The Great War
Published 11 Jul 2025In early 1917, the United States was still neutral in the First World War. Meanwhile, German leaders were getting desperate — if they couldn’t find a way to break the war of attrition on the Western Front, the Allies would probably defeat them. The result was multiple gambles that staked everything on a quick victory with the risk of drawing the US into the war.
(more…)
November 22, 2025
Why did the US Enter WW1?
November 18, 2025
Vickers Heavy Machine Gun
Forgotten Weapons
Published 14 Dec 2016I may be a bit biased here, but I believe that the Vickers gun is one of the best all-around firearms ever made. It was designed during an era of experimentation and craftsmanship, with a quality and care that would make it today prohibitively expensive. It was exemplary in action, and served in every environment on earth through six decades and in the hands of 50 different nations. It was an infantry gun, an aircraft gun, an armored vehicle gun, and a shipboard gun.
Captain Graham Hutchison recorded this account of the Vickers in action during an attack on High Wood in August 1916 (exerpted from “The Grand old Lady of No Man’s Land by Dolf Goldsmith):
“For this attack, [ten] guns were grouped in the Savoy Trench, from which a magnificent view was obtained of the German line at a range of about 2000 yards. These guns were disposed for barrage. On August 23rd and the night of the 23rd/24th the whole Company was, in addition to the two Companies of Infantry lent for the purpose, employed in carrying water and ammunition to this point. Many factors in barrage work which are now common knowledge had not then been learned or considered. It is amusing today to note that in the orders for the 100th Machine Gun Company’s barrage of 10 guns, Captain Hutchison ordered that rapid fire should be maintained continuously for twelve hours, to cover the attack and consolidation. It is to the credit of the gunners and the Vickers gun itself that this was done! During the attack on the 24th, 250 rounds short of one million were fired by ten guns; at least four petrol tins of water besides all the water bottles of the Company and urine tins form the neighborhood were emptied into the guns for cooling purposes; and a continuous party was employed carrying ammunition. Private Robertshaw and Artificer H. Bartlett between them maintained a belt-filling machine in action without stopping for a single moment, for twelve hours. At the end of this time many of the NCOs and gunners were found asleep from exhaustion at their posts. A prize of five francs to the members of each gun team was offered and was secured by the gun team of Sgt. P. Dean, DCM, with a record of just over 120,000 rounds.”
The attack on the 24th of August was a brilliant success, the operation being difficult and all objectives being taken within a short time. Prisoner examined at Divisional and Corps Headquarters reported that the effect of the Machine Gun barrage was annihilating, and the counterattacks which had attempted to retake the ground lost were broken up whilst being concentrated east of the Flers Ridge and of High Wood.
In 1963 in Yorkshire, a class of British Army armorers put one Vickers gun through probably the most strenuous test ever given to an individual gun. The base had a stockpile of approximately 5 million rounds of Mk VII ammunition which was no longer approved for military use. They took a newly rebuilt Vickers gun, and proceeded to fire the entire stock of ammo through it over the course of seven days. They worked in pairs, switching off at 30 minute intervals, with a third man shoveling away spent brass. The gun was fired in 250-round solid bursts, and the worn out barrels were changed every hour and a half. At the end of the five million rounds, the gun was taken back into the shop for inspection. It was found to be within service spec in every dimension.
During its service life, the Vickers was made in .303 British, .30-06, 0.50 Vickers, .50 High Velocity, 7×57 Mauser, 7.65×53, 8mm Mauser, 8mm Lebel, 7.7 Japanese, 6.5×54 Dutch, 7.9x57R Dutch, 7.62 NATO, 7.62x54R, 8x52R Siamese, 11mm Vickers, and three different 40mm cartridges.
The Vickers was retired from British military service in 1968, having finally become obsolete. Its GPMG role was taken over by the FN MAG, and its long range indirect fire role performed by 3″ mortars. The Vickers was a weapon which required training and dedication to master, but rewarded its users with phenomenal endurance and a wide range of capabilities. Among all contenders, only the Browning machine gun can attempt to compare to the outstanding qualities of the Vickers, and even the Browning fails to match the elegance of the stalwart Brit.
November 15, 2025
QotD: The innovation of infiltration tactics in trench warfare
One way to respond to a novel tactical problem is with novel tactics. And the impetus for this kind of thinking is fairly clear: if your own artillery is the problem digging you into a hole, then find a way to use less of it.
The mature form of this tactical framework is often called “Hutier” tactics, after German general Oskar Emil von Hutier, though he was hardly the sole or even chief inventor of the method. In its mature form, the technique went thusly: instead of attacking with large waves of infantry which cleared each objective in sequential order, attacks ought to be proceeded by smaller units, carefully trained with the layout of the enemy positions. Those units, rather than having a very rigid plan of attack, would be given those general objectives and left to figure for themselves how to accomplish them (“mission tactics” or Auftragstaktik)1, giving them more freedom to make decisions based on local conditions and the ground.
These elite spearhead units, called Stoßtruppen or “Stormtroopers” were well equipped (in particular with a higher amount of automatic firearms and hand grenades, along with flamethrowers). Importantly, they were directed to bypass enemy strong-points and keep moving forward to meet their objectives. The idea here was that the follow-up waves of normal infantry could do the slow work of clearing out points where enemy resistance was strong, but the stormtroopers should aim to push as deeply as possible as rapidly as possible to disorient the defenders and rapidly envelop what defenses remained.2
These sets of infantry tactics were in turn combined with the hurricane barrage, a style of artillery use which focused on much shorter but more intense artillery barrages, particularly associated with Colonel Georg “Breakthrough” Bruchmüller. Rather than attempting to pulverize defenses out of existence, the hurricane barrage was designed merely to force enemies into their dugouts and disorient the defenders; much of the fire was directed at longer ranges to disrupt roads and artillery in the enemy rear. The short barrage left the ground relatively more intact. Meanwhile, those elite infiltration units could be trained to follow the creeping barrage very closely (being instructed, for instance, to run into the shell explosions, since as the barrage advantages, no gun should ever strike the same spot twice; a fresh shell-hole was, in theory, safe). Attentive readers will recognize the basic foundations of the “move fast, disorient the enemy” methods of the “modern system” here.
So did infiltration tactics break the trench stalemate? No.
First, it is necessary to note that while infiltration tactics were perhaps most fully developed by the Germans, they were not unique to them. The French were experimenting with many of the same ideas at the same time. For instance, basic principles of infiltration were being published by the French General Headquarters as early as April, 1915. André Laffargue, a French infantry captain, actually published a pamphlet, which was fairly widely distributed in both the French and British armies by the end of 1915 and in the American army in 1916, on exactly this sort of method. In many cases, like at the Second Battle of Artois, these French tactics bore significant fruit with big advances, but ran into the problem that the gains were almost invariably lost in the face of German counter-attacks. The Russians, particularly under Aleksei Brusilov, also started using some of these techniques, although Brusilov was as much making a virtue of necessity as the Russians just didn’t have that much artillery or shells and had to make do with less and Russian commanders (including Brusilov!) seem to have only unevenly taken the lessons of his successes.
The problem here is speed: infiltration tactics could absolutely more efficiently overrun the front enemy lines and even potentially defeat multiple layers of a defense-in-depth. But after that was done and the shock of the initial push wore off, you were still facing the same calculus: the attacker’s reinforcements, shells, artillery and supplies had to cross broken ground to reach the new front lines, while the defender’s counter-attack could ride railways, move over undamaged roads and then through prepared communications trenches. In the race between leg infantry and trains, the trains always won. On the Eastern Front or against the Italians fighting under the Worst General In History at Caporetto (1917), the already badly weakened enemy might simply collapse, producing massive gains (but even at Caporetto, no breakthrough – shoving the enemy is not a breakthrough, to qualify as a breakthrough, you need to get to the “green fields beyond” that is open ground undefended by the enemy), but against a determined foe, as with the 1918 Spring Offensives, these tactics, absent any other factor, simply knocked big salients3 in the line. Salients which were, in the event, harder to defend and brought the Germans no closer to victory. Eventually – often quite rapidly – the front stabilized again and the deadlock reasserted itself. Restoring maneuver, the actual end-goal of these tactics, remained out of reach.
None of this is to say that infiltration tactics were useless. They represented a real improvement on pre-war infantry tactics and continue to serve as the basis for modern infantry tactics. But they could not break the trench stalemate or restore maneuver.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: No Man’s Land, Part II: Breaking the Stalemate”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-09-24.
- Because it doesn’t fit anywhere else, I want to make a rather long note here. There is an odd tendency which I find quite frustrating, in which military concepts, unit designations and terminology from other languages are all translated into English when used, except for German terms. I suspect this has to do with the high reputation German military thinking holds in among the general public and some military practitioners. I do not share this view; both the German Imperial Army and the Nazi Wehrmacht (another term we never translated yet we feel no need to call the French army l’armée de terre) managed to lose the only major wars they were in, leading to the end of the states they served. Both armies were capable at some things and failed at others; their record certainly does not make German some sort of Holy Language of War. Nevertheless, where German technical terms are notable, I will include them so that the reader will know, should they encounter them elsewhere, that this is a term they are already familiar with, albeit in translation.
- It should be noted that the emphasis here remained on envelopment and destruction rather than on disorientation. The latter is a feature of subsequent systems based on German maneuver warfare, but was not a goal of the doctrine itself initially.
- A salient is a bulge in the line such that your position is bordered by the enemy on three sides. Such positions are very vulnerable, since they can be attacked from multiple directions and potentially “pinched off” at the base.
November 14, 2025
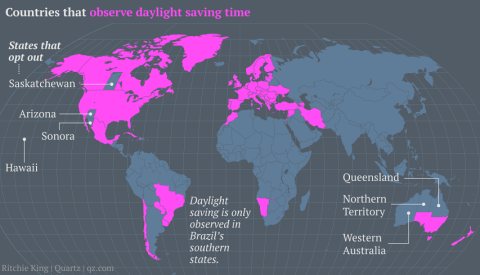
Isn’t it time we scrapped a temporary WW1 practice and stop moving the clocks back and forth?
I don’t know anyone who likes the twice-a-year exercise of resetting all the various clocks in the house, but we still end up doing it (I almost said “like clockwork”). Here in Ontario, we have a law on the books that allows us to dispense with the practice as soon as our immediate neighbours do (Quebec, Manitoba, New York, Michigan and Minnesota … not sure if Pennsylvania and Ohio are included). Mark Naylor says the pressure to get rid of it is certainly building in Europe:
The debate about Daylight Saving Time (DST) has reignited in both Europe and the United States. Spain’s Socialist prime minister Pedro Sánchez is lobbying the EU to put an end to the bi-annual clock change, although he hasn’t stated whether he favors permanent summer (DST) or winter time (also referred to as Standard Time/ST) — which means more light in the evening or morning, respectively. It is a rare point of agreement between the Spanish premier and Donald Trump, who also wants to scrap the clock change, in his case to make summer time permanent.
Both leaders seem to have the public on their side. In a 2018 survey of 4.6 million European citizens, 84% favored abolishing the twice-yearly time changes (in Spain, that figure rose to 93%). A recent poll in the US found that just 12% are in favor of retaining the status quo; 47% are opposed to DST (including 27% who are “strongly opposed”), while 40% are neutral. Legislation passed in 1966 enabled individual states to choose whether or not to implement the practice; today, the only states that don’t are Arizona and Hawaii.
[…]
Sánchez has a strong case. Studies in the US and Europe have shown that the energy saved by DST is negligible. In the 1970s, the US Department of Transportation found that changing the clocks reduced the nation’s electricity consumption by just 1%. A report on Slovakia’s energy usage between 2010 and 2017 put that figure at 0.8%. In Indiana, which switched to DST in 2006, researchers found that the practice led to a 1% increase in consumption, as households used more power for air conditioning on summer evenings and heating on late fall and early spring mornings.
Studies have also linked clock-changing to an increased risk of mood disorders, heart attacks, strokes, and traffic accidents—all a result of the disruption caused to our internal circadian rhythms. “Left to themselves,” says David Ray, a professor of endocrinology at Oxford University, “[these] naturally align with the light–dark cycle, so the only problem comes when you start arbitrarily defining time based on a clock.” A new study by scientists at Stanford University has found that adopting permanent ST, or winter time, would be the best way for us to align with the sun’s cycle, preventing 300,000 strokes a year and resulting in 2.6 million fewer people with obesity.
Trump, meanwhile, has flagged the economic case against bi-annual clock changes. In April, he wrote on Truth Social that the idea of switching to permanent summer time is “Very popular and, most importantly, [there would be] no more changing of the clocks, a big inconvenience and, for our government, A VERY COSTLY EVENT!”
November 12, 2025
The Jet Age: How War Put Us in the Sky – W2W 052
TimeGhost History
Published 10 Nov 2025From the Wright Brothers’ fragile first flight to supersonic jets that shattered the sound barrier — this is the story of how war turned humanity’s dream of flight into the most powerful force on Earth. In just fifty years, aviation evolved from wooden propellers and canvas wings to turbojet engines and supersonic bombers.
What began as a symbol of wonder became the defining weapon of the 20th century — an arms race in the skies that shaped our modern world.
In this episode of War 2 War, we trace how the Second World War and the Cold War pushed aviation to its limits: how Nazi Germany’s Me 262 and Britain’s Gloster Meteor launched the jet age, how the MiG-15 and F-86 Sabre clashed in the skies over Korea, and how the United States and Soviet Union raced for speed, power, and dominance.
Discover:
• How WW2 research built the first jet fighters
• Why the Me 262 and Meteor changed everything
• The jet dogfights of the Korean War (MiG-15 vs F-86 Sabre)
• The rise of supersonic flight and guided missiles
• How the Jet Age reshaped both war and peace
(more…)
November 11, 2025
Four battles of the Canadian Corps
Following on from part one (excerpted here), The Black Horse outlines four major battles that the Canadians fought on the western front during the First World War:
The first part of the series was a political biography of Currie; the second part attempts to tell the story of the Canadian Corps at war through somewhat detailed account of four important battles. The piece is only partly biographical, it partly tells the story of Currie’s war, and partly tells the story the Canadian men who fought for the British Empire in the Great War. It’s a story of incredible martial prowess, but the careful reader will also observe a story of warring duties placed upon the leader of a colonial army; duty to his men, duty to the political leadership of his colonial people and the future of that nation, duty to the objectives of the imperial power on whose behalf he fought, and finally duty to glorious Victory. Currie ended his life understood by those with eyes to see as a great warrior and a military genius; but disliked by his men and hated by the leadership of his people because he prioritized the needs to the Empire and of Victory; but after the war the Empire was of limited service to Currie and to the Canadian people. I leave to the reader, to history, and to God, to decide the value of Victory.
[…]
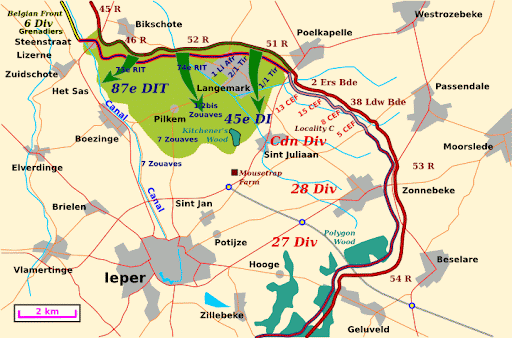
2nd Battle of Ypres
In the spring of 1915 the early dynamic advances of the German army were a distant memory faded behind the great defeat at the First Battle of the Marne. Through the winter both sides had dug in; and many German troops were redeployed to the Russian front. German chemists Walther Nernst and Fritz Haber brought forward the idea of using heavier-than-air Chlorine gas, carried on the wind, to overcome the mathematical impossibility of conventional attack. On April 22, 1915, Albrecht of Württemberg led 7 German divisions to attack 8 Allied divisions, including the 1st Canadian Division under the command of Sir Edwin Alfred Hervey Alderson. The attack began with the release of 168 tons of chlorine gas at about 1700h along a 4 mile stretch of the front around Langemark.
[…]
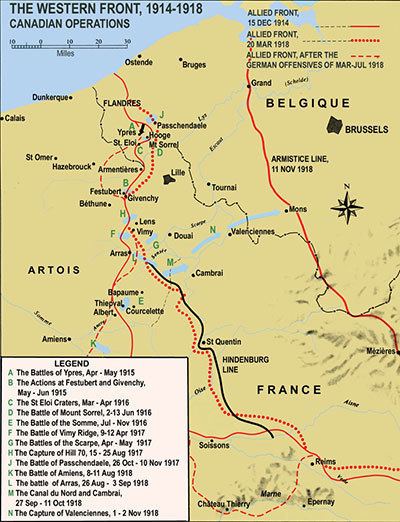
Vimy Ridge
For a year and a half after Ypres, Currie & the Canadian Corps continued to fight desperate engagements along the Western front with no clear strategic conclusion. After heavy losses and a lot of hard-learned lessons at the Somme from Sept 1915-Sept 1916, the Canadian Corps and Currie with them had become both hardened by bitter experience, and desperate to find better ways to prosecute the war. In September 1915 he was recorded to have said “I did not care what happened to me, but to my men, to their wives, their mothers, their children and to Canada I owed a duty which I wanted to fulfill to the very best of my ability”. Later that year as the division struggled with desertion, he ordered the execution of a deserter despite a three hour plea for clemency by the divisional cleric. The decision restored discipline, but haunted Currie’s dreams long afterwards.
In May 1916 Julian Byng took command of the Canadian Corps, replacing Sir Edwin Alderson. In the fall of that year, after heavy losses in a series of engagements at the Somme, Byng was given the opportunity to reorganize and refit the Canadian Corps; he looked to Currie as a key partner in the effort. They replaced the ineffective Ross Rifle with the Lee Enfield, reorganized the platoon structure to include heavy weapons within each platoon [machine guns, mortars, etc.], and implemented new training and tactics like rehearsals for advances, and the “creeping barrage”, carefully coordinated intended to keep artillery shells landing slightly ahead of advancing men.
[…]
Hill 70
After Vimy, Julian Byng was promoted. Currie was promoted in turn to lead the Canadian Corps. He would lead the Corps that he and Byng had made into one of the most effective fighting forces on any side of the conflict and lead it to bloody victory again and again. There is perhaps no better example of the mastery of the Canadian Corps, from top to bottom, than the battle of Hill 70. “Hill 70 was as close to a perfect battle as was ever fought on the Western Front” wrote historian Tim Cook.
[…]
The Hundred Days Offensive & the Pursuit to Mons
As the winter of 1917-18 passed, a new set of highly political decisions concerning whether and how to reorganize the Canadian Corps for the next round of fighting were taken. As noted in part one, Currie opted to split up the newly formed 5th division to reinforce the four divisions of the Canadian Corps and triple the size of the field engineering element. The decision optimized the Canadian Corps as an attacking force; and when they returned to the front that’s exactly how they would be used. Between August 8th and November 11th, 1918, the Canadian Corps fought nine major battles advancing 86 miles, and suffering 45,835 casualties [The force that began the offensive was ~100,000]. By comparison, the substantially larger American Expeditionary Force, over this same period, advanced only 34 miles while capturing only half the number of prisoners, suffering roughly twice the casualties per German division defeated.
In memoriam
A simple recognition of some of our family members who served in the First and Second World Wars:
The Great War
 Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
(Elizabeth’s great uncle)- Private Archibald Turner Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, mortally wounded 25 September, 1915 at Loos, age 27
(Elizabeth’s great uncle) - Private David Buller, Highland Light Infantry, died 21 October, 1915 at Loos, age 35
(Elizabeth’s great grandfather) - Private Harold Edgar Brand, East Yorkshire Regiment. died 4 June, 1917 at Tournai.
(My first cousin, three times removed) - Private Walter Porteous, Durham Light Infantry, died 4 October, 1917 at Passchendaele, age 18
(my great uncle, who had married the day before he left for the front and never returned) - Corporal John Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, wounded 2 September, 1914 (shortly before the First Battle of the Aisne), wounded again 29 June, 1918, lived through the war.
(Elizabeth’s great uncle) - John Eleazar (“Ellar”) Thornton, (ranks and dates of service unknown, served in the Royal Garrison Artillery, the East Surrey Regiment, and the Essex Regiment (dates of service unknown, but he likely joined the RGA in 1899). Put on the “Z” list after the war — recall list. He died in an asylum in 1943.
(my grandfather’s eldest brother) - Henry (Harry) Thornton, (uncertain) Lancashire Fusiliers. (We are not sure it is him as there were no identifying family or birth date listed. Rejected for further service.)
(my grandfather’s second older brother)
The Second World War
- Flying Officer Richard Porteous, Royal Air Force, survived the defeat in Malaya, was evacuated to India and lived through the war.
(my great uncle) - Able Seaman John Penman, Royal Navy, served in the Defensively Equipped Merchant fleet on the Atlantic convoys, the Murmansk Run (we know he spent a winter in Russia at some point during the war) and other convoy routes, was involved in firefighting and rescue efforts during the Bombay Docks explosion in 1944, lived through the war.
(Elizabeth’s father. We received his Arctic Star medal in July, 2024.) - Private Archie Black (commissioned after the war and retired as a Major), Gordon Highlanders, captured during the fall of Singapore (aged 15) and survived a Japanese POW camp (he had begun to write an autobiography shortly before he died)
(Elizabeth’s uncle) - Elizabeth Buller, “Lumberjill” in the Women’s Timber Corps, an offshoot of the Women’s Land Army in Scotland through the war.
(Elizabeth’s mother) - Trooper Leslie Taplan Russon, 3rd Royal Tank Regiment, died at Tobruk, 19 December, 1942 (aged 23).
Leslie was my father’s first cousin, once removed (and therefore my first cousin, twice removed). - Flight Sergeant Kenneth Alexander Porteous, Royal Air Force, air gunner in a Lancaster bomber of 15 Squadron, Bomber Command. Died when his plane was shot down at Wormlitz 10 miles northeast of the target during a raid on Magdeburg, 21 January 1944 (aged 28).
Kenneth was my first cousin, twice removed. - Reginald Thornton, rank and branch of service unknown, hospitalized during the war with shellshock and was never discharged back into civilian life. He died in York in 1986.
(my grandfather’s youngest brother)
My maternal grandfather, Matthew Kendrew Thornton, was in a reserved occupation during the war as a plater working at Smith’s Docks in Middlesbrough. The original design for the famous Flower-class corvettes came from Smith’s Docks and 16 of the 196 built in the UK during the war (more were built in Canada). My great-grandmother was an enthusiastic ARP warden through the war (she reportedly enjoyed enforcing blackout compliance in the neighbourhood using the rattle and whistle that came with the job).
For the curious, the Commonwealth War Graves Commission the Royal British Legion, and the Library and Archives Canada WW1 and WW2 records site provide search engines you can use to look up your family name. The RBL’s Every One Remembered site shows you everyone who died in the Great War in British or Empire service (Canadians, Australians, New Zealanders, South Africans and other Imperial countries). The CWGC site also includes those who died in the Second World War. Library and Archives Canada allows searches of the Canadian Expeditionary Force and the Royal Newfoundland Regiment for all who served during WW1, and including those who volunteered for the CEF but were not accepted.
In Flanders fields the poppies blow
Between the crosses row on row,
That mark our place; and in the sky
The larks, still bravely singing, fly
Scarce heard amid the guns below.We are the Dead. Short days ago
We lived, felt dawn, saw sunset glow,
Loved and were loved, and now we lie
In Flanders fields.Take up our quarrel with the foe:
To you from failing hands we throw
The torch; be yours to hold it high.
If ye break faith with us who die
We shall not sleep, though poppies grow
In Flanders fields.Lieutenant Colonel John McCrae, MD Canadian Army Medical Corps (1872-1918)
Here is Mark Knopfler’s wonderful song “Remembrance Day” from his Get Lucky album, set to a slideshow of British and Canadian images from World War I through to more recent conflicts put together by Bob Oldfield:
Vimy Ridge: Canada’s Finest Hour | History Traveler Episode 386
The History Underground
Published 20 Oct 2024Battle of Arras: Part 2
When it comes to the legendary actions of the Canadian soldiers in WWI, Vimy Ridge looms large above all of the others. This is where the four division of the Canadian Corps would fight side by side for the first time in The Great War. In this episode, we’re walking the ground on the left flank of the Canadian line, looking at the memorial and showing a few things that typically get overlooked in the Vimy Ridge area.
For more on the Battle of Arras, check out The Old Front Line Podcast with Paul Reed & his YouTube channel, @OldFrontLine.
This episode was produced in partnership with The Gettysburg Museum of History. See how you can support history education & artifact preservation by visiting their website & store at https://www.gettysburgmuseumofhistory…
Map animations by @SandervkHistory
QotD: Moltke the Younger and the Schlieffen Plan
Helmuth von Moltke the Younger is a difficult character to uncover, but one essential to understanding the panoply of forces that produced WWI.1 Moltke died in 1916, providing him little opportunity to defend his tenure. His widow had intended to publish an exculpatory collection of evidence of the chaos of German war planning before 1914. However, by then it was 1919, and the documents were deemed harmful to Germany’s attempt to avoid the blame for the war and so not published. This would prove fateful; the documents would be destroyed in World War II.
Moltke therefore proved an ideal scapegoat for the “Schlieffen School”. For the Schlieffen School (mostly officers trained by Schlieffen), the Schlieffen Plan was a true recipe for victory bungled by incompetent execution. However, recent scholarship has shown a more nuanced picture. While Schlieffen did not fully approve of his successor, Moltke was a faithful student of Schlieffen’s concepts. The modifications he made to the plan were not because of a difference in opinion, but of circumstance. Following Schlieffen’s retirement, the French army became more aggressive, necessitating a stronger defense of the Rhine. Likewise, Russian strength and mobilization speed increased, necessitating a greater force allocated to the East. Moltke was also more realistic about the logistical limitations of the all-important right wing of the German offensive. While Schlieffen (allegedly with his dying breath) insisted “keep the right wing strong”, there were simply only so many divisions that could practically advance there. Moltke did his best to adapt the Schlieffen Plan to these changing circumstances, though with mounting fear that the strength of the Entente had placed victory beyond Germany’s strength.
Despite awareness of the long odds, officers continued to press for preventative war in succeeding European crises.3 The term “preventative war” did not mean “preempting the attack of hostile powers” but rather to initiate a war while the strategic balance was most favorable for Germany. While, as mentioned, they had their doubts about the surety of victory, they believed the odds would only get worse. The Schlieffen Plan had been designed for a one-front war against France (in 1905, the year of Schlieffen’s retirement, Russia was in the throes of revolution). Though adapted in later years, the plan remained tenable only so long as Germany had the chance to defeat France before Russian mobilization was completed. As the Russian army expanded and its rail system modernized, the General Staff saw the Schlieffen Plan nearing its expiration date.
The General Staff saw no alternative to Schlieffen’s concept because of its axiomatic focus on total victory. The kind of limited victory that the Elder Moltke had settled for in his later war plans had never entered the vocabulary of the General Staff. As such, the General Staff pressed strongly for war (which it believed was inevitable) to break out before the balance of power swung further against Germany.
The only alternative to this would have been to frankly state the perilous situation in which Germany stood militarily and admit that total military victory was out of reach and German diplomacy would need to be reoriented around this fact. Not only would this course of action been antithetical to the proud traditions of the officer corps, but it would also have been viewed as unacceptably political. What’s more, the Kaiser would have likely viewed such behavior as cowardly if not outright insubordinate. Once again, the Kaiser’s power over personnel decisions meant uncomfortable topics were not broached for fear of instant dismissal.
It is not entirely unjust to accuse German leaders of cowardice or careerism in avoiding these conversations. However, they — like so many who serve under capricious or incompetent heads of state — justified their silence and continued service under the logic of harm reduction. If they resigned (or clashed with the Kaiser leading to their dismissal) they knew they would be replaced by someone more compliant. The Kaiser’s power over personnel meant they understood clearly that they had no leverage.
The Chiefs of the General Staff, for all their influence, were incentivized to focus on the areas of their exclusive responsibility. Nevertheless, the younger Moltke was not passive in his efforts for war. He resumed contact with the Austro-Hungarian General Staff, assuring it of German support should Austria choose war in a crisis. As aforementioned, when crises came to Europe (some instigated by the German foreign ministry) he pressed the chancellor and Kaiser for a preventative war. Both, to their credit, while willing to risk war, would not choose it.
Perhaps most decisively, Moltke and his deputy, Erich von Ludendorff,4 made the decision to hinge the operational plan on an attack on the Belgian city of Liège (hosting a critical rail juncture) before the neutral country could mobilize.5 This modification was made because Moltke desired to avoid violating Dutch neutrality (as Schlieffen had called for). He wisely understood Germany could afford no more enemies and that invading the Netherlands would mean increasing the distance the German right wing would have to cover to gain the French flank, decreasing the odds of success. What’s more, Moltke hoped that Dutch neutrality would allow it to act as a “windpipe” in the event of a long war and a British blockade. However, avoiding Dutch territory complicated German logistics, necessitating the swift seizure of Liège to allow the offensive to meet its strict timetables.
This was a strictly operational decision, made on technical grounds. As such, neither the chancellor nor the Kaiser were informed of this detail of the plan (operational plans were kept strictly secret, with the prior year’s being systematically burned). However, as perceptive readers may have noticed, the need for a coup de main against a neutral country before it mobilized severely limited German strategic flexibility. There was only one deployment plan for war in the West (and only one at all after 1913). In a crisis, Germany was therefore bound to attack before the Belgians manned Liège’s fortifications. Yet this all-important point-of-no-return was unknown to the Kaiser, chancellor, and foreign minister. The General Staff had effectively stripped the Kaiser and civilian leaders of their “right to be wrong”.
Thus, the General Staff had drastically increased the likelihood of war in that the point-of-no-return was kept obscured from those who would be responsible for bring Germany to the brink. As would occur in 1914 during the July Crisis, the Kaiser and his minister could not understand why Moltke was pressing so strongly for war. As historian Annika Mombauer puts it, “Only Moltke knew that every hour counted”.6 The General Staff had — intentionally or not — engineered a situation in which political leadership would have to choose war or abandon its only operational plan. While political leadership was reticent to take this step (especially without the details of the plan) contributing to Moltke’s nervous breakdown, the General Staff ultimately got the war it so desired at the next crisis Germany found itself in. If the coup de main on Liège had been devised as a ploy to force political leadership to engage in a preventative war, it had succeeded.
Ultimately, the predominance of the military over German policy — both foreign and domestic — created an environment in which civilian leaders like Bethmann Hollweg were sidelined, and aggressive military strategies took precedence. This imbalance of prestige, coupled with the narrow, fatalistic worldview of military leaders, contributed to Germany’s march toward war, with little room to acknowledge alternative diplomatic or strategic approaches.
Kiran Pfitzner and Secretary of Defense Rock, “The Kaiser and His Men: Civil-Military Relations in Wilhelmine Germany”, Dead Carl and You, 2024-10-02.
- Helmuth von Moltke the Elder was his uncle.
- Mombauer, Moltke, 109.
- Better known for other work.
- Mombauer, 96.
- Mombauer, 219.
- Rosinski, “Scharnhorst to Schlieffen”, 99.
November 10, 2025
Food in the Trenches of World War One
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 3 Jun 2025Mashed potatoes over a corned beef and onion filling with gravy
City/Region: United Kingdom
Time Period: 1914Many of the young men headed to fight in World War I didn’t already know how to cook, so the British government set up army schools of cookery to teach some of them how to make the most of the rations they were given. Even that ancient army standby, hardtack (clack clack), is better when you can cook it into a stew or pudding.
This potato pie, kind of a simplified preserved meat version of shepherd’s pie, isn’t half bad. If I were to make changes, I would leave out the additional salt (canned corned beef is plenty salty on its own) and add some more onions. While relatively tasty as-is, if you have any HP Sauce lying around, it makes this pie delicious, and many troops would have had access to it during World War I. Delicious and historically accurate: a win-win!
Potato Pie.
16 1/2 lbs. meat, 20 lbs. potatoes, 1 lb. onions, 3 ozs. salt, 1/2 oz. of pepper.
Cut up and stew the onions with jelly from the meat added; boil or steam the potatoes; when cooked mash them. Line the sides of the dish with one-third of the mashed potatoes; place the meat and cooked onions in the centre; season with pepper and salt; cover over the remainder of the mashed potatoes, and bake till the potato cover is brown. As the mashed potatoes absorb the moisture of the meat and render it dry, about 2 pints of gravy prepared from the liquor in which the onions were cooked, should be poured into the pie before serving.
— Manual of Military Cooking. Prepared at the Army School of Cookery, 1914
November 9, 2025
Sir Arthur Currie, commander of the famous Canadian Corps in WW1
As a counterpoint to the OTT summary of Sir Arthur posted last week, here’s The Black Horse with part one of a two-part look at the man’s early career before joining the Canadian Expeditionary Force in Europe:

Sir Arthur Currie with Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig, February 1918.
Libraries and Archives Canada item ID number 3404878.
The Red Ensign is a publication deeply interested in leadership; the good, the bad, and the ugly. For this reason, this Remembrance Day, I have chosen to draw the audience’s attention to the life and times of Sir Arthur Currie, the first Canadian commander of the Canadian Corps during the Great War. This presents an opportunity to both on honour and reflect upon the courage and sacrifice of the men who have fought under the flag of this great nation, but also offers the language to articulate the task facing any who would attempt to lead Canada today. As Currie’s war was defined by the challenge [of] leadership of Canadians in the context of the shifting priorities of the late British Empire, any who would seek to lead Canadians today face will struggle to harmonize efforts on behalf of the Canadian people and the priorities and policies of the American power block which he cannot eschew.
Dulce et decorum est pro patria mori; but when your country is an Imperial Dominion, who and what is “pro patria“, and how can one spend their life for them?
The Man Before the Great Man:
Arthur Currie was born in 1875 in Napperton, Ontario [50 km West of London], the third of eight children living on a homestead belonging to his grandfather. Raised with a the vigorous discipline of a Methodist home, Currie would remain a convicted Christian for his entire life, though he converted to Anglicanism as an adult. Currie was a good student, intending to pursue a career in law or medicine but dropped out of school twice, first temporarily because of the financial constraints brought on by the death of his father, and then for a second time at 19 because of a quarrel with one of his teachers. After leaving school he went West; after a string of failed efforts to establish himself via entrepreneurship and real-estate speculation he joined the Canadian militia as a gunner in 1897 in Victoria B.C. at the age of 23. A giant man (6’3″ at a time when the average Canadian height was 5’7″) with a noted eye for technical detail and, in the words of his son, a “tremendous command of profanity”, he quickly distinguished himself and was promoted to corporal before earning a commission as an officer in 1900. As an officer in peace time Currie was noted for his detailed inspections and his rapid transformation from “one of the boys”, into a rigid disciplinarian. This duality, an officer raised from the ranks, who could both embody the rigid tradition of the British military and who had an intimate familiarity with the life and ways of the enlisted men would become a defining feature of his career.
During Currie’s peace-time career as an officer he maintained a second career as a real-estate [agent]. After becoming head of Matson Insurance Firm 1904, he and the firm invested aggressively in the Victoria real-estate market. In 1913 Currie’s financial situation began to rapidly deteriorate as a consequence of price declines in the real-estate market. Currie’s financial problems nearly led him to refuse to stand up the 50th Regiment Gordon Highlanders of Canada in 1913. In July 1914 Curry used $10,833.34 of regimental funds intended for the purchase of uniforms and kit to pay his personal debts, and found himself facing forcible retirement just as the Canadian Army was being mobilized for war. At the intervention of one of his subordinates, Major Garnet Hughes, he instead accepted promotion as brigadier-general of the 2nd Brigade of the 1st Canadian Division, and ignored correspondence from the new commander of the 50th regiment, Major Cecil Roberts, about the missing funds until he was overseas.
Currie arrived at camp Valcartier on September 1st, 1914 to find himself charged with 10x as many men as he had ever led before, no staff, a shared tent as a command center, and the duty to prepare these men for one of the most difficult theatres of war the world has ever seen. The six months between taking command and the arrival of his brigade in the trenches near Ypres were marked by two mud besotted poorly supplied training camps, shoddy kit, rampant disease, and the company of a certain bear that was to become beloved by children around the world. Through this period Currie was well liked by the men, but known as a disciplinarian with an eye for technical detail. In March 1915 the brigade was deployed to what was expected to be a quiet part of the front with the intent of allowing the men to gain some experience with trench warfare before they were relied upon for action. Nobody anticipated what would happen next.
November 4, 2025
Sir Arthur Currie, Canada’s best general in WW1
On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, InfantryDort gives a lesson in Canadian military history that your kids are unlikely to ever get in school:
Canada: Let us remind you of what your nation was once capable of, and likely still is again. Time will tell. Courtesy of @grok UNHINGED👇
SIR ARTHUR CURRIE: The Ontario slide-rule psychopath who turned war into a goddamn spreadsheet and made the Kaiser cry uncle.
Listen up, you trench-foot tourists and armchair Haigs. While Europe’s aristocrats were using human meat to plug shell holes, some lanky insurance salesman from Napperton, Ontario rolled up with a protractor and a grudge against inefficiency so pure it could sterilize a field hospital. Six-foot-four of quiet Canadian fury. No Sandhurst polish. No inherited estate. Just a militia gunner who looked at the Western Front and said: “This is sloppy. Let me fix your murder math.”
Vimy Ridge: the ridge that laughed at French corpses for two years. Currie hands every platoon leader a map accurate to the latrine, rehearses the assault until the boys can do it blindfolded in a thunderstorm, then unleashes a creeping barrage so precise it’s basically a Roomba made of high explosives. Four days later the ridge is theirs. France needed therapy. Canada needed a birth certificate.
Hill 70: supposed to be a sideshow. Currie turned it into a German obituary — 9,000 Canadian casualties for 20,000 German ones. That’s not a battle, that’s a hostile takeover with extra steps.
Passchendaele: Haig wants it. Currie says, “Fine, but it’ll cost exactly 16,000 of my boys”. Mud eats them like clockwork. Sixteen thousand. He predicted it to the body. The man could forecast death better than the Farmer’s Almanac predicts frost.
Amiens: the day the German army discovered existential dread. Currie’s corps punches twenty-two kilometers through the Hindenburg Line in four days like it’s made of wet cardboard. Ludendorff calls it “the black day of the German Army” and probably wet his monocle.
The Hundred Days: wherever the Canadians go, the war ends faster — Arras, Cambrai, Canal du Nord. German prisoners start asking for Currie by name like he’s the Grim Reaper’s polite cousin. “Wenn Currie kommt, bricht die Linie.” When Currie shows up, your defense budget becomes a suggestion.
And the best part? He’s not screaming. He’s not posing for propaganda photos with a riding crop. He’s in the back, recalculating artillery tables while lesser generals are still figuring out which end of the horse goes forward.
Post-war? Becomes principal of McGill because apparently breaking the German army wasn’t challenging enough. Gets slandered for “wasting lives” at Mons, sues the bastard for libel, and wins with the same cold precision he used to win battles. Even his lawsuits had kill ratios.
Runner-ups:
Sir Richard Turner — the human participation ribbon. Managed the 2nd Division like success was contagious.Sir David Watson — followed Currie’s plans like IKEA instructions: mostly right, but slower.
Sir Henry Burstall — thought “supporting fire” meant “hope the shell lands somewhere in Europe”.
Currie carried their divisions like a Sherpa with a PhD in applied violence.
Verdict: Currie didn’t just win battles. He invented the modern battlefield while everyone else was still playing medieval siege with extra mustard gas. Montgomery called him “the best corps commander of the war”, and Monty would rather die than compliment anyone.
Share this if you’d let Currie balance your checkbook, plan your wedding, and end your existential crisis with a well-timed barrage. Canada’s greatest general was a nerd with a death wish for waste and a heart that bled maple syrup for every lost soul. Never forget.
October 16, 2025
“The ‘big secret’ of the Soviet archives was that the communists really were communist”
Big Serge talks to historian Sean McMeekin, the author of Stalin’s War and other works that some call “revisionist” for their different views of “settled” historical events:
Big Serge: “One of the first things that stands out about your work is that you have found success writing about topics which are very familiar to people and have a large extant corpus of writing. World War One, the Russian Revolution, World War Two, and now a broad survey of Communism – these are all subjects with no shortage of literature, and yet you have consistently managed to write books that feel refreshing and new. In a sense, your books help “reset” how people understand these events, so for example Stalin’s War was very popular and was not perceived as just another World War Two book. Would you say that this is your explicit objective when you write, and more generally, how do you approach the challenge of writing about familiar subjects?”
Dr. McMeekin: “Yes, I think that is an important goal when I write. I have often been called a revisionist, and it is not usually meant as a compliment, but I don’t particularly mind the label. I have never understood the idea that a historian’s job is simply to reinforce or regurgitate, in slightly different form, our existing knowledge of major events. If there is nothing new to say, why write a book?
Of course, it is not easy to say something genuinely new about events such as the First World War, the Russian Revolution, or World War Two. The scholar in me would like to think that I have been able to do so owing to my discovery of new materials, especially in Russian and other archives less well-trodden by western historians until recently, and that is certainly part of it. But I think it is more important that I come to this material – and older material, too – with new questions, and often surprisingly obvious ones.
For example, in The Russian Origins of the First World War, I simply took up Fritz Fischer’s challenge, which for some reason had been forgotten after “Fischerites” (most of them less than careful readers of Fischer, apparently) took over the field. In the original 1961 edition of Griff nach der Weltmacht (Germany’s “Bid” or “Grab” for World Power, a title translated more blandly but descriptively into English as Germany’s Aims in the First World War), Fischer pointed out that he was able to subject German war aims to withering scrutiny because basically every German file (not destroyed in the wars) had been declassified and opened to historians owing to Germany’s abject defeat in 1945 – while pointing out that, if the secret French, British, and Russian files on 1914 were ever opened, a historian could do the same thing for one of the Entente Powers. I had already done a Fischer-esque history on German WWI strategy, especially Germany’s use of pan-Islam (The Berlin-Baghdad Express), inspired by a similar epigraph in an old edition of John Buchan’s wartime thriller Greenmantle – Buchan predicted that a historian would come along one day to tell the story “with ample documents”, joking that when this happened he would retire and “fall to reading Miss Austen in a hermitage”. So it was a logical progression to ask, if Fischer can do this for Germany’s war aims, why not Russia?
Readers may have missed the obvious Fischer inspiration for Russian Origins owing to the editors at Harvard/Belknap, who thought my original title – the obviously Fischer-inspired Russia’s Aims in the First World War – was boring and unsexy. Probably this helped sell books, but it did lend my critics an easy line that I was “blaming Russia for the First World War” rather than simply applying a Fischer-esque lens to Russia’s war aims. Some also called me Russophobic, which is understandable, though I think it misses the point. To my mind, subjecting Russian strategic thinking, wartime diplomacy and maneuvering to the same scrutiny as those routinely applied to Germany and the other Powers is taking the country seriously on its own terms, rather than ignoring Russia, as nearly every historian of, say, Gallipoli has done.
A book on Russian war aims was also long overdue. Other than an underwhelming Chai Lieven study from 1983 and a few articles, no one had really done this for Russia since Soviet scholars and archivists had (with very different motivations) published annotated volumes of secret Russian diplomatic correspondence back in the 1920s. For me, this was a door wide open, and I walked right in. Stalin’s War is in many ways a sequel to Russia’s Aims in the First World War (my own title!), written in a similar spirit, albeit much longer and in some ways more ambitious.
With the Russian Revolution, it was probably still harder to say anything really new, particularly after the popular histories of Richard Pipes and Orlando Figes (and a huge new literature written partly in response to them) came out in the 1990s. And I do not think my “take” was quite as revisionist or controversial as those on WWI or WW2. What I did try to do, in order to add something new to the story, was to combine my own research in a number of areas (Russian army morale reports before and after Order No. 1, depositions taken after the July Days, police reports from 1917, Bolshevik finances and expropriation policies, etc.) with new work done by others since 1991 on, especially, Russia’s military performance in WWI (a topic almost completely ignored in Cold War era literature on the Revolution, both Soviet and western), to reinterpret both the February and October Revolutions. In full disclosure, I would have preferred to write an ambitious history on just 1917, where I had the most original material and new points to make, but my publisher wanted a one-volume “comprehensive” history of the Revolution, so that is what I wrote. Like most historians and writers, I like to think that I write entirely from inspiration with a free hand, but of course there are all kinds of factors that play into our work.
Getting back to your question – while I have certainly done original research for all of these books, I am hardly the only historian to take advantage of Russian archives opened after the collapse of the USSR in 1991 – including, I should add, all the incredible archival material compiled by Russian researchers in the 1990s and 2000s into huge published volumes of Soviet-era documents. I think it is my mindset that differentiates me from other scholars who have taken similar advantage of this opportunity. Simon Sebag Montefiore, for example, uncovered incredibly rich veins of new material for Stalin. Court of the Red Tsar, as Antony Beevor did for Stalingrad, both of which books made an enormous splash. They’re not exactly “revisionists”, though. Rather, these historians retell stories already partly familiar, but with reams of fascinating new details that greatly enrich the story. I think this is a wonderful way to write history, and thousands of readers evidently agree. It is just not what I do.”
Big Serge: “I’m glad you brought up The Russian Origins of the First World War. This was the first of your books that I read, and I found it interesting for a counterintuitive reason, in that its arguments seem like they should be obvious and not particularly controversial. The essence of the book is that the Tsarist state had agency and tried to use the First World War to achieve important strategic objectives. That should be obvious, after all this was an immensely powerful state with a long pedigree of muscular foreign policy, but people are very accustomed to the Guns of August sort of narrative where all the agency and initiative is with Germany, and everyone else is reduced to the role of objects in a story where Germany is the sole subject.
It makes me think somewhat of a quip that Dr. Stephen Kotkin has used in interviews about his Stalin biographies, when he says that the “big secret” of the Soviet archives was that the communists really were communist. His point is that, even in a very convoluted and secretive regime, sometimes what you see really is what you get. I think you made a similar sort of point with Russian Origins. If I could paraphrase you, the big reveal is that the big, powerful Tsarist Empire was behaving like a big powerful empire, in that it had cogent war aims and it consistently sought to work towards those – so consistently in fact that the war aims were initially largely unchanged after the fall of the monarchy in 1917. You’re saying something very similar with Stalin’s War: the shocking secret here is that a powerful, expansionist, heavily militarized Soviet regime acted like it and worked aggressively to pursue its own peculiar interests.
How do you conceptualize this? It strikes me as a little bit odd, because, as you say, there is sometimes a bit of a stigma round the label “revisionist”, but your books generally present schemas that are fairly intuitive: Tsarist Russia was a big, powerful empire that pursued big imperial aims; Stalin was the protagonist of his own story and exercised a muscular, self-interested foreign policy; the Bolsheviks used extraordinary violence to conquer an anarchic environment. Are you surprised that people are surprised at these things?”
Dr. McMeekin: “I wish I was surprised, and perhaps at first I was, but I suppose that, over the years, I have become inured to the shocked! Shocked! reactions I receive when I point out fairly obvious things. Historians, like most groups, tend to be pack animals, who like to run in safe herds. When it comes to a familiar subject such as the outbreak of World War I, the literature tends to groove around well-trodden themes and questions. Certainly it has done since Fischerites took over the field: it’s Germany all the time, with perhaps a nod to Austria-Hungary in the Serbian backstory, or Britain with the naval race. France and Russia had almost disappeared from the story, as if one of the two major continental alliance blocs was irrelevant. I was heartened that my own treatment of Russia’s role in the outbreak of the war and Russia’s war aims garnered attention and shaped the conversation, both in itself and through Christopher Clark’s bestseller Sleepwalkers (which draws on Russian Origins). By contrast, Stefan Schmidt’s pathbreaking 2009 study of the French role in the outbreak of the war (Frankreichs Aussenpolitik in der Julikrise 1914), which Clark and I draw on heavily, has still not been translated into English, making barely a ripple in the profession. Clark and I have poked around with English-language publishers, trying to gin up interest in a translation, but so far without luck.
With the Second World War, I suppose the “shock” value is still greater, and perhaps therefore even less surprising. In Germany, after all, there are laws on the books making it illegal to “trivialize” the Holocaust, for example by foregrounding Soviet war crimes on the eastern front, and of course whole areas of the war such as the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, Soviet war plans in 1941, and even Lend-Lease are highly sensitive in Russia, though I’ll note that there has been a curious exception for the “full-on” revisionism of Rezun-Suvorov (Icebreaker, etc.) – perhaps because his thesis is so extreme as to be easily caricatured, or maybe just because his books sell so well, it has never been difficult to find them in Russian bookstores. In a way, I also think the popularity of Suvorov’s books in Russia relates to the way they do take the Soviet Union seriously as a great power, as I do, of course – whether or not one agrees with his thesis, and I’m sure many of his Russian readers do not, it is less condescending than western histories that treat the Soviets as passive victims of fate in the Barbarossa story before Stalin woke them up.
I was perhaps more surprised at the visceral reaction to Stalin’s War in Britain, particularly my discussion of Operation Pike (eg British plans to bomb Soviet oil installations in Baku in 1940), which sent certain reviewers into paroxysms of rage I found absolutely bewildering. If anything, I should have thought my sharply critical treatment of Hopkins and Roosevelt would have offended Americans far more gravely than my slightly more sympathetic portrayal of Britain’s wartime statesmen, but it was quite the opposite. Certainly some American Roosevelt admirers were annoyed, but this was nothing like British reviewers’ hysteria over Operation Pike. Curiously enough I had dinner not long ago with one of these reviewers, and he brought up Stalin’s War. He was very civil, full of British charm, but he still wanted desperately to know why I had argued that Britain “should have gone to war against the Soviet Union instead of Nazi Germany”. As always when I am accused of this – another reviewer stated this point blank in the TLS – I simply asked him if he could locate a passage in the book where I had stated any such thing? The entire subject of World War II has become so encrusted with emotion and taboos that I think it clouds people’s vision. They see ghosts.”
October 9, 2025
Russia’s Great Retreat 1915
The Great War
Published 9 May 2025In May 1915, the Central Powers launched one of the greatest offensive operations of the First World War. The armies of Germany and Austria-Hungary planned to smash their way through Russia lines and tip the strategic balance in their favor. The result was one of the biggest and bloodiest campaigns of the war, known today as the Great Russian Retreat.
(more…)
September 20, 2025
Dutch Navy Luger: From World War One to the End of Neutrality
Forgotten Weapons
Published 12 May 2025The Dutch Navy first acquired Luger pistols in 1918 specifically for its aviators. They had 12 German P04 Lugers taken from a German submarine stranded in the (neutral) Netherlands, and 28 more were purchased from DWM in 1918 to round out the 40 guns needed to equip the Naval Air Service. The pistol was formally adopted as Automatische Pistool Nr.1. In 1928, the Dutch Army adopted the 1906 New Model Luger for its own service, and the Navy decided to update its revolvers at the same time. The Navy opted not to get grip safeties, and so took a copy of the German P08 model instead of what the Army had. The first order was placed in 1928 through BKIW in Germany, and deliveries would run until 1939 with a total of 2654 delivered before German invaded in May 1940.
Dutch Army Luger trials:
• Politicians Ruin Everything: Dutch Lu…Dutch East Indies Lugers:
• Lugers for the Dutch East Indies Army
(more…)