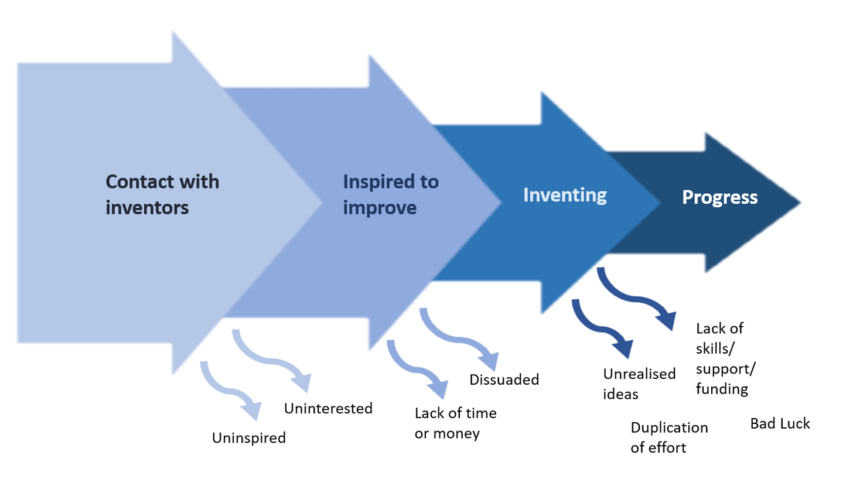
… it was one thing to be able to reach these new southern markets, and another thing to have something to sell in them. For the shift in the markets for wool cloth exports also required major changes in the kinds of cloth produced. In this regard, London may well have been a direct beneficiary of the 1560s-80s troubles in the Low Countries that had caused Antwerp’s fall, because thousands of skilled Flemish and Dutch clothmakers fled to England. In particular, these refugees brought with them techniques for making much lighter cloths than those generally produced by the English — the so-called “new draperies”, which could find a ready market in the much warmer Mediterranean climes than the traditional, heavy woollen broadcloths.
The introduction of the new draperies was no mere change in style, however. They were almost a completely different kind of product, involving different processes and raw materials. The traditional broadcloths were “woollens”. That is, they were made from especially fine, short, and curly wool fibres — the type that English sheep were especially famous for growing — which were then heavily greased in butter or oil in preparation for carding, whereby the fibres were straightened out and any knots removed (because of all the oil, in the Low Countries the cloths were known as the wet, or greased draperies). The oily, carded wool was then spun into yarn, and typically woven into a broad cloth about four metres wide and over thirty metres long. But it was still far from ready. The cloth had to be put in a large vat of warm water, along with some urine and a particular kind of clay, and was then trodden by foot for a few days, or else repeatedly compacted by water-powered machinery. This process, known as fulling, scoured the cloth of all the grease and shrunk it, compacting the fibres so that they began to interlock and enmesh. Any sign of the cloth being woven thus disappeared, leaving a strong, heavy, and felt-like material that was, as one textile historian puts it, “virtually indestructible”. To finish, it was then stretched with hooks on a frame, to remove any wrinkles and even it out, and then pricked with teasels — napped — to raise any loose fibres, which were then shorn off to leave it with a soft, smooth, sometimes almost silky texture. Woollens may have been made of wool, but they were no woolly jumpers. They were the sort of cloth you might use today to make a thick, heavy and luxuriant jacket, which would last for generations.
Yet this was not the sort of cloth that would sell in the much warmer south. The new draperies, introduced to England by the Flemish and Dutch clothworkers in the mid-sixteenth century, used much lower-quality, coarser, and longer wool. Later generally classed as “worsteds”, after the village of Worstead in Norfolk, they were known in the Low Countries as the dry, or light draperies. They needed no oil, and the long fibres could be combed rather than carded. Nor did they need any fulling, tentering, napping, or shearing. Once woven, the cloth was already strong enough that it could immediately be used. The end product was coarser, and much more prone to wear and tear, but it was also much lighter — just a quarter the weight of a high-quality woollen. And the fact that the weave was still visible provided an avenue for design, with beautiful diamond, lozenge, and other kinds of patterns. The new draperies, which included worsteds and various kinds of slightly heavier worsted-woollen hybrids, as well as mixes with other kinds of fibre like silk, linen, Syrian cotton, or goat hair, thus came in a dazzling number of varieties and names: from tammies or stammets, to rasses, bays, says, stuffs, grograms, hounscots, serges, mockadoes, camlets, buffins, shalloons, sagathies, frisadoes, and bombazines. To escape the charge that the new draperies were too flimsy and would not last, some varieties were even marketed as durances, or perpetuanas.
Curiously, however, while the shift from woollens to worsted saved on the costs of oiling, fulling, and finishing, it was significantly more labour-intensive when it came to spinning — even resulting in a sort of technological reversion. Given the lack of fulling, the strength of the thread mattered a lot more for the cloth’s durability, and the yarn had to be much finer if the cloth was to be light. The spinning thus had to be done with much greater care, which made it slower. Spinners typically gave up using spinning wheels, instead reverting to the old method of using a rock and distaff — a technique that has been used since time immemorial. Albeit slower, the rock and distaff gave them more control over the consistency and strength of the ever-thinner yarn. For the old, woollen drapery, processing a pack of wool into cloth in a week would employ an estimated 35 spinners. For the new, lighter worsted drapery it would take 250. As spinning was almost exclusively done by women, the new draperies provided a massive new source of income for households, as well as allowing many spinsters or widows to support themselves on their own. Indeed, an estimated 75% of all women over the age of 14 might have been employed in spinning to produce the amounts of cloth that England exported and consumed. Some historians even speculate that by allowing women to support themselves without marrying, it may have lowered the national fertility rate.
This spinning, of course, was not done in London. It was largely concentrated in Norfolk, Devon, and the West Riding of Yorkshire. But the new draperies provided employment of another, indirect kind. As a product that was saleable in warmer climes it could be exchanged for direct imports of all sorts of different luxuries, from Moroccan sugar, to Greek currants, American tobacco (imported via Spain), and Asian silks and spices (initially largely imported via the eastern Mediterranean). The English merchants who worked these luxury import trades were overwhelmingly based in London, and had often funded the voyages of exploration and embassies to establish the trades in the first place, putting them in a position to obtain monopoly privileges from the Crown so that they could restrict domestic competition and protect their profits. Unsurprisingly, as they imported everything to London, it also made sense for them to export the new draperies from London too.
Thus, despite losing the concentrating influence of nearby Antwerp, London came to be the principal beneficiary of England’s new and growing import trades, allowing it to grow still further. The city began to carve out a role for itself as Europe’s entrepôt, replacing Antwerp, and competing with Amsterdam, as the place in which all the world’s rarities could be bought (and from which they could increasingly be re-exported). Indeed, English merchants were apparently happy to sell wool cloth at below cost-price in markets like Spain or Turkey — anything to buy the luxury wares that they could monopolise back home.