Forgotten Weapons
Published 26 Feb 2012The Hino-Komuro pistol (sometimes spelled Komura) was developed by a young Japanese inventor named Kumazo Hino, and financed by Tomijiro Komuro in the first decade of the 20th century. The gun uses a virtually unique blow-forward mechanism, which makes it very interesting to study. The rear of the receiver houses a fixed firing pin, and the barrel is pushed forward upon firing. To cock the gun, the barrel is manually pulled forward about one inch (using serrations on the exposed front section of the barrel). As the barrel is pulled forward, it pulls with it a follower that pulls a cartridge forward out of the magazine and lifts it up into the axis of the bore. When the grip safety and trigger are depressed, the barrel is snapped backwards into the action by a spring. The ready cartridge is chambered and driven backwards with the barrel onto the fixed firing pin.
(more…)
August 20, 2023
1908 Japanese Hino Komura Pistol
QotD: Fear of death
The two basic drivers of social change are fear of death and caloric surplus. They exist, as Marxists would say if they cared about actual human behavior, dialectically — the fear of death prompts a frantic search for caloric surplus; once attained, caloric surplus makes the once-adaptive fear of death neurotic and dysfunctional, literally morbid.
[…]
As pretty much every Victorian anthropologist remarked, “savages” all seem deliriously happy — when life is a constant struggle, your every moment is filled with deep meaning, high purpose. So, too, with men at war — Robert Graves or someone like that once said that his time in the trenches were the greatest moments of his life, because everything other than the now disappeared. I can’t speak from personal experience, but I’d lay good money that no combat veteran completely re-enters the civilian world, largely for this reason.
Those are reasonable fears of death. We all accept, intellectually, that we could go at any time, and we will inevitably go eventually, but unless you’ve had a brush with death — a moment where you know, with perfect clarity, that there’s a significant chance you’re going now — you can’t really appreciate it, emotionally.
Severian, “Communal Salvation”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-11-19.
August 19, 2023
One Day in August – Dieppe Anniversary Battlefield Event (Operation Jubilee)
WW2TV
Published 19 Aug 2021One Day in August — Dieppe Anniversary Battlefield Event (Operation Jubilee) With David O’Keefe, Part 3 — Anniversary Battlefield Event.
David O’Keefe joins us for a third and final show about Operation Jubilee to explain how the plan unravelled and how the nearly 1,000 British, Canadian and American commandos died. We will use aerial footage, HD footage taken in Dieppe last week and maps, photos, and graphics.
In Part 1 David O’Keefe talked about the real reason for the raid on Dieppe in August 1942. In Part 2 David talked about the plan for Operation Jubilee. The intentions of the raid and how it was supposed to unfold.
(more…)
Dieppe Raid – 19 August, 1942
The History Chap
Published 15 Aug 2021The Dieppe Raid (codename Operation Jubilee) was a disastrous amphibious landing by the allies in France during World War 2. Nearly 4,000 allied soldiers (mainly Canadians) were killed, wounded or captured during the Battle of Dieppe.
1942 was turning out to be a bad year for the allies. The Nazis were sweeping forwards in Russia, the Japanese were sweeping though South East Asia. The British commonwealth troops were being pushed back by the Germans & Italians in North Africa and the Americans were still reeling from the attack on Pearl Harbour.
The British wanted to show that they were still willing to take the offensive in the war and were were being urged by Stalin to take some pressure off the Soviet Union. A plan was hatched to conduct a “smash & grab” raid on the port of Dieppe in northern France. The aim was to seize Dieppe and hold it for a limited time before evacuation, during which time the allied troops would collect intelligence and destroy German military infrastructure.
The Canadian government were keen to have their own troops play a role in the war and so the majority of the raiding force was made up of their troops. Initially planned for early July, Operation Jubilee was delayed for over a month due to bad weather and the need for a high tide at dawn. Eventually the Dieppe Raid took place just before 0400 on the 19th August 1942. 5,000 Canadians, 1,000 British and 50 US Rangers were to land at five different points along a 16km (10 mile front) either side of the port of Dieppe itself.
The result was a complete disaster. No major objectives were achieved, poor intelligence had not identified the strength of the German defences and the Germans were on high alert for a possible attack after the firefight at sea and the fact that there was high tide. Within less than 6 hours of the landing starting the order had been given to evacuate and by 1400 hours what remained of the allied force had been successfully removed.
The Dieppe Raid lasted 10 hours. They left behind 4,000 killed, wounded or prisoners of war — over 80% of whom were Canadians. The Royal Navy lost a destroyer and 33 landing craft whilst the RAF lost 106 planes.
The raid had sent a signal to the Germans that the Atlantic shoreline was not secure. That eventually they would have to fight the war on two fronts. It also raised morale within the population of occupied France. They were not alone. The best that can be said for the raid was that it taught the allies valuable lessons which were successfully implemented in the D-Day landings in Normandy in 1944. Maybe the sacrifice of the young men at Dieppe saved many more young men on D-Day.
(more…)
QotD: The third system (or “Modern system”) of war
Armies in this modern system [discussed here] still aim to control territory, as with second-system war, but they no longer square off in open fields. Rather, relying on cover and concealment to mitigate the overwhelming firepower a modern battlefield covered with machine guns, artillery and airpower, they aim to disorient and overwhelm the decision-making capabilities of their enemy with lightning mechanized offensives.
What happens when two current-day modern systems meet? We don’t really know, though there is a lot of speculation. One of the things which made the conflict between Azerbaijan and Armenia so closely watched last year (in 2020, for those reading this later) was that it provided a chance to see two sides both with (sometimes incomplete) access to the full modern kit of war – not only tanks, jets and artillery, but cyber warfare, drones and so on. The results remain to be much discussed analyzed, but it may well be that a fourth system of war is in the offing, defined by the way that drone-based airpower combined with electronic surveillance and cyber-warfare redefined the battle-space and allowed Azerbaijan in particular to project firepower deep into areas where Armenian forces considered themselves safe.
But I shouldn’t get too off track. The point of all of this is that these systems of war are not merely different, they are so radically different that armies created in one system often fundamentally fail to understand the others (thus the tendency for second and third system armies to treat first system war as some strange new innovation in war, when it is in fact the oldest system by far). As we’re going to see, the aims, experiences and outcomes of these systems are often very different. They demand and inculcate different values and condition societies differently as well.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Universal Warrior, Part IIa: The Many Faces of Battle”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-02-05.
August 18, 2023
One Day in August – Dieppe – Part 2 – The Plan
WW2TV
Published 17 Jan 2021Part 2 – The Plan With David O’Keefe
David O’Keefe joins us again. In Part 1 he talked about the real reason for the raid on Dieppe in August 1942. In Part 2 we talk about the plan for Operation Jubilee and David will share his presentation about the intentions of the raid and how it was supposed to unfold.
A final show sometime in the summer will come live from Dieppe to explain how the plan unravelled and how the nearly 1,000 British, Canadian and American commandos died.
(more…)
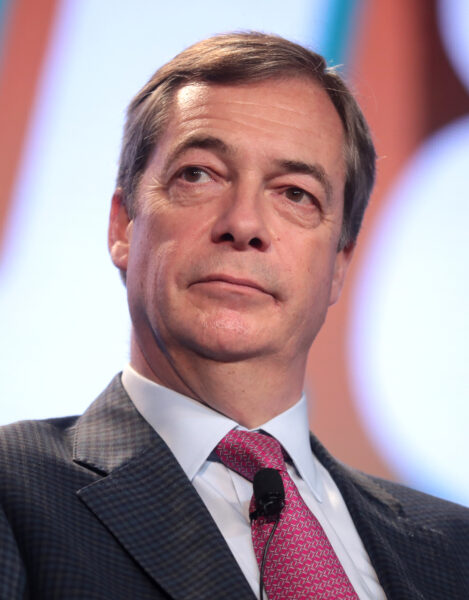
When your friendly local bank turns into a branch of the Stasi
Theodore Dalrymple on the British bank — probably not the only one to do things like this — that compiled a “dossier” of information on one of their long-term clients with a view to de-banking him, his family, and associates. It might have worked if the client was a private citizen with no particular public profile, but the client was someone who absolutely is not that kind of man:
The following day, [National Westminster Bank CEO Alison] Rose resigned, admitting to “a serious error of judgment”. The value of the bank fell by more than $1 billion.
The weasel words of Ms. Rose and the bank board are worth examination. They deflected, and I suspect were intended to deflect, the main criticism directed at Ms. Rose and the bank: namely, that the bank had been involved in a scandalous and sinister surveillance of Mr. Farage’s political views and attempted to use them as a reason to deny him banking services, all in the name of their own political views, which they assumed to be beyond criticism or even discussion. The humble role of keeping his money, lending him money, or perhaps giving him financial advice, was not enough for them: they saw themselves as the guardians of correct political policy.
It was not that the words used to describe Mr. Farage were “inappropriate”, or even that they were libelous. It is that the bank saw fit to investigate and describe him at all, at least in the absence of any suspicion of fraud, money laundering, and so forth. “The error of judgment” to which Ms. Rose referred was not that she spoke to the BBC about his banking affairs (it is not easy to believe that she did so without malice, incidentally), but that she compiled a dossier on Farage in the first place — and then “error of judgment” is hardly a sufficient term on what was a blatant and even wicked attempt at instituting a form of totalitarianism.
This raises the question of whether one can be wicked without intending to be so, for it is quite clear that Ms. Rose had no real understanding, even after her resignation, of the sheer dangerousness and depravity of what the bank, under her direction, had done.
As for the board’s somewhat convoluted declaration that “after careful consideration, it concluded that it retains full confidence”, etc., it suggests that it was involved in an exercise of psychoanalytical self-examination rather than of an objective state of affairs: absurd, in the light of Ms. Rose’s resignation within twenty-four hours. The board, no more than Ms. Rose herself, understood what the essence of the problem was. For them, if there had been no publicity, there would have been no problem: so when Mr. Farage called for the dismissal of the board en masse, I sympathised with his view.
Did Hitler Cancel the Sturmgewehr?
Forgotten Weapons
Published 10 May 2023It is often said that Hitler personally cancelled the Sturmgewehr development … could that really be true?
Yes! He actually nixed the program three separate times, and the German Army General Staff continued the project behind his back. They knew the rifle was what the Wehrmacht desperately needed if it was to have any hope of victory in the East, and they were determined to bring it to fruition. He did ultimately relent, and approved it to replace the Mauser K98k in early 1944 — but by that time a great deal of opportunity had been lost. Today we will delve into the details of just how the program developed as it pertains to his approval …
(more…)
August 17, 2023
“… the Chinese invented gunpowder and had it for six hundred years, but couldn’t see its military applications and only used it for fireworks”
John Psmith would like to debunk the claim in the headline here:

An illustration of a fireworks display from the 1628-1643 edition of the Ming dynasty book Jin Ping Mei (1628-1643 edition).
Reproduced in Joseph Needham (1986). Science and Civilisation in China, Volume 5: Chemistry and Chemical Technology, Part 7: Military Technology: The Gunpowder Epic. Cambridge University Press. Page 142.
There’s an old trope that the Chinese invented gunpowder and had it for six hundred years, but couldn’t see its military applications and only used it for fireworks. I still see this claim made all over the place, which surprises me because it’s more than just wrong, it’s implausible to anybody with any understanding of human nature.
Long before the discovery of gunpowder, the ancient Chinese were adept at the production of toxic smoke for insecticidal, fumigation, and military purposes. Siege engines containing vast pumps and furnaces for smoking out defenders are well attested as early as the 4th century. These preparations often contained lime or arsenic to make them extra nasty, and there’s a good chance that frequent use of the latter substance was what enabled early recognition of the properties of saltpetre, since arsenic can heighten the incendiary effects of potassium nitrate.
By the 9th century, there are Taoist alchemical manuals warning not to combine charcoal, saltpetre, and sulphur, especially in the presence of arsenic. Nevertheless the temptation to burn the stuff was high — saltpetre is effective as a flux in smelting, and can liberate nitric acid, which was of extreme importance to sages pursuing the secret of longevity by dissolving diamonds, religious charms, and body parts into potions. Yes, the quest for the elixir of life brought about the powder that deals death.
And so the Chinese invented gunpowder, and then things immediately began moving very fast. In the early 10th century, we see it used in a primitive flame-thrower. By the year 1000, it’s incorporated into small grenades and into giant barrel bombs lobbed by trebuchets. By the middle of the 13th century, as the Song Dynasty was buckling under the Mongol onslaught, Chinese engineers had figured out that raising the nitrate content of a gunpowder mixture resulted in a much greater explosive effect. Shortly thereafter you begin seeing accounts of truly destructive explosions that bring down city walls or flatten buildings. All of this still at least a hundred years before the first mention of gunpowder in Europe.
Meanwhile, they had also been developing guns. Way back in the 950s (when the gunpowder formula was much weaker, and produced deflagarative sparks and flames rather than true explosions), people had already thought to mount containers of gunpowder onto the ends of spears and shove them in peoples’ faces. This invention was called the “fire lance”, and it was quickly refined and improved into a single-use, hand-held flamethrower that stuck around until the early 20th century.1 But some other inventive Chinese took the fire lances and made them much bigger, stuck them on tripods, and eventually started filling their mouths with bits of iron, broken pottery, glass, and other shrapnel. This happened right around when the formula for gunpowder was getting less deflagarative and more explosive, and pretty soon somebody put the two together and the cannon was born.
All told it’s about three and a half centuries from the first sage singing his eyebrows, to guns and cannons dominating the battlefield.2 Along the way what we see is not a gaggle of childlike orientals marvelling over fireworks and unable to conceive of military applications. We also don’t see an omnipotent despotism resisting technological change, or a hidebound bureaucracy maintaining an engineered stagnation. No, what we see is pretty much the opposite of these Western stereotypes of ancient Chinese society. We see a thriving ecosystem of opportunistic inventors and tacticians, striving to outcompete each other and producing a steady pace of technological change far beyond what Medieval Europe could accomplish.
Yet despite all of that, when in 1841 the iron-sided HMS Nemesis sailed into the First Opium War, the Chinese were utterly outclassed. For most of human history, the civilization cradled by the Yellow and the Yangtze was the most advanced on earth, but then in a period of just a century or two it was totally eclipsed by the upstart Europeans. This is the central paradox of the history of Chinese science and technology. So … why did it happen?
1. Needham says he heard of one used by pirates in the South China Sea in the 1920s to set rigging alight on the ships that they boarded.
2. I’ve left out a ton of weird gunpowder-based weaponry and evolutionary dead ends that happened along the way, but Needham’s book does a great job of covering them.
Dieppe – One Day in August – Ian Fleming, Enigma and the Deadly Raid – Part 1
WW2TV
Published 29 Nov 2020In less than six hours in August 1942, nearly 1,000 British, Canadian and American commandos died in the French port of Dieppe in an operation that for decades seemed to have no real purpose. Was it a dry-run for D-Day, or perhaps a gesture by the Allies to placate Stalin’s impatience for a second front in the west?
Canadian historian David O’Keefe uses hitherto classified intelligence archives to prove that this catastrophic and apparently futile raid was in fact a mission, set up by Ian Fleming of British Naval Intelligence as part of a “pinch” policy designed to capture material relating to the four-rotor Enigma machine that would permit codebreakers like Alan Turing at Bletchley Park to turn the tide of the Second World War.
In this first show we will look at how the raid has been written about in previous books and the research David undertook and as importantly why he did it. In a future show, we will look at filming in Dieppe itself and explain the sequence of events.
(more…)
Lawfare as politics by other means
Chris Bray explains why getting rid of the Donald Trump candidacy wouldn’t even begin to solve the real problems in US politics today:
Donald Trump has been charged with crimes, so the Republican Party should drop him as a candidate and move on to someone else who hasn’t been indicted. That’ll solve the problem!
It won’t. The problem is lawfare. The Republican governor of Wisconsin defeated a recall effort, so Democratic district attorneys launched a long series of predawn raids on his supporters — until the courts made them stop. The Republican governor of Texas won four terms, but then was indicted by the office of a Democratic district attorney — for a budget veto, an action within his constitutional authority. Again, the courts intervened, and the legally absurd charges were dismissed.
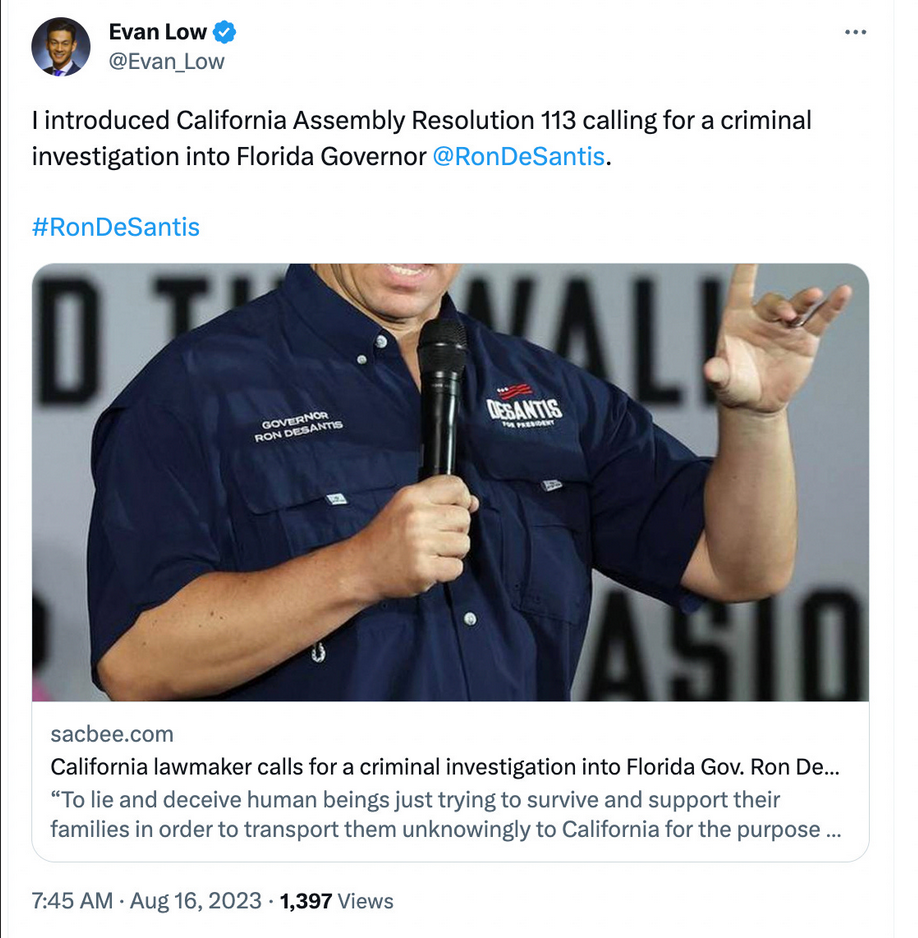
Today, scumbag California Assemblyman Evan Low, a uniquely craven publicity chaser even by the local standards, proudly announces that he’s just introduced a legislative resolution calling for the federal government to open a criminal investigation into Florida Governor Ron DeSantis.
So. Get rid of Trump and nominate DeSan— oh, wait. Okay, name someone, anyone: Chris Christie, Vivek Ramaswamy, a utility nominee to be named later in exchange for three rookie infielders. Oh no, it turns out that the new nominee is under criminal investigation for [TBD]! As of, uh, tomorrow.
I have mixed feelings about Donald Trump, who supported pandemic lockdowns and school closures and the rushed development of mRNA injections with limited testing. Dumping him as a candidate because he’s been indicted misses the point. No Republican candidate will run for the presidency without being indicted, unless he’s a court-eunuch Mitt Romney figure, too safe to bother attacking.
See Inside Char B1 | French Tanks of World War Two
The Tank Museum
Published 12 May 2023Chris Copson goes inside one of his personal favourite tanks, the Second World War French Char B1, to discover the quirks and surprises hidden within. Find out why these tanks performed so badly against the German onslaught of 1940, despite being bigger and more heavily armoured than the vehicles they faced.
(more…)
QotD: The decline of the British aristocracy
Probably the battle of Waterloo was won on the playing-fields of Eton, but the opening battles of all subsequent wars have been lost there. One of the dominant facts in English life during the past three quarters of a century has been the decay of ability in the ruling class.
In the years between 1920 and 1940 it was happening with the speed of a chemical reaction. Yet at the moment of writing it is still possible to speak of a ruling class. Like the knife which has had two new blades and three new handles, the upper fringe of English society is still almost what it was in the mid-nineteenth century. After 1832 the old landowning aristocracy steadily lost power, but instead of disappearing or becoming a fossil they simply intermarried with the merchants, manufacturers and financiers who had replaced them, and soon turned them into accurate copies of themselves. The wealthy ship-owner or cotton-miller set up for himself an alibi as a country gentleman, while his sons learned the right mannerisms at public schools which had been designed for just that purpose. England was ruled by an aristocracy constantly recruited from parvenus. And considering what energy the self-made men possessed, and considering that they were buying their way into a class which at any rate had a tradition of public service, one might have expected that able rulers could be produced in some such way.
And yet somehow the ruling class decayed, lost its ability, its daring, finally even its ruthlessness, until a time came when stuffed shirts like Eden or Halifax could stand out as men of exceptional talent. As for Baldwin, one could not even dignify him with the name of stuffed shirt. He was simply a hole in the air. The mishandling of England’s domestic problems during the nineteen-twenties had been bad enough, but British foreign policy between 1931 and 1939 is one of the wonders of the world. Why? What had happened? What was it that at every decisive moment made every British statesman do the wrong thing with so unerring an instinct?
The underlying fact was that the whole position of the monied class had long ceased to be justifiable. There they sat, at the centre of a vast empire and a world-wide financial network, drawing interest and profits and spending them – on what? It was fair to say that life within the British Empire was in many ways better than life outside it. Still, the Empire was underdeveloped, India slept in the Middle Ages, the Dominions lay empty, with foreigners jealously barred out, and even England was full of slums and unemployment. Only half a million people, the people in the country houses, definitely benefited from the existing system. Moreover, the tendency of small businesses to merge together into large ones robbed more and more of the monied class of their function and turned them into mere owners, their work being done for them by salaried managers and technicians. For long past there had been in England an entirely functionless class, living on money that was invested they hardly knew where, the “idle rich”, the people whose photographs you can look at in the Tatler and the Bystander, always supposing that you want to. The existence of these people was by any standard unjustifiable. They were simply parasites, less useful to society than his fleas are to a dog.
George Orwell, “The Lion And The Unicorn: Socialism and the English Genius”, 1941-02-19.