World War Two
Published 10 Nov 2022Hitler commemorates the twentieth anniversary of the failed Beer Hall Putsch, in Auschwitz 50 men are shot in celebration, and Arthur Liebehenschel replaces Rudolf Höss as commandant.
(more…)
November 14, 2022
The Auschwitz Business Model – War Against Humanity 086
November 12, 2022
QotD: The short careers of secret police chiefs
The first thing you learn on even the most cursory look at any secret police is: they aren’t. Secret, that is. Otherwise they wouldn’t be effective. Oh, they’d probably be a lot better at gathering certain kinds of intel, but intelligence gathering is really only their secondary function. Their primary function, of course, is intimidation. That’s why every Hans and Franz on the street in Nazi Germany could tell you exactly where the nearest Gestapo office was.
(The Romanian Securitate had public intimidation down to an art form. They’d follow random guys around using big, obvious details, the better to prove to the proletariat that everyone was suspect. It is to them, not Mafia dons or aspiring rappers, that we owe the now-standard Eurotrash track suit look).
Secret police goons suffer from two serious structural problems, though, that not even the guys in Stove’s book [The Unsleeping Eye] really ever solved. The first is the obvious one, that guys who know where the bodies are buried are always at risk of using that knowledge. Napoleon’s guy Joseph Fourche, and FDR’s main man J. Edgar, lived out their natural lives (as did Elizabeth’s spymaster Sir Francis Walsingham), but of them, only Fourche lived in anything approaching what we would call an ideologized society, and that was small beer.
The rest of those guys died in harness, because of course they did. Adolf Hitler was an especially stupid dictator, and Heinrich Himmler an especially servile little freak, but I have no doubt that if the Reich had gone on much longer [Himmler] would’ve shanked [Hitler]. If Heydrich hadn’t gotten perforated in Prague, he no doubt would’ve gone after [Himmler] even sooner. Lenin and especially Stalin burned through secret police chiefs on the regular, because they pretty much had to.
I don’t know about the goons in the Chinese etc. secret police, but I’d be shocked to find anyone with more than a few years’ tenure, because purges are simply a way of life in totally ideologized societies. For every Khrushchev who manages to hang on – n.b. he was a Red Army commissar during the war, i.e. a not-so-secret police goon — there are fifty guys who live fast and die hard, because that’s just how totalitarians rule.
The stoyaknik, of course, is well served to consider the current scene as if he were watching the Politburo of an exceptionally deluded Commie regime, one made up almost entirely of ruthless yet clueless retards … who still believe, for the most part, in Communism.
That was always the problem for Kremlinologists in evaluating the USSR — whatever the Boss of the moment decided would, of course, immediately be retconned into the Scriptures by the Academicians, but what did the Big Guy himself think about it? That constrained his choices. Stalin and Khrushchev were true Communists, there’s no question about that, but they came up in the school of the hardest possible knocks — if they needed to do something directly contrary to Leninism in order to hang on to power, then Comrade Ilych can suck it.
For anything short of mortal, though, they’d more often than not behave as stereotypical Commies, so the first thing any Kremlinologist had to do was determine the seriousness of the situation from the Politburo’s perspective. Not an easy task, as you might imagine, and what made it worse was: as the USSR gained stability and Communism matured, the old school hardasses all died off and were replaced by True Believers. Mikhail Gorbachev, for instance, didn’t start making his mark until after Stalin’s death, and he wasn’t a real up-and-comer until after Khrushchev — that is, he started rising through the ranks only after the hard boys were gone.
Thus, while Khrushchev was a true Commie, he still had some hard reality to constrain him. Gorby didn’t. He really believed all that Marxist-Leninist horseshit about democracy and etc.; he was far more doctrinaire than the earlier generation could possibly be. Thus Kremlinologists were forever baffled when he did stupid things that made no sense from the Realpolitik perspective, but were perfectly in keeping with the Scriptures. They thought Perestroika was some big 4D chess feint, for instance, instead of just a soft boy doing something noodle-headed.
Severian, “Book Review: The Unsleeping Eye by R.J. Stove”, Founding Questions, 2022-08-09.
November 6, 2022
Allies Launch New Phase in Pacific War – WW2 – 219 – November 5, 1943
World War Two
Published 5 Nov 2022The Allies hit the beaches of Bougainville, largest and last of the Solomon Islands. They create and expand a beachhead there and also win battles there at sea and in the skies. In the USSSR, the Soviets are closing in on Kiev and in the south have isolated the Crimea, but in spite of that, Adolf Hitler issues a new directive that Germany’s focus for the future should be in the west and the threat of an Allied invasion there.
(more…)
September 11, 2022
The Allies’ Latest Victory – WW2 – 211 – September 10, 1943
World War Two
Published 10 Sep 2022Dwight Eisenhower publicly announces the secret armistice signed last week, and Italy is now officially out of the war. The Italian fleet sails for Malta and Allied captivity. The Allies have landed in force in Southern Italy and they do face some heavy opposition from German forces — who have no intention of giving up Italy. In the USSR, though, the Soviets continue liberating territory all over Ukraine as they force the Germans back to the Dnieper River.
(more…)
September 10, 2022
QotD: “Working toward the Führer“
Sir Ian Kershaw was broadly right about how the Third Reich operated. He says Nazi functionaries were “working towards the Führer“. In other words, the Führer — the idealized, mythologized leader, not Adolf Hitler the individual — made it known that “National Socialism stands for X“. Hitler was famously averse to giving direct orders, so that’s often the only thing big, important parts of the government had to work from — the Führer‘s* pronouncement that “National Socialism means X“. It was up to them to put it into practice as best they could.
This had several big advantages. First, it’s in line with Nazi philosophy. The Nazis were Social Darwinists. Social Darwinists hold that “survival of the fittest” applies not only to humans as a whole, but to human social groups as well. Any given organization, then, must exist to do something, to advance some cause, to reach some goal. Ruthless competition between groups, and inside each group, is how the goal works itself out (you should be hearing echoes of Hegel here). The struggle refines and clarifies what the group’s goal is, even as the individual group members compete to reach it. The end result gets forced back up the system to the Führer, such that, dialectically (again, Hegel), “National Socialism means X” now encompasses the result of the previous struggle.
[…]
As with philosophy, “working towards the Führer” fit well with German military culture. Auftragstaktik is a fun word that means “mission-type tactics.” In practice, it delegates authority to the lowest possible level. Each subordinate commander is given an objective, a force, and a due date. High command doesn’t care how the objective gets taken; it only cares that the objective gets taken. Done right, it’s a wonderfully efficient system. It’s the reason the Wehrmacht could keep fighting for so long, and so well, despite being overpowered in every conceivable way by the Allies. The Allies, too, were constantly flabbergasted by their opponents’ low rank — corporals and sergeants in the Wehrmacht were doing the work of an entire Allied company command staff (and often doing it better).
Consider the career of Adolf Eichmann. In the deepest, darkest part of the war, this man pretty much ran the Reich’s rail network. Say what you will about the Nazi’s plate-of-spaghetti org chart, that’s some serious power. He was a lieutenant colonel.
The final great advantage of “working towards the Führer” is “plausible deniability”. Let’s stipulate Atrocity X. Let’s further stipulate that we’re in the professional historian’s fantasy world, where every conceivable document exists, and they’re all clear and unambiguous. It’s a piece of cake to pin Atrocity X on someone … and that someone would, in all probability, be a corporal or a sergeant. Maybe a lieutenant. What you wouldn’t be able to do is trace it up the chain any higher. Everyone from the captain to Hitler himself could / would give you the “Who, me?” routine. “I didn’t tell Sergeant Schultz to execute those prisoners. All I said was to go secure that objective / defeat that army / that National Socialism means fighting with an iron will.”
*I’m deliberately conflating them here — to make it clearer how confusing this could be — but in talking about this stuff the terminology is crucial. Adolf Hitler, the man, played the role of The Führer. What Hitler the man wanted was often in line with what the Führer role required, of course, but not always. This is one of the footholds Holocaust deniers have. Did Hitler-the-man actually put his name to a liquidation order? No. Did Hitler-the-man actually want it to happen? Unquestionably yes, but like all men, Hitler-the-man vacillated, had second thoughts, doubted himself, etc., and you can find documented instances of that. But The Führer very obviously wanted it to happen, and it was The Führer that motivated the rank-and-file. The man created the role, but very soon the role started playing the man …
Severian, “Working Towards the Deep State”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-01-06.
September 4, 2022
The War is Four Years Old this week – WW2 – 210 – September 2, 1943
World War Two
Published 3 Sep 2022Four years of war and no real end in sight, but as the week ends the Allies land their first troops on Italy, actively committing themselves to a front in Western Europe. In the USSR the Soviets are taking heavy casualties but still pushing back the enemy with big partisan help and in Pacific plans are made for offensive against yet more Japanese held islands.
(more…)
July 6, 2022
Decapitating the French Resistance – WAH 066 – June 26, 1943
World War Two
Published 5 Jul 2022The Gestapo deals a devastating blow to French Resistance, and in Bengal, British India the famine is only getting worse.
(more…)
July 5, 2022
How to Fool a Führer – Operation Mincemeat – WW2 – Spies & Ties 19
World War Two
Published 4 Jul 2022Glyndwr Michael, the dead secret agent, has deposited his deceptive letters in Spain. Now the next phase of Operation Mincemeat begins. If Charles Cholmondely of MI5 and Ewen Montagu of Naval Intelligence have done their job right, the letters should make their way into Hitler’s hands.
(more…)
May 15, 2022
The End of the War in Africa – WW2 – 194 – May 14, 1943
World War Two
Published 14 May 2022With the end of the Tunisian Campaign, the Allies have won the war for the African Continent. What next? They meet at the Trident Conference in Washington DC to try and figure that out. Meanwhile, the fight in the field continues — in Burma, the Aleutians, China, and the Kuban.
(more…)
May 8, 2022
Kilroy was Here! The fall of Tunis – WW2 – 193 – May 7, 1943
World War Two
Published 7 May 2022Tunis falls to the Allies, but the Axis are still fighting back from their little corner of Tunisia. There is more of the seemingly endless fighting in the Kuban in the Caucasus, and the Chinese Theater comes to life with a new Japanese offensive.
(more…)
April 17, 2022
Operation Mincemeat, 1943
Once an obscure bit of espionage and military disinformation, the events of Operation Mincemeat are being brought to the big screen (boy, does that term seem dated) in a feature film starring Colin Firth. Michael Curtis provides a look at the actual deception mission that inspired the film:
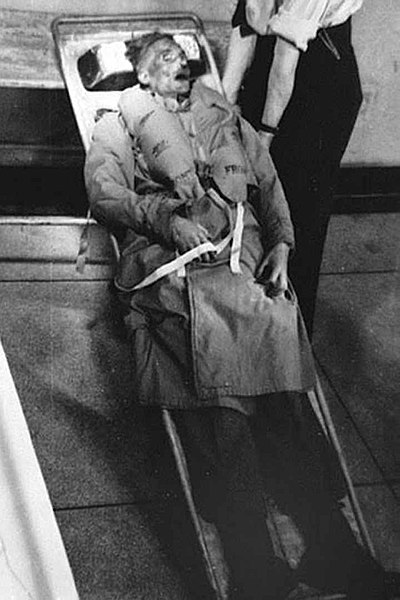
The corpse of Glyndwr Michael, dressed in a Royal Marine uniform with false documents and a fake ID, used in Operation Mincemeat, 1943.
Public domain image from The National Archives.
The story of the British deception, a fascinating story of Allied subterfuge, is now told in the film Operation Mincemeat. It is a remarkable and seemingly highly improbable story of a plan of Allied intelligence to deceive Hitler and misdirect German intelligence. Indeed, it is one of the best examples in history of military deception.
The concept of a plan starts with the Trout Memo, officially written in 1939 by Admiral John Godfrey, director of Naval Intelligence, but almost certainly written by his subordinate Lieutenant Commander Ian Fleming, not yet dreaming of 007, about the deception of an army in war time by fly fishing. Many ideas were suggested, including sending out tins of explosives disguised as food so that hungry sailors would pick them up. One idea, number 28 on the list, almost certainly the thought of Fleming who thought of elaborate deception options, was to use a dead body dressed as an airman dropped from a parachute that had failed and carrying false papers, and drop it where the Germans would find it and be deceived by it.
The deception was planned by a group, the Twenty Committee, XX, headed by Lieutenant Commander RNVR, Ewen Montagu, Cambridge, Harvard, a naval intelligence officer and prominent Jewish lawyer, who later became a judge, together with an RAF officer Squadron Leader Charles Cholmondeley. Montagu later wrote an account of the affair in a book, The Man who Never Was, 1953. The memory of the event is also simply commemorated in a mortuary in Hackney in East London where the body that was used in the plot is buried. In a rather unkind but truthful remark Montagu said of the man who was used, “The only worthwhile thing he ever did, he did after his death.”
The main deception in the plot was a personal letter purported to be from General Sir Archibald Nye to General Sir Harold Alexander, starting, “My dear Alex.” Nye’s letter contained details of sensitive topics, and of a new commander of the Guards brigade, and U.S. service medal awards. He also referred to Operation Husky, an imminent Allied invasion of Greece, that the Germans had been reinforcing and strengthening their defenses in Greece and Crete, and therefore the chief of the Imperial General Staff felt that the Allied troops planned for the assault were insufficient. Thus, it was agreed by the chiefs of staff that the 5th division should be reinforced by one brigade group for the assault on the beach south of Cape Araxos and that similar reinforcement should be made for the 56th division at Kalamata. The letter was a clever double bluff. Nye wrote that “we stand a very good chance of making the Germans think we will go for Sicily, it is an obvious objective and one about which they must be nervous.” To confuse Hitler, he therefore suggested the Allies would invade Sicily.
It is interesting but not surprising that a key figure in the deception appears to have been Ian Fleming, Mr. James Bond, who had written of methods to confuse the enemy, and was crucial to the Trout Memo.
The plot developed. After some difficulty a suitable body was found by a London coroner and kept on ice for few months. It was Glyndwr Michael, 34, homeless Welsh laborer, penniless, with mental health problems, who had died after ingesting rat poison in a London warehouse. He was transformed into Major William Martin, of the Royal Marines whose body contained love letters from a non-existent fiancé named Pam, a jewelry bill for an engagement ring, ticket stubs, religious medal, a copy of a letter marked “personal and most secret”, and above all the false Nye letter. The body had to look as if it had died in an air crash, but floated ashore and he had died at sea. Major Martin, his body wrapped in a life jacket, and with a black attaché case chained to his wrist, was found on April 30, 1943, by a Spanish fisherman off the coast of Huelva.
Even more unlikely than the plan itself was the impact the “secret” document had on Axis planning, summarized in the Wikipedia article:
On 14 May 1943 Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz met Hitler to discuss Dönitz’s recent visit to Italy, his meeting with the Italian leader Benito Mussolini and the progress of the war. The Admiral, referring to the Mincemeat documents as the “Anglo-Saxon order”, recorded
The Führer does not agree with … [Mussolini] that the most likely invasion point is Sicily. Furthermore, he believes that the discovered Anglo-Saxon order confirms the assumption that the planned attacks will be directed mainly against Sardinia and the Peloponnesus.
Hitler informed Mussolini that Greece, Sardinia and Corsica must be defended “at all costs”, and that German troops would be best placed to do the job. He ordered that the experienced 1st Panzer Division be transferred from France to Salonika, Greece. The order was intercepted by GC&CS on 21 May. By the end of June, German troop strength on Sardinia had been doubled to 10,000, with fighter aircraft also based there as support. German torpedo boats were moved from Sicily to the Greek islands in preparation. Seven German divisions transferred to Greece, raising the number present to eight, and ten were posted to the Balkans, raising the number present to 18.
On 9 July the Allies invaded Sicily in Operation Husky. German signals intercepted by GC&CS showed that even four hours after the invasion of Sicily began, twenty-one aircraft left Sicily to reinforce Sardinia. For a considerable time after the initial invasion, Hitler was still convinced that an attack on the Balkans was imminent, and in late July he sent General Erwin Rommel to Salonika to prepare the defence of the region. By the time the German high command realised the mistake, it was too late to make a difference.
April 10, 2022
Mussolini is Tired of War – WW2 – 189 – April 9th , 1943
World War Two
Published 9 Apr 2022Adolf Hitler meets with Benito Mussolini to hopefully restore his flagging morale and convince him that the Axis can hold out in North Africa, but the situation there grows more precarious and this week there the Allies advancing from the west and the east link up for the first time. The Axis are also holding out in the Caucasus, as new Soviet attacks to take Krymskaya begin.
(more…)
April 6, 2022
How To Build a Nazi Fortress – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 5 Apr 2022Few things of the Second World War are more intimidating than the iconic German bunker. Made out of reinforced concrete with a thickness of up to 3.5 meters, these casemates and pillboxes were incredibly tough to destroy. Built to withstand shells and bombs, they provided shelter to troops and civilians alike. But there were also some even larger super-structures. From giant U-Boat shelters and fearsome Flak-Towers, to the ultimate Führerbunker, the Germans perfected the art of bunker building.
(more…)
March 20, 2022
Kharkov Falls Once Again – WW2 – 186 – March 19, 1943
World War Two
Published 19 Mar 2022The British are attacking the Mareth Line in North Africa while the Americans hit the Axis flank, but the Allies are withdrawing in Burma. It’s the Germans who are pulling back in the USSR, though, and there is another attempt from within German command to assassinate Adolf Hitler.
(more…)
February 22, 2022
Triumph of the Will and the Cinematic Language of Propaganda
Folding Ideas
Published 10 Feb 2017Clickbait title: Nazis hate him! Secrets of propaganda exposed!
This took far longer to put together than I’d anticipated. It wasn’t even the work itself, it’s the emotional load. I eventually had to start chopping out huge planned segments, like looking at modern propaganda like that awful “Surfing in the DPRK” white guy rap video. I’m sorry about the downer ending, but there’s no way to spruce it up. To a certain degree we lost.
You should seriously read, and then re-read, Umberto Eco’s “Ur-Fascism”. It’s available online for free. It’s not that long. Here, I’ll even link it for you. http://www.nybooks.com/articles/1995/…
Books mentioned:
Urania’s Children
The Occult Roots of Nazism
The Origins of TotalitarianismWritten and performed by Dan Olson
Twitter: https://twitter.com/FoldableHuman




