… helots made up not only a simple majority of the human beings living under the Spartan state, but in fact a huge super-majority. For comparison, about a third of the population of the American South in 1860 was held in slavery and we rightly call that a “slave society”. Societies where an absolute majority of persons are held in slavery are extremely rare, but Sparta’s massive super-majority of enslaved persons is – to my knowledge – unique in human history.
We are very poorly informed about the helots. Our snobbish sources … are, for the most part, singularly uninterested in them, so we’re left putting together a patchwork of information. That in turn leads into situations where students of ancient Greece can can up with the wrong impression if they don’t have all of the sources in mind (we’ll see this is a common trend with Sparta – reading just Xenophon or just Plutarch can be deeply misleading).
First, let us dispense with the argument, sometimes offered, that the helots were more like medieval serfs than slaves as we understand the ideas and thus not really slaves – this is nonsense. Helots seem to have been able to own moveable property (money, clothing etc), but in fact this is true of many ancient slaves, including Roman ones (the Romans called this quasi-property peculium, which also applied to the property of children and even many women who were under the legal power (potestas) of another). Owning small amounts of moveable property was not rare among ancient non-free individuals (or, for that matter, other forms of slavery).
No, what legally separated helots from douloi (chattel slaves in most Greek societies) was that they were slaves of the Spartan state rather than of individual Spartans – this had nothing to do with any sense of greater freedom they might have had. Indeed, Plutarch relates the saying that “in Sparta the free man is more free than anywhere else in the world, and the slave more a slave” (Plut. Lyc. 28.5). He can only be referring to the helots here. Indeed, Plutarch’s statement is telling – the helots were treated poorly by the standards of ancient chattel slavery, which is, I must stress, an incredibly low bar. Ancient societies treated enslaved people absolutely horribly and yet somehow the helot lot was commonly thought worse.
But the final word on if we should consider the helots fully non-free is in their sanctity of person: they had none, at all, whatsoever. Every year, in autumn by ritual, the five Spartan magistrates known as the ephors declared war between Sparta and the helots – Sparta essentially declares war on part of itself – so that any spartiate might kill any helot without legal or religious repercussions (Plut. Lyc. 28.4; note also Hdt. 4.146.2). Isocrates – admittedly a decidedly anti-Spartan voice – notes that it was a religious, if not legal, infraction to kill slaves everywhere in Greece except Sparta (Isoc. 12.181). As a matter of Athenian law, killing a slave was still murder (the same is true in Roman law). One assumes these rules were often ignored by slave-holders of course – we know that many such laws in the American South were routinely flouted. Slavery is, after all, a brutal and inhuman institution by its very nature. The absence of any taboo – legal or religious – against the killing of helots marks the institution as uncommonly brutal not merely by Greek standards, but by world-historical standards.
We may safely conclude that the helots were not only enslaved persons, but that of all slaves, they had some of the fewest protections – effectively none, not even protections in-name-only.
But what do the helots do?
The answer is mostly “they farm” but getting more specific than that get sticky fast. But we may try to keep this brief: helots were enslaved agricultural laborers. Helots were owned not by individual spartiates, but by the Spartan state, where they were assigned – through whatever method we do not know – to work the plots of land (kleroi, see above) assigned to the spartiates who, as noted above, were forbidden from engaging in any kind of productive labor. The helots seem to have lived in their own villages and settlements – no great surprise, as the Messenian helots seem to have been far more numerous than the Laconian ones and the spartiates themselves did not live in Messenia in any great numbers. It does seem that the Messenian helots were gathered in a smaller number of nucleated villages rather than split up as farmsteads, probably to make it easier for the small number of spartiates stationed there to keep watch on them. And they seemed to have produced not only simple cereal staples, but the full range of agricultural products: wheat (Xen Lac. 5.3 – we’ll come back to this), barley, grapes and wine, figs, olives and olive oil, cheese, textiles (wool) and animal products, including meat and fish.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part II: Spartan Equality”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-08-23.
April 30, 2022
QotD: The position of helots in Spartan society
April 25, 2022
Miscellaneous Myths: Pygmalion and Galatea
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 7 Jul 2016Hey, any of you ever wanted a girlfriend? Statistically speaking, more than half of you just thought “yes”, and a non-trivial percentage probably even went so far as to think “HECK yes.” Well, this is the story of one brave pioneer who, rather than waiting for Miss Right to find him, decided to speed up the process by MAKING her! Don’t go getting any ideas, though — I’m afraid our boy didn’t quite think this through in advance.
MERCH LINKS:
Shirts – https://overlysarcasticproducts.threa…
All the other stuff – http://www.cafepress.com/OverlySarcas…
April 19, 2022
Alexander’s Successors (the Diadochi): Series Introduction and Historical Context
Thersites the Historian
Published 24 Nov 2018This video introduces my series on Alexander’s Successors by talking about what the series will be like and by going through the historical context that the viewer might need to understand the age of the Successors.
Patreon link: https://www.patreon.com/thersites
PayPal link: paypal.me/thersites
Twitter link: https://twitter.com/ThersitesAthens
Minds.com link: https://www.minds.com/ThersitestheHis…
Steemit/dtube link: https://steemit.com/@thersites/feed
Backup Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUrD…
April 17, 2022
Operation Mincemeat, 1943
Once an obscure bit of espionage and military disinformation, the events of Operation Mincemeat are being brought to the big screen (boy, does that term seem dated) in a feature film starring Colin Firth. Michael Curtis provides a look at the actual deception mission that inspired the film:
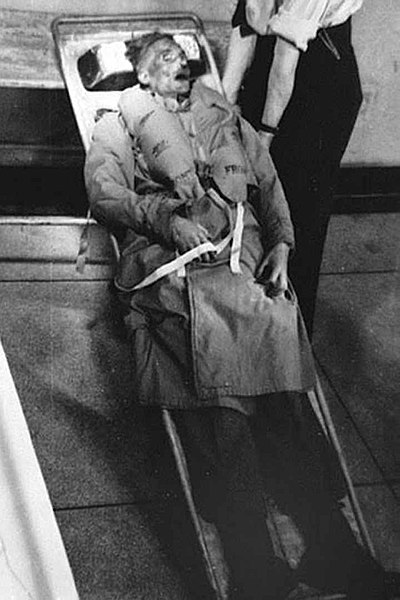
The corpse of Glyndwr Michael, dressed in a Royal Marine uniform with false documents and a fake ID, used in Operation Mincemeat, 1943.
Public domain image from The National Archives.
The story of the British deception, a fascinating story of Allied subterfuge, is now told in the film Operation Mincemeat. It is a remarkable and seemingly highly improbable story of a plan of Allied intelligence to deceive Hitler and misdirect German intelligence. Indeed, it is one of the best examples in history of military deception.
The concept of a plan starts with the Trout Memo, officially written in 1939 by Admiral John Godfrey, director of Naval Intelligence, but almost certainly written by his subordinate Lieutenant Commander Ian Fleming, not yet dreaming of 007, about the deception of an army in war time by fly fishing. Many ideas were suggested, including sending out tins of explosives disguised as food so that hungry sailors would pick them up. One idea, number 28 on the list, almost certainly the thought of Fleming who thought of elaborate deception options, was to use a dead body dressed as an airman dropped from a parachute that had failed and carrying false papers, and drop it where the Germans would find it and be deceived by it.
The deception was planned by a group, the Twenty Committee, XX, headed by Lieutenant Commander RNVR, Ewen Montagu, Cambridge, Harvard, a naval intelligence officer and prominent Jewish lawyer, who later became a judge, together with an RAF officer Squadron Leader Charles Cholmondeley. Montagu later wrote an account of the affair in a book, The Man who Never Was, 1953. The memory of the event is also simply commemorated in a mortuary in Hackney in East London where the body that was used in the plot is buried. In a rather unkind but truthful remark Montagu said of the man who was used, “The only worthwhile thing he ever did, he did after his death.”
The main deception in the plot was a personal letter purported to be from General Sir Archibald Nye to General Sir Harold Alexander, starting, “My dear Alex.” Nye’s letter contained details of sensitive topics, and of a new commander of the Guards brigade, and U.S. service medal awards. He also referred to Operation Husky, an imminent Allied invasion of Greece, that the Germans had been reinforcing and strengthening their defenses in Greece and Crete, and therefore the chief of the Imperial General Staff felt that the Allied troops planned for the assault were insufficient. Thus, it was agreed by the chiefs of staff that the 5th division should be reinforced by one brigade group for the assault on the beach south of Cape Araxos and that similar reinforcement should be made for the 56th division at Kalamata. The letter was a clever double bluff. Nye wrote that “we stand a very good chance of making the Germans think we will go for Sicily, it is an obvious objective and one about which they must be nervous.” To confuse Hitler, he therefore suggested the Allies would invade Sicily.
It is interesting but not surprising that a key figure in the deception appears to have been Ian Fleming, Mr. James Bond, who had written of methods to confuse the enemy, and was crucial to the Trout Memo.
The plot developed. After some difficulty a suitable body was found by a London coroner and kept on ice for few months. It was Glyndwr Michael, 34, homeless Welsh laborer, penniless, with mental health problems, who had died after ingesting rat poison in a London warehouse. He was transformed into Major William Martin, of the Royal Marines whose body contained love letters from a non-existent fiancé named Pam, a jewelry bill for an engagement ring, ticket stubs, religious medal, a copy of a letter marked “personal and most secret”, and above all the false Nye letter. The body had to look as if it had died in an air crash, but floated ashore and he had died at sea. Major Martin, his body wrapped in a life jacket, and with a black attaché case chained to his wrist, was found on April 30, 1943, by a Spanish fisherman off the coast of Huelva.
Even more unlikely than the plan itself was the impact the “secret” document had on Axis planning, summarized in the Wikipedia article:
On 14 May 1943 Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz met Hitler to discuss Dönitz’s recent visit to Italy, his meeting with the Italian leader Benito Mussolini and the progress of the war. The Admiral, referring to the Mincemeat documents as the “Anglo-Saxon order”, recorded
The Führer does not agree with … [Mussolini] that the most likely invasion point is Sicily. Furthermore, he believes that the discovered Anglo-Saxon order confirms the assumption that the planned attacks will be directed mainly against Sardinia and the Peloponnesus.
Hitler informed Mussolini that Greece, Sardinia and Corsica must be defended “at all costs”, and that German troops would be best placed to do the job. He ordered that the experienced 1st Panzer Division be transferred from France to Salonika, Greece. The order was intercepted by GC&CS on 21 May. By the end of June, German troop strength on Sardinia had been doubled to 10,000, with fighter aircraft also based there as support. German torpedo boats were moved from Sicily to the Greek islands in preparation. Seven German divisions transferred to Greece, raising the number present to eight, and ten were posted to the Balkans, raising the number present to 18.
On 9 July the Allies invaded Sicily in Operation Husky. German signals intercepted by GC&CS showed that even four hours after the invasion of Sicily began, twenty-one aircraft left Sicily to reinforce Sardinia. For a considerable time after the initial invasion, Hitler was still convinced that an attack on the Balkans was imminent, and in late July he sent General Erwin Rommel to Salonika to prepare the defence of the region. By the time the German high command realised the mistake, it was too late to make a difference.
April 11, 2022
Republic to Empire: The Ides of March to Actium
seangabb
Published 13 Mar 2021In 120 BC, Rome was a republic with touches of democracy. A century later, it was a divine right military dictatorship. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this transformation with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
April 1, 2022
Denazify the World. Resist Now. – WAH 055 – March 1943, Pt. 2
World War Two
Published 31 Mar 2022The Nazis and the Soviets discover each other’s atrocities, while resistance is on the rise, and a half-dormant conspiracy against Hitler comes back to life to take his life.
(more…)
March 25, 2022
QotD: Herodotus as Spartan propagandist
The greatest military asset the Spartans had was not actual military excellence – although, again, Spartan capabilities seem to have been somewhat better than average – but the perception of military excellence.
Herodotus seems to be at the start of it, at least in our sources – he relates a story where, after an embarrassing failure in an effort to reduce tiny Tegea to helotage (the Tegeans kicked the Spartans’ asses) in the mid-sixth century, the Spartans supposedly stole the bones of the hero Orestes. Consequently, Herodotus notes, the Spartans were from that point on able to always beat Tegea and subdued the Peloponnese (Hdt. 1.68), resulting in the creation of the Spartan-led Peloponnesian League. The unbeatable Spartans thus appear. It’s possible the Spartan reputation predated this, but – as we’ll see – Herodotus will be the one who codifies that reputation and cements it.
Except, hold on a minute – how hard was it to subdue the Peloponnese? It seems to have been done with a fairly adept mix of diplomacy and military force (champion one side in a local dispute, beat the other, force both into your alliance, repeat, see Kennell (2010), 51-3 for details). But it is little surprise that Sparta would be dominant in the Peloponnese. Messenia and Laconia together was around 2,600 square miles or so. This is – if you’ll pardon the expression – flippin’ massive by the standards of Greek poleis. More than twice as large as the next largest polis in all of Greece (Athens). Sparta is fully one-third of the Peloponnese (the peninsula Sparta is located on). The remaining two-thirds is home to many other poleis – Corinth, Argos, Elis, Tegea, Mantinea, Troezen, Sicyon, Lepreum, Aigeira and on and on. Needless to say, Sparta was several times larger than all of them – only Corinth and Argos came even remotely close in size. The population differences seem to have roughly followed land area. Sparta was just much, MUCH larger and more powerful than any nearby state by the start of the fifth century.
Sparta thus spends the back half of the 500s as the teenager beating up all of the little kids in the sandbox and making himself leader. When you are upwards of three times larger (and in some cases, upwards of ten times larger) than your rivals, a reputation for victory should not be hard to achieve. And, in the event, it turns out it wasn’t.
Which brings us back to Herodotus […] because he isn’t just observing the Spartan reputation, Herodotus is manufacturing the Spartan reputation. Herodotus is our main source for early Greek history (read: pre-480) and for the two Persian invasions of Greece. Herodotus’ Histories cover a range of places and topics – Persia, Greece, Scythia, Egypt – and contain a mixture of history, ethnography, mythology and straight up falsehoods. But – as François Hartog famously pointed out in his The Mirror of Herodotus (originally in French as Le Miroir d’Hérodote), Herodotus is writing about Greece, even when he is writing about Persia – those other cultures and places exist to provide contrasts to the things that Herodotus thinks bind all of the fractious and fiercely independent Greek poleis. And he is perfectly willing to manufacture the past to make it fit that vision.
Sparta has a role to play in that narrative: the well-governed polis, a bastion of freedom, ever opposed to tyranny, be it Greek or Persian. We’ll come back to Sparta’s … let’s say relationship … with Persian “tyranny” next week. But for Herodotus, Sparta is the expression of an ideal form of “Greekness” and in Herodotus’ logic, being well-governed (eunomia is the Greek term) results primarily in military excellence. For the story Herodotus is telling to work, Sparta – as one of the leading states resisting Persia – must be well governed and it must be militarily excellent. That’s what will make a good story – and Herodotus never lets the facts get in the way of a good story.
(Sidenote: Athens – at least post-Cleisthenic Athens – gets this treatment too. Athens ends up embodying a different set of “Greek” virtues and where Sparta shows its prowess on land, the Athenians do so at sea.)
And so, Herodotus – the myth-maker – talks up the Spartiates at Thermopylae (you know, the brave 300) and quietly leaves out the other Laconians (who, if you scrutinize his numbers, he knows must be there, to the tune of c. 900 men), downplaying the other Greeks. Spartan leadership is lionized, even when it makes stupid mistakes (Thermopylae, to be clear, was a military disaster and Spartan intransigence nearly loses the battle of Plataea, but Herodotus represents this as boldness in the face of the enemy; even more fantastically inept was the initial Spartan plan to hold on the Isthmus of Corinth as if no one had ever seen a boat before).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part VI: Spartan Battle”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-09-20.
March 18, 2022
Schindler’s First Rescue Mission – WAH 054 – March 1943, Pt. 1
World War Two
Published 17 Mar 2022In the weeks after Goebbels’ Sportpalast speech, we realize that Total War might mean an apocalyptic end for Germany, with Hitler’s blessing. No wonder that some Germans are looking to end Hitler before he ends them, and what a blessing that at least one Nazi with influence on the fate of thousands of Jews turns out to have a heart and soul.
(more…)
March 16, 2022
Etruscan Cities and Civilization
Thersites the Historian
Published 9 Apr 2020The Etruscans were one of the most interesting civilizations of antiquity. In this video, I explore some of the distinctive features of Etruscan civilization and also look at some of the key urban sites in Etruria.
Patreon link: https://www.patreon.com/thersites
PayPal link: paypal.me/thersites
Twitter link: https://twitter.com/ThersitesAthens
Minds.com link: https://www.minds.com/ThersitestheHis…
Steemit/dtube link: https://steemit.com/@thersites/feed
BitChute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/jbyg…
March 14, 2022
Roman Republic to Empire 04 Slavery in the Roman Republic and Empire
seangabb
Published 5 Feb 2021[Update 2023-03-02 – Dr. Gabb took down the original posts and re-uploaded them.]
Here is the fourth lecture, which discusses the nature and extent of slavery in the Roman Empire. It begins with legal definitions and the attempted justifications by philosophers, then proceeds, via the use of slaves as workers in all occupations, including as sex objects, to the great slave revolts of the Late Republic. There is also a section on the valuation of slaves.
In this series, Sean Gabb will explain how the Roman Constitution was transformed, in just over a century, from an oligarchical republic with strong elements of democracy to a divine right military dictatorship.
(more…)
March 12, 2022
QotD: Defining an empire
… an empire is a state where the core ruling population exercises control and extracts resources from a periphery which is composed of people other than the core group (linguistically/culturally/ethnically/religiously distinct). So an empire is a state where one set of people (the core) extract resources (typically by force) from another set of people (the periphery).
That definition goes back to the root of the word in Latin: imperium, literally meaning a command or control; imperium comes from the Latin verb imperio (lit: “to order or command”). Thus imperium was a sphere of command over others. In Roman politics, this could mean an individual had the authority to command an army or to set up courts (consuls, praetors and dictators had this sort of imperium), but the Romans understood their empire as a sort of command exercised by the Senate and People of Rome over non-Roman people, thus they called that too imperium – an imperium of the Roman people (imperium populi Romani), crucially over the non-Roman people; once cannot, after all, have imperium over one’s self. An imperium of the Roman people must be an imperium over someone else.
Contrary to the venerable Wikipedia, empire does not require a monarchy. Rome was an empire while it was still a Republic, and France continued to hold an empire after it stopped being a monarchy. Athens, famously, converted the Delian League into an Athenian Empire (the Greek word used is ἀρχή (“arche“, pronounced ar-KHAY) while it was still, internally, a democracy. Often, when discussing the internal politics of these states (especially for Rome and France) we will distinguish between a period of “empire” and “republic” to note the shift from a republic to a monarchy or vice-versa, but that sort of nomenclature should not be taken to disguise the fact that, for instance, the Roman Republic in 150 B.C. was very much possessed of an empire, while still functioning as a republic.
Empire, I should note, seems to be one of – if not the – dominant form of large-scale human social organization since at least the bronze age (which is to say: since as far back as our sources let us see clearly). Ideas like loose federations of states (e.g. the EU) or nation-states are relatively new; in many cases, our modern nation-states are merely the consolidated form of what were originally empires of various sizes (e.g. China, Russia, but also France (see: Crusade, Albigensian), etc.). We don’t think about them that way anymore, because the steady application of state power created the shared culture that subsequently formed the foundation for the nation […] In many respects, empire is normal (which, please note, does not mean it is good), whereas this modern world composed primarily of nation-states is an unusual aberration.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Why Are There No Empires in Age of Empires?”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-11-22.
March 1, 2022
Mycenaean Greece
Thersites the Historian
Published 25 Jan 2018In this video, I look at the Mycenaean civilization in Greece, which lasted from 1600-1100 BCE.
What was lost when the Library of Alexandria burned?
Kings and Generals
Published 18 Nov 2021⚔️Myth of Empires is out in Early Access on Steam, check it out and make sure to wishlist it https://click.fan/KingsGenerals-MoE
Kings and Generals’ historical animated documentary series on the history of Ancient Civilizations and Ancient Greece continue with a video on the Library of Alexandria, as we ask what was lost when the library burned.
Support us on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/KingsandGenerals or Paypal: http://paypal.me/kingsandgenerals … We are grateful to our patrons and sponsors, who made this video possible: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1o…
The video was made by animator Waily Romero and illustrator Simone González, while the script was researched and written by David Muncan. This video was narrated by Officially Devin (https://www.youtube.com/user/OfficiallyDevin).
✔ Merch store ► teespring.com/stores/kingsandgenerals
✔ Podcast ► Google Play: http://bit.ly/2QDF7y0 iTunes: https://apple.co/2QTuMNG
✔ Twitter ► https://twitter.com/KingsGenerals
✔ Instagram ► http://www.instagram.com/Kings_GeneralsProduction Music courtesy of EpidemicSound
#Documentary #AncientGreece #Alexandria
February 25, 2022
Total War NOW – WAH 053 – February 1943, Pt. 2
World War Two
Published 24 Feb 2022Germany declares total (unconditional war) putting its economy on a full war footing over three years into the war. Given the unconditional war they are already waging, and the resistance and opposition they now face, it’s unclear what it shall mean.
(more…)
February 23, 2022
QotD: Debunking the “Spartan one-man-army” myth
… the Spartans, like all hoplites, were oriented very strongly towards group combat. The one-man-army is simply not how they fought, nor how they ever intended to fight.
Well, ok, perhaps they fought in groups, but were individually better at it. There is something to this. Multiple sources – most notably Xenophon stresses the greater degree of physical fitness that the Spartiates display (Xen. Lac. 4.5, 5.9). The Spartiates were rich after all, so they were well fed and able to build muscle accordingly; they also had a pretty active life-style (mostly things like sport-hunting) and kept athletically active. Chances are the average Spartiate was thus larger and fitter than the average hoplite – although again, the other Lakedaemonians in the phalanx (perioikoi, hypomeiones, mothakes, neodamodes, even helots fighting as hoplites) would probably balance out this effect to at least some degree (more strongly as time went on and the number of Spartiates shrunk!)
But what about martial skills and combat expertise? The fact is, there isn’t much evidence for a Spartan military training regime – certainly nothing like what the Romans had, or even what later Hellenistic Greek poleis set up. We’ve already discussed the agoge and you will note that at no point did swordsmanship, spear use, shield use, or anything of the like come up. There is, to be fair, some mock battles with fennel stalks in place of spears and some war-dances which may have served to mimic combat, but the agoge isn’t a training program, it’s an indoctrination program. Plutarch and Xenophon – who describe it – are quite clear on this: the point is to produce men who are obedient to the laws and subservient to the community (Xen. Lac. 2.10-11; Plut. Lyc. 25.3). Any advantages to military quality are evidently secondary (e.g. Xen. Lac. 2.7).
Xenophon himself notes – in the words of Cyrus (who he presents as an ideal ruler) – that hoplite-style warfare in close-combat required little practice (Xen. Cyrop. 2.1.9-16). And I want to stress two things about this statement: first that Xenophon had seen a lot of hoplite battle when he knew this and was in a position to know and second that he had also seen a lot of Sparta. It is hard to imagine Xenophon – with his Laconophilia – saying that practice for hoplites was unimportant if the Spartans had relied on it heavily. Nevertheless, there he is, saying that all of the movements a hoplite actually needed to perform – blocking with the shield, striking with spear or sword – were instinctive and did not need to be taught or practiced.
Plato provides our first solid evidence for the hoplomachia – practice drills in hoplite warfare – but immediately suggests through the person of Laches that the Spartans, specifically do not practice it (Plat. Lach. 182d-183a), because they think it doesn’t work. There is clearly some practicing with arms in Sparta as elsewhere in Greece (see J. K. Anderson, Military Theory and Practice in the Age of Xenophon (1970), 84-93 for the best discussion of the evidence; note also Wheeler, “Hoplomachia and Greek Dances in Arms” (1982)), but it never approaches the formal weapons drills we see from the Romans, or the complex fighting systems of the late Middle Ages. Nor does Sparta appear to be meaningfully exceptional in this regard; they seem to be exactly as tutored – or untutored – as all the other Greeks.
Nor may we rely on the assumption that the Spartan has more battle experience than his foes. The fact is that Greek poleis went to war fairly regularly and that they tended to bring most of their hoplite class out to battle when they did and as such most Greeks of the hoplite class from anywhere will have likely experienced combat. The Spartans are not unique in this and it is not clear that Sparta fights more often – they murder helots more often, sure, but this is hardly effective preparation for open battle.
(The contrast with Rome is again instructive. Sparta is intermittently at war, but the Roman Republic is continuously at war for all but six years out of five centuries, with the average Roman citizen probably spending upwards of seven years under arms – and this is before the professionalization of the legion. The average Roman free-holding farmer (the technical term is assidui) of the Middle Republic might truthfully have considered Leonidas and his 300 as amateurish by comparison.)
So what can we conclude? Well, the Spartiates are probably, on the whole, better nourished and fitter than their average opponent. If they have an edge in weapons training, it is fairly small – some sort of martial arts experts or superlative weapon-masters they are not. Which, of course they aren’t; the way they fight doesn’t require them to be. Hoplite fighting was never about individual martial excellence or skill, but about holding a position in the formation, supporting and being supported in turn by the shields of the men around you. The hoplite didn’t need to be a spear-master and evidently – we must agree with Xenophon – gained little from becoming so.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part VI: Spartan Battle”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-09-20.