The past has always interested me more than the future. This backward-looking tendency has only been reinforced by reaching, somewhat unexpectedly, the age of 70. I can’t say that I don’t feel my age because I don’t know what feeling any particular age is like — but one repeatedly hears that 60 is the new 40, 70 is the new 50, and so on; certainly, the human aging process has slowed since I was born. When I look at photos of people who were 50 in the year of my birth, 1949, they look much older and more worn-out than do 50-year-olds now; and if I had lived only to my life expectancy at birth, I would be dead these last four years.
So progress must have occurred in the intervening time, despite the pessimism that infects those who, like me, are of retrospective temperament and hypersensitive to deterioration. It is not hard to enumerate many things that have improved. They relate principally, but not only, to material conditions. My best friend when I was very young was one of the last children in Britain to suffer from polio, which paralyzed him from the waist down. The quickest form of written communication was then the telegram, and anything other than local telephone calls had to go through an operator. To call across the Atlantic required a reservation and was ferociously expensive; the resultant conversation always seemed to take place during a violent storm. In England, the food was generally disgusting, and meals were to be endured as a regrettable necessity instead of enjoyed (it puzzles me still how people could have cooked so badly). Cars broke down frequently, and every November, pollution produced fogs so thick that you couldn’t see the hand in front of your face (I loved them). Rationing continued for eight years after the war, and disused bomb shelters, present in every park, were where illicit sexual fumbles and smoking took place. Incidentally, for an adult male not to smoke was unusual (75 percent did so); we must have lived in a perpetual fog of foul-smelling tobacco, to judge by the distaste caused by even a single lit cigarette in these virtuous times. Poverty, as raw necessity, still existed. Murderers were sometimes hanged — as well as, more rarely, the innocent. Overt racial prejudice was, if not quite the norm, certainly prevalent.
Yet not everything has improved, though the deterioration has been less tangible than the progress. To give one example: by age 11, I was free to roam London, or at least its better areas, by myself or with a friend of the same age. The sight of an 11-year-old child wandering the city on his own did not suggest to anyone that he was neglected or abused. I remember, too, the evening papers piled up at newsstands; people would throw coins on top of the pile and take their copy. It never occurred to anyone that the money might get stolen; nowadays, it would never occur to anyone that the money would not be stolen. The crime statistics bear out this sea change in national character.
Theodore Dalrymple, “What Seventy Years Have Wrought”, New English Review, 2019-10-26.
June 25, 2024
QotD: Progress and decline
June 24, 2024
Little humans, from “humorless little poop machines” to creatures with a sense of humour
Ted Gioia cross-posted an article from Daniel Parris that answers the eternal question “when do humans develop a sense of humour?”
… a large body of academic research examines the intersection of humor, aging, and cultural mores. So today, we’ll explore how our sense of humor forms and transforms with age, and the physiological factors driving our comedic sensibilities.
How Does Our Sense of Humor Change Over Time?
We are born humorless little poop machines. We can’t make funny voices, we can’t do bits, and we can’t engage in wordplay — we simply eat, sleep, poop, cry, and poop again. And then, amidst this onslaught of poop, a sense of humor begins to emerge.
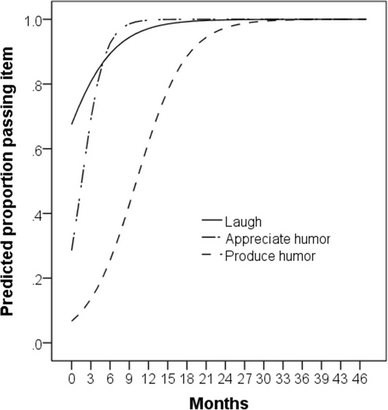
The Early Humor Survey (EHS) is a standardized questionnaire designed to assess a child’s humor-processing abilities in the first four years of life. EHS survey data (which is collected from parents) reveals that our sense of humor begins emerging in infancy, typically around the four-month mark. During this period, babies respond to simple stimuli with laughter and begin producing humor.
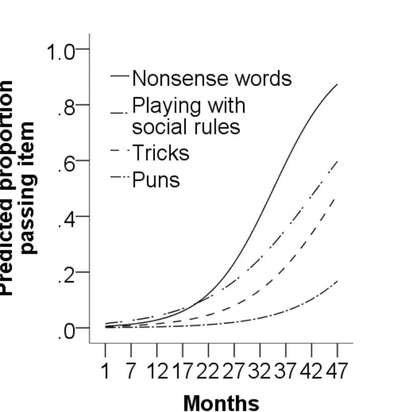
Even more striking is how humor development differs by task, as comprehension and appreciation of nonsense, puns, and trickery are all learned at varying rates.
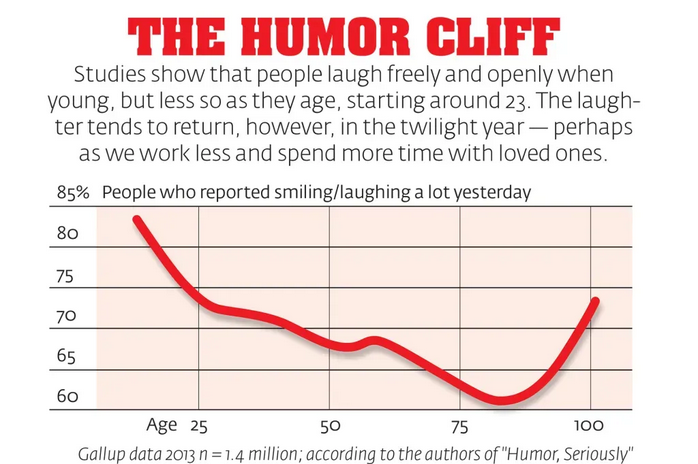
Once we exit adolescence, comedic interactions begin to wane, and we laugh less often.
A 2013 Gallup survey documenting the frequency of humorous interactions suggests the existence of a “humor cliff” as we age — each year, we laugh a little less than the previous one. Humor fades until we’re 80, at which point we chuckle a bit more (what a relief).
While captivating, this visualization is also misleading. Popular interpretations of this data suggest that as people mature, their appreciation for humor declines, as if this trait were a single stock trending up or down. Instead, a person’s comedic sensibilities are defined by an assortment of preferences that remain fluid throughout our lives.
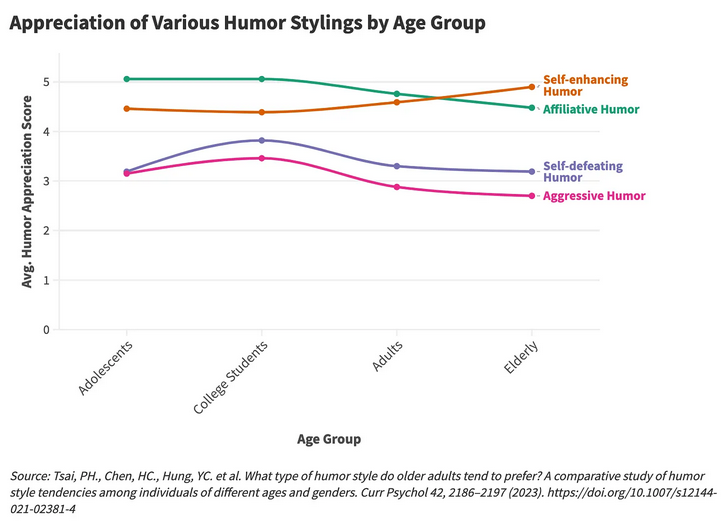
A substantial body of research examines how comedic taste varies with age, exploring our reactions to different humor styles at various life stages. One such study published in Current Psychology presented respondents with a series of humorous statements and then assessed each subject’s affinity for four distinct joke types:
- Self-enhancing Humor: finding comedy in everyday situations, often by humorously targeting oneself in a good-natured way.
- Affiliative Humor: using humor to strengthen social bonds and enhance relationships by sharing jokes and amusing stories that make others laugh while avoiding negativity.
- Self-defeating Humor: Involves individuals making jokes at their own expense to gain approval or avoid conflict, sometimes undermining their self-esteem.
- Aggressive Humor: Making jokes or remarks that ridicule, belittle, or demean others, often intended to assert dominance or express hostility.
Ultimately, the study found that with age, people appreciate self-enhancing humor more, and they value affiliative, self-defeating, and aggressive stylings less.
A similar study of 4,200 German participants found that we increasingly prefer incongruity resolution as we age, an approach marked by unexpected or contradictory elements that lead to a comedic surprise. In joke format, this genre includes a setup pointing toward one outcome, with a punchline that delivers a surprising twist, such as “I just flew in today, and boy, are my arms tired!”
Raise a glass of your favourite microbrew to … Jimmy Carter?
Glenn “The Instapundit” Reynolds visits a local brewing festival in Knoxville and remembers what it was like before — of all people — Jimmy Carter began the process of deregulating the beer industry by legalizing homebrewed beer in 1978:
This weekend I want to the Knox Brewfest at the Knoxville World’s Fair Grounds. As the name suggests, it was a collection of most of the local micro-breweries, each with a booth offering samples. (There were also a few bigger operations, like Sierra Nevada, Abita, and Paulaner). I wore my Hamm’s Beer Hawaiian shirt, which was a surprisingly big hit.
And there were some lessons, about which more later.
Hamm’s doesn’t really exist anymore except as a sometimes-produced minor product of Coors, which bought the trademark after it passed through the hands of numerous other companies. But it’s not forgotten!
The beer was good and the crowd was cheerful.
Mostly me, and my friend Jim (who I’ve known since junior high) were reflecting on the vast improvement in the world of beer in America, and particularly in Knoxville. As late as, oh, 1990 or so, you could go into almost any bar in Knoxville and if you asked what kind of beer they had you’d get an answer like this: “We’ve got everything! Bud, Bud Light, Miller, Miller Light, Coors, Coors Light – anything you want!”
It’s easy to take the craft-brewing revolution for granted, but it brought about huge changes and for the better. Nowadays, the beer scene in America tends to be better than that in Europe. No, really. In fact, one of my former research assistants, who practices law in Belgium now, brought over a couple of Belgian friends who wanted to see Tennessee. I met them for lunch at Barley’s in the Old City, to hear a bluegrass show and eat pizza and drink beer. They were very impressed with the fifty or so taps that Barley’s offers.
Back home they said, the bars are usually owned by the breweries and only sell their own brews, so you might have only three or four varieties, all from the same label. Nothing like this.
[…]
This deregulatory story started (like airlines and trucking deregulation) with Jimmy Carter of all people. Despite his (often true) reputation as a bossy micro-manager, he was an engineer and a rationalist. That worked out poorly in foreign policy, but led him to undo a number of irrational regulatory structures, one of which was the limit on home beer production. Carter signed a bill legalizing homebrewing in 1978, and those homebrewers were the nucleus of the craft beer movement a decade or so later.
History Summarized: Augustus Versus Antony
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published Apr 6, 2018Now that Caesar’s assassins are out of the picture, which would-be dictator will defeat the other to become the sole-ruler of Rome? In today’s episode of “How Long Before There’s Another Civil War?”: Not a lot … honestly not a very long time … BUT THEN WE GET THE ROMAN EMPIRE WOOOOOOOOO~~~
QotD: Raid warfare on the Eurasian Steppes and on the Great Plains
The other strategic aim nomads might fight over is for the acquisition of some kind of movable good, which is to say raiding for stuff. Because all of the warriors (which is generally to say all of the free adult males) of these societies are mounted and because they have a subsistence system which allows rapid, relatively along distance movements (often concealed; remember that Mongols need not light any camp fires), nomads make fearsome raiders, able to strike, grab the things they are looking for and quickly retreat before a counterattack can be mobilized. That goes just as well for raiding each other as it does for raiding the farmers at the edges of the grasslands.
But what are the things here that they are aiming to get? It depends on the targets; nomadic raids into the settled zone generally aim to capture the goods that agrarian societies produce which nomadic societies do not: stocks of cereal crops, metal goods and luxury goods. But most nomadic raiding was directed against other nomads, seeking to acquire either people or animals.
On the Great Plains, the animals in question were invariably horses; the act of stealing, or “cutting out” a horse gives McGinnis part of the title of his book (Counting Coup and Cutting Horses) and raids for horses dominate both McGinnis and Secoy’s discussion of Plains Native American warfare. Horses were, after all, a scarce commodity which only percolated into the Great Plains from the South (and which could only be raised in quantity in its southern reaches), but which all tribes required both to hunt and fight effectively. Stealing enemy horses thus both strengthened your tribe while weakening your enemies, both in military and subsistence terms. The Mongols also engaged in quite a lot of raiding for horses, but also – in a pastoral subsistence system – a lot of simple cattle rustling as well (e.g. Ratchnevsky, op. cit., 28-31).
Raiding for people is more complex, but undeniably part of this system of warfare. But crucially this raiding was generally not for slave-trading (though there are exceptions which I discussed last time), but instead incorporative raiding. What I mean by that is that the intent in gaining captives in the raid was to incorporate those captives, either as full or subordinate members, into the nomadic community doing the raiding. Remember: the big tribe is the safe tribe, so incorporating new members is a good way to improve security in the long run.
On the Eurasian Steppe, incorporated captives became the ötögus bo’ol “bonded serfs” that we mentioned previously (Ratchnevsky, op. cit., 12-4). Unlike warfare on the Great Plains, it seems possible for the bo’ol to include adult men, either captured or sold (by destitute parents) as children or else taken as prisoners when their tribe or clan was essentially dissolved by being conquered in war. Indeed, in his own conquests, Chinggis only decreed the annihilation of one tribe, the Mongols’ traditional enemies, the Tatars – there he ordered the death of any Tatar male taller than the linchpin of an oxcart (May, Mongols, 12). In other cases, it is clear that the incorporation of defeated nomad warriors into the successful tribe was fairly normal, though raids to capture women and children (also for incorporation) were just as common. Bride abduction in particular was very common on the Steppe, as Ratchnevsky notes (op. cit., 34-5).
The incorporation of males was far less common in Great Plains Native American warfare, but the capture of women and children to enhance tribal strength in the long term was a core objective in raiding. McGinnis (op. cit., 42-3) notes how the Crow, after suffering a massive defeat in the early 1820s which resulted in the deaths of many warriors and the capture of perhaps several hundred women and children, steadily built their tribe back up over the following decades with an intentional strategy of capturing women and children from their enemies. As McGinnis (op. cit., 24) notes, women captured in this way might be married into the capturing tribe, adopted into it, or sometimes kept as an enslaved laborer (under quite bad conditions). Adult males, by contrast, were almost always killed; unlike on the Steppe, the incorporation of formerly hostile warriors doesn’t seem to have been considered possible (though one wonders if this would have become cultural practice given enough time; both McGinnis and Secoy note how the increasing lethality of warfare post-gun/horse led to slow population decline overall, which may, had the system run without outside interference long enough, led to the emergence of norms more closely resembling the Eurasian Steppe. We should keep in mind that the Eurasian horse-system had many centuries to sort itself out, whereas the North American horse-system was essentially strangled in its crib).
Of course, taken together with the previous discussion of territorial warfare, we can see that all of these raids have a double purpose: they both aim to acquire resources (horses, sheep, humans) and at the same time inflict damage on an opponent with the long-term goal of forcing that enemy to move further away, opening their pastures or hunting grounds for exploitation by the victorious tribe. Thus in the long-term, each successful raid is intended to build a sense of threat which eventually results in territorial gains (though in cases of real power asymmetry, the long term could come very rapidly; people aren’t stupid and if you are being raided by a clearly superior opponent, you are likely to move on before you lose everything of value).
Squaring the ugly reality of nomadic raiding with [George R.R.] Martin’s depiction [of his nomadic Dothraki] is tricky. On the one hand, a raid in which exceptional victory results in enemy women and children taken captive and fit adult males slain fits within either the Great Plains Native American or Steppe nomad military tradition. On the other hand, the immediate declaration by Drogo’s men that female captives taken this way are not marriageable (AGoT, 559; the idea is treated as laughable) and the killing of all of the very valuable livestock (which, even if the Dothraki are not herdsmen, these animals could be eaten, or quite easily driven to a place where they could be sold or traded for other resources, like metalwork) suggests that Martin has not understood why those raids happened. Instead, it seems like his imagination is only able to view these raids from the perspective of the settled people on the receiving end.
Instead, Martin’s understanding of Native American warfare seems not conditioned by any actual Native Americans, but rather by Hollywood depictions of Native Americans during the Hollywood “Golden Age” which were in turn conditioned by sensational accounts of Western settlers who themselves didn’t understand how Native American warfare worked on the Great Plains. As we will see, the Game of Thrones showrunners took that unfortunate subtext when making the show itself, and turned it into actual text.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: That Dothraki Horde, Part IV: Screamers and Howlers”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-01-08.
June 23, 2024
California has “a governing class that wants you to give them power, then shut up and go away”
Chris Bray illustrates some of the many ways that California’s elected politicians are working to ensure that mere voters won’t interrupt their urgent and necessary work:
The Taxpayer Protection Act, a proposed referendum that got enough signatures to qualify for the November ballot, would have required voter approval for all new state and local taxes. State election officials agreed that it met the qualification threshold, and planned to put it before the voters. Democratic officeholders sued, with considerable support from public employee unions and interest groups, and the California Supreme Court ruled this week that the measure may not be placed on the ballot — because it improperly proposes to revise the state constitution, rather than merely amending it. You can watch them try to parse that distinction here, for seventy murky pages. You can change the state constitution through the referendum process, but you can’t change the state constitution through the referendum process. See, totally clear.
At the same time, California Governor Patrick Bateman is telling the organizers of a ballot measure that would increase penalties for drug and theft crimes — after a decade of sharply reduced penalties — that he’ll punish them by blocking criminal justice reform measures in the legislature unless they pull their measure from the ballot. The intended message is a very clear threat: If you insist on your ballot measure and lose at the polls, you’ll be punished with a complete blockade on your agenda through legislative means, for as long as we can manage it.
And a parental rights proposition that aimed for a place on the November ballot — falling short in its efforts to gather enough signatures — ran into a wall when the attorney general’s office assigned it a misleading label that would have described it to voters as a repressive measure that was intended to hurt children.
So a Progressive reform, the great 20th-century transition to direct democracy, is running into a progressive wall of resistance in the 21st century. California Democrats are fighting to limit the likelihood that voters will interfere with their agenda.
People outside California often shrug at the decline of the state, because Californians are just getting what they voted for. But that view misses a bunch of strangeness and ambiguity in a place that has tended to put Democrats in office, then limit their efforts with an ideologically inconsistent hodgepodge of conservative and libertarian ballot measures. The governor and the state legislature just sued to prevent their own voters, the people who sent them to public office, from voting on the new taxes they create. Democrats against direct democracy — a governing class that wants you to give them power, then shut up and go away.
This is not merely a California problem. I wrote a few days ago about the scumbag Robert Kagan and his idiotic book warning that America is facing a rebellion. Here’s the back cover of the book, and I’ve used sophisticated media software to circle the important part:
“The problem is and has always been the people and their beliefs.” This is what the American governing class believes, now. See also the pro-democracy warrior Tom Nichols and his recurring theme about the repulsive people of an ignorant country. We need to protect democracy by getting all the trash that makes up the population to somehow go away and stop bothering their wise and benevolent betters.
The great point of cognitive slippage in American governance has been the degree to which Americans have been willing to vote for officeholders whose agendas they then try to block through lawsuits, referendums, and popular resistance. We’ve voted for shit sandwich over and over again, then declined to eat the whole sandwich. The governing class is now announcing that we’re no longer allowed to refuse the complete meal. You may not have a ballot measure on that.
In the near term, and in the medium term, that pivot leads to greater friction and accelerated decline. In the longer term, preventing people from limiting the aggressive failure of the governing class can only make that failure more apparent. Geological faults that have a lot of small movements release tension in a series of minor earthquakes; faults that can’t release tension through small movements eventually have one big one. We’ll eventually recognize the California Supreme Court’s decision this week as a Pyrrhic victory. There will be more of these, in a political system of increasing brittleness.
Okinawa Ends – WW2 – Week 304 – June 22, 1945
World War Two
Published 22 Jun 2024Mitsuru Ushijima’s forces are defeated and the Battle of Okinawa is officially over. However, since most of the Japanese fought to the death, victory comes at a bloody cost – over 50,000 US casualties and over 100,000 Japanese and also possibly that many Okinawan deaths. The fight on North Borneo continues, there’s a raid on Wake Island, and the Japanese powers that be meet to actually discuss making some sort of peace with the Allies.
00:00 Intro
01:25 Truman And The Interim Committee
05:00 Battle Of Okinawa
08:06 The End Of Okinawa
13:22 Raid On Wake Island
14:23 Battle Of North Borneo
15:33 Hirohito Wants Peace
16:54 Conclusion
(more…)
The amazing range of things Britain’s Ofcom gets its tentacles into
Earlier this week, Mark Steyn discussed the British government’s Office of Communications (Ofcom) and the way it rigs regulates who can say what during British election campaigns:
Why do I think the UK state censor Ofcom should be put out of business? Because there are very few areas of British life that this strange, secretive body does not “regulate”. Take, for example, this current UK election campaign, which the media are keen to keep as a torpid Potemkin struggle between TweedleLeft and TweedleRight. So, on Thursday night, BBC bigshot Fiona Bruce will host a debate between the four party leaders – that’s to say, the head honchos of the Conservatives, Labour, the Liberal Democrats and the Greens.
Wait a minute: what about Nigel Farage, leader of the Reform party? Since the beginning of the year, Reform has been third-placed in the polls, ahead of the LibDems and Greens, and last week they rose to second place ahead of the unlovely Tories.
So why wouldn’t the second-place party get a spot in the leaders’ telly debate?
Ah, well, you’re looking at it all wrong, you hick. Here’s how the Beeb explain it:
The Ofcom guidance gives “greater weight on the actual performance of a political party in elections over opinion poll data” taking into account the “greater uncertainty associated with support in opinion polls”.
The “actual performance of a political party” refers to their results in the two previous elections — 2019 and 2015 — when Reform didn’t exist. A lot of other things didn’t exist in 2015: Brexit, Covid, lockdown, the Ukraine war, legions of vaccine victims, the massed ranks of Albanian males occupying English country-house hotels …
But, per “Ofcom guidance”, Campaign 2024 has to be conducted on the basis of how things stood a decade ago.
You know who would also be ineligible to participate under Ofcom’s rules? Everyone’s favourite Lana Turner sweater-girl in Kiev, Volodymyr Zelenskyyyyy. He only formed his Servant of the People party in late 2017, so no election debates for you, sweater-girl. And don’t try blaming it on Putin, because it’s “Ofcom guidance” so we all know it’s on the up-and-up.Because, as their barrister assured the High Court, Ofcom are “expert regulators”. Lord Grade and Dame Melanie Dawes probably did a module in regulation at Rotherham Polytechnic or whatever.
I can see why the likes of Naomi Wolf’s creepy stalker-boy Matthew Sweet like this system: it’s a club and they get to decide who’s admitted. It’s less obvious why the generality of the citizenry put up with it. At any rate, get set for another thrilling BBC election debate in which all four “opponents” agree on Covid, climate, Ukraine, the joys of mass Muslim immigration and the inviolability of the NHS … but ever more furiously denounce each other for not tossing enough money that doesn’t exist into the sinkhole.
Don’t get me wrong, I quite like that pixie Green leader who describes herself as a “pansexual vegan”, and I certainly don’t have the personal baggage with her that I have with Nige. But under what rational conception of media “regulation” does the six per cent basement-dweller get guaranteed a seat at the table but not Reform?
And you wonder why nothing changes?
The Original Chef Boyardee Spaghetti Dinner
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 13 Mar 2024Absolutely fantastic tomato and meat sauce served over spaghetti tossed with butter and parmesan
City/Region: Cleveland, Ohio
Time Period: 1930sChef Boyardee was not born in Cleveland (sorry, 30 Rock), but in Borganovo, just outside of Piacenza in Italy. And his name was not Hector Boyardee, but Ettore Boiardi (boy-AR-dee). He opened an Italian restaurant in Cleveland in 1924, where the food was so popular that he frequently sent patrons home with bottles of his spaghetti sauce.
We can’t know exactly what that original sauce was, but this is from a family recipe and is probably pretty close. And it’s phenomenal. It’s fairly simple, but so good. You get a lot of the fresh basil, and the creaminess from mixing the butter and parmesan directly with the pasta is delicious. I don’t often make dishes from the show again, but I can see myself making this any day of the week.
(more…)
QotD: Shoes
Mismatched shoes are also nicely subversive. There is somewhere in the clothing code a notion that holds over from the Elizabethan era that says a person’s shoes must show that they are in the Elizabethan lingo, unconcussable. Shoes, especially the shoes of the male and the young, are meant to show that the wearer is, all apologies, grounded. (High heel shoes take their semotic precisely from the way they break this rule. The wearer, a female, demonstrates her vulnerability, her fragility, her elegance, her powers of evocation by showing herself not at all grounded.)
Grant McCracken, “Cotton, Converse and co-creation”, This Blog Sits at the, 2005-07-27.
June 22, 2024
The End of Everything
In First Things, Francis X. Maier reviews Victor Davis Hanson’s recent work The End of Everything: How Wars Descend into Annihilation:
A senior fellow in military history and classics at Stanford University’s Hoover Institution, Hanson is a specialist on the human dimension and costs of war. His focus in The End of Everything is, as usual, on the past; specifically, the destruction of four great civilizations: ancient Thebes, Carthage, Constantinople, and the Aztec Empire. In each case, an otherwise enduring civilization was not merely conquered, but “annihilated” — in other words, completely erased and replaced. How such catastrophes could happen is the substance of Hanson’s book. And the lessons therein are worth noting.
In every case, the defeated suffered from fatal delusions. Each civilization overestimated its own strength or skill; each misread the willingness of allies to support it; and each underestimated the determination, strength, and ferocity of its enemy.
Thebes had a superb military heritage, but the Thebans’ tactics were outdated and their leadership no match for Macedon’s Alexander the Great. The city was razed and its surviving population scattered. Carthage — a thriving commercial center of 500,000 even after two military defeats by Rome — misread the greed, jealousy, and hatred of Rome, and Roman willingness to violate its own favorable treaty terms to extinguish its former enemy. The long Roman siege of the Third Punic War saw the killing or starvation of 450,000 Carthaginians, the survivors sold into slavery, the city leveled, and the land rendered uninhabitable for a century.
The Byzantine Empire, Rome’s successor in the East, survived for a millennium on superior military technology, genius diplomacy, impregnable fortifications, and confidence in the protection of heaven. By 1453, a shrunken and sclerotic Byzantine state could rely on none of these advantages, nor on any real help from the Christian West. But it nonetheless clung to a belief in the mantle of heaven and its own ability to withstand a determined Ottoman siege. The result was not merely defeat, but the erasure of any significant Greek and Christian presence in Constantinople. As for the Aztecs, they fatally misread Spanish intentions, ruthlessness, and duplicity, as well as the hatred of their conquered “allies” who switched sides and fought alongside the conquistadors.
The industrial-scale nature of human sacrifice and sacred cannibalism practiced by the Aztecs — more than 20,000 captives were ritually butchered each year — horrified the Spanish. It reinforced their fury and worked to justify their own ferocious violence, just as the Carthaginian practice of infant sacrifice had enraged the Romans. In the end, despite the seemingly massive strength of Aztec armies, a small group of Spanish adventurers utterly destroyed Tenochtitlán, the beautiful and architecturally elaborate Aztec capital, and wiped out an entire culture.
History never repeats itself, but patterns of human thought and behavior repeat themselves all the time. We humans are capable of astonishing acts of virtue, unselfish service, and heroism. We’re also capable of obscene, unimaginable violence. Anyone doubting the latter need only check the record of the last century. Or last year’s October 7 savagery, courtesy of Hamas.
The takeaway from Hanson’s book might be summarized in passages like this one:
Modern civilization faces a toxic paradox. The more that technologically advanced mankind develops the ability to wipe out wartime enemies, the more it develops a postmodern conceit that total war is an obsolete exercise, [assuming, mistakenly] that disagreements among civilized people will always be arbitrated by the cooler, more sophisticated, and more diplomatically minded. The same hubris that posits that complex tools of mass destruction can be created but never used, also fuels the fatal vanity that war itself is an anachronism and no longer an existential concern—at least in comparison to the supposedly greater threats of naturally occurring pandemics, meteoric impacts, man-made climate change, or overpopulation.
Or this one:
The gullibility, and indeed ignorance, of contemporary governments and leaders about the intent, hatred, ruthlessness, and capability of their enemies are not surprising. The retreat to comfortable nonchalance and credulousness, often the cargo of affluence and leisure, is predictable given unchanging human nature, despite the pretensions of a postmodern technologically advanced global village.
I suppose the lesson is this: There’s nothing sacred about the Pax Americana. Nothing guarantees its survival, legitimacy, comforts, power, or wealth. A sardonic observer like the Roman poet Juvenal — were he alive — might even observe that today’s America seems less like the “city on a hill” of Scripture, and more like a Carthaginian tophet, or the ritual site of child sacrifice. Of course, that would be unfair. A biblical leaven remains in the American experiment, and many good people still believe in its best ideals.
The Curious Case of Hitler’s Corpse – War Against Humanity 136
World War Two
Published 21 Jun 2024Joseph Stalin claims that Adolf Hitler managed to escape Berlin and is now living somewhere in hiding. It’s complete nonsense of course. But it raises some interesting questions. What remains do we have of Hitler? How do we know they belong to the Fuhrer? And, why is Stalin spreading these far-fetched lies?
(more…)
“We can learn a lot about our betters from looking at each exception to their rules”
Julie Burchill isn’t a soccer fan, but she points out that the “exceptions” to the usual “rules” that the kakistocrats allow during international soccer tournaments tell us a lot about them:
Patriotism is not the only “bad” thing we’re suddenly “allowed” to do in the weeks when the national team plays on the world stage. The BBC in particular reminds men that they can disregard the finger-wagging for a few brief weeks. In EastEnders, male characters cringingly ask their mates to “get the beers in for the game”. Alcohol would generally be condemned as a public-health menace by Auntie, but during “The Game”, one more “cheeky” tipple apparently won’t hurt you.
We can learn a lot about our betters from looking at each exception to their rules. Don’t be racist – except against Jews. Believe all women about sexual assault – unless they’re Israeli. Oh, and be careful not to “culturally appropriate” the slightest thing from any other nationality, even to the point of never wearing a sombrero in a Mexican restaurant – but it’s fine to be a cross-dressing man culturally appropriating my sex. Meanwhile, if you’re a woman, be a good little Transmaid and stand by smiling, even if you call yourself a feminist.
Like most other places in the West in these dog days of civilisation, England feels like a nation devoid of hope and pride. Even so, being allowed to take pride in some overpaid ball-kickers, but not in the fact that this country contributed massively to ending slavery – lest we be called out as White Saviours – is a somewhat surreal situation to find ourselves in, after all those centuries of blood, sweat and struggle.
Flying the flag for the duration of the Euros is like being a eunuch who’s permitted to have his nuts back for a couple of weeks – for old times’ sake – and wear them as earrings. But those who indulge must be sure to tear their St George’s down sharpish once the festivities are over, lest they be fingered as a fascist for liking their own flag more than others. Remember, the only flag that can be flown constantly now is the Pride flag. This must be saluted respectfully wherever it pops up – failure to do so may identify you as an unworthy citizen of Soft Play Pit Nation.
Why and when did the Romans start wearing different clothing and armor?
Maiorianus
Published Mar 5, 2024