Jago Hazzard
Published 13 Aug 2023Peep peep!
(more…)
December 19, 2023
Overthinking Thomas the Tank Engine: What Actually Is Thomas?
December 10, 2023
Engines of War: How Wars Were Won and Lost on the Railways
WW2TV
Published 15 Jun 2023Engines of War: How Wars Were Won and Lost on the Railways With Christian Wolmar
Before the nineteenth century, armies had to rely on slow and unreliable methods of transportation to move soldiers and equipment during times of conflict. But with the birth of the railroad in the early 1830s, the way wars were fought would change forever. In this show renowned expert Christian Wolmar tells the story of that transformation with a focus on railways in WWII and especially the Normandy campaign.
Christian Wolmar is a British journalist, author, railway historian and Labour Party politician. He is known for his commentary on transport, especially as a pundit on Britain’s railway industry, and was named Transport Journalist of the Year in the National Transport Awards in 2007.
(more…)
December 8, 2023
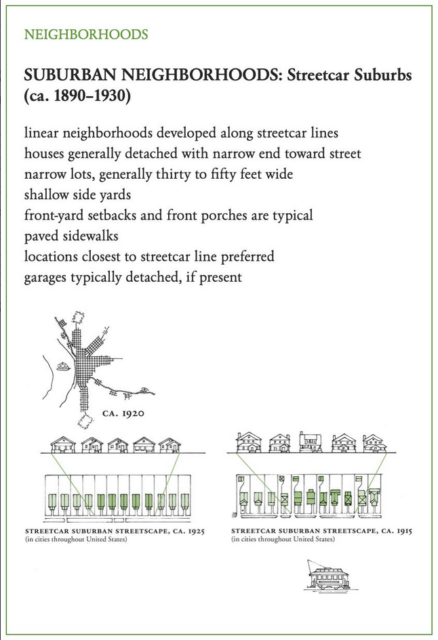
The development of the American suburb
In the latest book review from Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, Jane Psmith discusses A Field Guide to American Houses (Revised): The Definitive Guide to Identifying and Understanding America’s Domestic Architecture, by Virginia Savage McAlester. In particular, she looks at McAlester’s coverage of how suburbs developed:
After some brief but interesting discussion of cities,1 most of the page count is devoted to the suburbs. It’s a sensible choice: suburbs have by far the most varied types of house groupings, and more than half of Americans live in one. But what exactly is a “suburb”? It’s a wildly imprecise word, referring to anything that is neither truly rural nor the central urban core, and suburbs vary tremendously in character. As a working definition, though, a suburb is marked by free-standing houses on relatively larger lots. (If you can think of a counter-example that qualifies but is “urban”, I’ll bet you $5 it started out as a suburb before the city ate it.)
This means that building a suburb has a few obvious technological prerequisites, which McAlester lists as follows: First, balloon-frame construction, which enabled not just corners but quick and inexpensive construction generally and removed much of the incentive for the shared walls that were so common in the early cityscape. Second, the proliferation of gas and electric utilities in the late nineteenth century meant that the less energy-efficient free-standing homes could still be heated relatively inexpensively. Third, the spread of telephone service after 1880 meant that it was much easier to stay in touch with friends whose front doors weren’t literally ten feet away from yours.2 But by far the most important technological advances came in the field of transportation, which is obviously necessary if you’re going to live in the country (or a reasonable facsimile thereof) and work in the city.
The first of these transportation advances was the railroad. In fact “railroad suburb” is a bit of a misnomer, because most of the collections of houses that grew up around the new rail stops were fully functional towns that had their own agricultural or manufacturing industries. The most famous railroad suburbs, however, were indeed planned as residential communities serving those wealthy enough to pay the steep daily rail fare into the city. Llewellyn Park near New York City, Riverside near Chicago, and the Main Line near Philadelphia are all examples of railroad suburbs that have maintained their tony atmosphere and high property values.
The next and more dramatic change was the advent of the electric trolley or streetcar, first introduced in 1887 but popular until about 1930. (That’s what all the books say, but come on, it’s probably October 1929, right?) Unlike steam locomotives, which take quite a long time to build up speed or to slow down again, and so usually had their stations placed at least a mile apart, streetcars could start and stop far more easily and feature many more, and more densely-placed, stops. Developers typically built a streetcar line from the city veering off into the thinly-inhabited countryside, ending at an attraction like a park or fairground if possible. If they were smart, they’d bought up the land along the streetcar beforehand and could sell it off for houses,3 but either way the new streetcar line added value to the land and the development of the land made the streetcar more valuable.
You can easily spot railroad towns and streetcar suburbs in any real estate app if you filter by the date of construction (for railroad suburbs try before 1910, for streetcar before 1930) and know what shapes to look for. Railroad towns are typically farther out from the urban center and are built in clusters around their stations, which are a few miles from one another. Streetcar suburbs, by contrast, tend to be continuous but narrow, because the appeal of the location dropped off rapidly with distance from the streetcar line. (Lots are narrow for the same reason — to shorten the pedestrian commute.) They expand from the urban center like the spokes of a wheel.
And then came the automobile and, later, the federal government. The car brought a number of changes — paved streets, longer blocks, wider lots (you weren’t walking home, after all, so it was all right if you had to go a little farther) — but nothing like the way the Federal Housing Authority restructured neighborhoods.
The FHA was created by the National Housing Act of 1934 with the broad mandate to “improve nationwide housing standard, provide employment and stimulate industry, improve conditions with respect to mortgage financing, and realize a greater degree of stability in residential construction”. It was a big job, and the FHA set out to accomplish it in a typical New Deal fashion: providing federal insurance for private construction and mortgage loans, but only for houses and neighborhoods that met its approval. This has entered general consciousness as “redlining”, after the color of the lines drawn around uninsurable areas (typically old, urban housing stock),4 but the green, blue, and yellow lines — in order of declining insurability — were just as influential on the fabric of contemporary America.
A slow economy through the 1930s and a prohibition on nonessential construction during the war meant that FHA didn’t have much to do until 1945, but as soon as the GIs began to come home and take advantage of their new mortgage subsidies, there was a massive construction boom. With the FHA insuring both the builders’ construction loans and the homeowners’ mortgages, nearly all the new neighborhoods were built to the FHA’s exacting specifications.
One of the FHA’s major concern was avoiding direct through-traffic in neighborhoods. Many post-World War II developments were built out near the new federally-subsidized highways on the outskirts of the cities, so the FHA was eager to protect new subdivisions from heavy traffic on the interstates and the major arterial roads. Neighborhoods were meant to be near the arterials, but with only a few entrances to the neighborhood and many curved roads and culs-de-sac within it. Unlike the streetcar suburbs or the early automobile suburbs that filled in between the “spokes” of the streetcar lines, where retail had clustered near the streetcar stops, the residents of the post-World War II suburbs found their closest retail establishments outside the neighborhood on the major arterial roads. Lots became wider, blocks longer, and sidewalks less frequent; houses were encouraged to stay small by FHA caps on the size of loans. And although we tend to assume they were purely residential areas, the FHA encouraged the inclusion of schools, churches, parks, libraries, and community centers within the neighborhood.
1. America doesn’t have many urban neighborhoods that predate 1750, and even fewer that persist in their original layout, but if you’ve ever visited one it’s amazing how compact everything feels even in comparison to the rowhouses of the following century.
2. McAlester’s footnote for the paragraph that contains all this reads: “These three essentials were highlighted in an essay the author has read but has not been successful in locating for this footnote.”
3. This is still, I am told, how some of the more sensibly-governed parts of the world run their transit systems: whatever company has the right to build subways buys up the land around a planned (but not announced) subway line through shell corporations, builds the subway, then sells or develops the newly-valuable property. Far more efficient as a funding mechanism than fares!
4. This 2020 NBER working paper points out that redlined areas were 85% white (though they did include many of the black people living in Northern cities) and suggests that race played very little role in where the red lines were drawn; rather, black people were already living in the worst neighborhoods.
November 25, 2023
Crystal Palace Station is Needlessly Magnificent
Jago Hazzard
Published 9 Aug 2023Crystal Palace and the station built for it. Well, one of them.
(more…)
November 15, 2023
The Future of Railways (circa 1961)
Jago Hazzard
Published 26 Jul 2023The future is slightly dingy.
(more…)
November 11, 2023
The Mississauga Train Derailment (1979)
The Raven’s Eye
Published 8 Nov 2022It was called “The Mississauga Miracle” — a train derailment involving 26 cars of toxic and flammable materials, just a few miles from a major Canadian city center. Faced with the prospect of a cloud of killer phosgene gas being released, authorities had no choice but to order the mass evacuation of an entire city …
(more…)
QotD: Diary entry, 11 November, 1979
I hope you’ll forgive my self-insert here, but watching the video on the Mississauga train derailment prompted me to dig up a bit of personal history related to this thankfully non-tragic event in Canadian history. This is what I wrote about the events of that week not at the time (I was far too busy living it to record anything) but a couple of months after the fact. Samuel Pepys I wasn’t. I note in passing that my memories today don’t exactly match what I wrote in early 1980, which does bring home to me the fallibility of “eyewitness” reports after the fact.

On the night of November 10, 1979, a 106-car Canadian Pacific freight train derailed at Mavis Road, north of Dundas Street. As a result of the subsequent explosion, when one of the tank cars carrying propane exploded, and because other tank cars were carrying chlorine, the decision was made to evacuate nearby residents in one of the largest peace time evacuations in history. This photo shows flames from the wreckage, with hoses pouring water on it.
Photo from the Mississauga Library System website, Identifier M466. Full gallery here.
In November of ’79, on the 11th actually, a chemical train derailed just northwest of [our apartment near Dundas and Hurontario Streets]. It spilled 16 tank cars full of propane and one full of chlorine all over the Mavis Road crossing.
I was driving back to Hamilton on Saturday night to drop off [my girlfriend]. Rockney was inexplicably along with us that night. Around midnight, I noticed the road all around us light up as though dawn had come early. Also noticed a pronounced mushroom-type cloud and lots of incident light at its base. Right there, my mind kicked into Hyperdrive and I analyzed the data, assumed the worst, and nearly swung off the highway to protect us behind an embankment. [The others] saw that it wasn’t an H- or A-type of explosion, and so we didn’t worry too much. Flames [on the eastern horizon] were easily visible from Hamilton.
I went back [to Mississauga], dropped Rockney off [and] noticed a police car blocking the intersection of Dundas and Hurontario with its lights going. Talked to Mum, who was still up, and went to bed at 3:00am.
We were woken up at 10:00am by police evacuating the building. I called Rockney and we all trooped over to his place. I stayed for 1/2 an hour, and decided to go back to the house, change into [my army reserve] uniform, and go up to Brampton for our Remembrance Day parade. On the way, I was stopped by the police and directed to go to Square One, where an evacuation centre had been set up. As I arrived there, the last bus-load of evacuees left headed for Streetsville Secondary School. I arrived there in time [to be given responsibility for security] with 15 assorted army and navy cadets [who were in uniform for their respective Remembrance Day services] who had no officer handy. We cleared the halls [at the direction of police and school authorities] and tried to maintain calm among the evacuated throng.
By 8 that evening, my force had shrunk to seven cadets led by Petty Officer Linda P. An officer cadet of the Air Reserve and five air cadets with him refused to assist me or the police. [I was angry at the time, but he was probably worried about the legal side of providing “aid to the civil power” while in uniform without permission from his chain of command. I was a junior NCO, so that thought never crossed my mind until much later.]
By this time, I had attached Chris P. [a friend of Rockney’s who was evacuated to Streetsville] and several other husky teenagers to my “security force” and we were able to keep things fairly quiet.
As people [started to realize] that they would be there all night, most of them settled down very nicely. [My team of cadets] issued blankets we’d received on a truck from CFB Downsview and shared out the available gym mats [as makeshift mattresses].
A local McDonalds sent in a “breakfast” of cold Big Macs [I’m sure they were hot going out the door, but they took a long time to get to us] — [the non-cadet members of] my security force got more than their fair share, but that was expected. Most of the media had disappeared by this time so we soon got involved in minor disputes with some irate citizens.
Sometime during Monday afternoon a Master Corporal from CFB Downsview called me to arrange a coffee run down to the [emergency crews working to contain] the fire. Nothing came of it in the end [I have no idea why they thought I’d be a useful participant, as I had no transportation other than my own car … maybe I was the only member of the military in the immediate vicinity].
Tried calling Rockney’s place [to see how my family were doing] but got no answer, same at Bill & Clive’s apartment [several miles further east of Rockney’s]. No idea where my parents have gone. [After being evacuated a second time, they’d ended up at the International Centre with the family cat and stayed there until later in the week, as I found out later. My sister hadn’t been at home so she was evacuated elsewhere with her boyfriend’s family. I have no idea where she spent the week.]
Monday night wasn’t too bad, except for [media reports] that there were 3 escaped cons in the area so i couldn’t send girls out alone on security sweeps [outside the school building]. Me, Chris P., Jordan L., and John D. were the only [ones available to do exterior security] now, getting VERY tired. Got an hour’s sleep.
On Tuesday a bunch of students from Humber College showed up. They were all taking the Law Enforcement course and wanted to help me with security. [The] only problem was that the course was 9/10ths female [so] I couldn’t use them [for exterior patrols, which is where we needed help the most].
Also showing up [later on Tuesday] was a local CB radio group who tried to take over from me and my team. It took two hours [of argument] before they gave up and went off to try to take over some other evacuation centre. [Around this time,] vandalism started on the back side of the school and in the portable classrooms. No one was caught at it, unfortunately. [I didn’t note it here, but I strongly suspected that one or more of my volunteers had done some of the damage out of boredom, but I had no proof.]
The biggest problem, however, was racial. A large group of black teenagers had taken over one of the Home Economics classrooms and had 2 competing ghetto blasters to make mucho noise. 2 fights had to be broken up in there and we had to call the police in to cope with the second fight.
[Tuesday] night was uneventful for a change. Wednesday wasn’t, as rumours of being able to go home kept hitting the people in the evacuation centre and nearly overwhelming the security teams at the doors. One asshole, a guy about 20-25 years old, kept buttonholing me and other members of my team and demanding shampoo, of all things. Eventually, someone got him some and he “went to the showers”. [In hindsight, he probably had just come down from whatever drugs he’d been on for the previous few days.]
On Wednesday night, the evacuation centre in Streetsville was shut down and everyone was moved to other facilities on Mississauga Transit buses. Most were taken to the Royal York Hotel in downtown Toronto, but my remaining team members were sent to a Holiday Inn in Scarborough. [I was in rough shape by then and someone got me to hospital to get checked out. I was there for about 10 hours before they discharged me with advice to “get plenty of rest”.]
Thursday we spent in the hotel, charging everything to CP Rail. They must have hit the roof when the bill arrived — especially the bar bill! We threw an “exhaustion party” in our room on Thursday night and on Friday we were finally allowed to go home (most of us, anyway).
When I went back to school the following week, I was given the third degree by the vice principal because the Red Cross didn’t have me listed as an evacuee. I had to get the hospital records to show that I had actually taken part before I was allowed back into class. [A similar thing happened the next unit parade night, as I’d been on TV several times in my uniform during the event and my commanding officer was quite upset about it, thinking I’d been pretending to act in some sort of official capacity, which I hadn’t been.]
October 26, 2023
Look at Life – Draw the Fires (1963)
PauliosVids
Published 21 Nov 2018The railways are changing, with coal-powered steam being phased out and replaced by diesel engines by 1972. Crowds pay their respects to the Flying Scotsman‘s last departure from Kings Cross as it is replaced by a 3,300-horsepower diesel. The network is being modernised by new signalling, longer continuous track on concrete sleepers and flyovers, and controversial closures of lines.
September 28, 2023
North Korea’s special train for “Dear Leader”
In The Critic, Peter Caddick-Adams discusses the North Korean leader’s special train, used to transport Kim Jong Un to destinations within North Korea and further afield to Russia, China, and other rail-accessible destinations:
It was pulled by two heavy locomotives. Next an armoured anti-aircraft wagon. After the baggage car came the leader’s steel-plated Pullman, followed by a command coach containing a conference room and communications centre. Connected to them, the 22-man security detail travelled in their own rolling stock. Beyond was a dining car, two coaches for guests, and of all things a bathing wagon, then a second dining car. Bringing up the rear were two sleeping cars, a press wagon for the news hounds, another baggage car and finally another anti-aircraft wagon. The coachwork was of the finest materials, hardwoods and high-grade leather, armour-plated, and bristling with guns and radio antennae. Outside in all weathers, day and night, other protective guards swept along the tracks.
There was something charmingly old fashioned about the decision of Kim Jong Un, leader of North Korea, to travel by train to meet his fellow dictator, Vladimir Putin. Over here, even when buffered by a railcard, Network Rail can sometimes fail spectacularly as an ambassador for this effortless mode of transport. Yet, we forget how important journeying by train was and remains. Important figures frequently opt for the smooth clickety-clack over air or road for their expeditions. The method is discreet, away from prying eyes, yet connected to a nationwide network that avoids congestion. Passengers can wine and dine, sleep, relax, study, converse and think. Rail lines are easy to guard, whereas the boulevards are full of threatening traffic and potential ambush points. Franz Ferdinand, Reinhard Heydrich, Charles de Gaulle and John F. Kennedy found this out to their cost between 1914 and 1963. Fatally in three out of four cases.
Some leaders have a phobia about flying. Stalin was one, which was why the only summit meetings he attended, at Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam, were ones connected to Moscow by rail. Perhaps President Putin, a known fancier of custom-built rolling stock, will now fear a weird kind of Karma for having arranged the eternal flight of his former chef, Yevgeny Prigozhin. The president has several trains, each containing an identical office to those in his state dacha, the Kremlin and St Petersburg. All look the name, making it impossible for the viewer, and potential assassin, to know where he is. Maybe his long-distance travel plans will be dictated by iron roads from now on?
[…]
The North Korean’s father, Kim Jong Il, hated taking to the air, instead relying on his old green-and-yellow-liveried rolling stock to convey him around his hermit kingdom. Loaded with extravagant foods, fine wines and attended by glamorous staff, the elder Kim used it on the last state visit of a North Korean to Russia in 2002. “It was possible to order any dish of Russian, Chinese, Korean, Japanese or French cuisine,” remembered one journalist. “Live lobsters were taken to stations along the route, with cases of Bordeaux and Burgundy”. However, the size, opulence and weight of this upmarket rolling McDonald’s restricted its speed to a graceful 40mph. Kim Senior’s Great Continental Railway Journey took one month. Michael Portillo, eat your heart out.
Paranoid about their personal security, the Kim family have traditionally relied on around 90 special carriages, usually made into three trains. The first handles advance security; the next carries the Kim entourage; whilst the last houses bodyguards and other personnel. The middle train, with its wall-mounted lighting, beds, sofas and armchairs reupholstered in “tasteful” reddish-pink leather (I know), was the one in which the current Kim lounged on his way to summits in Beijing and Hanoi, and travelled south in 2019 to meet President Trump in the Korean Demilitarised Zone.
The recent state visit of Kim aboard the twenty-hour Pyongyang to Vladivostok Express, no stops, should give us pause for thought. With him travelled officials closely connected with his weapons development and military science teams, and his younger sister, Kim Yo Jong. In addition to being the regime’s propagandist-in-chief, she acts as gatekeeper to her overweight, chain-smoking brother, who became leader after the sudden death of their father in 2011. Kim’s North Korean Night Mail carried a significant assembly of his regime’s inner circle.
September 24, 2023
Architect Breaks Down Why All American Diners Look Like That | Architectural Digest
Architectural Digest
Published 1 Jun 2023Today Michael Wyetzner of Michielli + Wyetzner Architects returns to Architectural Digest to explore the design evolution of American diners. A cornerstone of American dining culture, their distinctive style has been emulated around the world making them a popular salute to the USA. Michael provides an expert look into the history behind their design evolution from the 1920s through to the 1960s and explains why all diners came to look like that.
(more…)
September 21, 2023
Iranian Railways, Red Cross Care Packages, and Tail Gunners – WW2 – OOTF 31
World War Two
Published 20 Sept 2023How did the Allies build and manage an enormous railway supplying the Soviet Union through Iran? How did the Red Cross deliver aid parcels through enemy territory to Allied POWs? And, how effective were the rear gunners in ground attack aircraft like the Stuka and Sturmovik? Find out in this episode of Out of the Foxholes.
(more…)
This is York
Jago Hazzard
Published 28 May 2023“Make all the railways come to York!”
(more…)
August 31, 2023
Why New York Destroyed 3 Iconic Landmarks | Architectural Digest
Architectural Digest
Published 6 Apr 2023Michael Wyetzner of Michielli + Wyetzner Architects returns to AD, this time to look at the history and creation of three New York City landmarks that have since been demolished — but are far from forgotten. From the once (and future?) majesty of Penn Station to the New York Herald building and the original 19th-century Madison Square Garden, Michael gives expert insight into these three historic architectural landmarks, why they were laid to ruin, and what came to replace them.
(more…)
August 21, 2023
Some good reasons why the Russo-Ukraine war is misunderstood in the West
A few days back, Bruce Gudmundsson outlined a few of the reasons the Western — particularly the English-language — reporting on the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine gets it wrong:

Railways have played a significant role in warfare since at least the Crimean War.
Navvies working on the Grand Crimean Central Railway, 1854. From Thomas Brassey, Railway Builder (1969).
As I live within a bowshot of a railroad crossing, the screech of metal wheels on metal rails frequently reminds me of one of the many things that so many Anglophone commentators get wrong about the war in Ukraine. Coming from places afflicted with (hat tip to Arlo Guthrie [NR: I’d give the credit to Steve Goodman, personally]) “the disappearing railroad blues”, these writers find it hard to imagine the degree to which Russian soldiers exploit the ability of the iron horse to move vast numbers of hundred-pound artillery shells. This blindspot, in turn, causes them to place far too much importance on means of movement, such as ships and trucks, that play second fiddle in the logistical symphony that supplies Russian forces in the field.
Tales of soldiers stealing pickles from convenience stores spark thoughts of another mistake that English-speaking critics have made with respect to the Russian supply system. Wise generals, from Alexander the Great to Francisco Franco, have long deployed vast quantities of food along with their armies. Nonetheless, the enduring fondness of English-speaking soldiers for bully beef, tinned biscuits, and other meals-ready-to-eat sets them apart from most other fighting men, past or present. To put things another way, we should not have been surprised that, when organizing an invasion of one of the great food-producing countries of our planet, Russian logisticians preferred the dispatch of fuel and ammunition to the delivery of items that could have been found in every bodega along the line of march.
Anglophone analysts also drew the wrong conclusions from reports of the loss, in battle, of Russian general officers. Such casualties, they argued, stemmed from an absence of trust. That is, Russian generals were killed because, lacking confidence in the competence of colonels, captains, and corporals, they felt obliged to exercise close supervision over forces engaged in combat.
The participation of generals in firefights, however, need not reflect an absence of faith in the fidelity and abilities of subordinates. Indeed, the original gangsters of “trust tactics” often recommended that the general officers commanding formations lead from the front. I suspect, moreover, that Russian leaders also understood that seeing a general die a soldier’s death usually exercises a positive influence on the morale of his subordinates. (“Say what you will about old General Strelkov, but he never asked us to do anything he wasn’t willing to do himself.”)
Finally, few who made much of the battle deaths of Russian general officers seem to have been aware that the Russian forces that crossed into Ukraine on 24 February 2022 were organized in a way that provided them with an extraordinarily high proportion of fighting generals. That is, when a peacetime formation formed a battalion tactical group, the general in charge of that organization usually took command of the unit it spawned. Thus, rather than having one general for every four or five battalions, the Russian forces of the first few months of the “special military operation” had five or six flag-rank officers for every four or five battalions.
August 11, 2023
The Weirdest Boats on the Great Lakes
Railroad Street
Published 5 May 2023Whalebacks were a type of ship indigenous to the Great Lakes during the late 1890s and mid 1900s. They were invented by Captain Alexander McDougall, and revolutionized the way boats on the Great Lakes handled bulk commodities. Unfortunately, their unique design was one of the many factors which led to their discontinuation.
(more…)