World War Two
Published 24 Apr 2024It’s time for another thrilling installment of Out of the Foxholes, but what sort of questions does Indy answer today? Well, it’s good stuff — about Allied security and logistics at the major conferences, about what the British navy was doing once the Atlantic and Mediterranean were secure, and about the skills (or lack thereof) of the soldiers of the Waffen SS. How can you live without knowing about such things? I suppose it’s possible, but it would be a sad life indeed, so check it out!
(more…)
April 25, 2024
Were the Waffen-SS Really Germany’s Elite Fighters? – WW2 – OOTF 35
April 19, 2024
QotD: The “Greatest Generation”
Our parents had learned some wrong lessons from the ’20s, ’30s, and ’40s. They learned to love government too well. They learned that government was what rescued you from depression and war. Our parents were very trusting of large governmental institutions. The liberalism that was a seed of the radicalism to come was in our parents, even when our parents were Republicans. They had taken large government for granted.
P.J. O’Rourke, interviewed by Scott Walter, “The 60’s Return”, American Enterprise, May/June 1997.
April 14, 2024
Soviets Take Vienna and Königsberg – WW2 – Week 294 – April 13, 1945
World War Two
Published 13 Apr 2024The prizes of Vienna and Königsberg fall to the Soviets as they continue what seems an inexorable advance. In the West the Allies advance to the Elbe River, but there they are stopped by command. The big news in their national papers this week is the death of American President Franklin Roosevelt, which provokes rejoicing in Hitler’s bunker. The Allied fighting dash for Rangoon continues in Burma, as does the American advance on Okinawa, although Japanese resistance is stiffening and they are beginning counterattacks.
Chapters
00:32 Recap
01:05 Operation Grapeshot
01:57 Roosevelt Dies
06:01 Soviet Attack Plans for Berlin
12:45 Stalin’s Suspicions
14:31 The fall of Königsberg
17:02 The fall of Vienna
18:38 Japanese Resistance on Okinawa
20:34 The War in China
21:09 Burma and the Philippines
22:38 Summary
22:57 Conclusion
25:05 Memorial
(more…)
April 13, 2024
The Death of Franklin Roosevelt
World War Two
Published 12 Apr 2024He lead his nation through the Great Depression, transformed it into a war-winning titan, and is working to shape the coming postwar world in his image. But today, 4,422 days into his record breaking presidency, Franklin Roosevelt dies. What was his final year really like?
(more…)
February 12, 2024
Yalta, When Stalin Split the World – a WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 11 February 2024Indy and Sparty take you through the negotiations at Yalta as The Big Three thrash out the shape of the postwar world. As the splits between East and West continue to deepen, who will come out on top?
(more…)
February 10, 2024
The War Goals to End WW2 in 1945 – a WW2 Special
World War Two
Published Feb 8, 2024While World War Two looks like it is about to end, the belligerent powers have vastly different goals for that end. Differences that may or may not prolong the war, will decide the survival of tens of millions of people, and the future fate of all of Humanity.
(more…)
December 24, 2023
QotD: Dreaming of George Bailey’s world while living in Pottersville
George Bailey, the hero of It’s a Wonderful Life, missed the two events that made the ideal man of his time, place, and social class: going to college and serving (as an officer, of course) in the Second World War. Instead of doing those things, either of which would have sent him out into the world beyond the limits of Bedford Falls, he remained at home, taking care of his family, his business, and his community. In other words, the hero of America’s favorite exercise in Yuletide nostalgia epitomized a way of life that, in the season of the film’s cinematic debut (the summer of 1946), was already on its way to the dustbin of history.
This, the most enduring of the many works of Frank Capra, became the Atlantis myth of post-war America. That is, those who, over the course of the last half-century, saw It’s a Wonderful Life on television, knew well that the age of community and connection depicted on their screens had already passed into the realm of legend. Moreover, to add injury to insult, they also knew that, if they wished to enjoy the fruits of a middle-class existence, they would have to live in the manner of vagabonds.
In the movie, slum-lord Henry Potter tries, but fails, to turn the provincial paradise of Bedford Falls into a run-down haunt of spinsters, drunks, and floozies. In the real world, it was Franklin D. Roosevelt who put the kibosh on the original Main Street, USA. To be more precise, the principal achievements of America’s greatest tyrant, the Great Depression and the Second World War, undermined the financial, legal, and cultural foundations of the “wonderful life”. Thus, by the time this process had run its course, inflation had made a fool’s game of simple thrift, the replacement of law with regulation had hobbled private enterprise, and people who had left home for the sake of college, work, or military service found themselves lost in a sea of strangers.
In response to these changes, colleges and universities stepped up to the proverbial plate, happy to offer substitutes for the things that had been lost. They gave young people a chance to obtain certificates that would attest to both their suitability for service in the ranks of corporate minions and their social respectability. At the same time, these institutions gave older people a way to convert their value-losing cash into an asset that promised to pay dividends that would benefit their children (and, indeed, their grandchildren) for decades to come.
Thus arose the people I have come to call the MICE (Mobile, Individualistic, College Educated) people. Bereft of regional accents, productive property, and deep connections to friends and relations, they wandered the world, building networks, acquiring degrees, and padding resumés. However, after two generations of such peripatetic solipsism, the age of the MICE people is coming to an end.
Young men of parts, who realize that college has nothing to do with either liberal learning or vocational training, are simultaneously taking up skilled trades and stocking their MP3 players with learned podcasts. At the same time, young women of quality are beginning to think that the traditional troika of Kirche, Küche, und Kinder offers better odds of deep satisfaction than life as a hormone-hobbled, Starbucks swilling, girl boss.
So, if you know young people like the ones I’ve just described, do posterity a favor, and put them in contact with each other. After all, they deserve a life as wonderful as that of George and Mary Bailey.
Bruce Ivar Gudmundsson, “College, Class, and Christmas”, Extra Muros, 2023-08-06.
December 8, 2023
The development of the American suburb
In the latest book review from Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, Jane Psmith discusses A Field Guide to American Houses (Revised): The Definitive Guide to Identifying and Understanding America’s Domestic Architecture, by Virginia Savage McAlester. In particular, she looks at McAlester’s coverage of how suburbs developed:
After some brief but interesting discussion of cities,1 most of the page count is devoted to the suburbs. It’s a sensible choice: suburbs have by far the most varied types of house groupings, and more than half of Americans live in one. But what exactly is a “suburb”? It’s a wildly imprecise word, referring to anything that is neither truly rural nor the central urban core, and suburbs vary tremendously in character. As a working definition, though, a suburb is marked by free-standing houses on relatively larger lots. (If you can think of a counter-example that qualifies but is “urban”, I’ll bet you $5 it started out as a suburb before the city ate it.)
This means that building a suburb has a few obvious technological prerequisites, which McAlester lists as follows: First, balloon-frame construction, which enabled not just corners but quick and inexpensive construction generally and removed much of the incentive for the shared walls that were so common in the early cityscape. Second, the proliferation of gas and electric utilities in the late nineteenth century meant that the less energy-efficient free-standing homes could still be heated relatively inexpensively. Third, the spread of telephone service after 1880 meant that it was much easier to stay in touch with friends whose front doors weren’t literally ten feet away from yours.2 But by far the most important technological advances came in the field of transportation, which is obviously necessary if you’re going to live in the country (or a reasonable facsimile thereof) and work in the city.
The first of these transportation advances was the railroad. In fact “railroad suburb” is a bit of a misnomer, because most of the collections of houses that grew up around the new rail stops were fully functional towns that had their own agricultural or manufacturing industries. The most famous railroad suburbs, however, were indeed planned as residential communities serving those wealthy enough to pay the steep daily rail fare into the city. Llewellyn Park near New York City, Riverside near Chicago, and the Main Line near Philadelphia are all examples of railroad suburbs that have maintained their tony atmosphere and high property values.
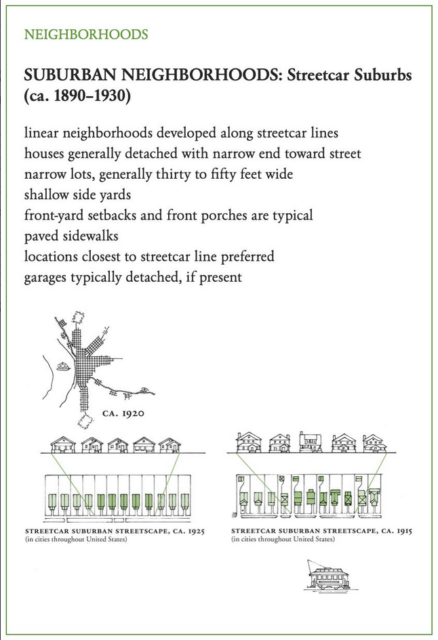
The next and more dramatic change was the advent of the electric trolley or streetcar, first introduced in 1887 but popular until about 1930. (That’s what all the books say, but come on, it’s probably October 1929, right?) Unlike steam locomotives, which take quite a long time to build up speed or to slow down again, and so usually had their stations placed at least a mile apart, streetcars could start and stop far more easily and feature many more, and more densely-placed, stops. Developers typically built a streetcar line from the city veering off into the thinly-inhabited countryside, ending at an attraction like a park or fairground if possible. If they were smart, they’d bought up the land along the streetcar beforehand and could sell it off for houses,3 but either way the new streetcar line added value to the land and the development of the land made the streetcar more valuable.
You can easily spot railroad towns and streetcar suburbs in any real estate app if you filter by the date of construction (for railroad suburbs try before 1910, for streetcar before 1930) and know what shapes to look for. Railroad towns are typically farther out from the urban center and are built in clusters around their stations, which are a few miles from one another. Streetcar suburbs, by contrast, tend to be continuous but narrow, because the appeal of the location dropped off rapidly with distance from the streetcar line. (Lots are narrow for the same reason — to shorten the pedestrian commute.) They expand from the urban center like the spokes of a wheel.
And then came the automobile and, later, the federal government. The car brought a number of changes — paved streets, longer blocks, wider lots (you weren’t walking home, after all, so it was all right if you had to go a little farther) — but nothing like the way the Federal Housing Authority restructured neighborhoods.
The FHA was created by the National Housing Act of 1934 with the broad mandate to “improve nationwide housing standard, provide employment and stimulate industry, improve conditions with respect to mortgage financing, and realize a greater degree of stability in residential construction”. It was a big job, and the FHA set out to accomplish it in a typical New Deal fashion: providing federal insurance for private construction and mortgage loans, but only for houses and neighborhoods that met its approval. This has entered general consciousness as “redlining”, after the color of the lines drawn around uninsurable areas (typically old, urban housing stock),4 but the green, blue, and yellow lines — in order of declining insurability — were just as influential on the fabric of contemporary America.
A slow economy through the 1930s and a prohibition on nonessential construction during the war meant that FHA didn’t have much to do until 1945, but as soon as the GIs began to come home and take advantage of their new mortgage subsidies, there was a massive construction boom. With the FHA insuring both the builders’ construction loans and the homeowners’ mortgages, nearly all the new neighborhoods were built to the FHA’s exacting specifications.
One of the FHA’s major concern was avoiding direct through-traffic in neighborhoods. Many post-World War II developments were built out near the new federally-subsidized highways on the outskirts of the cities, so the FHA was eager to protect new subdivisions from heavy traffic on the interstates and the major arterial roads. Neighborhoods were meant to be near the arterials, but with only a few entrances to the neighborhood and many curved roads and culs-de-sac within it. Unlike the streetcar suburbs or the early automobile suburbs that filled in between the “spokes” of the streetcar lines, where retail had clustered near the streetcar stops, the residents of the post-World War II suburbs found their closest retail establishments outside the neighborhood on the major arterial roads. Lots became wider, blocks longer, and sidewalks less frequent; houses were encouraged to stay small by FHA caps on the size of loans. And although we tend to assume they were purely residential areas, the FHA encouraged the inclusion of schools, churches, parks, libraries, and community centers within the neighborhood.
1. America doesn’t have many urban neighborhoods that predate 1750, and even fewer that persist in their original layout, but if you’ve ever visited one it’s amazing how compact everything feels even in comparison to the rowhouses of the following century.
2. McAlester’s footnote for the paragraph that contains all this reads: “These three essentials were highlighted in an essay the author has read but has not been successful in locating for this footnote.”
3. This is still, I am told, how some of the more sensibly-governed parts of the world run their transit systems: whatever company has the right to build subways buys up the land around a planned (but not announced) subway line through shell corporations, builds the subway, then sells or develops the newly-valuable property. Far more efficient as a funding mechanism than fares!
4. This 2020 NBER working paper points out that redlined areas were 85% white (though they did include many of the black people living in Northern cities) and suggests that race played very little role in where the red lines were drawn; rather, black people were already living in the worst neighborhoods.
October 15, 2023
The Isolation of Army Group North – WW2 – Week 268 – October 14, 1944
World War Two
Published 14 Oct 2023Churchill, Stalin, and Roosevelt meet at the Moscow Conference and talk about future “spheres of influence” in the Balkans. They also make plans for the future of Poland. In the field the Soviet Red Army completes the isolation of Army Group North and also advances in Hungary and Yugoslavia. The Allies enter Aachen in the west and cross the Rubicon in Italy. The Americans are still fighting the Japanese on Peleliu, and this week also make raids against Japanese airfields ahead of next week’s invasion of the Philippines.
01:00 Recap
01:22 The Moscow Conference begins
03:43 Isolating Army Group North
06:29 Soviet advances toward Belgrade
08:14 The Debrecen Operation
13:20 Horthy and Hungary
14:30 Chiang Kai-shek accuses Joe Stilwell
16:19 American raids on Formosa
19:29 The fight for Peleliu continues
20:01 Antwerp and Aachen
22:01 The Allies cross the Rubicon
(more…)
July 14, 2023
Bread rationing in the United States during WW2
I haven’t studied the numbers, but I strongly suspect that most US government food rationing during the war was effectively theatre to encourage more support of the war effort: except in a very few areas, the US was more than self-sufficient in most foodstuffs. At the Foundation for Economic Education, Lawrence W. Reed recounts one of the least effective government moves in food rationing:
According to an old joke from the socialist and frequently underfed Soviet Union, Stalin goes to a local wheat farm to see how things are going. “We have so many bags of wheat that, if piled on top of each other, they could reach God himself!” the farmer told Comrade Stalin.
“But God does not exist,” the dictator angrily replied. “Exactly!” said the farmer. “And neither does the wheat.” Nobody knows what happened to the farmer, but at least Stalin died in 1953.
Soviet socialism, with its forced collectivism and ubiquitous bread lines, gave wheat a bad name. Indeed, it was lousy at agriculture in general. As journalist Hedrick Smith (author of The Russians) and many other authorities noted at the time, small privately owned plots comprised just three percent of the land but produced anywhere from a quarter to a half of all produce. Collectivized agriculture was a joke.
America is not joke-free when it comes to wheat. We are a country in which sliced bread was both invented and banned, and a country in which growing wheat for your own consumption was ruled to be an act of “interstate commerce” that distant bureaucrats could regulate. No kidding.
On this anniversary — July 7 — of both the birth in 1880 of sliced bread’s inventor and of the day in 1928 that the first sliced bread from his machine was sold, it’s fitting to recall these long-forgotten historical facts.
The Iowa-born jeweler and inventor Otto Rohwedder turned 48 on the very day the first consumer bought the product of his new slicing machine. The bread was advertised as “the greatest forward step in the baking industry since bread was wrapped” and it quickly gave rise to the popular phrase, “the greatest thing since sliced bread.” Before 1928, American housewives cut many a finger by having to slice off every piece of bread from the loaves they baked or bought. Sliced bread was an instant sensation.
Rohwedder earned seven patents for his invention. The original is proudly displayed at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C. He likely made a lot more money from the bread slicing machine than he ever did as a jeweler. He died in 1960 at the age of 80.
Enter Claude Wickard, Secretary of Agriculture under Franklin Roosevelt from 1940 to 1945. On January 18, 1943, he banned the sale of sliced bread. Exactly why seems to be in dispute but the most likely rationale was to save wax paper and other resources for war production. He rescinded the ban two months later, explaining then that “the savings are not as much as we expected.”
I’m sure Hitler and Hirohito were relieved.
June 28, 2023
How to Fund a War: Lend Lease, Billion Dollar Gift, and Aid to Britain
OTD Military History
Published 27 Jun 2023Programs like Lend Lease, Mutual Aid, and the Billion Dollar Gift were support from Canada and the United States that helped Britain with war supplies and material in the darkest days of World War 2.
(more…)
June 7, 2023
QotD: A “second front” in 1943
Which brings us to the debate about the possibility of an invasion in 1943 – Roundup. Something that a surprising number of historians, and even a few not entirely incompetent generals, have suggested might have been possible, and should have been tried.
There are some points in their favour. The invasions of North Africa definitely took resources that could have been built up in Britain, and therefore slowed things down. (And the withdrawal of the new escort carriers, escort groups, and shipping from the Battle of the Atlantic for the North African adventure, definitely did huge damage in the loss of shipping and supplies, slowing things down further.) As a result the huge buildup in North Africa was much easier to use against Italy before moving on to France. Certainly another distraction or delay … but only if you don’t think that knocking Italy out of the war would make Germany weaker!
But once Sledgehammer [the plan to invade France in 1942] was abandoned, this operation was the only possible way to get US troops into combat in Europe, short of shipping some to Russia. It was also the only possible way of coming close to keeping Roosevelt’s ridiculous promise to the Russians.
[…]
Nonetheless it is wrong to think that the British never had any intention of [mounting Operation] Roundup. Despite what Roosevelt and many other Americans convinced themselves, the British were, at the start of 1942, far more optimistic about the possibility of invading Europe through France in 1943 than they had been about Sledgehammer. Their studies seemed to show that Germany would only have to be weaker, not suddenly collapse, to make invasion in 1943 a realistic possibility. Realistic that is as long as the rest of the plans for training and shipping troops, building and concentrating invasion craft, and moving enough supplies to make it sustainable, all came together.
They didn’t.
For the British, the middle of 1942 revealed how little would be available in time for the middle of 1943. Even on the best assumptions of American training and preparation, there was no chance that the majority of forces for Roundup would not be British … assuming they could supply them either. In practice mid-1942 saw the Axis continue to advance on every front. Burma collapsed; the Allied position in New Guinea was under threat; the Japanese were still expanding to places like Guadalcanal; Rommel was advancing in Egypt; the Germans were advancing on the Caucasian oil fields and towards the Middle East; and more and more was needed just to keep Russia in the war. As a result British troops, shipping and supplies were continuing to flow away from Britain, not towards it.
Much of the Royal Navy was trying to save the dangerous losses caused by [US Chief of Naval Operations Admiral] King’s refusal to have convoys in American waters (too “defensive-minded” he thought.) These alone, the worst eight months of the war, were threatening to scupper Roundup. The rest was so busily deployed in the Indian and Pacific Oceans against the Japanese, or North Atlantic trying to fight supplies through to Russia (a high proportion of tanks and planes defending Moscow were British-supplied), that there was virtually nothing left in the Med to slow Rommel’s advance. The merchant ships surviving the fight across the oceans were actually more vitally needed to take men and equipment from the UK to other places than to bring in a buildup for the UK.
Nor was the American buildup going to plan. Less well-trained troops were becoming available too slowly, could not be shipped in adequate numbers anyway, and were in no condition to face German veterans. (The very best US units to go into action in 1942 – the Marines in Guadalcanal – and 1943 – the 1st Infantry and 1st Armored divisions which were actually professional troops not conscripts in North Africa – had very steep learning curves. Particularly at Kasserine. They were clearly not fit to face German veterans yet.
And American resource buildup was also not up to promises. King and MacArthur were milking supplies far beyond what had originally been agreed under “Germany first”. In practical terms they were doing so for the same reasons the British were: an immediate desperate situation had to be saved before a future ideal one could be pursued.
Nonetheless I have read all sorts of apparently serious suggestions that after North Africa was cleared, or at the very least after Sicily was cleared, an invasion of France should have happened.
Delusional.
Nigel Davies, “The ‘Invasion of France in 1943’ lunacy”, rethinking history, 2021-06-21.
June 6, 2023
QotD: “A second front” in 1942
I have been reading the recent biography of the British CIGS Alanbrooke, and been struck by the clear and concise explanation of the differences between the British and Americans over the “second front” in Europe, and when it could be.
[…]
A plan put together for the incredibly unlikely event of sudden German collapse, was Sledgehammer. This was the understanding of Sledgehammer adopted by most Americans. A very limited offensive by very inadequate forces, which could only succeed had Germany already gone close to collapse. Given the circumstances this was somewhat delusional, but it never hurts to plan for eventualities, and the British were happy to go along with this sort of plan.
[…]
Any attempt at Sledgehammer would of course have failed. The German army had not yet been bled dry on the Eastern front, and the Luftwaffe was still a terrifying force which could be (and regularly was) easily moved from Russian mud to Mediterranean sunshine and back again in mere weeks. Even ignoring the opposition, the British were gloomily aware that the Americans had not a clue of the complexities of such a huge amphibious operation. At the time of discussion – May 1942 – the British were using their first ever Landing Ship Tanks and troopships equipped with landing craft to launch a brigade-size pre-emptive operation against the Vichy French on Madagascar. (Another move many historians think was useless. But coming only months after the Vichy had invited the Japanese into Indo-China – fatally undermining the defenses of Malaya – and the Germans into Syria, it was probably a very sensible precaution. Certainly Japanese submarines based in Madagascar [could] have finally caused the allies to lose the war at sea!)
The British deployed two modern aircraft carriers, and a fleet of battleships, cruisers, destroyers and escorts and a large number of support ships, on this relatively small operation. It was the first proper combined arms amphibious operation of the war, and was very helpful to the British to reveal the scale of amphibious transport needed for future operations. By contrast the US Marines hit Guadalcanal six months later from similar light landing craft, and with virtually the same Great War-vintage helmets and guns that the ANZACS had used at Gallipoli. Anyone who reads the details of the months of hanging on by the fingernails at Guadalcanal against very under-resourced Japanese troops, will be very grateful that the same troops did not have to face veteran German Panzer divisions for several years.
So I do not know of any serious historian who imagines that an invasion of France in 1942 could have led to anything except disaster. There are no serious generals who thought it either. (Only Marshall and his “yes-man” Eisenhower consistently argued that it might be possible. And Eisenhower later came to realise – when he was in charge of his third or fourth such difficult operation – that his boss was completely delusional in his underestimation of the difficulties involved. See Dear General: Eisenhower’s Wartime Letters to Marshall for Eisenhower’s belated attempts to quash Marshalls tactical ignorance about parachute drops and dispersed landings for D-Day.)
In practice no matter how much Marshall pushed for it, only British troops were availabe for such a sacrificial gesture, and the British were not unnaturally reluctant to throw away a dozen carefully nurtured and irreplaceable divisions on a “forlorn hope”, when they would prefer to save them for a real and practical invasion … when circumstances changed enough to make it possible.
Unfortunately Roosevelt told the Soviet foreign minister Molotov that “we expect the formation of a second front this year”, without asking even Marshall, let alone wihtout consulting his British allies who would have to do it with virtually no American involvement. The British Chiefs of Staff only had to show Churchill the limited numbers of landing craft that could be available, and the limited number of troops and tanks they could carry, to make it clear that this was ridiculous. Clearly this stupidity was just another example of Roosevelt saying stupid things without asking anyone (like “unconditional surrender”) that did so much to embitter staff relations during the war, and internationaly relations postwar. But it seems likely that the British refusal to even consider such nonsense was taken by Marshall and Stimson as a sample of the British being duplicitous about “examining planning options”.
The British fixed on a “compromise” to pretend that a “second front” could be possible. North Africa, could be conquered without prohibitive losses. It was not ideal, and in practical terms not even very useful. But it might satisfy the Americans and the Russians. Nothing else could.
Marshall in particular spent the rest of the war believing that when the British assessment clearly demonstrated that action in Europe was impractical and impossible, they had just been prevaricating to get what they always intended: operations in the Med. In some ways he was correct. The British had done the studies on France despite thinking that it was unlikely they would be practical, and were proved right. Marshall and Eisenhower had just deluded themselves into thinking an invasion might be practical, and could not accept that there was not a shred of evidence in favour of their delusion.
Nigel Davies, “The ‘Invasion of France in 1943’ lunacy”, rethinking history, 2021-06-21.
January 21, 2023
When the SS Go Too Far – War Against Humanity 096
World War Two
Published 20 Jan 2023The internal conflict between Poland and the other United Nations Allies deepens as Churchill faces them with diplomatic defeat over Soviet land grab. In the Occupied Netherlands and Poland the Nazis continue their atrocities.
(more…)
January 6, 2023
Will Stalin Liberate or Occupy Poland? – War Against Humanity 094
World War Two
Published 5 Jan 2023The last week of 1943 is a busy one. Stalin deports the Kalmyk minority from Kalmykia, the escapees from Fort IX get away, and the US President moves to found the post-war UN.
(more…)