N.S. Lyons admires what can only be described as potentially revolutionary protests across many of China’s big cities and resisting further lockdowns by the government:
Something extraordinary happened in China over the weekend. Not long ago I wrote at length, if in a rather different context, about the vital importance of courage in the defense of the true and the human against the cold, mechanistic evil that is nihilistic technocracy, the machine whose Conditioners forever lust after total control – not only over men, but ultimately over reality itself. Well, now we have just seen a stunning example of such courage in the streets of China, where people rose up to reassert their human dignity in the face of the most dehumanizing machine of control in the world today: the Chinese Communist Party’s “zero-Covid” terror-state.
For three years now, the Chinese government has maintained its policy of draconian city-wide lockdowns, endless daily mass testing and biomedical surveillance, digital Covid-passes that arbitrarily govern every aspect of daily life, vast camps to house those dragged into quarantine for weeks (or longer) at a time, and, more recently, such innovations as “closed-loop” factories, where workers are forced to work, sleep, and “live” completely isolated from the outside world so that they can continue to produce your iPhones.
But now over the past several days protests have erupted in at least a dozen cities and 79 universities across the country, with spontaneous demonstrations – often begun by only a handful of people, or even a single individual – quickly drawing crowds of hundreds, even thousands, of people willing to fearlessly demand an end to the zero-Covid nightmare.
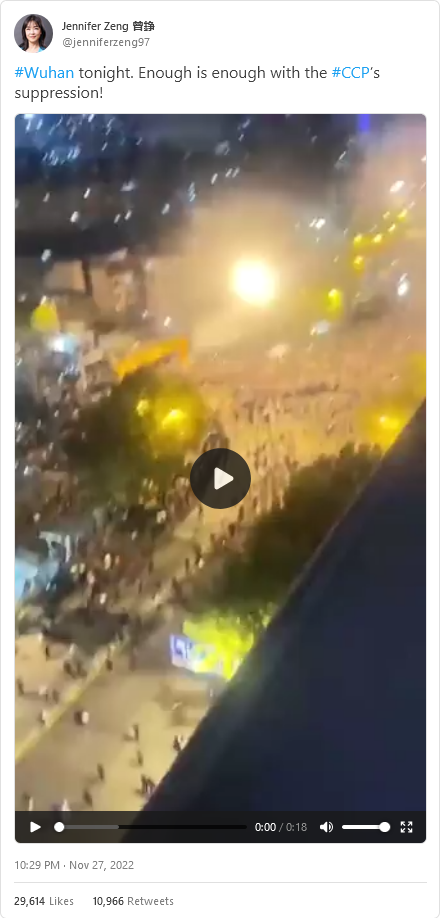
In Wuhan, where it all began, swarming crowds smashed down containment barriers and “liberated” locked-down neighborhoods:
[…]
All across the country, many thousands of these protesters spontaneously echoed many of the same lines:
We don’t want PCR tests. We want to eat.
We don’t want Cultural Revolution. We want reform.
We don’t want lockdowns. We want freedom.
We don’t want a Great Leader. We want the vote.
We don’t want lies. We want dignity.
We aren’t slaves. We are citizens.
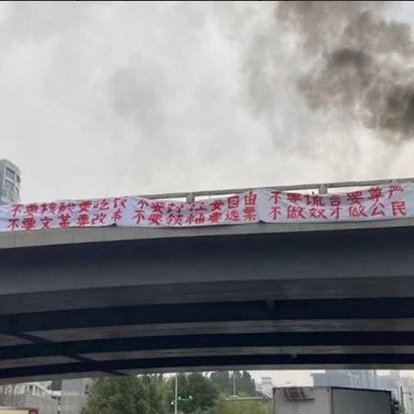
These are conspicuously the same lines as those of a banner hung from a Beijing bridge by a lone (since disappeared) protester, Peng Lifa, on the 13th of October, just ahead of the CCP’s 20th Party Congress and Xi Jinping’s re-coronation as Chinese leader for life.
Now, as recordings of the anti-lockdown protests are swiftly censored online, Chinese netizens have often simply been replying with “We saw it” – a phrase referring not just to the protests, but to Peng Lifa’s message.
His final and most striking line, on a second banner, happens to have been:
“Refuse to go to class. Go on strike. Remove the traitor Xi Jinping.”
And indeed in many protests over the last few days the people’s frustration with zero-Covid tyranny translated into something more: an outpouring of raw anger against the CCP and Xi.
Of course, China’s ruling Communist regime isn’t without its loyal supporters and useful idiots like Apple:
Maybe something will come of the COVID lockdown protests in China. Maybe not, if you’re old enough to remember the guy who stood in front of the tank in Tiananmen Square, and who was never identified nor ever seen again. More likely, the Chinese Communist Party will crack down again, and the people of China will become compliant again.
And the West will turn a blind eye. Again.
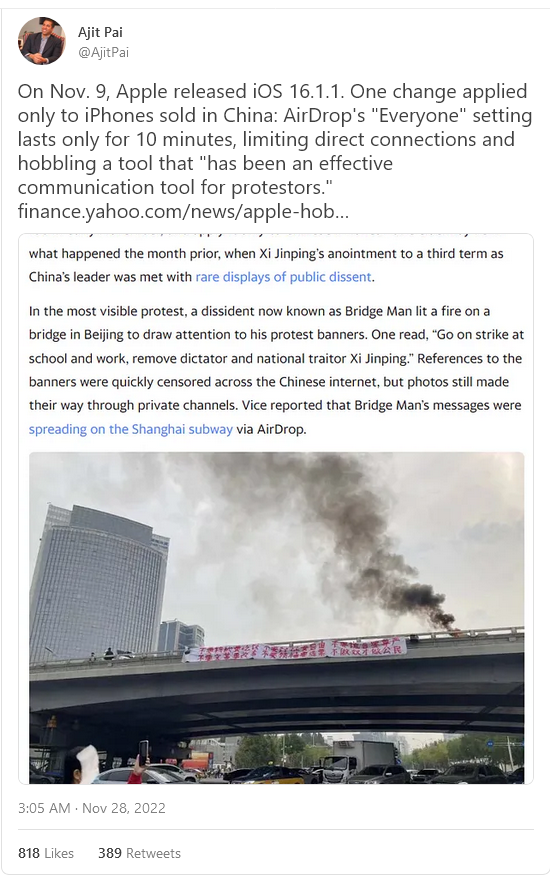
Here’s what was in the latest iPhone update, according to Zachary M. Seward of Quartz:
Hidden in the update was a change that only applies to iPhones sold in mainland China: AirDrop can only be set to receive messages from everyone for 10 minutes, before switching off. There’s no longer a way to keep the “everyone” setting on permanently on Chinese iPhones. The change, first noticed by Chinese readers of 9to5Mac, doesn’t apply anywhere else.
In other words, Chinese iPhone users can’t do or say anything without the CCP knowing about it. Dissent can be quashed before it even starts. The Chinese people can be kept under the CCP’s thumb. And Apple is helping.