Drachinifel
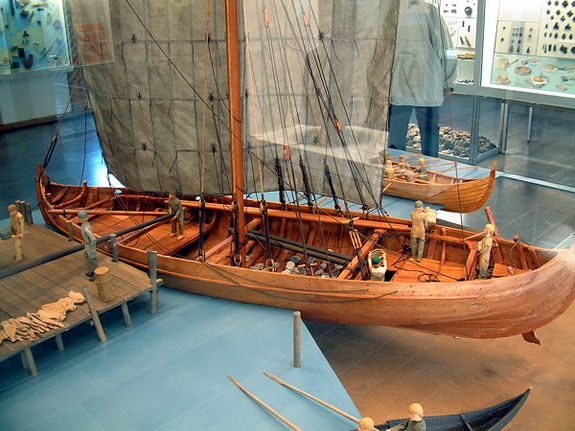
Published 25 May 2024HMS Canada / Almirante Latorre, a single dreadnought battleship of the British Royal Navy and Chilean Navy, is today’s subject.
(more…)
July 18, 2025
HMS Canada / Almirante Latorre – Guide 389
June 28, 2025
Breathtaking hypocrisy in the BC Ferries deal to buy ships from China
As you’d imagine, with the coastal geography of British Columbia, there’s a lot of demand for ferry service between the mainland and Vancouver Island (and other less-accessible-by-land locations). BC Ferries runs a fleet of ships to handle this traffic and needed some new ferries to replace older vessels. They decided, in the middle of a trade war, to source the ships from China rather than a Canadian shipyard. And the federal government financially backed the purchase:
So just to recap — because this one’s almost too absurd to believe: BC Ferries cuts a billion-dollar deal with a Chinese state-owned shipyard to build four new ferries. Canada’s Deputy Prime Minister Chrystia Freeland — always quick to perform outrage when the cameras are on — writes a stern letter saying how “dismayed” she is. She scolds British Columbia for daring to do business with a hostile foreign regime that’s literally attacking our critical infrastructure in real time.
And then — wait for it — it turns out her own federal government quietly financed the whole thing.
Yes, really.
According to an explosive report from The Globe and Mail, the Canada Infrastructure Bank — a federal Crown corporation — provided $1 billion in low-interest financing for the very same China shipbuilding deal Freeland claimed to oppose. The contract was signed in March 2025. The outrage? That only came later, when the public found out about it in June.
Freeland’s letter to BC’s Transportation Minister was loaded with warnings. She talked about China’s “unjustified tariffs” and “cybersecurity threats”. She demanded assurances that “no federal funding” would support the purchase. But what she didn’t mention — what she conveniently left out — was that Ottawa had already cut the cheque. The financing was already in place. The loan had been approved. Freeland just didn’t say a word.
And when reporters asked for clarification, what did her office say? Nothing. They passed the buck to another minister. The new Infrastructure Minister, Gregor Robertson, now claims the government had “no influence” in the procurement decision. No influence? You loan a billion dollars to a company and have no opinion on where it goes?
Let’s be clear: This wasn’t some harmless miscommunication. If it wasn’t a cover-up, then it was sheer incompetence — the same brand of incompetence that’s driven our shipyards into obsolescence, our economy into dependence, and our country into managed decline. An entire federal cabinet stood by, watched this unfold, signed the cheque — and then pretended they had nothing to do with it.
And British Columbia’s government? Just as bad. Premier David Eby, the man who pretends to champion “BC First”, claims he was “not happy” with the China deal but says it’s “too late” to change course. Too late? This isn’t an asteroid heading for Earth. It’s a contract. And contracts can be rewritten, canceled, renegotiated — if anyone in charge had the political will to stand up and say, “No, we don’t hand billion-dollar infrastructure projects to hostile regimes”.
But instead, we get excuse after excuse. They say BC Ferries is independent. They say there was no capacity in Canada. They say we had no choice. All the while, Canadian shipyards sit idle, unionized workers are frozen out, and the Canadian taxpayer is stuck subsidizing Chinese shipbuilding — and Chinese espionage.
June 26, 2025
A Basic Explanation Of The First Punic War
MoAn Inc.
Published 8 Jan 2025GEOGRAPHY NOTES
Messina is the modern name for Messana. Both are correct.
Acragas / Akragas was renamed as Agrigentum by the Romans. Most videos on YouTube use the name Agrigentum for convenience purposes … so again, both are correct.
Panormus is modern day Palermo.
Drepana / Drepanum is modern day Trapani.
Lilybaeum is modern day Marsala.!READ THE SOURCES FOR FREE!
Livy: https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/…
Polybius: https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/…
Cassius Dio: https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/…
(more…)
June 20, 2025
Generations of Battleships – A Reasonable Guide to Classifying your Capital Ships
Drachinifel
Published 24 Jan 2025Today we take a look at my proposed system for classifying battleships!
00:00 – Intro
01:55 – Ship Generations
(more…)
June 17, 2025
BC is buying ferries from China … to spite Trump!
After all the “buy Canadian” blather of the last federal election campaign, it was only a matter of time before the feds or one of the provinces did something astoundingly out-of-step with the mantra. Smart money was always on Quebec being the first (because that often makes sense for internal provincial political reasons), but no, this time it’s British Columbia going a long way out of their way to not buy Canadian for a huge government purchase:

BC Ferries’ MV Spirit Of Vancouver Island between Galiano Island (Bluffs Park) and Mayne Island, en route from Tsawwassen to Swartz Bay, BC on April 6, 2022.
Photo by Gordon Leggett via Wikimedia Commons.
British Columbia’s transportation minister claimed Friday that buying new ferries from European shipyards would have cost roughly $1.2 billion more than buying them from a Chinese government-owned shipyard in Weihai, Shandong province, which is a city roughly the size of Montreal that I had never heard of until this week. China knows how to build cities. They burst into existence from nothing, like popcorn. China also knows how to build ships, and highways, and high-speed rail, and just about anything else you would care to name, better and more efficiently than the Canadian public service can realistically comprehend.
The four ships B.C. Ferries is fixing to replace, of 1960s and 1970s vintage, were built at Seaspan in North Vancouver (which is an active shipyard), at the Victoria Machinery Depot (which is no longer an active shipyard), and at the Burrard Dry Dock (which is also defunct). Canada’s shipyards, for better or worse — certainly for expensive! — are very busy building things for the navy.
B.C. Ferries has plenty of experience with foreign-built vessels. Its current fleet includes ships built in Romania, Poland, Germany and Greece. Other than the Baynes Sound cable ferry on Vancouver Island — which is not especially popular — the Crown corporation’s newest Canadian-built boat went into service in 1997. So “foreign” obviously isn’t the problem.
But China is China, and that’s legitimately another thing. China is not a Canadian ally. They try to screw with our democracy, and most other democracies by the sounds of it. And right now we are in a profoundly protectionist moment: Across the political spectrum, mostly because of President Donald Trump, “buy Canadian” is the only philosophy really on offer.
But does that make sense? We should pay over the odds for ferries … because of Trump? There wasn’t half of all this foofaraw when Marine Atlantic on the East Coast bought its newest ferry from Weihai. Since last year it has safely been shepherding Canadians between Nova Scotia and Newfoundland, without a whisper of controversy in the Rest of Canada.
I don’t quite get the Trump angle, which is perhaps why I’m more interested in Dean Broughton‘s take:
… I’m not just disappointed — I’m furious — about the NDP government’s decision to award the construction of four new BC Ferries vessels to a Chinese state-owned shipyard. This isn’t just outsourcing. It’s betrayal dressed up as budget management.
Back in 2021, the NDP government unveiled a “Made-in-B.C.” shipbuilding strategy with great fanfare. They formed a Shipbuilding Advisory Committee, posed for cameras, and promised to rebuild a long-neglected industry. It was supposed to be a turning point, a real investment in local jobs and industrial capacity.
Now, many of those same politicians have turned their backs on everything they claimed to support. Not only did they ship the contracts overseas, but, according to Eric McNeely, president of the BC Ferry and Marine Workers’ Union, they didn’t even give B.C. shipyards a fair shot. The procurement process was so rushed and restrictive that no local yard could realistically compete. They didn’t lose the bid — they were boxed out.
That’s not fiscal prudence. That’s political cowardice.
The hypocrisy is staggering. This is the same government that talks endlessly about investing in clean industry and supporting working families, and they just handed a massive public contract to a country with a well-documented record of environmental abuses and human rights violations.
They talk about reconciliation and sustainable development—and then funnel hundreds of millions to an authoritarian regime.
Worse still, they did this knowing full well that B.C.’s industrial base is already in decline.
We have so little left beyond resource extraction. Shipbuilding could have been part of our economic renewal. Instead, it’s another casualty of government optics and empty promises.
I remember my father’s outrage in 1990 when the federal government cancelled the Polar 8 icebreaker — a Canadian-built vessel meant to defend our Arctic sovereignty. That decision was dismissed as a “cost-saving measure” and today our claim to the North has never been weaker.
The BC Ferries decision reeks of the same short-sighted logic.
June 15, 2025
Militarizing the Canadian Coast Guard (or not?)
Noah tries to get some solid information on the recent announcement by the Prime Minister that as part of changes to bring Canada into line with our decade-old NATO commitments, the Canadian Coast Guard would be moved from the civilian oversight of the Ministry of Fisheries and Oceans to the military oversight of the Ministry of National Defence. Oddly, the government seems to have been caught rather flat-footed by the PM’s announcement:
When Monday came I was invited to take part in a Media Briefing before [the PM] took questions. My immediate goal was to bring this topic up and get some sort of official words on what these plans were, especially after it wasn’t mentioned in [Carney’s] speech beforehand.
[…]
What we were told was that no such move was taking place, nor plans to arm the Coast Guard and that the current plan was to focus on augmenting their capabilities through new sensors and further collaboration with the RCN.
It was a definitive statement, one that we all agreed was cut and dry. I even reached out to other journalists before adding it to the livethread to make sure we were on [the same] page.
So imagine my surprise when Steven at the G&M came out blazing with a straight no, the plan is to move them. He even came backed up with a statement from the PMO, and credit to Steven, he was quick on this:
So as you can imagine my new goal was to figure out what exactly the hell was happening to the Coast Guard, with multiple competing statements on the subject. I made it my mission to have a definitive answer.
So it was back to asking, and emailing, everyone, from the DND to the PMO, CCG to the DFO. I got in contact, I dug into sources, even went as far as to ask people in industry if they had heard anything.
What I got for the first few days was chaos. Multiple statements saying that info wasn’t available, more time was needed. I got outright denial from the DND, only to be told they would email me back with info (they never did)
The PMO also told me info would be available when they had it. Evidently as of the time of this writing they have not responded. The only one to stay in contact and provide an answer to my question:
So as far as I was concerned this was a deal closer. The Coast Guard will be moving under the leadership of the Minister of National Defence. What will this look like? We don’t know. I had hit a dead end at this point, where sadly my reach was no longer wide enough for info.
Thankfully, there were others also keen on this, and wanting to get to the bottom of this, and they got farther than me. I will highly recommend my boy Stuart’s article on this as he got farther than me.
What has become evidently clear is:
- The Coast Guard is moving
- The idea is facing stiff resistance
This isn’t a shock at all. The DFO folks I talked to felt very caught off guard by everything, and the general reaction I have talking around was that this was a bit unexpected.
If accurate, then it is clear that this is the choice of the Prime Minister. He is the one who wants this, and so is making the final push. That isn’t to say he is the only one, but this has his backing and he will push that through.
June 13, 2025
HMS Eskimo (F75) – Guide 362
Drachinifel
Published 18 Nov 2023HMS Eskimo, a destroyer of the British Royal Navy, is today’s subject.
(more…)
June 6, 2025
“All the Little Ships” (1964 – CBC Telescope)
Royal Canadian Navy / Marine Royale Canadienne
Published 5 Jun 2025🇨🇦 Honouring 80 Years of Courage at Sea ⚓
To mark the 80th anniversary of the end of the Second World War and the Battle of the Atlantic, the Hamilton Naval Association is proud to reintroduce a long-lost Canadian treasure: “All the Little Ships”.
Originally aired in 1964 on CBC’s Telescope, this rare film features recently retired Admiral Harry DeWolf aboard HMCS Haida as he tells tales not only of HMCS Haida but of “All the Little Ships” of the wartime RCN. Never-before-seen footage shot by Bill Pugsley, a wartime officer who resigned his commission so he could serve two years on the lower deck, as a gunner, and document it.
🎥 A story of sacrifice, memory, and Canada’s naval legacy — rediscovered. A special thank you LCdr Doug Martin (Ret’d, former CO of HMCS Star).
The opinions expressed in this video are those of the original creators and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Royal Canadian Navy. Any references to outside organizations, products, or services do not constitute endorsement or affiliation.
#WeTheNavy #CanadaRemembers #HelpLeadFight
May 30, 2025
Was Germany Really Starved Into Surrender in WW1?
The Great War
Published 10 Jan 2025From 1914 to 1919, Allied warships in the Atlantic and Mediterranean controlled maritime trade to and from the Central Powers – stopping shipments of weapons and raw materials, but also food, from reaching their enemies. At the same time, hundreds of thousands of German civilians died of hunger-related causes. Often, these deaths and even the outcome of the war are attributed to the naval blockade – but did the British really starve Germany into surrender in WW1?
(more…)
May 12, 2025
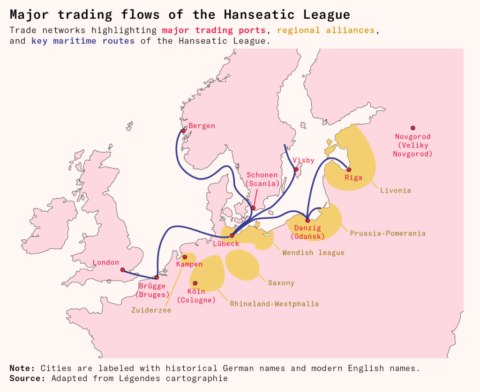
The rise of the Hansa
At Works in Progress, Agree Ahmed describes the conditions in northern Europe in the Middle Ages that helped create the Hanseatic League:
Today, we typically think of coalitions in the context of modern electoral politics. So it might be surprising that one of the greatest case studies in the history of coalitions is a community of medieval German merchants known as the Hansa.
Starting as individual traveling traders, the Hansa built up coalitions for collective bargaining, collective action, and collective security. Through this process, they formed Northern Europe’s first ever long-distance trade network.
Without corporate structures, they built supply chains that distributed goods between Northern Europe’s major ports, with capillaries that spread into each city’s hinterlands. Without formal territory, their laws governed trading hubs spanning thousands of miles, from London all the way to Western Russia. And, despite being composed of hundreds of member cities, the Hanseatic League had no head of state. Yet the Hansa still managed to sign treaty after treaty with foreign rulers and, a few times, even fought (and won!) wars.
[…]
Better climate, more arable land, and better farming techniques lifted Europe’s crop yields to above subsistence levels for the first time since the Roman period. After several centuries of decline, Europe’s population grew from 18 million in the 600s to over 70 million by the 1300s – nearly triple the population of the Roman period. The nutritional surplus allowed for Europe’s first significant artisan class since the Roman empire. Each town had common craftsmen like blacksmiths, leatherworkers, and carpenters. But local skills and resources allowed for the emergence of specialized crafts, which were unique to specific regions and could therefore be traded.
Tax-hungry lords across Europe began to set up permanent marketplaces for their growing communities. And so hundreds of towns formed in Europe, filled with workers who had flocked from countryside manors. These towns were the first substantial permanent markets in Northern Europe’s history.
As production accelerated, so did shipping. The warmer climate meant waterways in the North and Baltic Seas were navigable for longer stretches of the year. Meanwhile innovations in boatmaking dramatically improved shipping capacity. Excavations of the few surviving ships from this era show that, in the span of a few centuries, vessels tripled their average tonnage from 10 to 30 while dropping the number of rowers required by a factor of four.
The breakthrough in tonnage starting in 900 can be credited to the knarr, a Viking-style ship that was shorter and wider than the longboat that preceded it, allowing it to load substantially more cargo with a smaller crew. Prior to the knarr, trade convoys had to carry cargo on longboats, which were agile but could only carry small fractions of what the knarr could.
When Northern Europe’s first long-haul merchants set off on their voyages, they faced a world that had not yet been ordered for trade. Sailors had to worry about pirates in the Baltic and shipwrecks at icelocked winter ports.
Riverways gave merchants access to inland communities, where they could find products at lower prices to then sell for a profit in major port cities. But riverside towns were more interested in their own engineering projects or grinding their grain and so would block rivers with dams and water mills, and they would redirect water to irrigate fields.
And even if a river were clear of obstructive mills or dams, it might be heavily punctuated by toll stations. The Rhine River, a key shipping artery that connected inland Germany with the Baltic coast, had tolls approximately every five kilometers.
Under the laws of the Holy Roman Empire, the right to collect tolls on the Rhine could only be granted by the Emperor. But unauthorized tolling stations, or tolls levied in excess of what was authorized, were so rampant that the malpractice had a name: the lonia iniusta (Latin for “unjust tolls”). Some local authorities enforced toll collections along rivers by running chains from bank to bank, making it impossible for a boat to pass without paying. Others would patrol the river on their own boats and deny vessels passage until they paid up.
In the first four years of the Great Interregnum Period (1250–73), when the Empire had no emperor, the number of toll stations on the Rhine doubled to 20. This is the origin of the term “robber baron”: local barons, operating out of riverside castles, would set up illicit toll stations and demand significant shares of merchant cargo in order to pass.
The journey on land wasn’t much easier. Toll booths were similarly common. Nominally, these were to pay the landowner for the maintenance of the roads and bridges but in reality they were usually left dilapidated. Merchants voyaging on land had to load their wares on the backs of mules and horses (which were about a third the speed of ships). The narrow widths of medieval roads meant these caravans stretched out in long lines, leaving animals and cargo physically exposed. These vulnerable, slow moving, value-dense caravans attracted bandits who roamed the isolated roads between towns. It was nearly guaranteed a caravan would face an attempted robbery – either illegally by bandits or (somewhat) legally in the form of a toll shakedown – over the course of a sufficiently long trip.
As a matter of safety, Northern European merchants learned to move together in armed groups. These traveling merchant bands were called hansas, a Lower German word meaning “company” or “troop”. When a hansa formed for a trip, they elected an alderman (literally “elder man”) who would speak on behalf of the group to the various authorities – lords, princes, bishops, and other rulers – they might encounter along the way.
Once they completed the arduous journey, the merchants had to deal with the local governments of their destination cities, each of which had different and constantly changing laws. To protect the local merchants and craftsmen within their city walls from competition, princes might demand exorbitant taxes from foreign merchants or deny them access to the city altogether. Merchant bands had to negotiate collectively to secure the right to trade within each city in which they wished to conduct business. And if they made it into the city walls, they might not make it out: capricious lords might suddenly imprison foreign merchants (as happened to German merchants in England in 1468 and Novgorod in 1494), raid their offices, or seize their merchandise.
Local laws threatened foreign merchants more than they protected them. Most town courts, themselves newly formed, had minimal experience adjudicating long distance commercial disputes. When such disputes did arise, courts could take weeks or months to arbitrate them, and were heavily biased towards locals over foreign traders. Without sovereign states, merchants were left dealing with a fractured landscape of town courts, where each market had its own idiosyncratic laws. And because foreign traders could evade punishment by fleeing overseas, courts in England, France, Italy, and the Holy Roman Empire often collectively punished foreign merchant communities for the unpaid debts of their countrymen.
The lack of early medieval records makes it difficult to quantify just how much Northern European commerce grew as a result of continuous long distance trade. Before the late medieval period, Northern Europe’s archaeological record of trade shows just several dozen sites known as emporiums: small, temporary settlements outside of towns where foreign merchants traded with locals. But starting in the late medieval period (1300 to 1500), Lower German merchants began to change this.
H/T to Niccolo Soldo for the link.
April 9, 2025
Stretching the RCN’s limited number of AOPS too thin?
I admit that I doubted the overall utility of the Harry DeWolf-class of Arctic/Offshore Patrol Ships when they were announced, but aside from the typical teething troubles of new ship designs they seem to be doing a good job at their initial taskings. Noah, on the other hand, proudly describes himself as “perhaps their [the AOPS] biggest online defender“, but he’s raising concerns that the Harry DeWolf class will soon be expected to pick up the slack as the Kingston-class Maritime Coastal Defence Vessels come to the end of their working lives with no obvious replacements under construction:

Arctic Offshore Patrol Ship HMCS Harry DeWolf shortly after launch in 2018. The ship was commissioned into the Royal Canadian Navy in June, 2021.
It’s a common fact that I love the AOPS.
I am perhaps their biggest online defender, despite the hate, the early issues, and the slander. They, to me, are the perfect vessel for what we require up North, modular, flexible, with a whole world’s of potential.
The six vessels that make up the DeWolfe-class have kept themselves busy, so busy that you often forget that they are, primarily, Arctic vessels. Now that isn’t to say they can’t take other tasks, nor should they be limited.
OP CARRIBE, a trip to Antarctica, hosts of exercises. The AOPS manage to be kept busy, while still finding time for trips up North, although not nearly as much as many would seem to like.
Their ability to hold containerized payloads has also seen them used as testbeds for various capabilities, including towed arrays for ASW, submarine rescue equipment, and in the future, RMDS and unmanned systems like Cellula Robotics’ Guardian AUV.
Indeed, the AOPS are slowly, though surely coming into their own. Yet it is those things it does well, that potential, that puts them in the spotlight among a fleet that is aging and soon set to dwindle in numbers over the next decade.
The looming writing off of the Kingston-class is coming faster and faster everyday, and soon, they will be gone. The little workhorses, whom performed far more than anyone could have asked of them.
The Kingston-class Maritime Coastal Defence Vessel (MCDV) HMCS Moncton in Baltimore harbour for Sailabration 2012.
Photo by Acroterion via Wikimedia Commons.The Kingstons have been a backbone, beyond the littoral-patrolling minesweeper they were envisioned as when the MCDV project was first stood up.
Yet the Kingstons as we know them are to be retired with no true replacement, their original tasks overtaken by other systems and automation.
Their original replacement, as part of the OPV project has evolved into the Canadian Multi-Mission Corvette, a vessel envisioned to one day be a true second-line combatant to complement the River-class destroyers.
Instead the tasks of the Kingstons shall fall onto the small number of AOPS in service. They will be tasked, not only to fulfill their role as Arctic Patrol ships, but now take the mantle of fulfilling a host of growing secondary tasks that has been filled by these cheaper, smaller vessels.
Add on a Halifax-class that is struggling to stay afloat, bouncing around various states of condition and expected to keep sailing for another decade. Even as the River enter service, the tasks of the Kingstons will not be filled by them.
It’s a lot of strain and demand to put on vessels that are not only significantly larger than the Kingstons, but also significantly more expensive to operate on fulfilling tasks like OP CARRIBE, where while they may be very valuable assets, might not be optimal in lieu of smaller vessels that can easily fill the same role just as efficiently.
On that note it also can’t be understated that the more we put on the AOPS, the more we take it away from its Arctic taskings, and the more we expect of these six vessels to do almost every secondary task, the more we create gaps in our continental defence.
Six AOPS not only for Arctic Patrol, but MCM, Submarine Support, Seabed Warfare, things like OP CARRIBE … How can we expect these vessels to remain in service for the next quarter-century with all this strain?
We don’t talk about these vulnerabilities a lot, but as it stands Canada is severely vulnerable to adversaries and foreign actors ability to leverage asymmetric methods to limit our ability to respond abroad and severely harm Canada’s strategic infrastructure.
April 5, 2025
World of Warships – Battle Of Jutland
Sea Lord Mountbatten
Published 14 Jul 2024Hey guys! Today I am happy to bring you guys Jutland! Our cinematic on the 1916 Naval Battle of Jutland! Enjoy!
(more…)
March 27, 2025
Alaska legally required to use LNG ships that don’t exist thanks to the Jones Act of 1920
As J.D. Tuccille reports, Alaska is having to ask the US government for a waiver from the requirements of the 1920 Merchant Marine Act to allow them to legally transport their own liquid natural gas within the state:

“LNG Carrier Alto Acrux” by kenhodge13 is licensed under CC BY 2.0 .
Alaska is a cold state where residents need energy to keep the chill at bay. Fortunately, the state is blessed with natural resources, including abundant oil and natural gas that can help satisfy that need. Unfortunately, as I’ve written before, a nationalistic, century-old law requires that shipping between American ports be conducted only by U.S.–built and –flagged ships. And there aren’t any liquid natural gas tankers that satisfy the requirement. Now Alaska officials are seeking a waiver so they can use their own resources to resolve a growing energy crunch.
[…]
Over a century ago, Congress passed the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, better known as the Jones Act, mandating that “No merchandise … shall be transported by water…between points in the United States…in any other vessel than a vessel built in and documented under the laws of the United States and owned by persons who are citizens of the United States”. There’s more to it, but the nationalistic law, intended to protect American shipping, effectively barred transporting goods between American ports in foreign-built and foreign-flagged vessels. That means North Slope natural gas can be transported to Alaska’s populated south only in American tankers. If you can find any. You can’t.
“LNG carriers have not been built in the United States since before 1980, and no LNG carriers are currently registered under the U.S. flag,” the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) reported in 2015. And, while you’d think that demand — not just in isolated states like Alaska and Hawaii, but also territories like Puerto Rico — would drive supply, there’s a huge hurdle. “U.S. carriers would cost about two to three times as much as similar carriers built in Korean shipyards and would be more expensive to operate,” the GAO added.
The GAO created its report at a time when Congress was considering extending the Jones Act to require that exports of natural gas be carried only in U.S.-flagged shipping. The GAO concluded that such a law would “increase the cost of transporting LNG from the United States, decrease the competitiveness of U.S. LNG in the world market, and may, in turn, reduce demand for U.S. LNG”.
Congress wisely dropped the idea of extending the Jones Act, but Alaskans are still stuck with the original law, waiting for nonexistent domestically-built LNG tankers to show up with loads of North Slope natural gas. If they don’t wait but instead try to ignore a law with which it’s impossible to comply, they risk millions of dollars in fines, since the federal Department of Justice vigorously enforces the Jones Act.
In 2017, the feds fined an energy company $10 million for transporting a drill rig from the Gulf of Mexico to Alaska’s Cook Inlet in a foreign-flagged vessel. The company planned to bring more natural gas to the resource-rich but energy-starved state.
March 13, 2025
Leadership of HMCS Harry DeWolf take a TOUR of HMCS Haida National Historic Site, Parks Canada
Royal Canadian Navy / Marine Royale Canadienne
Published 10 Nov 2024Canada’s “most fightingest ship” served in our Navy for 20 years between 1943 and 1963. The last Tribal Class Destroyer in the world, it and its company persevered through the Second World War, Korean War and Cold War.
The ceremonial flagship of our Navy, HMCS Haida was saved from the scrapyards and now rests in Hamilton as a museum ship, a Parks Canada National Historic Site.
One of HMCS Haida‘s Captains was the Naval hero Harry DeWolf — the namesake of the Harry DeWolf Class of ships. The grandson of a Veteran who served on the ship recently took the leadership of HMCS Harry DeWolf for a tour after arriving alongside, showing the stark differences between the newest vessels of our fleet and this vintage destroyer showing the many differences between life in the Navy then and now.
#CanadaRemembers #HelpLeadFight
March 4, 2025
The Titanic Survivors Arrive in New York – Hamilton Pudding
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 18 Oct 2024A tart with apricot jam topped with a vanilla cookie-like filling, and toasted meringue
City/Region: Carpathia | United Kingdom | United States of America
Time Period: 1903 | 1912The menu from the last meal aboard RMS Carpathia before it docked in New York, carrying the survivors of the Titanic, lists Pouding Hamilton as one of the dessert options. After a fruitless search of my late 19th- and early 20th-century cookbooks, I finally found one recipe for it in a newspaper from 1903.
Honestly, I don’t know why there isn’t more mention of this tart. It’s delicious. The texture has kind of a wonderful crumbly shortcrust quality to it, and it’s not too sweet. It’s reminiscent of a vanilla cookie with jam, and you could really swap out the apricot jam for any flavor you like. I could see this being a great dessert for the holidays.
Hamilton Pudding –
Line a pie dish with a good short crust and cover the bottom with a layer of apricot jam; then fill up with the following mixture: Cream three ounces of butter with the same quantity of caster sugar, then add the yolks of two well beaten eggs and the white of one. Sift in by degrees three ounces of flour and flavor with a few drops of vanilla essence. Bake in a moderate oven and when nearly cooked beat the remaining white of egg to a stiff froth and lay it on top in tough lumps. Return the pudding to the oven till it is slightly browned.
— The Gazette, York, Pennsylvania, Sunday, August 9, 1903.