2021This video is #sponsored by NordVPN.
Sources:
Andrews, Gordon, Canadian Professional Engineering and Geoscience: Practice and Ethics, Thomson Nelson Canada Ltd, 2005
Kipling, Rudyard, “The Hymn of Breaking Strain”, 1935, http://www.cuug.ab.ca/~branderr/risk_…
2 Esdras 4:5-10, https://thekingjamesversionbible.com/…
Bateman, Chris, The Secrets of Engineering’s Strange and Mysterious Initiation Ritual, TVO, April 24, 2018, https://www.tvo.org/article/the-secre…
“Background: The Calling of an Engineer, The Ritual of the Calling of an Engineer”, https://www.ironring.ca/background-en/
Anderson, Bill, “Why Engineering is Purple”, April 16, 2019, https://profbillanderson.com/2019/04/…
September 16, 2021
QotD: The youthful Utopian
More than half a century ago, I had a friend in junior high school I could never figure out or drum much common sense into. He was quite the dreamer. He loved science fiction. His nickname was “Angus” — derived from the fact that he was rather rotund, and our school was surrounded by farm fields. When we grazed at the same lunch table, he would speculate endlessly about what life on other planets might be like. He was very earnest, and very entertaining.
One day I suggested facetiously that Angus stop speculating and go find out for himself. “Build a spaceship someday and fly to the planet of your choice,” I recommended. To my surprise, he took me seriously.
Some days later, Angus excitedly told me he had it all worked out. He had designed the spaceship and even brought the plans to show me. Then he unfolded a large sheet of brown wrapping paper. There it was — the entire cockpit control panel of the craft that would take Angus to the cosmos. There was a button for everything.
“This is not a plan!” I declared with a laugh. “It’s just a bunch of buttons with labels on them.”
“But it’s all here,” Angus insisted. “I’ve thought of everything — Start, Stop, Land, Take-off, Dodge Asteroids, you name it, everything you need to know.” He even had an all-purpose button to take care of anything unexpected, which he thought was a genius innovation.
What I remember most vividly about this experience was not the fine detail of my friend’s sketch. It was my frustrating inability to convince him he was delusional, that his plan was no plan at all, that as a 14-year-old he wasn’t yet ready for a senior position at NASA. He was what philosopher Eric Hoffer might call a “true believer” — convinced beyond any hope of convincing otherwise that his plan was thorough, perfect, and sure to work.
I lost track of Angus after graduation, but I am quite certain his spaceship never left the ground.
Lawrence W. Reed, “The Dark Side of Paradise: A Brief History of America’s Utopian Experiments in Communal Living”, Foundation for Economic Education, 2021-06-13.
September 9, 2021
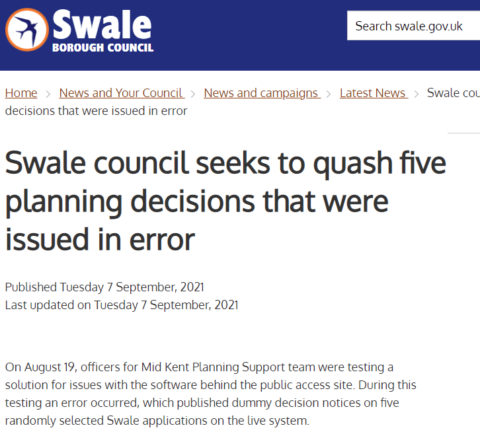
When you mess around in a software testing environment … make sure it actually is a test
A British local government found out the hard way that they need to isolate their software testing from their live server:
A borough council in the English county of Kent is fuming after a software test on the council’s website led to five nonsensical dummy planning application documents being mistakenly published as legally binding decisions.
According to a statement from Swale Borough Council, staff from the Mid Kent Planning Support Team had been testing the software when “a junior officer with no knowledge of any of the applications” accidentally pressed the button on five randomly selected Swale documents, causing them to go live on the Swale website.
After learning what had happened, the council moved to remove the erroneous decisions from public display, but according to the statement: “Legal advice has subsequently confirmed they are legally binding and must be overturned before the correct decisions are made.”
Publishing randomly generated planning decisions is obviously bad enough, but the problems got worse for Swale when it was discovered that the “junior officer” who made the mistake had also added their own comments to the notices in the manner of somebody “who believed they were working solely in a test environment and that the comments would never be published,” as the council diplomatically described it.
So it was that despite scores of supportive messages from residents, the splendidly named Happy Pants Ranch animal sanctuary had its retrospective application for a change of land use controversially refused, on the grounds that “Your proposal is whack. No mate, proper whack,” while an application to change the use of a building in Chaucer Road, Sittingbourne, from a butchers to a fast-food takeaway was similarly denied with the warning: “Just don’t. No.”
The blissfully unaware office junior continued their cheerful subversion of Kent’s planning bureaucracy by approving an application to change the use of a barn in the village of Tunstall, but only on condition of the numbers 1 to 20 in ascending order. They also approved the partial demolition of the Wheatsheaf pub in Sittingbourne and the construction of a number of new flats on the site, but only as long as the project is completed within three years and “Incy Wincy Spider.”
Finally, Mid Kent’s anonymous planning hero granted permission for the demolition of the Old House at Home pub in Sheerness, but in doing so paused to ponder the enormous responsibility which had unexpectedly been heaped upon them, commenting: “Why am I doing this? Am I the chosen one?”
For their part, Swale Borough Council’s elected representatives were less than impressed by the work of their colleagues at the Mid Kent Planning Support Team and wasted no time in resolutely throwing them under the bus.
“These errors will have to be rectified but this will cause totally unnecessary concern to applicants,” thundered Swale councillors Roger Truelove, Leader and Cabinet Member for Finance, and Mike Baldock, Deputy Leader and Cabinet Member for Planning in a shared statement. “This is not the first serious problem following the transfer of our planning administration to Mid Kent shared services. We will wait for the outcome of a proper investigation and then consider our appropriate response as a council.”
September 2, 2021
Charles Stross predicts that Elon Musk will become a multi-trillionaire
Charles Stross isn’t exactly a fan of Musk’s, but he outlines why he thinks Musk is on a potentially multi-trillion dollar path:
So, I’m going to talk about Elon Musk again, everybody’s least favourite eccentric billionaire asshole and poster child for the Thomas Edison effect — get out in front of a bunch of faceless, hard-working engineers and wave that orchestra conductor’s baton, while providing direction. Because I think he may be on course to become a multi-trillionaire — and it has nothing to do with cryptocurrency, NFTs, or colonizing Mars.
This we know: Musk has goals (some of them risible, some of them much more pragmatic), and within the limits of his world-view — I’m pretty sure he grew up reading the same right-wing near-future American SF yarns as me — he’s fairly predictable. Reportedly he sat down some time around 2000 and made a list of the challenges facing humanity within his anticipated lifetime: roll out solar power, get cars off gasoline, colonize Mars, it’s all there. Emperor of Mars is merely his most-publicized, most outrageous end goal. Everything then feeds into achieving the means to get there. But there are lots of sunk costs to pay for: getting to Mars ain’t cheap, and he can’t count on a government paying his bills (well, not every time). So each step needs to cover its costs.
What will pay for Starship, the mammoth actually-getting-ready-to-fly vehicle that was originally called the “Mars Colony Transporter”?
Starship is gargantuan. Fully fuelled on the pad it will weigh 5000 tons. In fully reusable mode it can put 100-150 tons of cargo into orbit — significantly more than a Saturn V or an Energiya, previously the largest launchers ever built. In expendable mode it can lift 250 tons, more than half the mass of the ISS, which was assembled over 20 years from a seemingly endless series of launches of 10-20 ton modules.
Seemingly even crazier, the Starship system is designed for one hour flight turnaround times, comparable to a refueling stop for a long-haul airliner. The mechazilla tower designed to catch descending stages in the last moments of flight and re-stack them on the pad is quite without precedent in the space sector, and yet they’re prototyping the thing. Why would you even do that? Well, it makes no sense if you’re still thinking of this in traditional space launch terms, so let’s stop doing that. Instead it seems to me that SpaceX are trying to achieve something unprecedented with Starship. If it works …
There are no commercial payloads that require a launcher in the 100 ton class, and precious few science missions. Currently the only clear-cut mission is Starship HLS, which NASA are drooling for — a derivative of Starship optimized for transporting cargo and crew to the Moon. (It loses the aerodynamic fins and the heat shield, because it’s not coming back to Earth: it gets other modifications to turn it into a Moon truck with a payload in the 100-200 ton range, which is what you need if you’re serious about running a Moon base on the scale of McMurdo station.)
Musk has trailed using early Starship flights to lift Starlink clusters — upgrading from the 60 satellites a Falcon 9 can deliver to something over 200 in one shot. But that’s a very limited market
As they say, read the whole thing.