Whitehall Moll History Clips
Published 11 Feb 2019Dr David Starkey reveals how Winston Churchill’s biography of his ancestor John Churchill marked out Winston as the only politician who truly understood war — just as WWII loomed.
January 20, 2022
David Starkey — The Churchills episode 2
January 19, 2022
Neville Chamberlain, the “great appeaser”
Alexander Larman considers an attempt to paint British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain in a much more positive light than his popular image after appeasement failed:

Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain at Heston Aerodrome, holding up a copy of the Anglo-German Declaration he had negotiated with Adolf Hitler, 30 September, 1938.
Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe via Wikimedia Commons.
On 30 September 1938, the Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain waved a piece of paper in his hand and declared “My good friends, for the second time in our history, a British Prime Minister has returned from Germany bringing peace with honour. I believe it is peace for our time.” He was, of course, incorrect. Less than a year later, Britain was at war with Germany, and the piece of paper was rendered meaningless.
Posterity has been hard on Chamberlain, regarding him as one of the least effective British premiers, and he has been entirely overshadowed by his more charismatic and successful replacement, Winston Churchill. Yet the bestselling author Robert Harris took a more sympathetic view of Chamberlain, and suggested in his 2017 novel Munich that, far from the Prime Minister being a hapless blunderer, he was in fact a canny tactician who bought his country an invaluable extra year to prepare for the coming conflict. This novel has now been filmed by Netflix, and has attracted particular attention for Jeremy Irons’ sympathetic and warm portrayal of Chamberlain.
Harris has even suggested that “I could perhaps show him as a tragic hero rather than merely the gullible old fool of popular myth … it is a mark of maturity to be able to hold two competing views in one’s head at the same time: that Churchill was vital to the defeat of Germany, and so, in a different way, was Neville Chamberlain.” Does he have a point, or is this just the canny spin of a novelist who has found a new and profitable angle to bring a well-worn story to life?
For my forthcoming book The Windsors at War, dealing with the royals in WWII and their relationships with the politicians of the day, I researched many letters and documents written by Chamberlain, members of the Royal Family and those around him in Downing Street. Several things came to light. There was residual antipathy between Chamberlain, who was an instinctive appeaser, and Churchill, who was not, and the Prime Minister privately derided the other politician as “a bandit” and “a pirate”. He also despised Attlee’s Labour party, calling them experts in “sob-stuff” sentimentality. He can undeniably be accused of high-handedness and complacency. Yet the charge of incompetence is a more deadly one.
Chamberlain himself came from a distinguished political family. His father Joseph was a ruthless Liberal parliamentarian who was said to have originated the phrase “you cannot teach old dogs new tricks”, and his elder brother Austen, one-time Chancellor of the Exchequer and leader of the Conservative Party, demonstrated a confidence in his intellectual abilities that his sibling did his best to emulate. He was not universally popular with his own side – the Conservative MP and diarist Harold Nicolson called him “a bourgeois shit” – but he generally had the support of his party in pursuing his policy of appeasement towards Hitler and Germany, believing – correctly – that Britain could not win the conflict outright.
January 18, 2022
David Starkey – The Churchills episode 1
Whitehall Moll History Clips
Published 7 Jan 2019David Starkey weaves the stories of two great British war leaders: John and Winston Churchill. Hear how John Churchill rose from obscurity to be King James II’s right-hand man.
January 17, 2022
December 24, 2021
How Hitler, Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin Spent Christmas – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 23 Dec 2021They might be four of the most powerful politicians and/or military leaders on earth, but they are also citizens of their respective countries and today we take a look at what they do over the traditional Christmas holidays in 1942.
(more…)
December 17, 2021
Those Olympic rings are more than just tarnished
In First Things, George Weigel notes the, ah, Olympian disdain for mere morality and human decency is far from a new thing as the IOC prepares for the Beijing games in 2022:
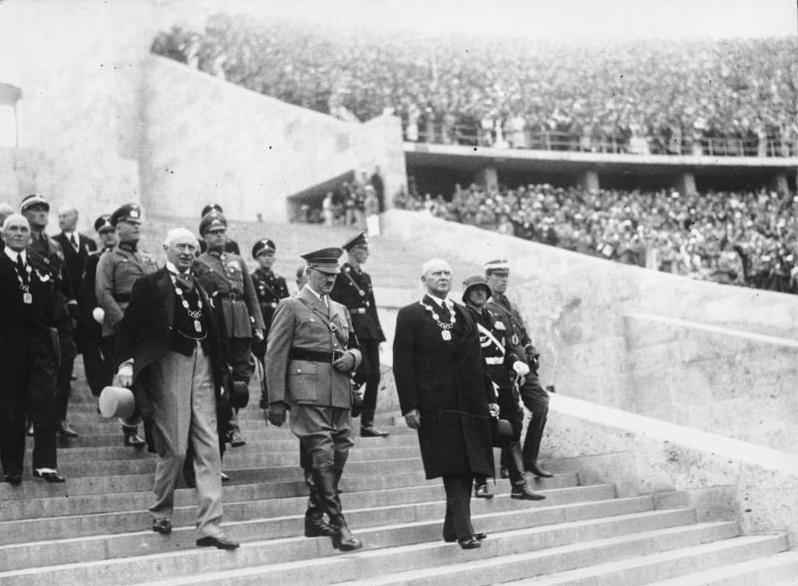

Google translation of the original German caption: “Before the ceremonial opening of the XI Olympic Games. Together with the members of the International and National Olympic Committee, the Führer and Reich Chancellor enters the stadium through the marathon gate. On the left of Adolf Hitler [Henry] Graf Baillet-Latour, on the right His Excellency [Theodor] Lewald.”
German Federal Archives (Accession number Bild 183-G00372) via Wikimedia Commons.
In July 2016, as we were sitting on the fantail of the Swiss sidewheeler Rhone while she chugged across Lake Geneva, my host pointed out the city of Lausanne, where a massive, glass-bedecked curvilinear building was shimmering in the summer sun. “Isn’t that the headquarters of the International Olympic Committee?” I asked. When my friend replied in the affirmative, I said, “I thought I smelled it.”
That rank odor — the stench of greed overpowering the solidarity the Olympics claim to represent — has intensified recently.
Even the casual student of modern Olympic history knows about the August 1936 Berlin Games, at which America’s Jesse Owens, a black man, took four gold medals and trashed Hitler’s Aryan supremacy myth. Fewer may be aware that, in February that year, the Olympic Winter Games were held in the Bavarian town of Garmisch-Partenkirchen. How, we ask today, could two Olympics be held in the Third Reich? How could people not know?
There was some controversy about holding the summer and winter Olympics under Nazi auspices. But in 1936, the German situation was not as comprehensively ghastly as it would become in later years. Yes, the Dachau concentration camp for political prisoners had opened in March 1933, and the Nuremberg Laws banning Jews from German citizenship and prohibiting marriage between Jews and “Aryans” had been enacted in 1935. The horrors of the Kristallnacht pogrom in November 1938 were two years in the future, however, and the satanic Wannsee Conference to plan the “Final Solution” to the “Jewish Question” would come six years later. Clear-minded people ought to have discerned some of the implications of the Nuremberg Laws. But the industrialized mass slaughter of millions, simply because they were children of Abraham, was beyond the imagination of virtually everyone.
So Hitler and his thugs temporarily behaved themselves (sort of) in the run-up to the Garmisch-Partenkirchen and Berlin Olympics. And the International Olympic Committee could salve whatever conscience it had in those days and proceed with the games.
The IOC has no excuses today, two months before the XXIV Olympic Winter Games open in Beijing. Because today, everyone knows.
November 15, 2021
Fighting Nazis with Radios and Funerals – WAH 046 – November 1942, Pt. 1
World War Two
Published 14 Nov 2021As the Winter of 1942/43 is beginning, the German Nazis are under more and more pressure, both on the frontlines and in the occupation zones.
(more…)
November 11, 2021
QotD: War and human capital
… perhaps there is a parallel between the state of human capital in the American elite [today] and the German elite during the war. The German soldiers were the best in the world, but the people further up the line were not the best tacticians. At the upper reaches, the strategists were terrible in all sorts of ways, starting with Hitler, who was laughably inept at running a war. Winning was never an option, but the Germans could have avoided total obliteration if they had better leaders.
The blame for this is always put on Hitler and that’s a good place to start, but the Germans had a brain power problem throughout the planning layer. This is obvious in how they went about making tanks. Instead of going for a tank that was cheap and easy to produce by a civilian workforce, they tried to build tanks that were complex and required specialists to produce. The effects of allied bombing raids were amplified by this strategic blunder in production planning. This is a very basic error in planning and execution.
One possible cause of this was that the middle-aged men who would have been sorting these production and design problems had died during the Great War. The German army tended to “use up” their units, rather than cycle them in and out of lines. That meant that a lot of experience with supply and logistics was lost in the trenches. The British and the Americans rotated units in and out of the lines, thus they came out of the war with a vast number of people with experience in the nuts and bolts of war fighting.
The current ruling class needs the Germans to be seen as the ultimate in super villains, but the truth is the Germans were dumb about a lot of important things. The Russians came up with sloped armor, for example, and the Germans never bothered to steal the idea, even after Kursk. The Germans got their hands on the Churchill tank, but never bothered to learn anything from it. They never learned from the Americans how to use communications to coordinate their artillery and their armor.
In many respects, the story of the tank in the war is a great proxy for the story of human capital and cultural intelligence. The Germans had the best trained military on earth, but they lacked human capital in the strategy and tactics layer. Either the culture was unable to produce it or there was simply not enough smart people to create the necessary smart fraction. That was ultimately why Germany was wiped from the map. It’s probably why no new culture has arisen from that place on the map either.
The Z Man, “Tanking It”, The Z Blog, 2019-03-01.
October 17, 2021
Stalingrad, Stalingrad, Stalingrad, No Retreat! – WW2 – 164 – October 16, 1942
World War Two
Published 16 Oct 2021The Americans win a naval victory off Guadalcanal and even manage to reinforce the Marines there with the first Army units to arrive, but as the week ends the Japanese launch a major offensive on the island. Meanwhile far across the globe, Adolf Hitler orders that all German offensive operations except those at Stalingrad and in the Caucasus cease. There is plenty to do in Stalingrad, though, because this week all hell breaks loose there.
(more…)
September 28, 2021
Debunking the notion that Stalin was an innocent victim of Hitler
At Instapundit, Ed Driscoll links Jakub Grygiel’s review of a new look at World War 2 in Europe, Stalin’s War by Sean McMeekin, which includes a bit of debunking about the relationship between Hitler and Stalin from 1939 to 1941:

Translation of the Russian caption for this image:
People’s Commissar of Foreign Affairs of the USSR V.M. Molotov signs a friendship and border treaty between the USSR and Germany. Among those present: I.V. Stalin, translator of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs V.N. Pavlov, German diplomat G. Hilger (“truncated” version of the photograph of M. Kalashnikov distributed on the net)
Photograph attributed to Mikhail Mikhaylovich Kalashnikov (1906-1944) via Wikimedia Commons.
Stalin was always interested in a war, especially one that would pit the other powers against each other. The expansion of Soviet influence and control required the weakening of the other powers, in particular the Western ones that were opposed to the Communist virus. For Stalin, therefore, the growth of Nazi Germany was a great opportunity: a violent and expansionistic power in the middle of Europe that could take the first swing against the polities standing on his path. Unsurprisingly, the Soviet tyrant was deeply disappointed when France and Britain signed the Munich Agreement with Nazi Germany in 1938 postponing the great European war that he desired. The 1939 Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact coordinated the efforts of Hitler and Stalin, but it benefited the latter more, allowing him to conquer a large swath of Polish territory with minimal effort, eliminating one of the staunchest opponents to Russian westward expansion. A year later, by murdering almost 22,000 Polish officers in Soviet captivity, Stalin further weakened the Polish obstacle to his expansion. “Nations which had been ruled by powerful aristocracies,” Stalin told once to the Yugoslav Milovan Djilas, “like the Hungarians and the Poles, were strong nations” — and, fearing them, he sought to eliminate them. Then, while Germany invaded France, Stalin took over the three Baltic states in a further step westward.
Hitler’s decision to invade Russia in mid-1941 was a surprise to Stalin, but not because he was expecting a lasting peace on his western frontier. Rather, as McMeekin documents, Stalin had ordered very rapid and large military preparations, building airbases and placing forces near the border with the Third Reich in the first half of 1941. None of them were in a defensive posture, and presented a vulnerable high value target to Nazi attacks. When Hitler decided to attack the USSR in June 1941, these Soviet forces were easy pickings for the well-organized, trained, and war tested German army. McMeekin here expands and amends a bold thesis offered in 1990 by Viktor Suvorov, a pseudonym for a GRU agent who defected to the West in the late ’70s and became a historian, that argued that Stalin was actively planning an attack on Germany but was preempted by Hitler. While Suvorov was excessive in his claim that the Red Army was ready for an offensive campaign in 1941 (because, among other reasons, the officer corps was still in shambles after Stalin’s purges) and that Stalin had plans to conquer Europe, he argued that the USSR was never a status quo power satisfied in its borders. After all Soviet Russia had already attempted to march westward in 1920 and was stopped only by the Poles in a desperate battle near Warsaw (the “Miracle on the Vistula”). This westward vector and ambition of Moscow did not abate, and had to pause because of Hitler’s rise and the might of Nazi Germany. As McMeekin points out, the Soviet military posture in 1941 makes no sense if the goal was to defend Soviet-held lands, suggesting that Stalin was thinking of pouncing on Berlin, now the last remaining continental power in Europe. As the Soviet tyrant himself put it, the USSR no longer needed to be locked in a defensive posture, and was “a rapacious predator, coiled in tense anticipation, waiting for the chance to ambush its prey.”
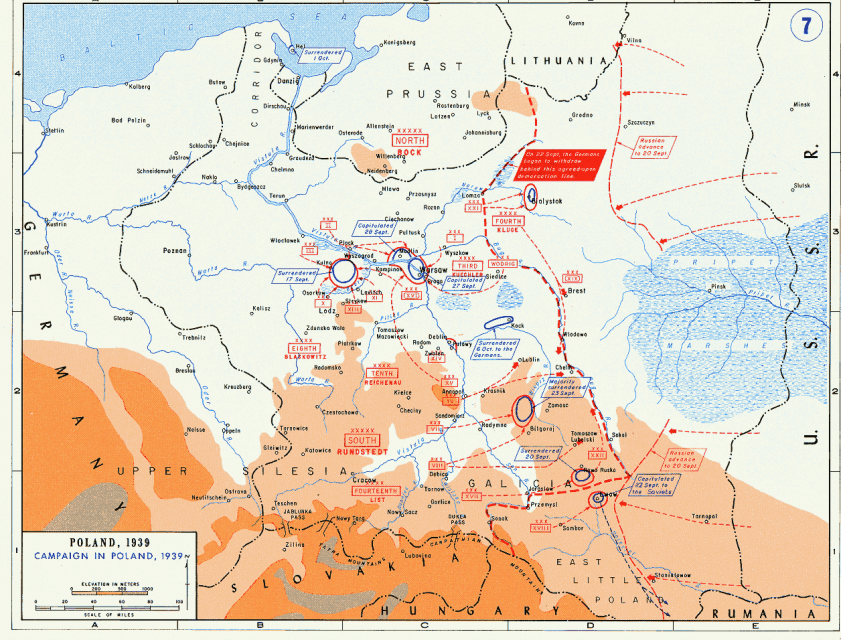
Military situation in Poland, 14 September 1939 (map does not show Slovak Army activity in southern Poland).
United States Military Academy, Department of History via Wikimedia Commons.Stalin, that is, was not an innocent victim of Hitler. Not only he was an active partner from 1938 until 1941, but also he had geopolitical aspirations that were more ambitious than those held by Hitler. And he pursued them methodically and ruthlessly, leaving a trail of death that dwarfed the one produced by the Nazis.
McMeekin then focuses on how the Western allies, Churchill but especially FDR, abetted Stalin’s ambitions. This part of the book is fascinating and depressing at the same time. In a nutshell, Stalin obtained from FDR more than he expected: territory, influence, and materiel. And he did not give anything in exchange for it because FDR and his advisors never asked him for it. For instance, FDR supported the Lend-Lease program, putting his friend Harry Hopkins in charge. Under this program of military aid, the United States supplied a massive amount of weapons, trucks, airplanes, tanks, foodstuff to the Soviet Union in the months of its greatest need, as German troops were driving deep into Russia while the vaunted Soviet armies were melting away. Without such aid, the USSR would have likely been unable to stop the German onslaught and certainly would have been incapable of mustering the resources necessary to push westward. Hence, in this moment there was a good strategic rationale for the American support of Stalin’s defensive efforts against Nazi Germany.
Prior to the launch of Operation Barbarossa, you’d have been hard-pressed to find a more anti-Soviet leader than Winston Churchill, but he immediately recognized that Stalin was more useful to the British as an ally than as a passive enemy. Earlier this year, McMeekin wrote that Stalin “could not have asked for a friendlier British government” than Churchill’s wartime coalition. As Connor Daniels wrote in response at The Churchill Project:

The “Big Three” meet at Tehran, 28 November-1 December, 1943.
Photo attributed to US Army photographer, via Wikimedia Commons.
Churchill’s support for Stalin during the Second World War followed from a simple calculus of the lesser of two evils. Britain could only take on one evil empire at a time, and, of the two, Churchill believed that Nazi Germany posed the greater threat to liberty. He famously remarked, “If Hitler invaded Hell I would make at least a favourable reference to the Devil in the House of Commons.” McMeekin attempts to sidestep this harsh reality, writing: “Whether or not the payoff was worth the price is a question well worth debating.” Churchill’s alliance with the Soviets stands or falls on this question: was Nazi Germany or the Soviet Union the greater danger in 1939?
With hindsight, one can easily marshal facts that portray Soviet communism as the greater evil. According to the best available estimates, the Stalin regime killed 20 millions of its own citizens. Nearly six million of those deaths occurred during the 1932–33 famine brought about by Stalin’s collectivization policies. While Nazi Germany also killed 17 million civilians, most of those deaths occurred after Hitler’s invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941. Thus, on the eve of the Second World War, one could argue — as Chamberlain and the appeasers did — that Nazi Germany served as a useful bulwark against a greater danger: the Soviet Union.
This analysis, however, misses a crucial point — one that Churchill recognized. Until 1939, the horrors of the Soviet regime had been primarily restricted to its own borders, while Nazi Germany had already made its expansionist ambition clear. In 1938, Germany annexed Austria. Later that year, Germany seized the Sudetenland. In 1939, the rest of Czechoslovakia passed under Hitler’s control. The Nazi doctrine of Lebensraum dictated even greater expansion. By contrast, Stalin’s doctrine of “socialism in one country” had kept the Soviet Union relatively peaceful until the Second World War began.
September 26, 2021
Stalingrad, Factory by Factory, Room by Room – WW2 – 161 – September 25, 1942
World War Two
Published 25 Sep 2021Franz Halder, German Army Chief of Staff since the war began, loses his job this week, but the offensive this summer has failed to gain any of its objectives and someone has to take the blame. In the Caucasus it’s slowing to a crawl, and in Stalingrad the fighting is now block by block. Meanwhile, the Japanese are making new plans for a big offensive of their own, to take Guadalcanal once and for all.
(more…)
September 14, 2021
Stalingrad, Hitler’s Obsession – WW2 – 159B – September 13, 1942
World War Two
Published 13 Sep 2021Here’s an extra weekly episode for you. The suburbs of Stalingrad have fallen and the fight for the city proper is about to begin, but before it does, three conferences take place that will decide the scope, the tactics, and the strategy of this battle.
(more…)
Sturmgewehr MP-44 Part II: History & Implementation
Forgotten Weapons
Published 27 Sep 2016Cool Forgotten Weapons Merch! http://shop.bbtv.com/collections/forg…
The Sturmgewehr was the result of a German intermediate cartridge development program that began in the mid-1930s. It was sidelined for a period as the focus of German Ordnance shifted to full-power rifles in 8x57mm with telescopic sights, but as the German fighting in Russia became more desperate, many Ordnance officers realized that the greater firepower offered by the Sturmgewehr concept was one of the few options that might be able to allow depleted German units to effectively hold ground against Russian attacks.
To this end, the guns were issued primarily in the East, with whole companies being equipped in order to focus a maximum amount of firepower, rather than spreading the new rifles piecemeal across all units. Ultimately, of course, this was insufficient to prevent the growing Soviet advance — but for the individual German soldier, an MP-43/44/StG-44 would have been a much more comforting weapon than a Kar98k Mauser!
September 12, 2021
Hitler Finally Fed Up with his Army – WW2 – 159 – September 11, 1942
World War Two
Published 11 Sep 2021Adolf Hitler sacks Wilhelm List, Army Group Commander in the Caucasus. His replacement does not have military command experience. The fighting there is still successful this week, though, as is the advance through the suburbs of Stalingrad. The Japanese are advancing along the Kokoda Trail and on Guadalcanal, but the Axis attacks in North Africa have failed badly.
(more…)
September 10, 2021
The Channel Dash / Operation Cerberus — How to win through refuge in audacity
Drachinifel
Published 9 Jan 2019Today we look at the Channel Dash, also known as one of the few times Hitler was right, the British were asleep and the Germans succeeded in spite of thinking they were all doomed. An operation made up purely of rolling natural 1’s and 20’s.