One is viewed as among America’s greatest presidents; the other perhaps the worst of all. One is hailed as a savior; the other as a failure. One is given memorials to enshrine his name for all time; the other is pushed into the sea of forgetfulness.
Driven by academia, this is where American history has placed Franklin Delano Roosevelt (in office 1933-1945) and Warren Gamaliel Harding (in office 1921-1923). It is impossible to see FDR absent a “great presidents” ranking; it is likewise impossible to see Harding absent the lowest rungs.
Both men came into office with an economy in tatters and both men instituted ambitious agendas to correct the respective downturns. Yet their policies were the polar opposite of one another and, as a result, had the opposite effect. In short, Harding used laissez faire-style capitalism and the economy boomed; FDR intervened and things went from bad to worse.
Despite these clear facts, in C-SPAN’s latest poll ranking US presidents, FDR finished third in the rankings, while Harding finished 37th. Surveying how both handled the economy, scholars ranked FDR third in that category, while Harding came in at 32. This is a tragedy of history.
America in 1920, the year Harding was elected, fell into a serious economic slide called by some “the forgotten depression“. Coming out of World War I and the upheavals of 1919, the economy struggled to adjust to peacetime realities, falling into a serious slump.
The depression lasted about 18 months, from January 1920 to July 1921. During that time, the conditions for average Americans steadily deteriorated. Industrial production fell by a third, stocks dropped nearly 50 percent, corporate profits were down more than 90 percent. Unemployment rose from 4 percent to 12, putting nearly 5 million Americans out of work. Small businesses were devastated, including a Kansas City haberdashery owned by Edward Jacobson and future president Harry S. Truman.
The nation’s finances were also in shambles. America had spent $50 billion on the Great War, more than half the nation’s GNP (gross national product). The national debt jumped from $1.2 billion in 1916 to $26 billion in 1919, while the Allied Powers owed the US Treasury $10 billion. Annual government spending soared more than twenty-five times, from around $700 million in 1916 to nearly $19 billion in 1919.
Harding campaigned on exactly what he wanted to do for the economy – retrenchment. He would slash taxes, cut government spending, and roll back the progressive tide. He would return the country to fiscal sanity and economic normalcy.
“We need a rigid and yet sane economy, combined with fiscal justice,” he said in his inaugural address, “and it must be attended by individual prudence and thrift, which are so essential to this trying hour and reassuring for our future”.
The business community expressed excitement about the new administration. The Wall Street Journal headlined on Election Day, “Wall Street sees better times after election”. The Los Angeles Times headlined the following day, “Eight years of Democratic incompetency and waste are drawing rapidly to a close”. Others read “Harding’s Advent Means New Prosperity” and “Inauguration ‘Let’s Go!’ Signal to Business”.
The day after Harding’s inauguration, the Times editors predicted “good times ahead”, writing, “The inauguration yesterday of President Harding and the advent of an era of Republicanism after years of business harassment and uncertainty under the Democratic regime were hailed” by the nation’s business leaders. I. H. Rice, the president of the Merchants and Manufacturers Association, told the press, “Good times are now ahead of us. Prosperity is at our door. We are headed toward pre-war conditions … Business men are well pleased with President Harding’s selections for his Cabinet and by the caliber of men he has chosen we know that he means business”.
Under Harding and his successor, Calvin Coolidge, and with the leadership of Andrew Mellon at Treasury, taxes were slashed from more than 70 percent to 25 percent. Government spending was cut in half. Regulations were reduced. The result was an economic boom. Growth averaged 7 percent per year, unemployment fell to less than 2 percent, and revenue to the government increased, generating a budget surplus every year, enough to reduce the national debt by a third. Wages rose for every class of American worker. It was unparalleled prosperity.
Ryan S. Walters, “The Two Presidents Whose Economic Policies Are Most Misunderstood by Historians”, Foundation for Economic Education, 2022-03-05.
February 21, 2026
QotD: Warren G. Harding’s successful depression-breaking policies
February 18, 2026
It’s not just Britain that gives asylum-seekers better care than citizens – Canada does too
We had a look at how well the British government looks after asylum-seekers yesterday, but other nations are probably doing similarly inequitable things to give money and services to non-citizens than they ever would for the people who pay the taxes for these over-generous programs. In the National Post, Tristin Hopper outlines the findings of a recent analysis from the Parliamentary Budget Office on the costs of supporting huge numbers of foreign nationals in Canada:

An asylum seeker, crossing the US-Canadian border illegally from the end of Roxham Road in Champlain, NY, is directed to the nearby processing center by a Mountie on 14 August, 2017.
Photo by Daniel Case via Wikimedia Commons.
Paying the health-care premiums of refugee claimants will cost Canadians a record $1 billion this year, with some of the beneficiaries continuing to receive free health care despite their claims having already been rejected.
That’s according to a new analysis by the Office of the Parliamentary Budget Officer, and it’s just one of several ballooning costs wrought by the unprecedented number of foreign nationals currently living in Canada by virtue of a claim of refugee status.
The Interim Federal Health Program, which offers premium health benefits to asylum claimants, is soon set to hit $1 billion in annual costs for the first time, according to an analysis last Thursday by the Office of the Parliamentary Budget Officer.
This is a five-fold increase from just six years ago, when the program was costing $211 million per year. The analysis also projects that costs are expected to surge for the foreseeable future, with the annual budget likely to hit $1.5 billion as early as 2029.
All told, between now and 2030, Canadians are on track to spend $6.2 billion on health care for refugees or refugee claimants.
“The rising volume of asylum claims, along with the longer duration of eligibility caused by extended determination times, has been an important growth driver in recent years,” reads the PBO report.
The report was commissioned following a Conservative-led request made at the House of Commons standing committee on health. In a Thursday statement, the Conservative party noted that the Interim Federal Health Program can be accessed even by asylum claimants who have had their case rejected.
It also offers a higher level of care than that enjoyed by the average Canadian citizen. In addition to hospital care and surgical care, the IFHP also covers dental care, vision care, pharmacare and other services not typically covered by public health plans.
“Rejected asylum claimants are now receiving better health care than many Canadians who have paid into a system their entire life,” read a joint statement by Dan Mazier and Michelle Rempel Garner, the shadow ministers of health and immigration, respectively.
It added, “at a time when six million Canadians cannot find a family doctor and are waiting for care, it’s unacceptable that bogus asylum seekers are receiving better health benefits than Canadians”.
February 17, 2026
The ludicrous idea of an “unrealized gains tax”
Governments everywhere are always on the lookout for more ways to raise revenue, so any suggestion of an untapped resource they can tax will get their attention. Apparently the current hot idea is an unrealized gains tax, which @wokeandwoofing satirized thusly:
Also on the social media site formerly known as Twitter, @Yogi frames the proposed new tax for Gen Z readers:
Unrealized gains tax for Gen-Z:
You buy a Pokémon card for $50.
Someone offers you $500 for it. You say no. You love that card. You’re keeping it.
The government says: “Cool, but that card is worth $500 now. You owe us $100 in taxes.”
You: “… I didn’t sell it.”Government: “Don’t care. Pay up.”
You don’t have $100 lying around. So you’re forced to sell the card you love just to pay a tax on money you never received.
Next month? That card drops back to $50.
Your card is gone. Your money is gone. And the government shrugs.
That’s a wealth tax on unrealized gains. They don’t pay you back the tax …
Now picture this.
Your mom calls you crying. She has to sell the house she raised you in. Not because she can’t afford it. She’s lived there 30 years. It’s paid off.
But some website says it’s worth more now and the government says she owes $15,000 she doesn’t have.
So she sells your childhood home. The kitchen where she made you breakfast. The doorframe where she marked your height every birthday.
Gone.
To pay a tax on money that was never real.
Now picture the opposite.
Your dad put everything into his small business. For 20 years he built it from nothing. One year the business is “valued” at $2 million on paper. He owes a massive tax bill. He empties his savings. Sells his truck. Borrows money. Pays it.
Next year the market crashes. His business is worth $200,000.
He lost everything to pay a tax on a number that doesn’t exist anymore.
Does the government give him his money back?
No.Does the government give him his truck back?
No.Does the government care?
No.They sold this idea as “taxing billionaires”. But billionaires have armies of lawyers, offshore accounts, and trusts. They’ll be fine.
You know who won’t be fine? Your mom. Your dad. Your neighbor with a small business. The farmer down the road who’s had the same land for four generations and now has to sell it because dirt got expensive.
You’re not taxing wealth. You’re taxing people for owning things.
It’s like getting a parking ticket for a car you might drive somewhere someday.
They want you to own nothing and be happy. To fund the fraud, waste and abuse of the welfare state they created.
There is enough money. More tax isn’t needed. It’s all a lie. But you’ve been gaslit into believing this is a rich vs poor debate.
I hope you understand what’s at stake.
February 16, 2026
“Multiculturalism” should really be called “anti-cultural slop” for it destroys real culture in favour of bland genericism
At Without Diminishment, Geoff Russ traces the rise of the “global hub” among western cultures and identifies why we shouldn’t strive to drown distinct local cultures under a tide of “could be anywhere” multicultural slop:
Multiculturalism is the false prophet of celebrating difference, presented as the ultimate engine for “diversity”.
In practice, it is a factory of global homogenisation, and a solvent that erases local cultures. Cities like Sydney, Toronto, and London now compete to be the top “global hub”, which is no unique identity at all.
There is no preservation of character under the hegemony of the global hub, only its erasure. The officially multicultural city is uniform across continents, like clones of each other in all but the most superficial ways. It sounds contradictory on the surface, but makes perfect sense once it is understood that multiculturalism as a policy and identity is inherently anti-cultural.
The multicultural city has nearly identical urban design, and its bureaucrats and professionals weaponise the same moral vocabulary, deploying terms like “inclusivity” and “openness“. It has all the charm of an airport lounge, justified with the same slogans, decorated with the same grey glass-and-steel architecture, and guided by the same self-reinforcing sensibilities.
It makes people docile, and rewards them with sensory appeasement, like supposedly exotic cuisine. A fusion rice bowl is the consolation for the disappearance of the environment you grew up in.
In Canada, it first came to the Anglo cities like Toronto and Vancouver. Now it has broken linguistic and cultural containment into Quebec. For decades, Montreal was the metropolis of the Québécois. Now, as Kevin Paquette outlined last month, the city has changed. It mirrors the anti-culture that took over Toronto, and has no use for the legacy of those who built it.
Paquette described how Montreal has become a “filter” that promotes an internationalist identity that renders it alien to Quebec’s exurban regions. Bloc Québécois (BQ) leader Yves-François Blanchet has warned that “two Quebecs” have emerged, which are disconnected and alienated from each other.
Jean-François Lisée has gone further, and written of the emergence of an “anti-Québécois identity” in an increasingly diverse Montreal. In public schools, students openly mock the Québécois, and English is more commonly spoken than French in the hallways.
Lisée writes that an alternate, anti-Quebec dynamic now exists among some newcomers. In this dynamic, attachment and assimilation into the Québécois identity become contemptible.
This is the essence of multiculturalism when treated as an end in itself. “Inclusion” is the hollowing out of the obligation to belong, and the transformation of identity into a lifestyle choice.
Not even Quebec City is immune. It was long a living, breathing exception to Canadian multiculturalism, with a dominant Québécois culture and ethos. However, the mayor, Bruno Marchand, has embarked on a mission to destroy what makes it distinct.
The following sentence is from a glowing feature in the Globe and Mail last week: “Mr. Marchand says his hometown’s traditional pure laine image is changing, and it’s a good thing”.
Quebec City’s inherited way of life is being targeted so that it can become just one more global hub. The city’s established symbols, traditions, and habits stand in the way. It takes remarkable ideological and moral heavy lifting to dismiss provincial identities as unworthy, and as something that must inevitably be replaced.
The city still carries deep meaning for francophones across the country.
“I’ve never lived there, or in the province of Quebec, and yet it speaks to me profoundly,” said one resident of Ontario I spoke to. “This is where my ancestors landed 400 years ago and it still bears witness to them.”
What was the point of Quebec’s 400-year effort to survive if it becomes a mirror image of what has happened to the rest of Canada?
Ontario, and the rest of Anglo-Canada, have long been conditioned to regard its own inheritance as unworthy of loyalty or respect.
Anglo-Canada is bound up in the history of the British Empire, the most fashionable whipping boy of leftist academics and activists. Due to the institutional power of these malcontents, it naturally follows that Canada’s historic and cultural self is treated as an embarrassment, whose memory is a problem that must be solved, or rather dissolved.
Update, 17 February: Welcome, Instapundit readers! Have a look around at some of my other posts you may find of interest. I send out a daily summary of posts here through my Substack – https://substack.com/@nicholasrusson that you can subscribe to if you’d like to be informed of new posts in the future.
M1918A2 MOR: How to Make a Non-NFA BAR
Forgotten Weapons
Published 24 Sept 2025Prior to 1986, Group Industries imported BAR parts kits and then manufactured and registered full-auto receivers for them. This produced transferrable guns which were subject to NFA registration and the $200 transfer tax — which was a much more significant sum at that time than it is today. Some of the potential customers were people (like reenactors) who wanted guns that looked and handled like real BARs but were not regulated by the NFA. To satisfy this subgroup of customers, Group designed a receiver which neither had nor could be adapted to have a gas piston, rendering the gun manually operated. It would fire from an open bolt, but had to be manually recocked after each shot. This was not legally a machine gun, and he made 68 of them.
When the Hughes Amendment to the FOPA passed in 1986, manufacture of new transferrable machine guns ceased, and Group Industries went out of business. Its assets were sold off, including a number of parts kits and unbuilt M.O.R. receivers. One of the buyers was Ohio Ordnance Works (then called Collector’s Corner). They got ten receivers and after selling them, decided to develop a semiautomatic BAR for that same non-NFA BAR market. That gun ended up being the M1918A3, which is still available from them today.
(more…)
February 15, 2026
Everything you see in the media is kayfabe
Wikipedia defines kayfabe as “the portrayal of staged elements within professional wrestling (such as characters, rivalries, and storylines) as legitimate or real. Although it remains primarily a wrestling term, it has evolved into a code word for maintaining the pretense of ‘reality’ in front of an audience.” It’s hard not to see modern political theatre in that light, as Damian Penny points out:
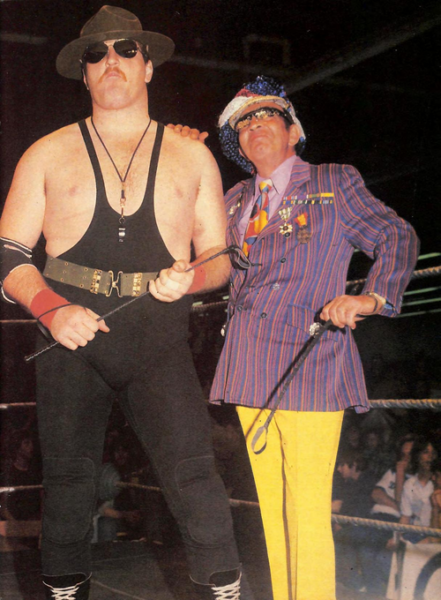

Sgt. Slaughter and The Grand Wizard, February 1984.
Photo from Wrestling’s MAIN EVENT magazine via Wikimedia Commons.
I know a guy who was obsessed with WWF wrestling (yes, I said WWF wrestling, because you kids better get off my lawn before Diagnosis Murder comes on) when he was younger and got to see it live when it came to his city. After the show, he was shocked to see several of the wrestlers — some of them good-guy “faces”, others bad-guy “heels” — being driven from the arena in the same minivan.
For someone who took the “sport” of professional wrestling seriously1 and was extremely emotionally invested in the performer rivalries, this was kind of like finding out that Santa Claus wasn’t real.2
That’s the first thing I thought about when I came across this piece by Christianity Today‘s Russell Moore, a rare evangelical leader who actually held on to his integrity in the age of Trump, about the Epstein Files:
Reading through the names of those connected with Epstein, one can hardly believe the range listed there. Some were unsurprising: for instance, creepy filmmaker Woody Allen or the man formerly known as Prince Andrew. But even then, the scope is unsettling. Even the Dalai Lama had to put out a statement noting that he was never involved with Epstein. Just as incredible, many of the people listed were partying with those they spend a lot of time telling the rest of us to hate.
Both Donald Trump and Bill Clinton were apparently friendly with Epstein. The New Age syncretist Deepak Chopra is in the documents many times — often with shady, enigmatic phrases — but so are those who accused the pope of New Age syncretism. With Middle Eastern tensions what they are, still the files include both sheikhs and Israelis. All over the files are connections with both left-wing populist provocateur Noam Chomsky and right-wing populist provocateur Steve Bannon. Epstein makes fun of evangelicals yet recommends a James Dobson article.
How can this be?
Maybe one reason is that Jeffrey Epstein figured out the deep, dark secret of this moment: The people who fight culture wars often believe what they say, but the people who lead culture wars often don’t.
[…] And if the Epstein revelations didn’t blackpill you hard enough, check this out:
To be fair, I’m not sure it’s an entirely bad thing that so many decision-makers and “thought leaders” who are sworn enemies in public get along just fine when the cameras are turned off. If they really hated each other, our political culture might be even more messed up.
- YouTuber Drew Allen says you should take wrestling seriously, and honestly he makes a darned good argument.
- I’ll never forget when I found out Santa Claus wasn’t real, and how I was so depressed and hopeless and wouldn’t leave my bed for days. Finally my mother came into my bedroom, sat down on the side my bed and said, “honey, I know you’re sad but you’re in your second year of law school and really we thought you’d have figured this out long ago“.
February 14, 2026
“People don’t need conspiracies to be absolute utter rabid bastards”
If you search here for the word “Epstein”, you won’t find a lot of relevant hits other than the reporting when he was arrested in 2019 and occasional mentions in posts on other topics. I don’t breathlessly report every little driblet of news or rumour as it floats past, because I’ve seen other moral panics play out in the past (like the Cleveland child abuse scandal back in the late 80s). Ian at The Bugscuffle Gazette has not only seen things like this before, he’s worked in law enforcement on similar (if lower-profile) cases:

Mug shot of Jeffrey Epstein made available by the Palm Beach County Sheriff’s Department, taken following his indictment for soliciting a prostitute in 2006.
Image via Wikimedia Commons.
The Epstein Files have been released to a tremendous amount of outrage, and I find myself conflicted. There are definitely victims of that virulent parasite, but I worry they’re about to be overlooked.
I’m afraid that this whole mess is starting to remind me a great deal of the Satanic Panic of the 1980s – 1990s.
For those who may be a little too young to remember that little blot on the Copybook of History, it started with a “psychiatrist”1 who had a fondness for the woo-woo — and incredibly debunked — practice of “Recovered Memory Therapy“2, and was spark-plugged by well-meaning3, yet clueless, people who used suggestive questions and leading questions when interviewing children … and wound up with about 12,000 reports of ritual abuse of children — including, but not limited to: child sexual abuse, ritual sacrifice of children, cannibalism of children, child pornography, child prostitution, murder of children, torture of children, and incestuous orgies.
A large part of the American population became convinced that paedophiles associated with Satanism were running child care centers across the country for the express purpose of providing a steady supply of children for devil-worshipping rites.
As one might expect day-care workers and pre-schools took it in the neck … but so did fathers. The “experts” — untrained, inexperienced, unqualified — had a particular case of the ass towards fathers, with the result that several fathers spent years in prison for crimes never committed.
Yeah. Not a one of those reported 12,000 cases turned out to be substantiated. And when I say “Not substantiated” we’re talking about stuff like:
- Children were coached to testify that they had been taken to a cemetery where the graves were dug up and the corpses used for violation. It is physically impossible to dig up an entire cemetery and leave abso-bloody-lutely no trace behind.
- Children were coached to testify that a teenager with Noonan Syndrome had cut the throat of a giraffe, and used the dying corpse for ritual violations. Seriously.
- Children were coached to testify that they had been given to aliens, flown up into space, and violated.
In addition to the coaching, case files were built from statements given by diagnosed schizophrenics; anonymous statements given by people who were later tracked down and found to be — let us be precise here — flat barking bugnuts; and was fueled by the political desire to make hay, or make the other guy look bad rather than — you know — justice.
What does this have to do with the price of tea in China? Other than the fact that innocent people got dragged through the legal wringer, spent years in prison, and had their lives ruined for nothing; the mass-hysteria moral panic4 went that actual, provable cases of child molestation got short shrift.
A vast underground network of Satanic peadophiles conducting ritualistic abuse, cannibalism, and unholy rituals was far more toothsome to prosecutors, the Media, and the public at large than Uncle Badtouch.
Given the choice of making his name by becoming the hero taking on a vast international cabal of highly-connected Satanists … or the day-to-day boring grind of prosecuting the creepy dude at the park — well, District Attorneys are politicians. And politicians gotta politick. Heroes poll better than the unsung.
Which brings us to the Epstein Files.
- I use the scare quotes because he should have been struck off for his wanton destruction of families and innocent people.
- Really good at implanting false memories, not worth a bucket of warm rat spit at recovering memories.
- And let’s face it: Some ill-intentioned folks.
- This went on for years.
The EU’s plans to drain the “wine lake” … again
Canada isn’t the only place with rigidly governed agricultural cartels … the European Union has always been a big fan of governing agricultural markets by fiat rather than allowing the markets to sort out how much of which product should be produced. One of the biggest markets actively distorted by EU regulation is the wine industry, where faulty regulations ended up paying for a vast over-supply of wine in the 1980s and 90s. Rather than eliminating the regulatory structures, the EU continues to prefer letting bureaucrats dictate to producers:
When the Common Agricultural Policy was established, it was quickly determined that one of its core objectives would be the protection of farmers, ensuring stable incomes and food security. In the wine sector, this logic translated into strong interventionism aimed at expanding and stabilizing production.
For decades, Brussels subsidized vineyard planting, protected minimum prices, and absorbed producers’ economic risk, disconnecting production decisions from signals of demand. Producing more ceased to be an economic choice and became a politically safe decision.
This approach created a structural market distortion. As wine consumption began to decline across Europe for demographic, cultural, and economic reasons, the artificially incentivized productive structure remained intact and unable to adjust.
It was in this context that, during the 1980s and 1990s, the first major shock occurred, known as the wine lake: massive wine surpluses with no outlet. Even then, Brussels treated this episode as an isolated and temporary phenomenon, ignoring the fact that it was the direct consequence of existing policies. By persisting with the same strategies, the problem ceased to be episodic and became structural.
In the early 2000s, the European Union was finally forced to recognize that the wine crisis was not temporary. However, instead of removing production incentives and restoring the market’s adjustment function, it opted for a new form of intervention: subsidizing the voluntary uprooting of vineyards. The decision to destroy productive capacity ceased to be economic and became administrative, decreed from the European political center, with profound effects across several countries.
This model, presented as temporary, set a dangerous precedent. Rather than allowing less viable producers to exit the market through prices and economic choice, the state began paying for withdrawal, subsidizing the costs of adjustment and normalizing the idea that the correction of public policy errors should be financed with more public money.
This policy did not solve the underlying problem. It merely reduced cultivated area temporarily, while leaving intact the regulatory architecture which had created the initial distortion. The sector became trapped in a cycle of incentivized expansion, predictable crisis, and administrative correction.
It is within this framework that the Wine Package emerges as the European Union’s latest set of measures for the wine sector. The package relies on an administratively planned reduction of supply through financial incentives for vineyard uprooting, complemented by regulatory adjustments, temporary support measures, and crisis management instruments. Instead of allowing the market to adjust to declining consumption, Brussels once again opts for the destruction of productive capacity as a policy tool. Although the package includes support measures and environmental framing, its central axis remains the administrative reduction of supply.
The impact of these decisions is not marginal. The European wine sector represents a significant share of the European Union’s economy, sustaining approximately 2.9 million direct and indirect jobs and contributing more than €130 billion to EU GDP.
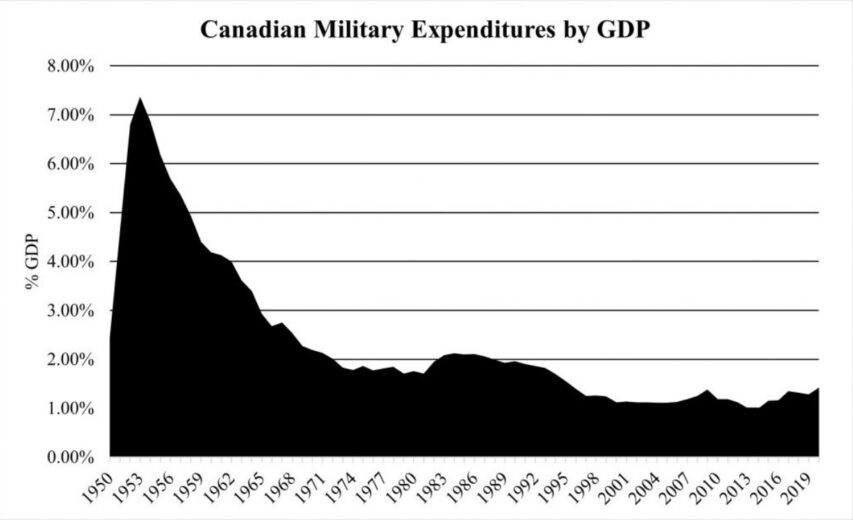
QotD: Canada and its military – a history of neglect
Canada’s military was not always a punchline. At the end of World War II Canada had the world’s third-largest navy, complete with our own aircraft carrier, and over a million men under arms. Since then military spending has steadily declined, from a high of around 7% of GDP in the early 50s to around 1% today, where it’s hovered since the end of the Cold War.
Canada is protected to its east and west by the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, both of which are patrolled by the powerful navy of the friendly superpower to the south, the only country with which Canada shares a land border, which we have long bragged is the longest undefended frontier in the world. Our only other neighbouring country is Russia, and while Russia is a decidedly unfriendly superpower, in practice Canada’s populated south is separated from the Russian Federation by thousands of kilometres of howling arctic wastes which provide an even better natural defence than the oceans.
Cozy and secure in our continental cocoon, Canada has allowed its military to atrophy into a vestigial appendage akin to the stubby wings of flightless birds on isolated Pacific islands, useful only for emotive displays. So far as the Liberal Party is concerned, “emotive display” is, indeed, the only real purpose of the military. Ever since Lester B. Pearson1 was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for inventing the concept of “peacekeeping” to de-escalate the Suez Crisis (thereby helping to drive the final nail into the coffin of the British Empire), the Canadian military’s primary purpose has been to conduct third-world relief missions. Peacekeeping carries no particular benefit to Canada, but it is of great benefit to politicians, who get to preen in front of the camera as important humanitarian statesmen. The purpose of the Canadian military isn’t to win wars, to defend the country, or to conquer distant lands: it’s to make Liberal Party politicians feel good about themselves.
When the CAF fails to live up to its making-liberals-feel-good mission, Canada’s liberal establishment reacts like a frustrated child taking out her vindictive cruelty by throwing her dolls against the wall. The Somalia Affair is probably the best example of this dynamic. The Canadian Airborne Regiment, an elite commando unit whose core competencies were jumping out of airplanes to break things and kill people, was deployed in Somalia with the contradictory goal of keeping a non-existent peace, a mission to which they were singularly ill-suited. Somalis being Somalis, the Airborne base was immediately subjected to continuous infiltration and theft. A handful of the violent lunatics in the regiment reacted by capturing thieves and torturing them to death, which they had the poor sense to document with photographic evidence; later, photographs emerged of one of the airborne troopers wearing a moustache man t-shirt while raising his arm at a prohibited angle, which wasn’t criminal exactly but was very bad PR. Instead of punishing the guilty troops individually, for instance with field courts martial followed by summary hanging, the Liberal Party flew into a rage and disbanded the regiment for having committed the unforgivable sin of making them look bad. This dragged on in the media for years, sullying the honour of not only the Airborne Regiment but of the entire military. The Somalia affair unfolded over thirty years ago, but the liberal establishment holds it over the heads of the CAF to this day.
In addition to providing politicians with regular hits of the pleasantly addictive buzz of telescopic philanthropy, peacekeeping also has the great advantage of being cheap. Not only does peacekeeping not require all that many troops, you don’t even need tanks, fighter jets, destroyers, or aircraft carriers to distribute aid packages to refugees. Therefore the Canadian military essentially does not have these things. The CAF has a grand total of 112 forty-six-year-old Leopard II main battle tanks (of which roughly half are down for maintenance at any given time), a whole 138 forty-two-year-old CF-18 Hornet fighter jets (of which 89 are operational), twelve Halifax class frigates (of which about half are in drydock at any given time), an intimidating four Victoria class diesel-electric submarines (which are forty-five years old, and all but one of which is out of commission), and zero bombers, zero attack helicopters, zero destroyers, zero troop transports, zero battleships, and zero aircraft carriers. The pathetic size of the Royal Canadian Navy is particularly embarrassing given that Canada has the longest coastline in the world, at 243,042 kilometres, essentially all of which Ottawa expects Washington to defend on its behalf. Airlift capacity is so limited that the CAF essentially cannot deploy overseas without allied logistical assistance.
By contrast with its decrepit armaments, the CAF has 145 generals: it has more generals than it does tanks. This top-heavy general staff is only about a third the size of the US military’s, despite the American military being 20x larger by personnel and 32x larger by budget.
From the perspective of the Laurentian elite, a weak military is actually a political advantage. If Canada effectively does not have the ability to project military force, Ottawa can simply plead lack of capacity when America asks for assistance. It enables Canada to duck out of involvement in America’s various imperial wars, letting Washington shoulder the burden of the Pax Americana while chirping from the sidelines about how the big bad bible-thumbing American bully is so mean, and how peaceful, ethical, liberal, humanitarian Canada is so nice because Canada spends its money on healthcare instead of bombs. It isn’t a morally superior position, of course: it’s simply shameless dependence and shameful parasitism.
John Carter, “The Canadian Political Class is Ideologically Incapable of Rebuilding the Military”, Postcards From Barsoom, 2025-11-13.
- The man who, as prime minister, replaced the red ensign’s ethnic heraldry with the maple leaf’s corporate logo.
February 13, 2026
The selective ability to override any non-criminal law is a “useful tool to have”
The Canadian government is trying to get even more power to exempt their friends and favoured companies from needing to comply with any federal laws or regulations through a provision in an omnibus bill before Parliament. It may sound like a tool to dispense privileges and favours to politically well-connected individuals and organizations, but that’s only because that’s exactly what it does:
In a little-noticed provision included in the government’s latest omnibus bill, Carney government ministers would be able to override almost any non-criminal law they wanted, and provide special treatment to any person or corporation who requested it.
When pressed about the clause in a House of Commons committee this week, Minister of Canadian Identity Marc Miller called it a “useful tool to have”.
The provision is included in C-15, the 634-page “budget implementation” bill currently before the House of Commons.
Among its hundreds of amendments and orders are new powers allowing ministers to hand out special exemptions from any “Act of Parliament” under their purview.
This means that the minister of health would be able to issue exemptions from the Canada Health Act, the Indigenous services minister could oversee exemptions from the Indian Act and the minister of finance would be able to override the Income Tax Act.
Furthermore, ministers could hand out these exemptions to any “entity” they wanted. Under federal guidelines, an “entity” can mean everything from an individual to “a corporation” to an “unincorporated organization”.
You don’t need to be a conspiracy theorist to see all kinds of ways that this provision could be abused to circumvent the normal rules everyone else is bound by. On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, Wall Street Apes reacts:
I can’t even believe this is real
Canada Minister Marc Miller is questioned about their new bill under the Liberal government led by Prime Minister Mark Carney that would EXEMPT ALL MINISTERS FROM ALL LAWS
Yes, you heard that correctly
Hidden in the omnibus budget implementation bill, section 208 or clause 12 amends the Red Tape Reduction Act to grant federal cabinet ministers broad discretionary powers
Ministers would be able to temporarily exempt any individual, company, organization, or entity from the application of almost any provision of any federal law (or regulations made under those laws) that the minister is responsible for administering or enforcing, with the sole exception of the Criminal Code
They can themselves, and deem anyone they choose exempt from ALL laws. The only exception is the criminal code
He says you can trust them because “Canadians expect us to act reasonably”
(Holy cr*p)
On her Substack, Melanie in Saskatchewan explains why the rule of law is not optional in Canada:
So let us play this forward. A Beijing connected firm establishes operations in Canada. It hires lobbyists. It meets with the appropriate minister. It argues that certain federal regulations are barriers to innovation or economic growth. Under Bill C 15, that minister could grant a temporary exemption. The company does not need to change Canadian law. It does not need to persuade Parliament. It only needs to persuade the right minister.
That is what should alarm Canadians.
When laws become selectively waivable by political discretion, they cease to be stable guardrails and become negotiable privileges. And power, once granted, is never granted because someone intends to leave it unused.
You tell us this is about economic growth amid trade tensions. Yet Canadians were told you were elected to steady the ship on trade and tariffs, to negotiate strength abroad, to stabilize economic uncertainty. Instead, trade tensions persist, tariffs remain contentious, and what advances efficiently is domestic policy architecture that conveniently aligns with the climate finance world you know so well.
Brookfield’s climate investment arm stands to benefit enormously from aggressive climate frameworks. You remain heavily invested. The potential for substantial personal financial gain is not speculation. It is disclosed reality.
You were not elected to refashion Canada into a climate investment thesis calibrated to suit global asset management portfolios. You were elected to manage trade pressures and protect Canadian economic interests.
This exemption clause is not a minor technical detail. It is a structural shift in how power is exercised. If it is so defensible, extract it from the omnibus bill and introduce it as standalone legislation. Let it be debated openly. Let Canadians see it clearly.
Implement a robust foreign agent registry immediately. Answer why a government that acknowledges compromised parliamentarians believes this is the moment to expand ministerial discretion over who must follow federal law.
The rule of law is not optional.
And Canadians did not vote for a system where compliance is mandatory for citizens but negotiable for the well connected.
February 10, 2026
Trump’s bullying gets NATO members to get serious about defence
Living in a country that’s starting to feel a bit like little Melos facing the might of Athens in its prime, I can assure you that, for all of his other questionable moves, Trump has succeeded in forcing the NATO allies to address their freeloading on defence where every president before him had come up empty:
There are downsides to insulting and threatening friends and acting like a Mafia don slapping around his goons. You risk turning them against you, for one thing. But if those friends have been freeloading off you for years, well, there are some upsides, too. We’re seeing that as President Donald Trump’s rough treatment of our European allies has driven them to huffily make steps to actually defend themselves rather than continue to rely on the American defense umbrella.
There’s No Incentive Like a Kick in the Rear
For years, Trump has pointed out that the prosperous nations of Western Europe have long free-loaded off of American military might to maintain their security—especially against Russia’s threat from the East. He claims that, during his first term, he told NATO leaders if they didn’t meet the alliance target of 2 percent of GDP on military spending per member, they’d be on their own. According to him:
One of the presidents of a big country stood up, said, “Well, sir, if we don’t pay and we’re attacked by Russia, will you protect us?” I said, “You didn’t pay. You’re delinquent?” He said, “Yes, let’s say that happened.”
“No, I would not protect you. In fact, I would encourage them to do whatever the hell they want. You got to pay. You got to pay your bills.”
Those were rough words for supposed allies. They didn’t stand alone. Since then, Trump has also threatened to acquire Greenland over the protests of Europeans, Denmark (which governs the island territory), and Greenlanders themselves. That’s on top of his trade war antics which imperil the commerce that most effectively binds people together in peaceful relations. Such bullying has an impact.
“European governments and corporations are racing to reduce their exposure to U.S. technology, military hardware and energy resources as transatlantic relations sour,” Politico‘s Nicholas Vinocur and Zoya Sheftalovich wrote last week. “At a weekend retreat in Zagreb, Croatia, conservative European leaders including [German Chancellor Friedrich] Merz said it was time for the bloc to beef up its homegrown mutual-defense clause, which binds EU countries to an agreement to defend any EU country that comes under attack.”
“Military spending across the European Union is ramping up in what observers have noted is a significant and ‘extraordinary’ pivot from the comparatively placid postwar decades,” Northeastern University’s Tanner Stening observed last summer. “As part of the ReArm Europe plan, EU member states hope to mobilize up to 800 billion euros. In June, NATO leaders agreed to increase defense spending up to 5% of each country’s gross domestic product by 2035.”
Commenting on the Trump administration, eugyppius clearly understands something that a lot of Trump’s critics (and many fans) don’t seem to comprehend:
An unstudied impression: Donald Trump is like a shark, in that he must always swim forward or risk suffocation. He, his administration and the media ecosystem that has grown up around Trump’s political persona depends upon action and controversy. In fallow news cycles, Trump steadily loses the initiative and two things happen: First, the media establishment and the leftist activist machine begin gathering their own critical momentum. Second, the vast MAGA-adjacent social media sphere must turn to other controversies to keep the clicks and the ad revenue flowing. Both of these work against the forty-seventh president and his purposes.
Since Trump’s initial barrage of executive orders has subsided, the media cycle has therefore lurched from one moment of hysteria and excitement to the next. Each new controversy totally eclipses the last. Hardly anybody remembers or talks about Nicolás Maduro any longer; the twin Minneapolis ICE shootings and associated protests, too, have faded. What were hailed as pivotal events which would finally discredit Trump’s programme this time look, in retrospect, like passing trivialities – not necessarily because they didn’t matter, but because sustained attention in this crazy messaging environment is impossible.
And on Trump’s pimp-handed dealings with the NATO allies:
Trump and NATO: Much of Trump’s MAGA base remains firmly isolationist and demands that the United States abandon the NATO alliance. Trump himself knows this and he has periodically questioned the utility of NATO. Formally, however, Trump’s administration stands behind the alliance, as anyone can see from reading the 2026 National Defense Strategy and the 2025 National Security Strategy. Yes, Trump wants European countries to increase defence spending. Yes, he still hopes to complete a strategic pivot away from Europe towards China. And yes, in the longer term, he probably nurtures ambitions of reducing the importance of NATO in favour of separate bilateral agreements with various European states. Such arrangements would also provide a lever for present and future administrations to disrupt the various policies and initiatives of the European Union, which Trump clearly despises and which at least as presently constructed amounts to a suicide pact for all of us on the Continent. These populist pressures and future ambitions, together with a general distrust and legitimate scorn for Eurocrat elites, seem to be why NATO periodically fades from Trump’s favour, although never for very long. All of this is to say that I really don’t think Trump’s January bluster was a mere Art-of-the-Deal negotiating tactic, but a reflection of real tensions and contradictions within Trumpism.
Trump and Europe: Here again, we see two competing tendencies. Generally, the Trump administration has followed a sly strategy of pursuing ties with the more or less aligned and presently ascendant populist-right movements of Europe. The Trump administration has also defended our rights to free speech, particularly on social media; relentlessly attacked our insane energy transition; and criticised our elites for their failure (or refusal) to stop mass migration. The purpose of these efforts is to isolate the Eurotards by fertilising the hostile populism that is growing ominously just beneath their double chins. If you are wondering why Trump bothers with this, I refer you to my previous paragraph: Sympathetic governments in key European states, joined to the United States, would be a means of sidelining the European Union and remaking Atlanticism in Trump’s image.
Exactly how to help the populist right into power is a much harder nut to crack. Expressing overt support for parties like Alternative für Deutschland can hurt more than it helps, and the Americans don’t have more direct means of influencing domestic politics over here. At the very least, this a long-term project requiring tactics and strategies we have yet to explore, and probably some institutions we have yet to create.
Update, 11 February: Welcome, Instapundit readers! Have a look around at some of my other posts you may find of interest. I send out a daily summary of posts here through my Substack – https://substack.com/@nicholasrusson that you can subscribe to if you’d like to be informed of new posts in the future.
Heightening tensions in the Indian Ocean
On Substack, Fergus Mason updates us on what’s happening around the UK/US military base on Diego Garcia in the Chagos Islands in the Indian Ocean:
One of the great mysteries of Keir Starmer’s government is why he’s so determined to give the Chagos Islands to Mauritius, which is 1,200 miles away and has never owned them. Even now, as he desperately fights for his political survival, Starmer is pushing ahead with plans to give away the strategic archipelago then pay tens of billions of pounds to lease back one of the islands. It’s an odd thing to be so focused on — but whether his compulsion to surrender the islands is driven by corruption or naivete, it’s sending out signals of weakness. And those signals are being noticed.
The Maldives Makes A Grab
Last Thursday the Republic of Maldives announced that it had rejected the UN International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea’s ruling on its maritime boundaries, and sent an armed boat to carry out a “special surveillance operation” in the northern part of the Chagos island’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). The Chagos EEZ is claimed by Mauritius, but of course actually belongs to Britain until Starmer’s surrender deal is approved by Parliament. However, the Maldivian government has now decided to make its own claim on the area — and it’s very publicly doing something about it. The “coast guard vessel” CGS Dharumavantha — a former Turkish Navy fast attack craft — is now operating in the area, along with drones from the Maldives National Defence Force Air Corps.
Of course, the Maldives has no real claim to the Chagos islands or any part of their waters. The country — a tiny group of islands southwest of Sri Lanka, with a land area of just 115 square miles — was a British crown colony from 1796 to 1953, and a British protectorate until 1965. Like Mauritius, it has never owned the Chagos Islands. However, it’s just 300 miles away from them, much closer than Mauritius. It appears that its leader, President Mohamed Muizzi, has decided that if the key British territory is up for grabs the Maldives should be the ones to grab it. It’s true the Maldives doesn’t have much of a navy, but then Mauritius doesn’t have much of a navy either and is a lot further away. If the Maldives can seize control over part of the extremely valuable Chagos Marine Protected Area (MPA), and even possibly some of the northern islands, there isn’t a lot Mauritius can do about it.
Why would the Maldives be so keen to seize part of the Chagos EEZ? That one’s simple. Under British protection, the Chagos MPA (which is the largest marine nature reserve in the entire world) has been officially off limits to commercial fishing since 2010 but, in practice, has barely been fished at all since 1968. This makes it a unique and potentially lucrative resource in the Indian Ocean region, which has seen its ecosystems devastated by destructive fishing methods. The wealth of the MPA is the main reason Mauritius wants the Chagos islands. Its own coastal waters have been blighted by overfishing, including the destruction of coral reefs by explosives and bleach injection, and now it wants to plunder the MPA. The Maldives is also busily engaged in destroying its own fish stocks (fishing is the country’s largest industry and employs half the population) and is desperate for new waters to pillage. They don’t just want access for their own boats, either. Like Mauritius, the Maldives under Muizzi’s rule is an increasingly close ally of China.
The Scourge Of The Seas
China has the world’s largest fishing fleet, and it’s not even close. Over 44% of all commercial fishing is carried out by Chinese boats — and they’re notorious for flouting international law. Chinese boats regularly change their names and disable their satellite tracking systems to conceal their identity, then fish illegally in other countries’ waters. They violate quotas, catch protected species and strip whole swathes of ocean clean of any life much larger than plankton with massive, indiscriminate drift nets. Chinese fishing boats have also been implicated in people trafficking, drug smuggling and acting as spying and covert action platforms for the Chinese navy.
If either Mauritius or the Maldives gain control of the Chagos MPA it’s a certainty they will immediately give Chinese boats access, and this priceless nature reserve will rapidly be trawled and drift-netted into a barren, lifeless wasteland. From China’s point of view, of course, it doesn’t matter which of their lackeys takes over the Chagos islands as long as one of them does, so don’t expect them to step in to help Mauritius. They don’t care who they get the fishing rights from.
February 9, 2026
Jamil Jivani on his trip to Washington DC
If you depend on the CBC, the Toronto Star or other legacy Canadian media, if you heard anything at all about Bowmanville-Oshawa North MP Jamil Jivani’s visit to key American leaders in Washington DC, you probably got the story framed as Liberals tut-tutting and disapproving of Jivani, his initiative to make the trip, and how he should leave everything to the government. If nothing else, it further proved that Prime Minister Carney doesn’t actually want better relations with the US, as his entire campaign was based on opposition to Trump and its success in riling up Canadian boomers with the moronic eLbOwS uP nonsense.
In the National Post Jivani discusses the trip and what he’s learned from it:
It was a whirlwind of a trip, full of excellent conversations. I had meetings with the White House and State Department, including conversations with President Donald Trump, Vice-President JD Vance, and Secretary of State Marco Rubio. Senators from Montana, Ohio, and Wisconsin, as well as the United States Trade Representative, each sat down with me to share their priorities. Businesses and industries employing thousands of Canadians shared their insights with me on where Canada-U.S. trade fits into their vision for economic growth.
Doors were open for dialogue about how Canada and the U.S. can work together at a time when pessimism gets most of the media attention. Certainly, my 15-year friendship with the vice-president played a key role in opening those doors. But what I found across the board was optimism about how we can move trade negotiations forward. I was particularly happy to hear key insights on how we can make progress on specific sectoral priorities, and the importance of strategic diplomacy. I offered my perspective on why CUSMA is so important to communities like mine in Bowmanville—Oshawa North, and I expressed my hope that CUSMA will continue to ensure Canada and the U.S. both benefit from a special economic and security relationship.
There is only so much I can share without first having the chance to speak with Prime Minister Mark Carney and Minister Dominic LeBlanc. Out of respect for their unique responsibilities in negotiating trade with the United States, it’s important that I debrief them before saying too much publicly and see how we can work together moving forward as Conservatives and Liberals.
However, I do want to point out a key observation related to the need for strategic diplomacy. Mexico — the third partner in our trilateral trade agreement with the U.S. — is further ahead in its engagement with the U.S. than Canada is. On Jan. 28, 2026, Mexico and the U.S. announced formal talks on CUSMA reforms. A week later, Mexico and the U.S. announced a joint action plan for critical minerals. Neither of these announcements included Canada.
Observers of this news would be right to worry that the current Canadian government may be making similar mistakes as were made under Prime Minister Justin Trudeau during the 2017 CUSMA negotiations. At that time, Mexico advanced its negotiations with the U.S. while Canada was largely left out of the process. It was only at the last minute, when a bilateral agreement between Mexico and the US was a real possibility, that Canada was included and our unique trilateral arrangement continued.
It would be a mistake to relive 2017 all over again, if for no other reason than Canadian workers and businesses deserve to have full representation in a process that has such a significant impact on our economy. The workers at the GM plant in Oshawa deserve to know that their government did everything possible to protect their jobs and encourage investment in their industry. All Canadians deserve to know that their elected officials are making the best effort possible to advance our national interests.
Full disclosure: Jamil Jivani is my Member of Parliament, and I fully support his decision to go and I hope that it actually does help make for improved trade relations between Canada and the United States. Bitterness and uncertainty only benefit the Liberal Party and Mark Carney, not ordinary Canadians. Attacking and criticizing Donald Trump plays well in our deranged and sycophantic media, but it makes Trump less willing to deal fairly with Canada on trade or other issues of critical importance to both nations.
February 7, 2026
Liberal horror at a Conservative MP going to Washington to talk trade
Jamil Jivani, Conservative Member of Parliament for the riding of Bowmanville-Oshawa North, is being called all sorts of names by Liberals and their creatures in the mainstream media for his temerity in actually going to Washington DC to try to encourage trade talks between Canada and the United States:
Mark Carney, I want to speak to you directly for a moment, because this whole episode has your fingerprints all over it.
You have spent months telling Canadians we live in a more dangerous and divided world. You have warned us that this is not a transition but a rupture. You have explained, repeatedly, that Canada must adapt, that middle powers must act differently, that old assumptions no longer apply. It is very serious language. Big language. The kind you deliver slowly, as if the room should be taking notes.
So imagine my surprise when a Conservative MP behaved exactly the way your speeches suggest Canada must behave, and Ottawa promptly short-circuited.
Jamil Jivani went to Washington to try to open a door you and your government have been telling Canadians does not exist. He used a personal relationship with JD Vance, not for applause, not for theatrics, but for the radical act of actually talking to someone who matters. And suddenly, Mark, this was not adaptive diplomacy. It was alarming. Inappropriate. A problem.
This is the part where your credibility starts to wobble.
Because let’s be honest. When people asked you about engaging Donald Trump directly, your response boiled down to “Who cares?” Either because it bored you or because you preferred not to acknowledge that door at all. So when a Conservative tries anyway, the issue is not that the door was touched. It is that someone proved it was never locked in the first place.
Jivani did not freelance. He did not sneak off. He offered this connection to your government first. Openly. Calmly. And it was dismissed. Brushed aside. Not interested. And when he went anyway, your side did not react with curiosity or even grudging respect. It reacted with outrage.
The kind of outrage you see when someone fixes a problem you have been holding meetings about for weeks without ever intending to solve it. Like an office that has spent months discussing a flickering lightbulb, only to panic when someone quietly screws in a new one and sits back down before the chair can call the meeting to order.
And then, almost on cue, came the shiny object.
I am not accusing you of anything, Mark. I am simply asking whether it is coincidence that the outrage over Jivani going to Washington was followed almost immediately by a dramatic announcement about dropping the EV mandate. Was that timing accidental, or was it a convenient way to make Canadians look over there while a Conservative threatened to come back with something measurable. I am not saying it was a distraction. I am just saying the choreography was impressive.
Now, let’s talk about cooperation, because you and your allies invoke that word constantly.
When generalized liberals complain that Conservatives will not “play ball”, what they seem to mean is that Conservatives are not being obedient. Cooperation, in practice, appears to mean standing aside politely while you govern unchallenged. It does not mean Conservatives doing something useful that might work. Especially not if it works where you did not.
And this is where your rhetoric corners you.