Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Jul 2, 2024Deep dish cheese pizza with a bready crust
City/Region: Chicago
Time Period: 1945 | 1947The unsung hero of deep dish pizza is a woman named Alice Mae Redmond, who was the head chef at famous pizzerias like Pizzeria Uno and Gino’s. It seems like wherever she went, that was the best pizza place in town. She’s also the one who changed deep dish pizza crust from the bready version in this recipe to a butterier, more biscuit-like version that is found in modern deep dish.
This crust is still delicious, and the sauce is super flavorful. Be sure to cook the sauce down enough so that it’s nice and thick (mine was a bit too watery for my taste). In the 1940s, you could get cheese OR anchovies OR sausage, but not any of them together. I made a cheese pizza with my preferred ratio of about 50/50 cheese to sauce, but feel free to change things up however you like. You could even add more than one topping, though it won’t be quite as historically accurate.
(more…)
October 20, 2024
The True History of Deep Dish Pizza
October 11, 2024
QotD: Fascists are inherently bad at war
For this week’s musing, I wanted to take the opportunity to expand a bit on a topic that I raised on Twitter which draw a fair bit of commentary: that fascists and fascist governments, despite their positioning are generally bad at war. And let me note at the outset, I am using fascist fairly narrowly – I generally follow Umberto Eco’s definition (from “Ur Fascism” (1995)). Consequently, not all authoritarian or even right-authoritarian governments are fascist (but many are). Fascist has to mean something more specific than “people I disagree with” to be a useful term (mostly, of course, useful as a warning).
First, I want to explain why I think this is a point worth making. For the most part, when we critique fascism (and other authoritarian ideologies), we focus on the inability of these ideologies to deliver on the things we – the (I hope) non-fascists – value, like liberty, prosperity, stability and peace. The problem is that the folks who might be beguiled by authoritarian ideologies are at risk precisely because they do not value those things – or at least, do not realize how much they value those things and won’t until they are gone. That is, of course, its own moral failing, but society as a whole benefits from having fewer fascists, so the exercise of deflating the appeal of fascism retains value for our sake, rather than for the sake of the would-be fascists (though they benefit as well, as it is, in fact, bad for you to be a fascist).
But war, war is something fascists value intensely because the beating heart of fascist ideology is a desire to prove heroic masculinity in the crucible of violent conflict (arising out of deep insecurity, generally). Or as Eco puts it, “For Ur-Fascism there is no struggle for life, but, rather, life is lived for struggle … life is permanent warfare” and as a result, “everyone is educated to become a hero“. Being good at war is fundamentally central to fascism in nearly all of its forms – indeed, I’d argue nothing is so central. Consequently, there is real value in showing that fascism is, in fact, bad at war, which it is.
Now how do we assess if a state is “good” at war? The great temptation here is to look at inputs: who has the best equipment, the “best” soldiers (good luck assessing that), the most “strategic geniuses” and so on. But war is not a baseball game. No one cares about your RBI or On-Base percentage. If a country’s soldiers fight marvelously in a way that guarantees the destruction of their state and the total annihilation of their people, no one will sing their praises – indeed, no one will be left alive to do so.
Instead, war is an activity judged purely on outcomes, by which we mean strategic outcomes. Being “good at war” means securing desired strategic outcomes or at least avoiding undesirable ones. There is, after all, something to be said for a country which manages to salvage a draw from a disadvantageous war (especially one it did not start) rather than total defeat, just as much as a country that conquers. Meanwhile, failure in wars of choice – that is, wars a state starts which it could have equally chosen not to start – are more damning than failures in wars of necessity. And the most fundamental strategic objective of every state or polity is to survive, so the failure to ensure that basic outcome is a severe failure indeed.
Judged by that metric, fascist governments are terrible at war. There haven’t been all that many fascist governments, historically speaking and a shocking percentage of them started wars of choice which resulted in the absolute destruction of their regime and state, the worst possible strategic outcome. Most long-standing states have been to war many times, winning sometimes and losing sometimes, but generally able to preserve the existence of their state even in defeat. At this basic task, however, fascist states usually fail.
The rejoinder to this is to argue that, “well, yes, but they were outnumbered, they were outproduced, they were ganged up on” – in the most absurd example, folks quite literally argued that the Nazis at least had a positive k:d (kill-to-death ratio) like this was a game of Call of Duty. But war is not a game – no one cares what your KDA is if you lose and your state is extinguished. All that matters is strategic outcomes: war is fought for no other purpose because war is an extension of policy (drink!). Creating situations – and fascist governments regularly created such situations. Starting a war in which you will be outnumbered, ganged up on, outproduced and then smashed flat: that is being bad at war.
Countries, governments and ideologies which are good at war do not voluntarily start unwinnable wars.
So how do fascist governments do at war? Terribly. The two most clear-cut examples of fascist governments, the ones most everyone agrees on, are of course Mussolini’s fascist Italy and Nazi Germany. Fascist Italy started a number of colonial wars, most notably the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, which it won, but at ruinous cost, leading it to fall into a decidedly junior position behind Germany. Mussolini then opted by choice to join WWII, leading to the destruction of his regime, his state, its monarchy and the loss of his life; he managed to destroy Italy in just 22 years. This is, by the standards of regimes, abjectly terrible.
Nazi Germany’s record manages to somehow be worse. Hitler comes to power in 1933, precipitates WWII (in Europe) in 1939 and leads his country to annihilation by 1945, just 12 years. In short, Nazi Germany fought one war, which it lost as thoroughly and completely as it is possible to lose; in a sense the Nazis are necessarily tied for the position of “worst regime at war in history” by virtue of having never won a war, nor survived a war, nor avoided a war. Hitler’s decision, while fighting a great power with nearly as large a resource base as his own (Britain) to voluntarily declare war on not one (USSR) but two (USA) much larger and in the event stronger powers is an act of staggeringly bad strategic mismanagement. The Nazis also mismanaged their war economy, designed finicky, bespoke equipment ill-suited for the war they were waging and ran down their armies so hard that they effectively demodernized them inside of Russia. It is absolutely the case that the liberal democracies were unprepared for 1940, but it is also the case that Hitler inflicted upon his own people – not including his many, horrible domestic crimes – far more damage than he meted out even to conquered France.
Beyond these two, the next most “clearly fascist” government is generally Francisco Franco’s Spain – a clearly right-authoritarian regime, but there is some argument as to if we should understand them as fascist. Francoist Spain may have one of the best war records of any fascist state, on account of generally avoiding foreign wars: the Falangists win the Spanish Civil War, win a military victory in a small war against Morocco in 1957-8 (started by Moroccan insurgents) which nevertheless sees Spanish territory shrink (so a military victory but a strategic defeat), rather than expand, and then steadily relinquish most of their remaining imperial holdings. It turns out that the best “good at war” fascist state is the one that avoids starting wars and so limits the wars it can possibly lose.
Broader definitions of fascism than this will scoop up other right-authoritarian governments (and start no end of arguments) but the candidates for fascist or near-fascist regimes that have been militarily successful are few. Salazar (Portugal) avoided aggressive wars but his government lost its wars to retain a hold on Portugal’s overseas empire. Imperial Japan’s ideology has its own features and so may not be classified as fascist, but hardly helps the war record if included. Perón (Argentina) is sometimes described as near-fascist, but also avoided foreign wars. I’ve seen the Baathist regimes (Assad’s Syria and Hussein’s Iraq) described as effectively fascist with cosmetic socialist trappings and the military record there is awful: Saddam Hussein’s Iraq started a war of choice with Iran where it barely managed to salvage a brutal draw, before getting blown out twice by the United States (the first time as a result of a war of choice, invading Kuwait!), with the second instance causing the end of the regime. Syria, of course, lost a war of choice against Israel in 1967, then was crushed by Israel again in another war of choice in 1973, then found itself unable to control even its own country during the Syrian Civil War (2011-present), with significant parts of Syria still outside of regime control as of early 2024.
And of course there are those who would argue that Putin’s Russia today is effectively fascist (“Rashist”) and one can hardly be impressed by the Russian army managing – barely, at times – to hold its own in another war of choice against a country a fourth its size in population, with a tenth of the economy which was itself not well prepared for a war that Russia had spent a decade rearming and planning for. Russia may yet salvage some sort of ugly draw out of this war – more a result of western, especially American, political dysfunction than Russian military effectiveness – but the original strategic objectives of effectively conquering Ukraine seem profoundly out of reach while the damage to Russia’s military and broader strategic interests is considerable.
I imagine I am missing other near-fascist regimes, but as far as I can tell, the closest a fascist regime gets to being effective at achieving desired strategic outcomes in non-civil wars is the time Italy defeated Ethiopia but at such great cost that in the short-term they could no longer stop Hitler’s Anschluss of Austria and in the long-term effectively became a vassal state of Hitler’s Germany. Instead, the more standard pattern is that fascist or near-fascist regimes regularly start wars of choice which they then lose catastrophically. That is about as bad at war as one can be.
We miss this fact precisely because fascism prioritizes so heavily all of the signifiers of military strength, the pageantry rather than the reality and that pageantry beguiles people. Because being good at war is so central to fascist ideology, fascist governments lie about, set up grand parades of their armies, create propaganda videos about how amazing their armies are. Meanwhile other kinds of governments – liberal democracies, but also traditional monarchies and oligarchies – are often less concerned with the appearance of military strength than the reality of it, and so are more willing to engage in potentially embarrassing self-study and soul-searching. Meanwhile, unencumbered by fascism’s nationalist or racist ideological blinders, they are also often better at making grounded strategic assessments of their power and ability to achieve objectives, while the fascists are so focused on projecting a sense of strength (to make up for their crippling insecurities).
The resulting poor military performance should not be a surprise. Fascist governments, as Eco notes, “are condemned to lose wars because they are constitutionally incapable of objectively evaluating the force of the enemy”. Fascism’s cult of machismo also tends to be a poor fit for modern, industrialized and mechanized war, while fascism’s disdain for the intellectual is a poor fit for sound strategic thinking. Put bluntly, fascism is a loser’s ideology, a smothering emotional safety blanket for deeply insecure and broken people (mostly men), which only makes their problems worse until it destroys them and everyone around them.
This is, however, not an invitation to complacency for liberal democracies which – contrary to fascism – have tended to be quite good at war (though that hardly means they always win). One thing the Second World War clearly demonstrated was that as militarily incompetent as they tend to be, fascist governments can defeat liberal democracies if the liberal democracies are unprepared and politically divided. The War in Ukraine may yet demonstrate the same thing, for Ukraine was unprepared in 2022 and Ukraine’s friends are sadly politically divided now. Instead, it should be a reminder that fascist and near-fascist regimes have a habit of launching stupid wars and so any free country with such a neighbor must be on doubly on guard.
But it should also be a reminder that, although fascists and near-fascists promise to restore manly, masculine military might, they have never, ever actually succeeded in doing that, instead racking up an embarrassing record of military disappointments (and terrible, horrible crimes, lest we forget). Fascism – and indeed, authoritarianisms of all kinds – are ideologies which fail to deliver the things a wise, sane people love – liberty, prosperity, stability and peace – but they also fail to deliver the things they promise.
These are loser ideologies. For losers. Like a drunk fumbling with a loaded pistol, they would be humiliatingly comical if they weren’t also dangerous. And they’re bad at war.
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday, February 23, 2024 (On the Military Failures of Fascism)”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2024-02-23.
September 30, 2024
Sulla, civil war, and dictatorship
Adrian Goldsworthy. Historian and Novelist
Published Jun 5, 2024The latest instalment of the Conquered and the Proud looks at the first few decades of the first century BC. We deal with the final days of Marius, the rise of Sulla, the escalating spiral of civil wars and massacres as Rome’s traditional political system starts breaking down.
Primary Sources – Plutarch, Marius, Sulla, Pompey, Crassus, Cicero and Caesar. Appian Civil Wars and Mithridatic Wars.
Secondary (a small selection) –
P. Brunt, Social Conflicts in the Roman Republic & The Fall of The Roman Republic
A. Keaveney, Sulla – the last Republican
R. Seager, Pompey the Great: A political Biography
August 17, 2024
Caesar Marches on Rome – Historia Civilis Reaction
Vlogging Through History
Published Apr 23, 2024See the original here –
• Caesar Marches on Rome (49 B.C.E.)
See “Caesar Crosses the Rubicon” here –
• Caesar Crosses the Rubicon – Historia…#history #reaction
August 13, 2024
The Original Secret History
Tom Ayling
Published Apr 28, 2024This is the story of Procopius’s Secret History Of Justinian – originally written around 550, but not published until 1623.
In this video we look at how Procopius wrote the text, how it survived, almost unknown, for 1,000 years, how it came to be published in the 1620s, and the extraordinary ramifications when it was.
00:00 Introduction
00:44 The Original Composition Of The Secret History
02:40 The Survival Of The Text In Greek Manuscripts
05:56 The Rediscovery And Publication Of The Secret History
08:23 Secret Histories Go ViralTo learn more about Secret Histories, sign up to receive my catalogue of rare books devoted to the subject – https://www.tomwayling.co.uk/register
I couldn’t have made this video without the help of two works in particular. The first is Brian Croke’s magisterial Procopius: From Manuscripts To Books: 1400-1850. The second is The Secret History In Literature, 1660-1820 which is edited by Rebecca Bullard and Rachel Carnell.
My name’s Tom and I’m an antiquarian bookseller – you can browse the books I have for sale on my website: https://www.tomwayling.co.uk/
July 23, 2024
Why Most “Ancient” Buildings are Fakes
toldinstone
Published Apr 12, 2024Almost every ancient monument has been at least partially reconstructed, for a wide range of reasons …
Chapters:
0:00 Introduction
1:06 The Forum and Colosseum
2:27 The Ara Pacis
3:24 Early restorations
4:37 Mondly
5:47 Roman forts and baths
6:42 Knossos
7:23 The Stoa of Attalus
8:59 The Acropolis
10:05 When to restore?
(more…)
June 23, 2024
The Original Chef Boyardee Spaghetti Dinner
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 13 Mar 2024Absolutely fantastic tomato and meat sauce served over spaghetti tossed with butter and parmesan
City/Region: Cleveland, Ohio
Time Period: 1930sChef Boyardee was not born in Cleveland (sorry, 30 Rock), but in Borganovo, just outside of Piacenza in Italy. And his name was not Hector Boyardee, but Ettore Boiardi (boy-AR-dee). He opened an Italian restaurant in Cleveland in 1924, where the food was so popular that he frequently sent patrons home with bottles of his spaghetti sauce.
We can’t know exactly what that original sauce was, but this is from a family recipe and is probably pretty close. And it’s phenomenal. It’s fairly simple, but so good. You get a lot of the fresh basil, and the creaminess from mixing the butter and parmesan directly with the pasta is delicious. I don’t often make dishes from the show again, but I can see myself making this any day of the week.
(more…)
June 18, 2024
QotD: The peoples incorporated or “allied” to Rome in the Republic’s Italian expansion
In one way, pre-Roman Italy was quite a lot like Greece: it consisted of a bunch of independent urban communities situated on the decent farming land (that is the lowlands), with a number of less-urban tribal polities stretching over the less-farming-friendly uplands. While pre-Roman urban communities weren’t exactly like the Greek polis, they were fairly similar. Greek colonization beginning in the eighth century added actual Greek poleis to the Italian mix and frankly they fit in just fine. On the flip side, there were the Samnites, a confederation of tribal communities with some smaller towns occupying mostly rough uplands not all that dissimilar to the Greek Aetolians, a confederation of tribal communities and smaller towns occupying mostly rough uplands.
In one very important way, pre-Roman Italy was very much not like Greece: whereas in Greece all of those communities shared a single language, religion and broad cultural context, Roman Italy was a much more culturally complex place. Consequently, as the Romans slowly absorbed pre-Roman Italy into the Roman Italy of the Republic, that meant managing the truly wild variety of different peoples in their alliance system. Let’s quickly go through them all, moving from North to South.
The Romans called the region south of the Alps but north of the Rubicon River Cisalpine Gaul and while we think of it as part of Italy, the Romans did not. That said, Gallic peoples had pushed into Italy before and a branch of the Senones occupied the lands between Ariminum and Ancona. Although Gallic peoples were always a factor in Italy, the Romans don’t seem to have incorporated their communities as socii; indeed the Romans were generally at their most ruthless when it came to interactions with Gallic peoples (despite the tendency to locate the “unassimilable” people on the Eastern edge of Rome’s empire, it was in fact the Gauls that the Romans most often considered in this way, though as we will see, wrongly so). That’s not to say that there was no cultural contact, of course; the Romans ended up adopting almost all of the Gallic military equipment set, for instance. In any event, it wouldn’t be until the late first century BCE that Cisalpine Gaul was merged into Italy proper, so we won’t deal too much with the Gauls just yet. I do want to note that, when we are thinking about the diversity of the place, even to speak of “the Gauls” is to be terribly reductive, as we are really thinking of at least half a dozen different Gallic peoples (Senones, Boii, Inubres, Lingones, etc) along with the Ligures and the Veneti, who may have been blends of Gallic and Italic peoples (though we are more poorly informed about both than we’d like).
Moving south then, we first meet the Etruscans, who we’ve already discussed, their communities – independent cities joined together in defensive confederations before being converted into allies of the Romans – clustered on north-western coast of Italy. They had a language entirely unrelated to Latin – or indeed, any other known language – and their own unique religion and culture. The Romans adopted some portions of that culture (in particular the religious practices) but the Etruscans remained distinct well into the first century. While a number of Etruscan communities backed the Samnites in the Third Samnite War (298-290 BC) culminating in the Battle of Sentinum (295) as a last-ditch effort to prevent Roman hegemony over the peninsula, the Etruscans subsequently remained quite loyal to Rome, holding with the Romans in both the Second Punic and Social Wars. It is important to keep in mind that while we tend to talk about “the Etruscans” (as the Romans sometimes do) they would have thought of themselves first through their civic identity, as Perusines, Clusians, Populinians and so on (much like their Greek contemporaries).
Moving further south, we have the peoples of the Apennines (the mountain range that cuts down the center of Italy). The people of the northern Apennines were the Umbri (that is, Umbrian speakers), though this linguistic classification hides further cultural and political differences. We’ve met the Sabines – one such group, but there were also the Volsci and Marsi (the latter particularly well known for being hard fighters as allies to Rome; Appian reports that the Marsi had a saying prior to the Social War, “No Triumph against the Marsi nor without the Marsi”). Further south along the Apennines were the Oscan speakers, most notably the Samnites (who resisted the Romans most strongly) but also the Lucanians and Paelignians (the latter also get a reputation for being hard fighters, particularly in Livy). The Umbrian and Oscan language families are related (though about as different from each other as Italian from Spanish; they and Latin are not generally mutually intelligible) and there does seem to have been some cultural commonality between these two large groups, but also a lot of differences. Their religion included a number of practices and gods unknown to the Romans, some later adopted (Oscan Flosa adapted as Latin Flora, goddess of flowers) and some not (e.g. the “Sacred Spring” rite, Strabo 5.4.12).
Also Oscan speakers, the Campanians settled in Campania (surprise!) at some early point (perhaps around 1000-900 BC) and by the fifth century were living in urban communities politically more similar to Latium and Etruria (or Greece, which will make sense in a moment) than their fellow Oscan speakers in the hills above, to the point that the Campanians turned to Rome to aid them against the also-Oscan-speaking Samnites. The leading city of the Campanians was Capua, but as Fronda (op. cit.) notes, they were meaningful divisions among them; Capua’s very prominence meant that many of the other Campanians were aligned against it, a division the Romans exploited.
The Oscans struggled for territory in Southern Italy with the Greeks – told you we’d get to them. The Greeks founded colonies along the southern part of Italy, expelling or merging with the local inhabitants beginning in the seventh century. These Greek colonies have distinctive material culture (though the Italic peoples around them often adopted elements of it they found useful), their own language (Greek), and their own religion. I want to stress here that Greek religion is not equivalent to Roman religion, to the point that the Romans are sticklers about which gods are worshipped with Roman rites and which are worshipped with the ritus graecus (“Greek rites”) which, while not a point-for-point reconstruction of Greek rituals, did involve different dress, different interpretations of omens, and so on.
All of these peoples (except the Gauls) ended up in Rome’s alliance system, fighting as socii in Rome’s wars. The point of all of this is that this wasn’t an alliance between, say, the Romans and the “Italians” with the latter being really quite a lot like the Romans except not being from Rome. Rather, Rome had constructed a hegemony (an “alliance” in name only, as I hope we’ve made clear) over (::deep breath::) Latins, Romans, Etruscans, Sabines, Volsci, Marsi, Lucanians, Paelignians, Samnites, Campanians, and Greeks, along with some people we didn’t mention (the Falisci, Picenes – North and South, Opici, Aequi, Hernici, Vestini, etc.). Many of these groups can be further broken down – the Samnites consisted of five different tribes in a confederation, for instance.
In short, Roman Italy under the Republic was preposterously multicultural (in the literal meaning of that word) … and it turns out that’s why they won.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Queen’s Latin or Who Were the Romans, Part II: Citizens and Allies”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-06-25.
June 11, 2024
EUquake 2024
Although the European elites have managed to move as much as they can out of the reach of democratic institutions, they still have to allow the illusion that the few things ordinary people can vote for still kinda, sorta matter. Ordinary people seem to have noticed this:
“I cannot act as if nothing has happened”, said a weary, dejected Emmanuel Macron, in an unplanned address to his nation last night. The French president, bruised by an unprecedented showing for the right-wing populist National Rally (RN) on Sunday’s European Parliament elections, immediately dissolved the French parliament and announced snap legislative elections. The first round will take place in just three weeks’ time.
When Macron was elected president in 2017, he promised the French people that they will “no longer have a single reason to vote for the extremes”. Pro-EU centrists hailed his apparent defeat of nationalist, populist forces. Seven years later, RN is on course to achieve its best-ever result in an EU election. Marine Le Pen’s party is projected to win double the vote share of the president’s liberal, centrist Renaissance group. Clearly, the French feel that they have more reasons than ever to revolt against the mainstream.
The French are not alone in this. The hard-right Alternative for Germany (AfD), despite two of its leading MEP candidates being dogged by major scandals, came second behind the centre-right CDU. Crucially, it beat all three of the parties in Germany’s governing coalition. The Social Democrats (SPD), led by chancellor Olaf Scholz, suffered its worst result of any nationwide election since the 1940s. According to one pollster, around a million people who supported the left-leaning parties in the “traffic light” coalition have since defected to the AfD. Pressure is now mounting on Scholz to call his own snap election. In Italy, meanwhile, Giorgia Meloni and her Brothers of Italy topped the European polls, exceeding the vote share that swept her into power in 2022’s national elections. Populist, right-wing and hard-right parties, therefore, came in first or second place in all three of the major EU nations.
Even Belgium, at the epicentre of the EU empire, has been struck by the populist earthquake. Prime minister Alexander de Croo announced his resignation last night as his party was beaten to below 10 per cent in Sunday’s federal parliamentary elections and to around five per cent in the European elections – squeezed by Flemish separatist parties. Hard-right parties also came first in Austria and second in the Netherlands.
While Macron has been forced to react to the scale of his defeat, acknowledging euphemistically that these elections were “not a good result for the parties that defend Europe”, others in the Brussels oligarchy have tried to bury their heads in the sand. On Sunday evening, European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen declared – delusionally – that “the centre is holding”.
She is right in one, very narrow, sense. The centre-left Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats (S&D), the centre-right European People’s Party (EPP) and the liberal Renew group have likely gained enough seats between them for business as usual to resume in the European Parliament. The two groupings to their right – the European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR) and Identity and Democracy (ID) – have not made enough gains, even when combined, to start throwing their weight around in Brussels. Von der Leyen’s own position as Commission president is likely secure, not least because her EPP is the single largest grouping in parliament. The new populist MEPs will likely be shut out of key decisions, including the vetting of new EU commissioners. The EU has never allowed the democratic wishes of the public to intrude on its affairs before, so it is unlikely to start now.
But Brussels cannot hide from reality forever. These elections clearly show that the EU and its boosters are failing to contain the public’s anger. European elites have pulled every trick in the book to try to put the brakes on the populist surge, seemingly to little avail.
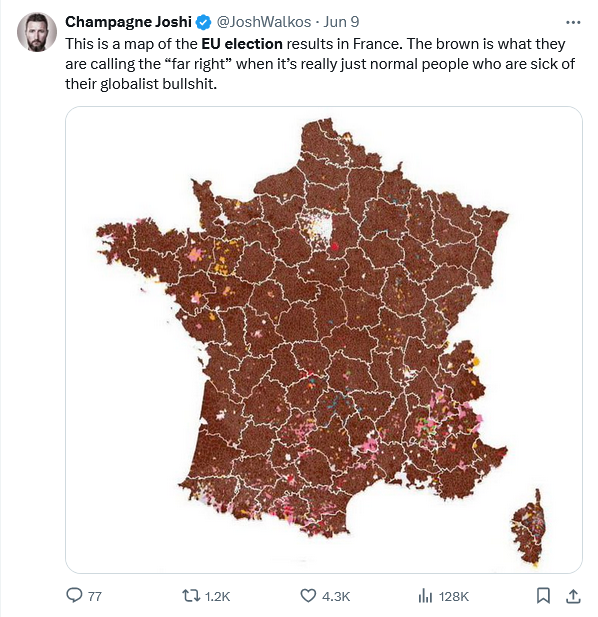
How bad was the rejection of the kakistocrats in France? This bad:
June 4, 2024
Snipers in World War 1
The Great War
Published Feb 9, 2024In fall 1914, the British and French armies on the First World War’s Western Front were wrestling with a problem: unseen German riflemen were picking off any man who showed himself above the trench. Something had to be done about it – and the result was the birth of the modern sniper.
(more…)
May 23, 2024
The Roman Colosseum: What It Was Like to Attend the Games
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Feb 13, 2024Like at sports events today, you could get snacks and souvenirs in and around the Colosseum in ancient Rome. There were sausages and pastries and small sweet snacks, like these dates. Not the same as modern hot dogs and soft serve, but kind of in the same spirit.
These dates are really, really good. You could grind the nuts into a fine paste, but I like the texture a lot when they’re left a little coarse. They’re very sweet from the dates and the honey, but the salt and pepper balance it so well (highly recommend the long pepper here). Definitely give these a try!
(more…)
May 13, 2024
Roman Legions – Sometimes found all at sea!
Drachinifel
Published Feb 2, 2024Today we take a quick look at some of the maritime highlights of the new special exhibition at the British Museum about the Roman Legions:
https://www.britishmuseum.org/exhibit…
(more…)
May 9, 2024
The Liri Valley: Canada’s Breakthrough to Rome
WW2TV
Published 8 May 2024The Liri Valley: Canada’s Breakthrough to Rome
With Mark Zuehlke
Part of our “Italy 1944 – Monte Cassino and Beyond” series
• Monte Cassino and BeyondFor the Allied armies fighting their way up the Italian boot in early 1944. Rome was the prize that could only be won through one of the greatest offensives of the war. The Liri Valley was a long, flat corridor through miles of rugged mountains. At one end stood the formidable Monte Cassino, at the other, Rome. In May 1944, I Canadian Corps drops up this valley toward the Italian capital, facing the infamous Hitler Line — a bastion of concrete bunkers fronted by wide swaths of tangled barbed wire, minefields, and “Tobruk” weapon pits. The ensuing battle resulted in Canada’s single bloodiest day of the Italian campaign. But the sacrifice of young Canadians during the twenty-four days of relentless combat it took to clear the valley paved the way for the Allies to take Rome.
Mark Zuehlke is an award-winning author generally considered to be Canada’s foremost popular military historian. His Canadian Battle Series is the most exhaustive recounting of the battles and campaigns fought by any nation during World War II to have been written by a single author.
(more…)
May 5, 2024
Allied Victory in Berlin, Italy, and Burma! – WW2 – Week 297 – May 4, 1945
World War Two
Published 4 May 2024So much goes on this week, and this is the longest episode of the war by like 15 minutes. But there’s so much to cover! The Battle of Berlin ends; the war in Italy ends; the war in Burma ends- well, it ends officially, though there are still tens of thousands of Japanese soldiers scattered around Burma. And there’s a whole lot more to these stores and a whole lot more stories this week in the war. You can’t miss this one.
01:27 The End of the War in Italy
03:40 Western Allied Advances
07:02 Relief Operations in the Netherlands
15:45 Hitler’s Death and the Surrender of Berlin
24:20 Walther Wenck’s Retreat
28:00 The Polish Situation
31:09 What About Prague?
32:44 The End of the Burma Campaign
36:04 THE FIGHT FOR TARAKAN ISLAND BEGINS
37:24 Okinawa
40:11 Other Notes
41:04 Summary
41:43 Conclusion
(more…)
April 28, 2024
The Battle of Berlin! – WW2 – Week 296 – April 27, 1945
World War Two
Published 27 Apr 2024The battle for the German capital rages on all week, as the Soviets get ever closer to the Reich Chancellery, under which lies Hitler’s bunker. Berlin is surrounded, but can it be relieved? There are also Allied advances in East Prussia, Czechoslovakia, and in Western Germany, but beyond that, it looks like the Axis lines have completely collapsed in Italy. The Allies are also advancing — and quickly — in Burma toward Rangoon, though not much at all on Okinawa, and it is the Japanese who are on the move in Western Hunan. It’s a real rollercoaster of a week.
Chapters
01:10 Recap
01:43 Soviets fight their way into Berlin
07:45 Berlin surrounded
10:28 Rokossovsky advances
12:48 Göring and Himmler betray Hitler
13:57 Fighting on the Eastern Front
15:23 Allied advance in the West
15:51 German collapse in Italy
17:31 4th Corps racing through Burma
19:36 The Battle of Western Hunan
21:40 Okinawa and the Philippines
22:59 Notes
23:59 Conclusion
(more…)