Forgotten Weapons
Published 10 May 2023It is often said that Hitler personally cancelled the Sturmgewehr development … could that really be true?
Yes! He actually nixed the program three separate times, and the German Army General Staff continued the project behind his back. They knew the rifle was what the Wehrmacht desperately needed if it was to have any hope of victory in the East, and they were determined to bring it to fruition. He did ultimately relent, and approved it to replace the Mauser K98k in early 1944 — but by that time a great deal of opportunity had been lost. Today we will delve into the details of just how the program developed as it pertains to his approval …
(more…)
August 18, 2023
Did Hitler Cancel the Sturmgewehr?
August 17, 2023
Dieppe – One Day in August – Ian Fleming, Enigma and the Deadly Raid – Part 1
WW2TV
Published 29 Nov 2020In less than six hours in August 1942, nearly 1,000 British, Canadian and American commandos died in the French port of Dieppe in an operation that for decades seemed to have no real purpose. Was it a dry-run for D-Day, or perhaps a gesture by the Allies to placate Stalin’s impatience for a second front in the west?
Canadian historian David O’Keefe uses hitherto classified intelligence archives to prove that this catastrophic and apparently futile raid was in fact a mission, set up by Ian Fleming of British Naval Intelligence as part of a “pinch” policy designed to capture material relating to the four-rotor Enigma machine that would permit codebreakers like Alan Turing at Bletchley Park to turn the tide of the Second World War.
In this first show we will look at how the raid has been written about in previous books and the research David undertook and as importantly why he did it. In a future show, we will look at filming in Dieppe itself and explain the sequence of events.
(more…)
See Inside Char B1 | French Tanks of World War Two
The Tank Museum
Published 12 May 2023Chris Copson goes inside one of his personal favourite tanks, the Second World War French Char B1, to discover the quirks and surprises hidden within. Find out why these tanks performed so badly against the German onslaught of 1940, despite being bigger and more heavily armoured than the vehicles they faced.
(more…)
QotD: The decline of the British aristocracy
Probably the battle of Waterloo was won on the playing-fields of Eton, but the opening battles of all subsequent wars have been lost there. One of the dominant facts in English life during the past three quarters of a century has been the decay of ability in the ruling class.
In the years between 1920 and 1940 it was happening with the speed of a chemical reaction. Yet at the moment of writing it is still possible to speak of a ruling class. Like the knife which has had two new blades and three new handles, the upper fringe of English society is still almost what it was in the mid-nineteenth century. After 1832 the old landowning aristocracy steadily lost power, but instead of disappearing or becoming a fossil they simply intermarried with the merchants, manufacturers and financiers who had replaced them, and soon turned them into accurate copies of themselves. The wealthy ship-owner or cotton-miller set up for himself an alibi as a country gentleman, while his sons learned the right mannerisms at public schools which had been designed for just that purpose. England was ruled by an aristocracy constantly recruited from parvenus. And considering what energy the self-made men possessed, and considering that they were buying their way into a class which at any rate had a tradition of public service, one might have expected that able rulers could be produced in some such way.
And yet somehow the ruling class decayed, lost its ability, its daring, finally even its ruthlessness, until a time came when stuffed shirts like Eden or Halifax could stand out as men of exceptional talent. As for Baldwin, one could not even dignify him with the name of stuffed shirt. He was simply a hole in the air. The mishandling of England’s domestic problems during the nineteen-twenties had been bad enough, but British foreign policy between 1931 and 1939 is one of the wonders of the world. Why? What had happened? What was it that at every decisive moment made every British statesman do the wrong thing with so unerring an instinct?
The underlying fact was that the whole position of the monied class had long ceased to be justifiable. There they sat, at the centre of a vast empire and a world-wide financial network, drawing interest and profits and spending them – on what? It was fair to say that life within the British Empire was in many ways better than life outside it. Still, the Empire was underdeveloped, India slept in the Middle Ages, the Dominions lay empty, with foreigners jealously barred out, and even England was full of slums and unemployment. Only half a million people, the people in the country houses, definitely benefited from the existing system. Moreover, the tendency of small businesses to merge together into large ones robbed more and more of the monied class of their function and turned them into mere owners, their work being done for them by salaried managers and technicians. For long past there had been in England an entirely functionless class, living on money that was invested they hardly knew where, the “idle rich”, the people whose photographs you can look at in the Tatler and the Bystander, always supposing that you want to. The existence of these people was by any standard unjustifiable. They were simply parasites, less useful to society than his fleas are to a dog.
George Orwell, “The Lion And The Unicorn: Socialism and the English Genius”, 1941-02-19.
August 16, 2023
Hitler Youth Murder Canadian Soldiers – War Against Humanity 109
[NR: Between me scheduling this to post and it going live, there’s a strong possibility that YouTube will have retro-actively decided it must be restricted to viewing only on YouTube. My apologies if this is the case when you see this post.]
World War Two
Published 15 Aug 2023In Normandy, the Waffen SS butcher their military and civilian enemies while some Allied soldiers play fast and loose with the laws of the war. In China, hundreds of thousands flee their homes as friend, foe, and famine take their toll. Meanwhile, the spectre of deportation haunts Eastern Europe as Stalin reshapes his new empire.
(more…)
August 15, 2023
Gnome et Rhône R5: A Foiled Communist Arms Plan
Forgotten Weapons
Published 26 Apr 2023The R-5 was a French-made copy of the Sten produced after the 1944 liberation of France. It was built by Gnome et Rhône, a French company best known for making aircraft engines. The Sten was familiar to French forces, as many had been supplied as military aid to the Free French as well as Resistance organizations — and it was also a simple and cheap weapon to make.
In the aftermath of Liberation, there was a lot of political jockeying for power in France. Many different factions had armed themselves during occupation, from the far right to the far left, and everyone wanted to be in a position of power in post-war France. Gnome et Rhône was contracted to make 20,000 of the R-5 submachine guns specifically for the PCF, the French Communist Party (Parti communiste français). The Gaullist government found out about the production and took the guns for itself before any reached the PCF.
The R-5 (named because it was produced in Limoges, in the 5th Region of France as organized during the Resistance) was parts-interchangeable with the standard British MkII Sten, despite having a number of unique features. The R5 used a barrel 60mm (2.5 inches) longer than the standard Sten barrel, a solid wooden stock of the same shape as the MkII, and a vertical front grip inspired by the Thompson. Although missing on this example, it also had a rotating receiver cover that could be used to lock the bolt in the forward position.
Of the 20,000 R-5s ordered, only 8,000 were delivered as best we can tell today. They were used by the military within France and also in Indochina and even into Algeria. In the immediate postwar years France was heavily dependent on US and UK war material, but wanted to equip a larger force than the Anglo-American allies were planning to supply. The R-5 made a useful interim weapon while the French arms industry reestablished itself and eventually developed the MAS-49 rifle family and the MAT-49 submachine gun.
(more…)
August 14, 2023
QotD: The US Army in the Korean War
Korea was the kind of war that since the dawn of history was fought by professionals, by legions. It was fought by men who soon knew they had small support or sympathy at home, who could read in the papers statements by prominent men that they should be withdrawn. It was fought by men whom the Army — at its own peril — had given neither training nor indoctrination, nor the hardness and bitter pride men must have to fight a war in which they do not in their hearts believe.
The Army needed legions, but society didn’t want them. It wanted citizen-soldiers.
But the sociologists are right — absolutely right — in demanding that the centurion view of life not be imposed upon America. In a holy, patriotic war — like that fought by the French in 1793, or as a general war against Communism will be — America can get a lot more mileage out of citizen-soldiers than it can from legions.
No one has suggested that perhaps there should be two sets of rules, one for the professional Army, which may have to fight in far places, without the declaration of war, and without intrinsic belief in the value of its dying, for reasons of policy, chessmen on the checkerboard of diplomacy; and one for the high-minded, enthusiastic, and idealistic young men who come aboard only when the ship is sinking.
The other answer is to give up Korea-type wars, and to surrender great-power status, and a resultant hope of order — our own decent order — in the world. But America is rich and fat and very, very noticeable in this world.
It is a forlorn hope that we should be left alone.
In the first six months America suffered a near debacle because her Regular Army fighting men were the stuff of legions, but they had not been made into legionaries.
America was not more soft or more decadent than it had been twenty years earlier. It was confused, badly, on its attitudes toward war. It was still bringing up its youth to think there were no tigers, and it was still reluctant to forge them guns to shoot tigers.
Many of America’s youth, in the Army, faced horror badly because they had never been told they would have to face horror, or that horror is very normal in our unsane world. It had not been ground into them that they would have to obey their officers, even if the orders got them killed.
It has been a long, long time since American citizens have been able to take down the musket from the mantelpiece and go tiger hunting. But they still cling to the belief that they can do so, and do it well, without training.
This is the error that leads some men to cry out that Americans are decadent.
If Americans in 1950 were decadent, so were the rabble who streamed miserably into Valley Forge, where von Steuben made soldiers out of them. If American society had no will to defend itself, neither did it in 1861, at First Manassas, or later at Shiloh, when whole regiments of Americans turned tail and ran.
The men who lay warm and happy in their blankets at Kasserine, as the panzers rolled toward them in the dawn, were decadent, by this reasoning.
The problem is not that Americans are soft but that they simply will not face what war is all about until they have had their teeth kicked in. They will not face the fact that the military professionals, while some have ideas about society in general that are distorted and must be watched, still know better than anyone else how a war is won.
Free society cannot be oriented toward the battlefield — Sparta knew that trap — but some adjustments must be made, as the squabbling Athenians learned to their sorrow.
The sociologists and psychologists of Vienna had no answer to the Nazi bayonets, when they crashed against their doors. The soldiers of the democratic world did.
More than once, as at Valley Forge, after Bull Run, and Kasserine, the world has seen an American army rise from its own ashes, reorient itself, grow hard and bitter, knowledgeable and disciplined and tough.
In 1951, after six months of being battered, the Eighth Army in Korea rose from its own ashes of despair. No man who was there still believes Americans in the main are decadent, just as no man who saw Lieutenant General Matt Ridgway in operation doubts the sometime greatness of men.
T.R. Fehrenbach, This Kind of War: A Study in Unpreparedness, 1963.
August 13, 2023
Panzer Revenge in Normandy – WW2 – Week 259 – August 12, 1944 (CENSORED)
World War Two
Published 12 Aug 2023The Germans launch a counter-attack to sabotage the Allied positions in France. In the Baltics the Soviet advances grind to a halt, but the Soviets are busy making plans to invade Romania in the south. Meanwhile in the center the Warsaw Uprising continues. Across the world the siege of Hengyang comes to its end with a Japanese victory, but the Battle for Guam ends with a Japanese loss.
[Promoted from the comments]: An increasingly persistent challenge for us at TimeGhost is that a growing number of our videos are being age restricted. While this was always the case with War Against Humanity, it’s started affecting this weekly series now too. This most recent video was restricted before it was even publicly published. As such we made the difficult decision to publish a censored version instead this week.
Why is it such a big issue? Well it doesn’t only limit the access to educational content for young people, but also to adult audiences. Age restricted videos have a barrier to viewing that ranges from territory to territory, with some countries requiring viewers not only to have a YouTube account, but to link it with their credit card. Even if an account belongs to a verified adult, it’s still less likely to be recommended an age restricted video.
Our core mission at TimeGhost is making the lessons of our past free and accessible to people around the world. While it’s challenging, especially with the new obstacles from YouTube, it’s still possible thanks to everyone in the TimeGhost Army who backs these videos. To all of you that signed up, or who watch regularly, thank you for joining us on this mission.
August 12, 2023
Churchill and India
Andreas Koureas posted an extremely long thread on Twitter, outlining the complex situation he and his government faced during the Bengal Famine of 1943, along with more biographical details of Churchill’s views of India as a whole (edits and reformats as needed):
The most misunderstood part of Sir Winston Churchill’s life is his relationship with India. He neither hated Indians nor did he cause/contribute to the Bengal Famine. After reading through thousands of pages of primary sources, here’s what really happened.
A thread 🧵
I’ve covered this topic before, but in a recent poll my followers wanted a more in-depth thread. Sources are cited at the end. I’m also currently co-authoring a paper for a peer reviewed journal on the subject of the Bengal Famine, which should hopefully be out later this year.
I’ll first address the Bengal Famine (as that is the most serious accusation) and then Churchill’s general views on India. It goes without saying that there will be political activists who will completely ignore what I have to say, as well as the primary sources I’ll cite. I have no doubt, that just like in the past, there will be those who accuse me of only using “British sources”.
This is not true. I have primary sources written by Indians as well as papers by Indian academics.
Moreover, I have no doubt that such activists will, choose to “cite” the ahistorical journalistic articles from The Guardian or conspiratorial books like Churchill’s Secret War by Mukerjee — a debunked book that ignores most of what I’m about to write about, and is really what sparked the conspiracy of Churchill and the Bengal Famine. For everyone else, I hope you find this thread useful.
(more…)
August 9, 2023
America Plans to Incinerate Japan – War Against Humanity 107
World War Two
Published 8 Aug 2023The Allied Strategic bombing campaign has claimed hundreds of thousands of civilian lives across Europe and has made little real impact on the Axis war machine. Even so, the United States is determined to extend the campaign to Japan. Until now, the vast distances of the Asia-Pacific theatre have protected the imperial enemy. That all changes when the USAAF unleashes the Superfortress.
(more…)
Russian 1895 Nagant Revolver
Forgotten Weapons
Published 20 May 2013One of the mechanically interesting guns that is really widely available in the US for a great price (or was until very recently, it seems) is the Russian M1895 Nagant revolver. It was adopted by the Imperial Russian government in 1895 (replacing the Smith & Wesson No.3 as service revolver), and would serve all the way through World War II in the hands of the Red Army.
As with its other standard-issue arms, the Russian government intended to manufacture the M1895 revolvers domestically. However, when the Nagant was officially adopted the major Russian arsenals were already working at capacity to make the relatively new M1891 rifle, so the first 20,000 revolvers were made by Nagant in Liege, Belgium. In 1898 space had been freed up to start production at the Tula arsenal, where they would be made until 1945 (Ishevsk put the Nagant revolver into production as well during WWII).
The common version available in the US today is a 7-shot, double action revolver chambered for 7.62x38mm. That cartridge is a very long case with the bullet sunk down well below the case mouth. The cylinder of the Nagant cams forward upon firing, allowing the case mount to protrude into the barrel and seal the cylinder gap, thus increasing muzzle velocity slightly. This also allows the Nagant to be used effectively with a suppressor, unlike almost all other revolvers (in which gas leaking from the cylinder gap defeats the purpose of a suppressor).
The Nagant’s 7.62x38mm cartridge pushes a 108 grain jacketed flat-nose projectile at approximately 850 fps (I believe a lighter 85-grain load was also used by the military later, but I haven’t fired any of it), which puts it roughly between .32 ACP and .32-20 ballistics. Not a hand cannon by any stretch, but fairly typical for the era (the 8mm Nambu and 8mm French revolver cartridges were both pretty similar in performance to the 7.62mm Nagant).
As far as being a shooter, the Nagant is mediocre, but reliable. The grip and sights are acceptable (but not great), and the cylinder loads and unloads one round at a time. The low pressure round doesn’t stick in the cylinder, at least. The worst part for a recreational shooter is the trigger, which is very heavy in double action. Single action is also heavy, but very crisp. Recoil is mild, and not uncomfortable at all. The design was simple and effective, and really a good fit for the Red Army and WWII fighting conditions.
August 6, 2023
The Warsaw Uprising Begins! – WW2 – Week 258 – August 5, 1944
World War Two
Published 5 Aug 2023As the Red Army closes in on Warsaw, the Polish Home Army in the city rises up against the German forces. Up in the north the Red Army takes Kaunas. The Allies take Florence in Italy this week, well, half of it, and in France break out of Normandy and into Brittany. The Allies also finally take Myitkyina in Burma after many weeks of siege, and in the Marianas take Tinian and nearly finish taking Guam. And in Finland the President resigns, which could have serious implications for Finland remaining in the war.
(more…)
August 3, 2023
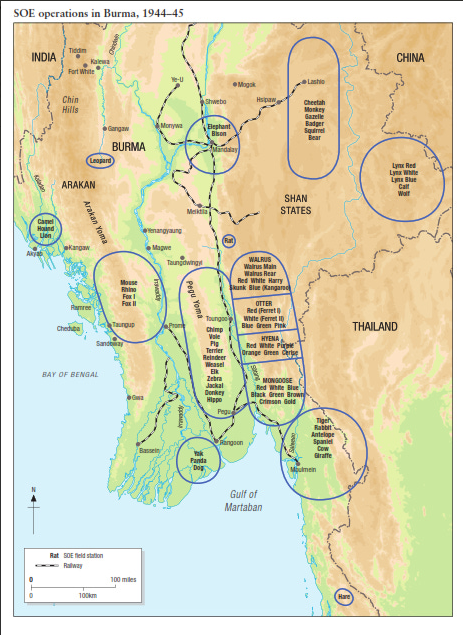
Behind Japanese lines in Burma – SOE and Karen tribal guerillas in 1944/45
Bill Lyman outlines one of the significant factors assisting General Slim’s XIVth Army to recapture Burma from the Japanese during late 1944 and early 1945:
If Lieutenant General Sir Bill Slim (he had been knighted by General Archibald Wavell, the Viceroy, the previous October, at Imphal) had been asked in January 1945 to describe the situation in Burma at the onset of the next monsoon period in May, I do not believe that in his wildest imaginings he could have conceived that the whole of Burma would be about to fall into his hands. After all, his army wasn’t yet fully across the Chindwin. Nearly 800 miles of tough country with few roads lay before him, not least the entire Burma Area Army under a new commander, General Kimura. The Arakanese coastline needed to be captured too, to allow aircraft to use the vital airfields at Akyab as a stepping stone to Rangoon. Likewise, I’m not sure that he would have imagined that a primary reason for the success of his Army was the work of 12,000 native levies from the Karen Hills, under the leadership of SOE, whose guerrilla activities prevented the Japanese from reaching, reinforcing and defending the key town of Toungoo on the Sittang river. It was the loss of this town, more than any other, which handed Burma to Slim on a plate, and it was SOE and their native Karen guerrillas which made it all possible.
In January 1945 Slim was given operational responsibility for Force 136 (i.e. Special Operations Executive, or SOE). It had operated in front of 20 Indian Division along the Chindwin between 1943 and early 1944 and did sterling work reporting on Japanese activity facing 4 Corps. Persuaded that similar groups working among the Karens in Burma’s eastern hills – an area known as the Karenni States – could achieve significant support for a land offensive in Burma, Slim authorised an operation to the Karens. Its task was not merely to undertake intelligence missions watching the road and railways between Mandalay and Rangoon, but to determine whether they would fight. If the Karens were prepared to do so, SOE would be responsible for training and organising them as armed groups able to deliver battlefield intelligence directly in support of the advancing 14 Army. In fact, the resulting operation – Character – was so spectacularly successful that it far outweighed what had been achieved by Operation Thursday the previous year in terms of its impact on the course of military operations in pursuit of the strategy to defeat the Japanese in the whole of Burma. It has been strangely forgotten, or ignored, by most historians ever since, drowned out perhaps by the noise made by the drama and heroism of Thursday, the second Chindit expedition. Over the course of Slim’s advance in 1945 some 2,000 British, Indian and Burmese officers and soldiers, along with 1,430 tons of supplies, were dropped into Burma for the purposes of providing intelligence about the Japanese that would be useful for the fighting formations of 14 Army, as well as undertaking limited guerrilla operations. As Richard Duckett has observed, this found SOE operating not merely as intelligence gatherers in the traditional sense, but as Special Forces with a defined military mission as part of conventional operations linked directly to a military strategic outcome. For Operation Character specifically, about 110 British officers and NCOs and over 100 men of all Burmese ethnicities, dominated interestingly by Burmans mobilised as many as 12,000 Karens over an area of 7,000 square miles to the anti-Japanese cause. Some 3,000 weapons were dropped into the Karenni States. Operating in five distinct groups (“Walrus”, “Ferret”, “Otter”, “Mongoose” and “Hyena”) the Karen irregulars trained and led by Force 136, waited the moment when 14 Army instructed them to attack.
Between 30 March and 10 April 1945 14 Army drove hard for Rangoon after its victories at Mandalay and Meiktila, with Lt General Frank Messervy’s 4 Indian Corps in the van. Pyawbe saw the first battle of 14 Army’s drive to Rangoon, and it proved as decisive in 1945 as the Japanese attack on Prome had been in 1942. Otherwise strong Japanese defensive positions around the town with limited capability for counter attack meant that the Japanese were sitting targets for Allied tanks, artillery and airpower. Messervy’s plan was simple: to bypass the defended points that lay before Pyawbe, allowing them to be dealt with by subsequent attack from the air, and surround Pyawbe from all points of the compass by 17 Indian Division before squeezing it like a lemon with his tanks and artillery. With nowhere to go, and with no effective means to counter-attack, the Japanese were exterminated bunker by bunker by the Shermans of 255 Tank Brigade, now slick with the experience of battle gained at Meiktila. Infantry, armour and aircraft cleared General Honda’s primary blocking point before Toungoo with coordinated precision. This single battle, which killed over 1,000 Japanese, entirely removed Honda’s ability to prevent 4 Corps from exploiting the road to Toungoo. Messervy grasped the opportunity, leapfrogging 5 Indian Division (the vanguard of the advance comprising an armoured regiment and armoured reconnaissance group from 255 Tank Brigade) southwards, capturing Shwemyo on 16 April, Pyinmana on 19 April and Lewe on 21 April. Toungoo was the immediate target, attractive because it boasted three airfields, from where No 224 Group could provide air support to Operation Dracula, the planned amphibious attack against Rangoon. Messervy drove his armour on, reaching Toungoo, much to the surprise of the Japanese, the following day. After three days of fighting, supported by heavy attack from the air by B24 Liberators, the town and its airfields fell to Messervy. On the very day of its capture, 100 C47s and C46 Commando transports landed the air transportable elements of 17 Indian Division to join their armoured comrades. They now took the lead from 5 Indian Division, accompanied by 255 Tank Brigade, for whom rations in their supporting vehicles had had been substituted for petrol, pressing on via Pegu to Rangoon.
August 1, 2023
QotD: US Army culture before the Korean War
The Doolittle Board of 1945-1946 met, listened to less than half a hundred complaints, and made its recommendations. The so-called “caste system” of the Army was modified. Captains, by fiat, suddenly ceased to be gods, and sergeants, the hard-bitten backbone of any army, were told to try to be just some of the boys. Junior officers had a great deal of their power to discipline taken away from them. They could no longer inflict any real punishment, short of formal court-martial, nor could they easily reduce ineffective N.C.O.’s. Understandably, their own powers shaky, they cut the ground completely away from their N.C.O.’s.
A sergeant, by shouting at some sensitive yardbird, could get his captain into a lot of trouble. For the real effect of the Doolittle recommendations was psychological. Officers had not been made wholly powerless — but they felt that they had been slapped in the teeth. The officer corps, by 1946 again wholly professional, did not know how to live with the newer code.
One important thing was forgotten by the citizenry: by 1946 all the intellectual and sensitive types had said goodbye to the Army — they hoped for good. The new men coming in now were the kind of men who join armies the world over, blank-faced, unmolded — and they needed shaping. They got it; but it wasn’t the kind of shaping they needed.
Now an N.C.O. greeted new arrivals with a smile. Where once he would have told them they made him sick to his stomach, didn’t look tough enough to make a go of his outfit, he now led them meekly to his company commander. And this clean-cut young man, who once would have sat remote at the right hand of God in his orderly room, issuing orders that crackled like thunder, now smiled too. “Welcome aboard, gentlemen. I am your company commander; I’m here to help you. I’ll try to make your stay both pleasant and profitable.”
This was all very democratic and pleasant — but it is the nature of young men to get away with anything they can, and soon these young men found they could get away with plenty.
A soldier could tell a sergeant to blow it. In the old Army he might have been bashed, and found immediately what the rules were going to be. In the Canadian Army — which oddly enough no American liberals have found fascistic or bestial — he would have been marched in front of his company commander, had his pay reduced, perhaps even been confined for thirty days, with no damaging mark on his record. He would have learned, instantly, that orders are to be obeyed.
But in the new American Army, the sergeant reported such a case to his C.O. But the C.O. couldn’t do anything drastic or educational to the man; for any real action, he had to pass the case up higher. And nobody wanted to court-martial the man, to put a permanent damaging mark on his record. The most likely outcome was for the man to be chided for being rude, and requested to do better in the future.
Some privates, behind their smirks, liked it fine.
Pretty soon, the sergeants, realizing the score, started to fraternize with the men. Perhaps, through popularity, they could get something done. The junior officers, with no sergeants to knock heads, decided that the better part of valor was never to give an unpopular order.
The new legions carried the old names, displayed the old, proud colors, with their gallant battle streamers. The regimental mottoes still said things like “Can Do”. In their neat, fitted uniforms and new shiny boots — there was money for these — the troops looked good. Their appearance made the generals smile.
What they lacked couldn’t be seen, not until the guns sounded.
T.R. Fehrenbach, This Kind of War: A Study in Unpreparedness, 1963.
July 30, 2023
Bradley Unleashes His Cobra – WW2 – Week 257 – July 29, 1944
World War Two
Published 29 Jul 2023Operation Cobra is the drop that finally opens the floodgates and the Allies make a breakthrough in Normandy; up in the Baltics the Soviets take Shaulyai, Dvinsk, and finally Narva, though their big prize this week is Lvov further south. This happens during the Poles’ Lvov Uprising, which ends badly for the Poles. Things also go badly for the Japanese on Guam, though, as their assault this week devastates their own troops.
(more…)