BBC Comedy Greats
Published 26 Jul 2021Bernard (Derek Fowlds) walks Jim Hacker (Paul Eddington) through the red-tape of signing his Christmas cards, but Jim Hacker is more concerned with worrying plans from Brussels to rename the British sausage.
(more…)
December 22, 2022
The Emulsified High-Fat Offal Tube | Yes, Minister: 1984 Christmas Special | BBC Comedy Greats
QotD: Sparta as the pre-eminent foe of tyranny
One of the ways that Sparta positioned itself was as the state which championed the freedom of the Greeks. Sparta had fought the Persian tyrant, had helped to oust tyrants in Athens and had later framed Athens itself as a “tyrant city”. Sparta itself had never had a tyrant (until Cleomenes III seized sole power in the 220s). On the flip side, Spartan hegemony was, apparently, little better than Athenian hegemony, given how Sparta’s own allies consistently reacted to it and Sparta would, in the end, do absolutely nothing to stop Philip II of Macedon from consolidating sole rule over Greece. When the call went out to once again resist a foreign invader in 338, Sparta was conspicuous in its absence.
It also matters exactly how tyranny is understood here. For the ancient Greeks, tyranny was a technical term, meaning a specific kind of one-man rule – a lot like how we use the word dictatorship to mean monarchies that are not kingdoms (though in Greece this word didn’t have quite so strong a negative connotation). Sparta was pretty reliable in opposing one-man rule, but that doesn’t mean it supported “free” governments. For instance, after the Peloponnesian War, Sparta foisted a brutal oligarchy – what the Athenians came to call “The Thirty Tyrants” – on Athens; their rule was so bad and harsh that it only lasted eight months (another feat of awful Spartan statecraft). Such a government was tyrannical, but not a tyranny in the technical sense.
But the Spartan reputation for fighting against tyrannies – both in the minds of the Greeks and in the popular consciousness – is predicted on fighting one very specific monarchy: the Achaemenids of Persia. […] This is the thing for which Sparta is given the most credit in popular culture, but Sparta’s record in this regard is awful. Sparta (along with Athens) leads the Greek coalition in the second Persian war and – as discussed – much of the Spartan reputation was built out of that. But Sparta had largely been a no-show during the first Persian war, and in the subsequent decades, Sparta’s commitment to opposing Persia was opportunistic at best.
During the late stages of the Peloponnesian War, Sparta essentially allied with Persia, taking funding and ships first from the Persian satrap Tissaphernes and later from Cyrus the Younger (a Persian prince and satrap). Sparta, after all, lacked the economic foundation to finance their own navy and the Spartans had – belatedly – realized that they needed a navy to defeat Athens. And of course the Persians – and any Spartan paying attention – knew that the Athenian navy was the one thing keeping Persia out of Greek affairs. So Sparta accepted Persian money to build up the fleets necessary to bring down the Athenian navy, with the consequence that the Ionian Greeks once again became subjects to the Persian Empire.
Subsequent Spartan diplomatic incompetence would lead to the Corinthian War (395-387), which turned into a nasty stalemate – due in part to the limitations of Spartan siege and naval capabilities. Unable to end the conflict on their own, the Spartans turned to Persia – again – to help them out, and the Persians brokered a pro-Spartan peace by threatening the Corinthians with Persian intervention in favor of Sparta. The subequent treaty – the “King’s Peace” (since it was imposed by the Persian Great King, Artaxerxes II) was highly favorable to Persia. All of Ionian, Cyprus, Aeolia and Carnia fell under Persian control and the treaty barred the Greeks from forming defensive leagues – meaning that it prevented the formation of any Greek coalition large enough to resist Persian influence. The treaty essentially made Sparta into Persia’s local enforcer in Greece, a role it would hold until its defeat in 371.
If Sparta held the objective of excluding Persian influence or tyranny from Greece, it failed completely and abjectly. Sparta opened not only the windows but also the doors to Persian influence in Greece – between 410 and 370, Sparta probably did more than any Greek state had ever or would ever do to push Greece into the Persian sphere of influence. Sparta would also refuse to participate in Alexander’s invasion of Persia – a point Alexander mocked them for by dedicating the spoils of his victories “from all of the Greeks, except the Spartans” (Arr. Anab. 1.16.7); for their part, the Spartans instead tried to use it as an opportunity to seize Crete and petitioned the Persians for aid in their war against Alexander, before being crushed by Alexander’s local commander, Antipater, in what Alexander termed “a clash of mice”.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part VII: Spartan Ends”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-09-27.
December 21, 2022
The rise of David Bowie
In Quillette, David Cohen outlines the career of David Bowie:
With impeccable timing, the thin white stork had dropped David Robert Jones out of London’s skies nearly three-score-and-ten years earlier. The suburban Bromley Boomer fell to Earth on January 8th, 1947, and landed smack in the middle of the bulge years, a wonderfully fertile period for anyone looking to forge a career in recorded music. His first instrument was the saxophone, which he was blowing on by the age of 14. Within a few years, the transistor radio would be ubiquitous, young people would be awash with disposable cash to buy records, and the mass adoption of international air travel would open up new vistas for fans and artists alike. Could any moment have been better suited to a rock-star-in-waiting?
But he also came of age as the youngest child in a doomy household. Three of his maternal aunts suffered from acute mental health issues — one of whom was eventually lobotomized — and the family was riven with more dark secrets than the Tolstoy home. His schizophrenic step-brother, Terry, would spend much of his adult life in psychiatric care. His beloved father dropped dead when Bowie was just 22, while his mother — a children’s home publicist with whom he was emphatically not close — lived on. “Everyone says, ‘Oh yes, my family is quite mad,'” Bowie later recalled. “Mine really is.”
The greatest dream of the era in which Bowie grew up — the promise of putting Man on the Moon — became one of his first signature artistic nightmares. Space Oddity, the most famous track from his eponymous second album, conjured one such scenario, and provided him with his first real hit after the false start of his debut. The earlier album had its moments, but it left unresolved the question of whether the singer wanted to be a fey-voiced Anthony Newley or a strange young man called Dylan.
By the time he recorded his second album — and, especially, his third — Bowie had decided he would be a bit of both. The cover art for 1970’s The Man Who Sold the World presented him elegantly reclining on a chaise longue in a dress. He smoked copious amounts of hash and assembled a crack band for 10 days of whirling Moog synthesizers and hard rock guitars. The experience was so enjoyable and creatively rewarding that bassist Trevor Bolder, guitarist Mick Ronson, and drummer Mick Woodmansey stayed on. The tracks were laid down at a London residence called Haddon Hall, in Beckenham, and it is here that he would write and rehearse the material for his next three albums that would send his career stratospheric.
Commercially, the sex, drugs, and frock ‘n’ roll of The Man Who Sold the World didn’t find much of an audience. It was too heavy, perhaps, for the folk followers he had accrued with its acoustic predecessor. And too gay for rock fans certainly, the singer’s voracious heterosexuality notwithstanding. He followed it a year later with Hunky Dory, which is generally thought to be the record on which the Bowie alchemy first cohered into something truly new. It was also the curtain-raiser for what’s generally regarded as his classic period, and it provided him with his first American hit, “Changes”. More critically, it saw him discard the claustrophobic sound of The Man Who Sold the World for textured melodies, creamy arrangements, seat-of-the-pants lyrics, and further cameos from extraterrestrials.
On Hunky Dory, Bowie also turned in tribute tracks about Lou Reed, Andy Warhol, and Bob Dylan. Warhol hated the song Bowie had written about him. Reed would eventually smack Bowie about the head during an altercation at a London restaurant in April 1979. And when Bowie finally met Dylan, he later told Playboy, they “didn’t have a lot to talk about. We’re not great friends. Actually, I think he hates me.” Small wonder that he preferred the company of spacemen. The razzle-dazzle of “Oh! You Pretty Things” conjures hordes of them. As does “Life on Mars?” which features a chord progression nicked from Frank Sinatra’s “My Way”. The album closes with “The Bewlay Brothers”, in which the 24-year-old singer paid a tribute of sorts to his own step-brother, Terry.
But it was the release of The Rise and Fall of Ziggy Stardust and the Spiders from Mars in 1972 that made David Bowie a superstar. Picking the space songs out of that record is difficult because, by that point, almost everything Bowie was writing seemed to have an explicitly alien streak. During his appearance on Top of the Pops, he draped an arm across Ronson’s shoulders, and glowered out at a world that was about to repay the attention. In the wake of the album’s release, he returned to the United States a sensation (although the stormy flight en route only confirmed his fear of flying).
A generation on, Ziggy Stardust still routinely appears at or near the top of critics’ lists of the all-time greatest rock albums. It is strange to recall then, that in 1972, while it picked up its share of warm reviews, the album was by no means universally well received (the work of a “competent plagiarist”, sniffed Sounds). Some critics never got it. “I always thought all that Ziggy Stardust homo-from-Aldebaran business was a crock of shit,” wrote Lester Bangs in Creem four years later, “especially coming from a guy who wouldn’t even get in a goddam airplane.”
The Nazi Quest for Thor’s Hammer – WW2 Documentary Special
World War Two
Published 20 Dec 2022Books, films, and comics are filled with Nazi scientists and explorers travelling the globe to get their hands on ancient artifacts or summoning daemons with black magic. But how much of it is grounded in reality? Well, some of it. In the neo-pagan religion invented by Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler, the world can only be explained through the occult.
(more…)
Tom Holland’s Dominion
Ed West expands on the review he wrote when Holland’s book was first published in 2019:
The Romans are the most “epic” figures in history, to use my young son’s favourite word, exerting a glamour and allure that no civilisation has successfully matched. This magnetism can also appear heightened by what followed, the illiterate bleakness of the early Middle Ages, and the fun-sucking religion that came with it. Many down the years have lamented the switch from the Rome of the Caesars to the Rome of the popes.
The young Tom Holland was one of them. Raised as an Anglican, the historian’s childhood fascination with dinosaurs evolved into one for the equally glamorous ancients. “Although I vaguely continued to believe in God,” he writes: “I found him infinitely less charismatic than the gods of the Greeks: Apollo, Athena, Dionysus. I liked the way that they did not lay down laws, or condemn other deities as demons; I liked their rock-star glamour. As a result, by the time I came to read Edward Gibbon and his great history of the decline and fall of the Roman Empire, I was more ready to accept his interpretation of the triumph of Christianity: that it had ushered in an ‘age of superstition and credulity’. My childhood instinct to see the biblical God as the po-faced enemy of liberty and fun was rationalised.”
This, indeed, is a widespread view. Since Gibbon wrote his great work in the late 18th century there has existed the popular idea that the Renaissance, with its return to classical values, and the Enlightenment, which saw the birth of reason over superstition, were a reaction to Christianity, which had in those thousand dark medieval years suppressed science and freedom.
Yet the truth and paradox, as Holland shows in this truly epic account of how Christianity came to shape the West, is that the western idea of secularism is itself a very Christian one. Liberalism was never a reaction to Christianity, it was a product, perhaps one might heresy; ditto Marxism, socialism and the various progressive creeds of the modern era, right up to the current Great Awokening with its focus on the sanctity of victimhood.
All our assumptions about progress, the rights of the individual, our horror of racism and sexual exploitation, even the acceptance of gay marriage, are the products of Christianity. They are not in themselves universal or “natural”, and to the Romans these ideas of human rights and dignity would have been incomprehensible, laughable even.
Holland made his name with thrilling popular histories set in the ancient world, yet the more he studied antiquity, the more alien it became to him. It wasn’t just that Spartans or Romans killed innocents in large numbers, but that they lacked even the suggestion that the weak might be worth pitying. “That my belief in God had faded over the course of my teenage years did not mean that I had ceased to be Christian,” he writes.
Cruelties such as the exposure of infants – especially female infants – were almost universally accepted in antiquity, except among one or two small German tribes and, at the other end of the empire, a monotheistic people in the eastern Mediterranean. Perhaps the obscenest horror, however, was the practice of crucifixion, a death so cruel that Roman writers barely touched on the subject. Indeed only “four detailed accounts of the process by which a man might be sentenced to the cross, and then suffer his punishment, have survived from antiquity. Remarkably, they all describe the same execution.”
This is the story of how on that one Friday in Judea the world was changed forever — with a moral revolution like nothing before or since.
Is Regifting a Crime?
It’s a Southern Thing
Published 10 Dec 2019To regift or not to regift? The Southern People’s Court brings their unique brand of justice to this tough issue.
(more…)
QotD: The Spoon Theory
The blogger Christine Miserandino, who has lupus, coined the term spoonie in a 2003 post called “The Spoon Theory”. A spoon, Miserandino explained, equates to a certain amount of energy. The Healthy have unlimited spoons. The Sick — the spoonies — only have a few. They might use one spoon to shower, two to get groceries, and four to go to work. They have to be strategic about how they spend their spoons.
Since then, the theory has ballooned into an illness kingdom filled with micro-celebrities offering discounts on supplements and tinctures; podcasts on dating as a spoonie; spoonie clubs on college campuses; a weekly magazine; and online stores with spoonie merch. In the past few years, spoonie-ism has dovetailed with the #MeToo movement and the ascendance of identity politics. The result is a worldview that is highly skeptical of so-called male-dominated power structures, and that insists on trusting the lived experience of individuals — especially those from groups that have historically been disbelieved. So what do spoonies need from you? “To believe; Be understanding; Be patient; To educate yourself; Show compassion; Don’t question”.
Spoonie illnesses include, but are not limited to, serious diseases like multiple sclerosis and Crohn’s disease, but also harder-to-diagnose ones that manifest differently in different people: polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), endometriosis, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, dysautonomia, Guillain-Barré Syndrome, gastroparesis, and fibromyalgia. Another spoonie illness is myalgic encephalomyelitis — or chronic fatigue syndrome — which has now been linked to long Covid.
These illnesses are often “invisible”: To most people, spoonies may appear healthy and able-bodied, especially when they’re young. Many of the conditions affect women more frequently, and most are chronic illnesses that can be managed, but not cured. A diagnosis often lasts for a lifetime, while symptoms come, go, morph, and multiply.
Spoonies find community in having complicated conditions that are often hard to identify and difficult to treat. That’s why a lot of spoonies include a zebra emoji in their social media bios, borrowed from the old doctor’s adage: “When you hear hoof beats, look for horses, not zebras.” In other words: assume your patient has a more common illness, rather than a rare one.
The spoonie mantra might be: I am the zebra.
Although the term is relatively new, the spoonies fit into a long history of women having amorphous, hard-to-diagnose conditions. Since ancient times, women who were diagnosed under the general category of “hysteria” were prescribed treatments such as sex, hanging upside down, and the placement of leeches on the abdomen. Then, in the 19th century, the new field of psychoanalysis concluded that women with hysteria were not suffering from physical disorders, but mental ones. Whether the women’s inexplicable pain was a function of their brains or of their bodies — or of each other (see mass hysteria), or of the devil (see Salem, 1692) — has always been a fraught subject.
And then the internet arrived and created a 21st century version of Freud’s Vienna, in which everyone was always on the couch, perpetually the patient.
Suzy Weiss, “Hurts So Good”, Common Sense, 2022-09-06.
December 20, 2022
A true behind-the-scenes look at George Orwell’s Nineteen Eighty-Four
In Spiked, Alexander Adams reports on a new, limited edition of the surviving portion of George Orwell’s manuscript for the novel:

A photo from SP Books’ web page showing the reproduction of Orwell’s manuscript.
SP Books, https://www.spbooks.com/150-1984-9791095457114.html
Published by SP Books, this is Nineteen Eighty-Four as you’ve never seen it before. It reproduces, in colour facsimile, the 197 surviving pages of Orwell’s manuscript, held by the John Hay Library at Brown University, Rhode Island. We see Orwell’s work in fountain pen and ballpoint (complete with ink blots), as well as 14 typewritten sides. We are even given his doodles and pen tests. Readers will remember how Winston also marvels at the beauty of the paper and binding of a blank book he buys from a junk shop.
This edition contains what amounts to 44 per cent of the text of the published novel. It is in a jumbled state, with pages missing and drastic changes made. There are many crossings out and additions. The handwriting can be a little tricky to decipher – Orwell had a habit of using cursive joining lines between words and using abbreviations. Added to that, the script can be somewhat crabbed, especially where Orwell adds text between existing lines. With a little patience, though, the reader can adjust to Orwell’s writing, especially if familiar with the text, and glimpse this most familiar of novels anew.
This version includes an introduction by Orwell scholar DJ Taylor. He tells us that although Orwell usually wrote quickly, he took five years to complete Nineteen Eighty-Four. Taylor details the difficult conditions that explain the novel’s long gestation. The death of Orwell’s first wife in 1945, the effort of raising their young son alone and the toll of tuberculosis all slowed work and drained the author’s energy (tuberculosis would kill him in 1950, only months after the novel’s publication). There are indications that Orwell let the book go to publication even though he thought it was not properly finished.
Looking at this draft, we can see Orwell revising heavily as he wrote. Some revisions are minor, such as Trotsky-figure Goldstein’s description of the workings of the Party and his description of the geopolitics of Oceania, Eurasia and Eastasia. Other changes are more significant. Here, in the propaganda film described by Winston at the start of his diary, there is a graphic passage about the lynching of a pregnant black woman. Orwell seems to have cut these lines on grounds of decency. He also reduced the references to race overall, perhaps uncomfortable about the implications of speaking so generally about groups and types. Orwell’s background as a policeman in Burma no doubt made him sensitive to racial issues.
Coming of the Sea Peoples: Part 2 – The Old and New Chronology of the Bronze Age
seangabb
Published 2 May 2021The Late Bronze Age is a story of collapse. From New Kingdom Egypt to Hittite Anatolia, from the Assyrian Empire to Babylonia and Mycenaean Greece, the coming of the Sea Peoples is a terror that threatens the end of all things. Between April and July 2021, Sean Gabb explored this collapse with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
The forgotten Thomas Savery
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes remembers the work of inventor Thomas Savery:

Screenshot from “Savery’s Miners Friend – 1698”, a YouTube video by Guy Janssen (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dt5VvrEIj8w)
We know surprisingly little about Thomas Savery — the inventor of the first widely-used steam engine. Unfortunately, his achievements were almost immediately overshadowed by the engine of Thomas Newcomen, and so he’s often only mentioned as a sort of afterthought — a loose and rather odd-seeming pebble before the firmer stepping stones of Newcomen, Watt, Trevithick, and other steam engine pioneers in the standard and simple narratives of technological progress that people like to tell. I’ve often seen Savery’s name omitted entirely.
He is even neglected by the experts. The Newcomen Society, of which I am a new member, has an excellent journal — it is the best place to find scholarly detail about all steam pioneers, and about the history of engineering in general. Yet even it only mentions Savery in passing. In over a century, Savery has been named in the titles of just three of its articles, and the last was published in 1986.
I think Savery is extremely under-rated, and deserves to be studied more. Fortunately, we do know quite a bit about the engine he designed, which he intended primarily for raising the water out of mines. Steam was admitted into a chamber, and then sprayed with cold water to condense it. This caused mine water to be sucked up a pipe beneath it, by creating a partial vacuum within the chamber and thus exploiting the relative pressure of the atmosphere on the surface of the mine water. Then, hot steam was readmitted to the chamber, this time pushing the raised water further up through another pipe above. Two chambers, the one sucking while the other pushed, created a continuous flow. (Video here.) We have dozens of images and technical descriptions of Savery’s engine, as it continued to be used for decades, especially in continental Europe.
But we know essentially nothing about Savery’s background, training, inspiration, or profession, and most of the supposedly known biographical details we have for him are simply wrong. There is no evidence that he was a “military engineer” or a “trenchmaster”, for example — mere speculation that has been repeated so often as to take on the appearance of fact. Savery simply appears out of nowhere in the 1690s, with his inventions almost fully formed.
Yet in Savery’s own writings we can see a few tantalising hints of how he thought, including some flashes of brilliance. I kept coming across them by chance, when investigating various energy-related themes with Carbon Upcycling. Take the following aside, from Savery’s 1702 prospectus for his steam engine: “I have only this to urge, that water in its fall from any determinate height, has simply a force answerable and equal to the force that raises it”. Savery here seems to be hinting at some idea of the conservation of energy, and perhaps of a theoretical maximum efficiency — in a phrase that is remarkably similar to that used by the pioneers of water wheel theory half a century later, and to Sadi Carnot when he applied the same ideas to early thermodynamics.
Savery, frustratingly, doesn’t expand any further on the point, except to then casually mention the notions of both mechanical work and horsepower — over eighty years before James Watt. Savery noted that when an engine will raise as much water as two horses can in the same time, “then I say, such an engine will do the work or labour of ten or twelve horses” — ten horsepower, rather than two, because you’d need a much larger team of horses from which to rotate fresh ones while the others rested, to keep raising water as continuously as the force of a stream could turn a water-wheel, or his steam engine could pump. (Incidentally, Watt wasn’t even the second person to use horsepower — the same concept was also mentioned by John Theophilus Desaguliers in the 1720s and John Smeaton in the 1770s. Watt just managed to get all the credit later on. Perhaps watts should really be called saveries, even if he was less precise.)
Eggnog: A Christmas History
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 22 Dec 2020
(more…)
QotD: Myrna Loy
In the first couple of pages of her 1987 memoir Being and Becoming, Myrna Loy gets down to business. Talking about the sex lives of Hollywood stars such as herself, she tells us that “any business involving so many beautiful and high-strung people working together on such intense and intimate terms is bound to breed an easy promiscuity. God knows I’ve fended off my share of amorous men – attractive, desirable men.”
She goes on to provide a short list: John Barrymore (“just because he felt like a little redhead now and then didn’t incline me to join the club …”), Clark Gable (she shoved him off her back porch one night after he made a pass “and, boy, did he punish me for that!”), Spencer Tracy (“he chased me for years, then sulked adorably when I married someone else …”) and Leslie Howard (despite both of them being married he “wanted to whisk me off to the South Seas, and, believe me, that was tempting …”).
“These days you’re made to feel dull and defensive if you weren’t the Whore of Babylon,” Loy writes. “Well, succumbing isn’t the only interesting aspect of a relationship.”
It’s no surprise that a woman who understands this much was such a natural in screwball comedies, where succumbing is usually held at bay until the last shot, the better to draw out the difficulties, obstacles and improbabilities set up like an obstacle course along the way.
Of the over 120 films she made, most of the first half of her career – largely bit parts, vamps and “exotics” – is forgotten, her reputation based on the fourteen she made with William Powell (six of which were Thin Man pictures), along with titles like The Best Years of Our Lives, The Bachelor and the Bobby Soxer, Mr. Blandings Builds His Dream House and Cheaper by the Dozen.
If she had a type onscreen – and Loy tried hard to avoid becoming a type – she would become Nora Charles, the paragon of wives: supportive but not obsequious, the equal of any spouse, ready with a wisecrack and a bit of fun, and always beautifully turned out. Quite a stretch, she’d admit, for a woman divorced four times, childless and openly dismissive of her domestic skills.
Rick McGinnis, “Do You Take This Woman? Myrna Loy and Third Finger, Left Hand“, Steyn Online, 2022-09-17.
December 19, 2022
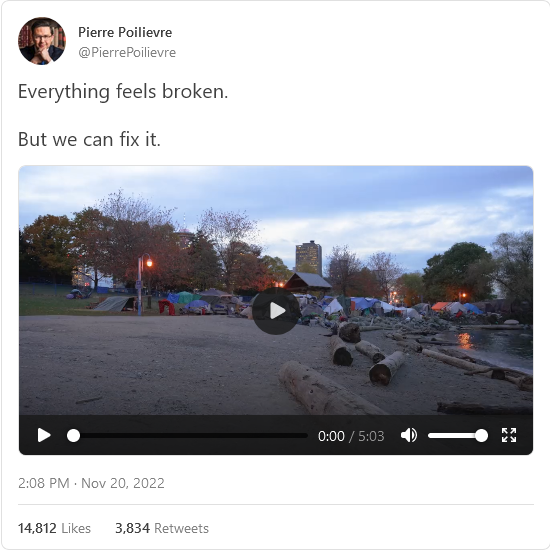
“[T]he major promoter of the ‘Canada is broken’ thesis over the past few years has been … Justin Trudeau”
In the free-to-cheapskates exerpt from this week’s Dispatch from The Line, they set up the possible lines of attack for the next federal election:
What was more interesting to us this week were the comments made by Prime Minister Justin Trudeau to thousands of Liberals at a large in-person Christmas party. As one does at any good Christmas party, the PM took the chance to, uh, savage his rivals. To wit: “Canada is not broken … Mr. Poilievre might choose to undermine our democracy by amplifying conspiracy theories. He might decide to run away from journalists when they ask him tough questions. That’s how he brands himself. That’s his choice. But, when he says that Canada is broken, that’s where we draw the line.” (Full video of the speech is available via CTV News).
The PM was responding, of course, to a recent line of attack favoured by the Conservatives: that Canada is broken, and we need the Conservatives to fix it.
There are three comments we’ll make in response to this.
The first is strictly an analysis: Trudeau is staking out some interesting rhetorical ground. We aren’t sure this will be the ground on which the next campaign is fought over — God only knows what’ll happen between now and whenever we are next headed to the polls. But if this is the subject of our next “ballot question”, well, that’s just fascinating. “Sunny Ways” vs. “Everything Is Broken and It’s Your Fault.”
How fun! Both men would be able to make an honest pitch for their case. As we’ve written before, the Liberals seem exhausted and spent. They’ve accumulated baggage since their first smiley-faced win back in 2015, and the country has been thoroughly battered by events since then. That suggests that Poilievre, who is at his best when on the attack, could mop the floor with Trudeau.
That said, we don’t take that outcome as a given. First, Trudeau is a damned good politician, better than the Conservatives still give him credit for, and though we are starting to wonder if Trudeau is past the point of no return, we will never count him out. We also think that if the Conservatives make “Things are terrible” the centrepiece of their next campaign, may find that Canadians recoil. Canadian pride is a fragile, brittle thing, and while many of us may feel like things are bad, it’s not clear to us that Poilievre saying so won’t rub a lot of voters the wrong way.
But we honestly don’t know. That’s why it’s fascinating.
The second point is a bit of a reminder: It is worth noting that the major promoter of the “Canada is broken” thesis over the past few years has been … Justin Trudeau. We don’t think we — your Line editors, the media, Canadians in general — should let him take such casual re-occupation of the “Sunny Ways” position, since he’s spent the last five years absolutely dumping on Canada, its history (genocide), its symbols (the flag), and its institutions (the military, amongst others). No one has done more to proclaim Canada broken than Justin Trudeau. Is he now claiming that he’s fixed all the problems he’s spent the last half decade making political hay over?
We mean … the guy won’t even fix his house.
The third point is our own view: of course Canada is broken. And Trudeau has done nothing to fix it.
Now, we have to define our terms here. “Broken” isn’t “destroyed”. We don’t think we’re descending into some kind of post-apocalyptic wasteland. It remains undeniably true that Canada is, in global terms, a nice place to live. Safe. Lots of food. No one is firing missiles at us. Sweet! But, like, gosh, folks. Look around. If the PM really wants to assert that Canada isn’t broken, we’ll agree insofar as it’s not so broken that the average person fears starvation and violent death. Sure. But that average person also probably can’t get a passport, or a family doctor, or timely care in an emergency room, or a house in a big city where the jobs are clustering, or Tylenol for their kids.
Napoleon’s Downfall: German Wars of Liberation 1813
Real Time History
Published 16 Dec 2022After Napoleon’s defeat in Russia in 1812, the situation on the European continent is rapidly shifting. Prussia and Austria are leaving their unhappy alliance with the French. Prussian general Yorck even pledges his support to the Russian Army which is on the move towards Berlin. At Lützen and Bautzen Napoleon still manages to beat the new coalition, but his losses from Russia put him on the backfoot.
(more…)