July 25, 2022
Stalin, Hitler, and Churchill – Architects of Death – WAH 070 – July 24, 1943
“Yond Cassius has a lean and hungry look; He thinks too much: such men are dangerous“
Rob Henderson considers the character of Julius Caesar (as filtered through Plutach and Shakespeare), and the “Dominance-Oriented Status Seekers” identified in a recent paper:

La morte di Cesare (The death of Caesar)
Oil painting by Vincenzo Camuccini between 1804 and 1805. via Wikimedia Commons.
In the opening scene of Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar (which is drawn from Plutarch’s Lives), the commoners of Rome are seen celebrating Caesar’s recent triumph over Pompey.
Two tribunes (elected officials), Flavius and Marullus, accost two of the commoners, asking them to name their trades and explain why they are out in their best attire rather than working.
The commoners respond to the tribunes’ condescension with indirect answers and puns that annoy the tribunes even more.
Eventually, Flavius and Marullus learn that the plebeians are cheering Caesar. The tribunes scorn them for doing this.
They tell the commoners that Pompey was a Roman too. So Caesar’s success was not truly a triumph for Rome.
Flavius later tells Marullus that they should remove the decorations from Caesar’s statues during Caesar’s parade.
Marullus questions this plan, stating that it also happens to be the Feast of Lupercal, a celebration of fertility.
But Flavius is adamant that they remove the ornaments, because the removal will help prevent Caesar from seeing himself as too great.
This first scene of Julius Caesar shows that the tribunes want to prevent the rise of a potential tyrant. But they themselves are more than willing to push the commoners around.
Later, two other prominent Romans — Brutus and Cassius — are likewise shown expressing their concerns about Caesar’s growing popularity.
Cassius asks Brutus how Caesar has any more right to greatness than Brutus or himself.
Cassius tells Brutus a story: When they were young, Cassius saved young Julius Caesar from drowning. Cassius always viewed himself as superior for rescuing Caesar. He is now aggravated that Caesar has risen above him.
Cassius decides to orchestrate Caesar’s assassination. Cassius gradually convinces other members of the Roman elite to help him carry out the conspiracy.
Meanwhile, Caesar himself, speaking privately with Mark Antony, expresses suspicions about Cassius:
CAESAR
Let me have men about me that are fat,
Sleek-headed men, and such as sleep a-nights.
Yond Cassius has a lean and hungry look.
He thinks too much. Such men are dangerous.
ANTONY
Fear him not, Caesar; he’s not dangerous.
He is a noble Roman, and well given.
CAESAR
Would he were fatter! But I fear him not.
Yet if my name were liable to fear,
I do not know the man I should avoid
So soon as that spare Cassius. He reads much,
He is a great observer, and he looks
Quite through the deeds of men. He loves no plays,
As thou dost, Antony; he hears no music;
Seldom he smiles, and smiles in such a sort
As if he mocked himself and scorned his spirit
That could be moved to smile at anything.
Such men as he be never at heart’s ease
Whiles they behold a greater than themselves,
And therefore are they very dangerous.
I rather tell thee what is to be feared
Than what I fear; for always I am Caesar.
Come on my right hand, for this ear is deaf,
And tell me truly what thou think’st of him.Caesar is saying all men are hungry, either for food, entertainment (“he loves no plays … he hears no music”), or power. If prosperous men aren’t tempted by food and entertainment, then they crave power. Thus, prosperous men who are lean are dangerous.
Mark Antony dismisses Caesar’s concerns about Cassius, because Cassius is a “noble Roman”. But as events unfold, we see that Antony was misguided.
Caesar was correct in his judgment of Cassius.
The eminent literary critic (and my former professor) Harold Bloom has stated that Caesar’s “estimate of Cassius shows him to be the best analyst of another human being in all of Shakespeare”.
Bloom goes on to characterize Cassius as embodying a “spirit of resentment, unhappy as he is at contemplating greatness beyond him”.
Cassius secretly arranges to have fake notes sent to Brutus, who is fooled into thinking the notes have been written by ordinary Roman citizens who want the Roman elites to stand up against Caesar.
When persuading the other conspirators to help him carry out the assassination plot, Cassius’s stresses his concern for the future of Rome.
But Cassius’s story to Brutus indicates that the assassination was in part fueled by his resentment that Caesar grew into someone more powerful than himself, thus upending their former status disparity.
Rowan Atkinson & Hugh Laurie – Shakespeare and Hamlet (1989)
Nathaniel Brechtmann
Published 1 Sep 2011A sketch called “A Small Rewrite”, performed by Hugh Laurie (aka House) as Shakespeare and Rowan Atkinson (aka Mr Bean) as the editor.
QotD: Napoleon Bonaparte, the Great Man’s Great Man
The point is, a culture can survive an incompetent elite for quite a while; it can’t survive a self-loathing one. This is because the Great Man theory of History, like everything in history, always comes back around. History is full of men whose society doesn’t acknowledge them as elite, but who know themselves to be such. Napoleon, for instance, and isn’t it odd that as much as both sides, Left and Right, seem to be convinced that some kind of Revolution is coming, you can scour all their writings in vain for one single mention of Bonaparte?
That’s because Napoleon was a Great Man, possibly the Great Man — a singularly talented genius, preternaturally lucky, whose very particular set of skills so perfectly matched the needs of the moment. There’s no “social” explanation for Napoleon, and that’s why nobody mentions him — the French Revolution ends with the Concert of Europe, and in between was mumble mumble something War and Peace. The hour really did call forth the man, in large part, I argue, because the Directory was full of men who were philosophically opposed to the very idea of elitism, and couldn’t bear to face the fact that they themselves were the elite.
Since our elite can’t produce able leaders of itself, it will be replaced by one that can. When our hour comes — and it is coming, far faster than we realize — what kind of man will it call forth?
Severian, “The Man of the Hour”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2019-05-22.
July 24, 2022
After a Victory at Kursk, The Soviets Attack Everywhere – WW2 – 204 – July 23, 1943
World War Two
Published 23 Jul 2022The Allied invasion of Italy powers on and puts the future of a key axis power at play. In the USSR, the Soviets have learnt to deal with German offensives, as the Wehrmacht struggles to make a dent.
(more…)
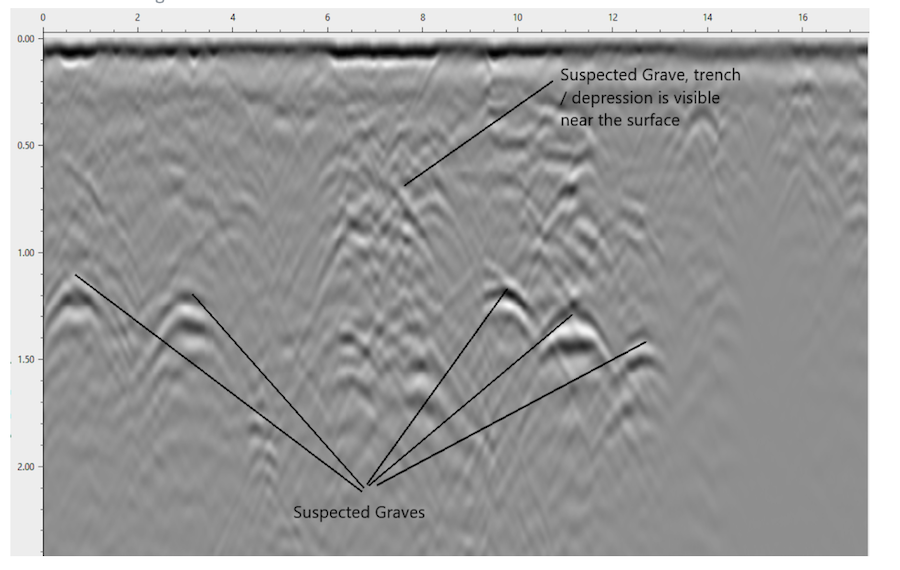
Still no actual evidence of unmarked graves for Residential School children
In Quillette, Jonathan Kay updates the year-old sensational stories about First Nations children being buried in unmarked (in more unhinged reporting it might have been “mass”) graves on the grounds of former Residential Schools in Canada:
Canada’s unmarked-graves story broke on May 27th, 2021, when the Tk’emlúps te Secwépemc First Nation reported the existence of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) data that indicated regularly spaced subterranean soil disturbances on the grounds of a former Indigenous Residential School that had operated in Kamloops, BC between 1893 and 1978. In addition, the First Nation’s leaders asserted their belief that these soil disturbances corresponded to unmarked graves of Indigenous children who’d died while attending the school.
The story became an immediate sensation in the Canadian media; and remained so for months, even after the GPR expert on whom the First Nation relied, Sarah Beaulieu, carefully noted that the radar survey results didn’t necessarily indicate the presence of graves — let alone graves that had been unmarked, graves of Indigenous people, or graves of children. Contrary to what many Canadians came to believe during that heady period, GPR survey data doesn’t yield X-ray-style images that show bodies or coffins. What it typically shows are disruptions in soil and sediment. Investigators then need to dig up the ground to determine what actually lies underneath.
An explanatory image posted by GeoScan, a Canadian Ground-Penetrating-Radar service provider, showing how mapped GPR data can indicate the possible presence of graves.
Image via Quillette.But those details were swept aside during what, in retrospect, appears to have been a true nation-wide social panic. As other Indigenous groups announced that they’d be conducting their own GPR surveys, media figures confidently asserted that the original Canadian Residential-School student death-toll estimate of 3,201 would soon double or even triple. One op-ed writer went so far as to declare that “the discovery of the graves of the children in Kamloops may be Canada’s Holocaust moment.” Dramatic, tear-drenched acts of public atonement unfolded everywhere, with many July 1st Canada Day celebrations being either cancelled or transformed into opportunities for morose self-laceration.
I was one of many Canadians who initially got swept up with all of this — in large part because it seemed as if everyone in the media was speaking with one voice, including journalists I’d known and respected for many years. Looking back on the coverage, I note that headline writers mostly skipped over the technical bits about soil dislocations and such, and went straight to “bodies” and “graves”. And the stories often were interspersed with credulous recitations of dubious tales featuring live babies being thrown into furnaces or buried alive.
The whole mission of Canada’s church-run Residential School system was to assimilate Indigenous people into white Canadian society, usually against their will, while forcing children to leave their families and communities for months or even years at a time. No one disputes that many students were subject to cruel (and sometimes even predatory) treatment and substandard medical care. Certainly, the death rate for Indigenous children attending these schools was much higher than that for children in the general population. No, I never bought into the idea that there was any kind of mass-murder plot going on at these schools. But it hardly seemed far-fetched that some victims of mistreatment and neglect had been buried in unmarked graves — “off the books”, so to speak—by malevolent white teachers, school administrators, and priests seeking to evade responsibility for their actions.
The other important aspect to mention is that — like most other Canadians, I’m guessing — I believed we were only a few days or weeks from seeing real physical evidence plucked from the earth. So it didn’t much matter to me that early commentators were temporarily playing fast and loose with the distinction between GPR data and actual corpses.
Canadians were being told that the old orchard in Kamloops where the GPR data had been collected was a crime scene — a site of mass murder, and the final resting place of 215 child homicide victims. As I’ve reasoned elsewhere: If you told Canadians that, say, 215 murdered white children were buried somewhere in Toronto, or Ottawa, or Vancouver, there’d be investigators and police crawling all over the place, looking for remains that could be tested and identified. And so I naturally assumed the same thing soon would be happening in Kamloops.
But … no. Not at all, in fact.
As I wrote over a year ago, the way the story swept the media was as if the whole Residential School history was somehow new and previously unknown:
Despite being Canadian, my interest in Canadian history centres mostly on economic, naval, and military aspects, but I was certainly aware that the residential school system was a black mark on Canada’s historical dealings with First Nations and that the general outline of events — if not the gruesome details — had been known for many years. The first time I found out about it was in middle school, through what we’d now call a “Young Adult” novel about a young First Nations boy escaping from the residential school he’d been sent to and his attempts to travel hundreds of miles to get home. I read it in the early 70s and it may have been published up to a decade before then (I no longer remember the author’s name or the title of the book, unfortunately).
If I, as a schoolchild, knew something of this fifty years ago, why have people younger than me been shocked and appalled to be hearing about this widespread tragedy for the first time now?
Stoner 63A Automatic Rifle – The Original Modular Weapon
Forgotten Weapons
Published 17 Mar 2018The Stoner 63 was a remarkably advanced and clever modular firearm designed by Eugene Stoner (along with Bob Fremont and Jim Sullivan) after he left Armalite. This was tested by DARPA and the US Marine Corps in 1963, and showed significant potential — enough that the US Navy SEALs adopted it and kept it in service into the 1980s. It was a fantastic balance of weight and controllability, offering a belt-fed 5.56mm platform at less than half the weight of the M60. The other fundamental characteristic of the Stoner 63 was modularity. It was built around a single universal receiver component which could be configured into a multitude of different configurations, from carbine to medium machine gun. Today we have one of the rarer configurations, an Automatic Rifle type. In addition, today’s rifle is actually a Stoner 63A, the improved version introduced in 1966 to resolve some of the problems that had been found in the original.
Ultimately, the Stoner system was able to achieve its remarkably light weight by sacrificing durability. The weapon was engineered extremely well and was not a danger to itself (like, for example, the FG-42), but it was prone to damage when mishandled by the average grunt. This would limit its application to elite units like the SEALs, who were willing to devote the necessary care to the maintenance and operation of the guns in exchange for the excellent handling characteristics it offered.
(more…)
QotD: British armour from BAOR to the first Gulf War
During the Cold War there was a clear threat in the form of the Soviet 3rd Shock Army, which was lined up, facing off against BAOR [British Army of the Rhine] units. It made an enormous amount of sense to contribute to a NATO operation to deter Moscow from chancing their luck, and ensure that they could not force the border and take over Western Germany.
To that end generations of British soldiers were stationed there training for a war that they hoped would never come. To this day there are still serving Cold War veterans who even into the late 1980s knew where they would deploy to, and the likely exact spot in the field or woods where they would dig their trenches and realistically be killed.
This force though was essentially a static one, designed to operate defensively and underpinned by an enormous static logistical and support network stretching from the Inner German Border all the way back to Antwerp and then the UK. The British Army was able to sustain armour in large numbers in part because it had the threat to face, the space to operate and the support network in place to enable this to occur. To this day the subject of how well supported BAOR was through the extensive rear communications zone efforts, and the widespread workshops (such as in Belgium) designed to repair and support UK units is not widely known or told, but deserves much greater recognition.
This matters because when people look back to the size of the British Army in 1990 and look at how many tanks we had then compared to now, they forget that the Army’s MBT capability was essentially a static garrison force waiting to conduct a defensive campaign against a peer threat where it expected to take heavy losses and probably operate very quickly in an NBC environment. It was not intended to be a deployable force capable of operating across the planet on an enduring basis.
This is why when people talk about how many tanks were deployed in 1991 to the Gulf War (some 220 Challenger 1’s were deployed) they forget that this was the first time since Suez that the UK had operated heavy armour overseas. It took many months to get this force into place, and it came at the cost of gutting the operational capability of the remaining BAOR units, who found their logistical support chains hammered in order to support the forces assigned to GRANBY.
The harsh, and perhaps slightly uncomfortable reality for the UK is that OP GRANBY required nearly 6 months of build up at the cost of gutting wider armoured warfare capability – proving that away from home, having 900 tanks is irrelevant if you are operating outside normal parameters and are having to effectively cannibalise or mothball most of them to keep 220 in the Gulf.
By contrast OP TELIC saw over 100 tanks deployed, but a significantly shorter lead in time for the deployment – testament to the significant investments made in the intervening period in logistical capabilities.
Sir Humphrey, “Tanks for nothing — Why it does not matter if the British Army has fewer tanks than Cambodia”, Thin Pinstriped Line, 2019-04-24.
July 23, 2022
Barbarian Europe: Part 3 – Barbarism and Christianity
seangabb
Published 1 May 2021In 400 AD, the Roman Empire covered roughly the same area as it had in 100 AD. By 500 AD, all the Western Provinces of the Empire had been overrun by barbarians. Between April and July 2021, Sean Gabb explored this transformation with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
Some of the events that lead to the Dutch farmers’ revolt
In UnHerd, Senay Boztas provides a useful chronology of how the Netherlands government managed to piss off so many Dutch farmers, leading to the protests we are still seeing (even if the legacy media is doing their best to ignore it):
“For many farmers it’s the end of their business and they will fight until the last. Sometimes these farms go back generations, they were built by hand, and people feel farmers heart and soul. This is all being taken away.”
Jan Brok, vice chairman of the BoerBurgerBeweging (BBB) party, understands why Netherlands farmers have spent the past month blockading food distribution centres, roads and ministers’ driveways. They are horrified by a new environmental policy that will mean a likely 30% reduction in livestock.
The Netherlands is a country of four million cattle, 13 million pigs, 104 million chickens, and just over 17 million people. It is Europe’s biggest meat exporter with a total area of just over 41,000 square kilometres, and a fifth of this is water. It is one of the world’s most densely populated countries, with the EU’s highest density of livestock.
But there is a significant cost to this abundance: the local environmental impact. Such intensive agriculture, and livestock farming in particular, creates harmful pollution. Manure and urine mix to produce ammonia, and together with run-off from nitrogen-rich fertiliser on fields ends up in lakes and streams, where it can promote excessive algae that smothers other life. Manure here is not a vital fertiliser but a problem waste product.
For decades, this success in trade and agriculture has been accompanied by high emissions of harmful nitrogen compounds, including nitrogen oxides emitted by industry and transport. Levels were dropping, and in 2015, the Dutch introduced a “trading scheme” known as the Programmatische Aanpak Stikstof (PAS) to try to reduce the pollution.
But a Council of State court ruling in 2019 — on a case brought by two local environmental organisations against various farms — ruled that this offsetting scheme was invalid. Permission could not be granted for polluting projects or farm expansion in exchange for promised nitrogen-related reductions in the future: the reductions needed to come first.
The government panicked: national shutdowns were put in place, building projects were put on hold and traffic speeds reduced to 100 kph in the daytime on major roads; it was also obvious that farming was a problem — something needed to be done about all ammonia, nitrogen oxide and nitrous oxide emissions.
Then, in January, the conservative-liberal-Christian coalition pledged to halve nitrogen production by 2030, with a €25 billion budget to back it up. That money was the loud part. The quiet part included the possibility of expropriation, of the government forcibly purchasing farmland. Plans drawn up by civil servants include slashing livestock numbers by 30%. More than €500 million is being brought forward for regional government to buy out farmers this year and next.
Leading the charge among the coalition partners are the Democrats 66 (D66) party. They insisted on “real action for the climate” in their last manifesto. Tjeerd de Groot, the D66 nature and farming spokesman, pointed out that the Netherlands is Europe’s biggest nitrogen emitter, followed by Belgium and Germany. He told a current affairs programme last week: “It is absolutely essential — but also painful — that the plans go through.”
In June, the government published two documents. One: a map showing the areas that need to reduce emissions by between 12% and 95%. The second was a statement that aimed to help farmers — which De Groot admits failed spectacularly. Farmers saw ruin, not a pair of documents. They looked at the percentage reduction figures next to their farms, and began interpreting how many cattle they would need to cull. It was an enormous blow. Many of them had made huge, expensive investments in new equipment to reduce the environmental impact of their herds.
Hence the massive uprising.
Tank Chat #152 | Swiss Centurion | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 25 Mar 2022
(more…)
QotD: “The New Journalism” and “narrative journalism”
Most of what we consider public life in modern societies is public reactions to things done by the powerful. The New York Times makes up a new hoax and the week is spent on the hoax. The usual suspects swear by the obvious lies and normal people spend days picking apart the lies. Occasionally, we get the reverse where some uncomfortable truth gets loose and the usual suspect go bananas trying to “debunk” it while normal people cling to it as blessed relief.
This is the news cycle in a nutshell. There is very little news. It has been at least a generation since the major news outlets in America have done reporting. Most of it is just stenography. The “journalist” copies what a government spokesbot has sent to them and dresses it up with some commentary. Then there are the narratives that are designed to give the public a way to repeat the official truth that sounds convincing to them and their acquaintances.
The source of this is the “new journalism” that emerged in the 1960’s. The late British reporter Chris Munnion chronicled this in his book Banana Sunday. He spent most of his life covering Africa for the Telegraph. In the 1960’s he noticed Americans showing up with pre-written narratives. They would seek out quotes and pictures to fill out the story they had prepared for the trip. Even if the facts contradicted the narrative, they stuck with the narrative because that was the new journalism.
Narrative journalism is just accepted these days. The “news” has always been a form of passive-aggressive political activism so its evolution into story telling on behalf of powerful interests seems natural. When you think of the New York Times, Washington Post and Wall Street Journal as propaganda arms of their respective clients in the managerial elite, it all makes sense. Instead of the Ministry of Truth we have the mainstream media “speaking truth to power”.
That last bit gets mocked by normal people on this side of the great divide because they have woken up to the reality of this age. As if often the case, however, there is a kernel of truth locked in this media fabrication. The people inside these disinformation operations genuinely fear the public. When they say “speak truth to power” they mean broadcast their truth to you in the hopes that you will buy it. Modern mass media is mostly a defensive weapon of the elites.
The Z Man, “The Lying Liars”, The Z Blog, 2022-04-20.
July 22, 2022
Inventing historical connections with slavery where they don’t exist
In Quillette, David Foster recounts the story from the National Museum of Wales which effectively fabricated a connection to the slave trade as part of their politically correct performative “decolonization” efforts:

A replica of Richard Trevithick’s 1802 steam locomotive at the National Waterfront Museum in Swansea.
Photo by Chris55 via Wikimedia Commons.
In March, Britain’s Daily Telegraph and GB News channel both reported that the National Museum of Wales would be relabelling a replica of the first steam-powered locomotive, unveiled by its Cornish inventor Richard Trevithick in 1804. Trevithick had no links to slavery, but the amendment has apparently been included anyway as part of the museum’s commitment to “decolonizing” its collection. In a statement defending what it described as the addition of “historical context”, the museum said: “Although there might not be direct links between the Trevithick locomotive and the slave trade, we acknowledge the reality that links to slavery are woven into the warp and weft of Welsh society.” The statement continued:
Trade and colonial exploitation were embedded in Wales’ economy and society and were fundamental to Wales’ development as an industrialised nation. As we continue to audit the collection, we will explore how the slave trade linked and fed into the development of the steam and railway infrastructure in Wales.
[…]
When a society compulsively disrespects its historical accomplishments — when it obsessively seeks to turn every good thing into a bad thing — the outlook for that society is bleak. It destroys social cohesion, and sends the wrong kind of message to actual and potential opponents. The matter of the steam locomotive display in Wales may seem minor, and certainly trivial when compared with the appalling events in Ukraine or the threat of Iranian nuclear weapons. But it is not.
The behavior of the museum administrators in Wales is of a piece with other contemporary symptoms, such as the eagerness within influential circles in the US to embrace the conclusions of the New York Times‘s revisionist 1619 project. It is part of the politicization of everything. Science, technology, and art cannot — indeed, must not — be appreciated simply on the grounds of beauty, utility, or truth; everything must be reduced to race, gender, and other academically and media-approved categories of analysis.
Trends such as these have real-world implications, including the growth and decline of nations and their relative power. Writing in 1940, C.S. Lewis, warned about the dangers of what he called the National Repentance Movement, which focused on the need to apologize for Britain’s sins (thought to include the Treaty of Versailles) and to forgive Britain’s enemies.
Certainly, the British State had done many bad things during its long and eventful history — as well as many good things. But the excessive focus on its sins was part of a phenomenon manifested in a 1933 motion debated at the Oxford Union: “This House will under no circumstances fight for King and country”. To the Nazis and the Imperial Japanese, attitudes like these indicated that aggression would not meet much resistance. They also informed a policy of appeasement.
Liberals and progressives (as they call themselves) claim to be greatly concerned with physical sustainability of resources and ecosystems. But they are too eager to undercut the social sustainability of their own societies and the physical infrastructures on which those societies depend, however fond they may be of repeating the word “infrastructure”.
Why Did The First World War Break Out? (July Crisis 1914)
[My 2014 series on “The Origins of World War I” can be read here. Although I’d read a fair bit of history on the period, once I began researching the period, even I was surprised at how many different contributing causes there were.]
The Great War
Published 15 Jul 2022The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife in Sarajevo on the 28th of June 1914 kicked off a crisis among the European Powers. Tensions that built up in the decades before erupted and in early August 1914 the world was at war. But what happened in these fateful July weeks 1914?
(more…)