It will be seen that British cookery displays more variety and more originality than foreign visitors are usually ready to allow, and that the average restaurant or hotel, whether cheap or expensive is not a trustworthy guide to the diet of the great mass of the people. Every style of cookery has its peculiar faults, and the two great shortcomings of British cookery are a failure to treat vegetables with due seriousness, and an excessive use of sugar. At normal times the average consumption of sugar per head is very much higher than in most countries, and all British children and a large proportion of adults are over-much given to eating sweets between meals. It is, of course, true that sweet dishes and confectionery – cakes, puddings, jams, biscuits and sweet sauces – are the especial glory of British cookery but the national addiction to sugar has not done the British palate any good. Too often it leads people to concentrate their main attention on subsidiary foods and to tolerate bad and unimaginative cookery in the main dishes. Part of the trouble is that alcohol, even beer, is fantastically expensive and has therefore come to be looked on as a luxury to be drunk in moments of relaxation, not as an integral part of the meal. The majority of people drink sweetened teas with at least two of their daily meals, and it is therefore only natural that they should want the food itself to taste excessively sweet. The innumerable bottled sauces and pickles which are on sale in Britain are also enemies of good cookery. There is reason to think, however, that the standard of British cookery – that is, cookery inside the home – has gone up during the war years, owing to the drastic rationing of tea, sugar, meats and fats. The average housewife has been compelled to be more economical then she used to be, to pay more attention to the seasoning of soups and stews, and to treat vegetables as a serious foodstuff and less a neglected sideline.
George Orwell, “British Cookery”, 1946. (Originally commissioned by the British Council, but refused by them and later published in abbreviated form.)
June 10, 2024
QotD: The British sweet tooth
June 9, 2024
QotD: The biological importance of salt to humans
… regardless of whether it was used in agriculture, for preservation, or for cooking, salt was also essential. The human body is constantly losing salt through sweat, and to a certain extent urine, but it tries to keep the blood’s salt concentrations maintained at a certain level. So as the blood loses salt, the body also ejects water to adjust. Ironically, as you lose salt your body responds by drying you out. Without constantly replacing the salt in your body — which is only ever stored for a couple of days at a time — you will at first feel fatigued and a little breathless, but increasingly weak and debilitated, as though sapped of all energy. The slightest exertion would start to bring on cramps, then problems with your heart and lungs, as your body continually shed water. If these did not kill you — and they probably would — you would essentially die through desiccation. The process would be all the faster if you became ill, rendering even the slightest dehydrating fever or bout of diarrhoea utterly lethal.1
A population deprived of salt was thus one that was weaker and more prone to disease — and at a time when the vast majority of the economy’s energy supply came from the straining of muscle, both human and animal, that weakness in effect meant a severe energy shortage. Although the main fuels for muscle power were carb-heavy grains like wheat, rye, oats, and rice, the indispensable ingredient to getting the most out of these grains was salt — just as how nuclear power uses uranium as its fuel, but also requires a suitable neutron moderator. A population deprived of salt would quite literally be more lethargic and sluggish, making it less productive and poorer too.
Salt’s unique properties made it a serious tool of state. In 1633 king Charles I’s newly-appointed Lord Deputy for Ireland, Baron Wentworth, advised controlling its salt supply as a way to make the Irish utterly economically dependent on England. Given salt was “that which preserves and gives value to all their native staple commodities” — herrings, butter and beef — then “how can they depart from us without nakedness and beggary?” Salt would be a method of control, and a profitable one too, being “of so absolute necessity” that it could be sold to the Irish at inflated prices without much dampening demand: salt “must be had whether they will or no, and may at all times be raised in price”.2 Much like economists today, Wentworth saw revenue-raising potential in taxing goods with such unresponsive or “inelastic” demand.
Wentworth’s scheme to control the Irish never came to be. But a great many other countries did choose to tax it. Given a minimum amount of salt had to be consumed by absolutely everyone, monopolising its sale — and levying what was effectively a tax by inflating the price well above the costs of importing or producing it — could function as kind of indirect poll tax, levied more or less per head of both people and livestock, but without any of the administrative hassle of taking and maintaining an accurate census in order to impose such a tax directly.
When compared to other necessities like grain, salt did not need to be traded in especially large quantities either, meaning that its supply could be monopolised with relative ease. And it could not be produced everywhere. Salt tended to be lacking the further you got from the sea coast, unless there happened to be some relatively rare inland sources like salt lakes, brine springs, or rock salt mines. And it could even be lacking on the sea coast where it was either too humid or too cold to get salt cheaply by evaporating seawater using the sun, or where there was insufficient fuel for boiling the brine. These places were thus prone to being charged inflated prices, while the states that controlled places where the costs of production were low — in warmer and drier climes where the salty water of coastal marshes could cheaply be evaporated using only the heat of the summer sun — could extract especially large monopoly profits from the difference. The revenue from controlling solar salt thus became the basis of many kingdoms, some unusually powerful republics, and even empires.
Anton Howes, “The Second Soul”, Age of Invention, 2024-03-08.
1. Roy Moxham, “Salt Starvation in British India: Consequences of High Salt Taxation in Bengal Presidency, 1765 to 1878”, Economic and Political Weekly 36, no. 25 (2001): p.2270–74.
2. George O’Brien, The Economic History of Ireland in the Seventeenth Century (Maunsel and Company Limited, 1919), p.244, which has the transcription of Wentworth’s proposal
June 6, 2024
QotD: Herbert Hoover as Woodrow Wilson’s “Food Dictator”
In 1917, America enters World War I. Hoover […] returns to the US a war hero. The New York Times proclaims Hoover’s CRB work “the greatest American achievement of the last two years”. There is talk that he should run for President. Instead, he goes to Washington and tells President Woodrow Wilson he is at his service.
Wilson is working on the greatest mobilization in American history. He realizes one of the US’ most important roles will be breadbasket for the Allied Powers, and names Hoover “food commissioner”, in charge of ensuring that there is enough food to support the troops, the home front, and the other Allies. His powers are absurdly vast – he can do anything at all related to the nation’s food supply, from fixing prices to confiscating shipments from telling families what to eat. The press affectionately dubs him “Food Dictator” (I assume today they would use “Food Czar”, but this is 1917 and it is Too Soon).
Hoover displays the same manic energy he showed in Belgium. His public relations blitz telling families to save food is so successful that the word “Hooverize” enters the language, meaning to ration or consume efficiently. But it turns out none of this is necessary. Hoover improves food production and distribution efficiency so much that no rationing is needed, America has lots of food to export to Europe, and his rationing agency makes an eight-digit profit selling all the extra food it has.
By 1918, Europe is in ruins. The warring powers have declared an Armistice, but their people are starving, and winter is coming on fast. Also, Herbert Hoover has so much food that he has to swim through amber waves of grain to get to work every morning. Mountains of uneaten pork bellies are starting to blot out the sky. Maybe one of these problems can solve the other? President Wilson dispatches Hoover to Europe as “special representative for relief and economic rehabilitation”. Hoover rises to the challenge:
Hoover accepted the assignment with the usual claim that he had no interest in the job, simultaneously seeking for himself the broadest possible mandate and absolute control. The broad mandate, he said, was essential, because he could not hope to deliver food without refurnishing Europe’s broken finance, trade, communications, and transportation systems …
Hoover had a hundred ships filled with food bound for neutral and newly liberated parts of the Continent before the peace conferences were even underway. He formalized his power in January 1919 by drafting for Wilson a post facto executive order authorizing the creation of the American Relief Administration (ARA), with Hoover as its executive director, authorized to feed Europe by practically any means he deemed necessary. He addressed the order to himself and passed it to the president for his signature …
The actual delivery of relief was ingeniously improvised. Only Hoover, with his keen grasp of the mechanics of civilization, could have made the logistics of rehabilitating a war-ravaged continent look easy. He arranged to extend the tours of thousands of US Army officers already on the scene and deployed them as ARA agents in 32 different countries. Finding Europe’s telegraph and telephone services a shambles, he used US Navy vessels and Army Signal Corps employees to devise the best-functioning and most secure wireless system on the continent. Needing transportation, Hoover took charge of ports and canals and rebuilt railroads in Central and Eastern Europe. The ARA was for a time the only agency that could reliably arrange shipping between nations …
The New York Times said it was only apparent in retrospect how much power Hoover wielded during the peace talks. “He has been the nearest approach Europe has had to a dictator since Napoleon.”
Once again, Hoover faces not only the inherent challenge of feeding millions, but opposition from the national governments he is trying to serve. Britain and France plan to let Germany starve, hoping this will decrease its bargaining power at Versailles. They ban Hoover from transporting any food to the defeated Central Powers. Hoover, “in a series of transactions so byzantine it was impossible for outsiders to see exactly what he was up to”, causes some kind of absurd logistics chain that results in 42% of the food getting to Germany in untraceable ways.
He is less able to stop the European powers’ controlled implosion at Versailles. He believes 100% in Woodrow Wilson’s vision of a fair peace treaty with no reparations for Germany and a League Of Nations powerful enough to prevent any future wars. But Wilson and Hoover famously fail. Hoover predicts a second World War in five years (later he lowers his estimate to “thirty days”), but takes comfort in what he has been able to accomplish thus far.
He returns to the US as some sort of super-double-war-hero. He is credited with saving tens of millions of lives, keeping Europe from fraying apart, and preventing the spread of Communism. He is not just a saint but a magician, accomplishing feats of logistics that everyone believed impossible. John Maynard Keynes:
Never was a nobler work of disinterested goodwill carried through with more tenacy and sincerity and skill, and with less thanks either asked or given. The ungrateful Governments of Europe owe much more to the statesmanship and insight of Mr. Hoover and his band of American workers than they have yet appreciated or will ever acknowledge. It was their efforts … often acting in the teeth of European obstruction, which not only saved an immense amount of human suffering, but averted a widespread breakdown of the European system.
Scott Alexander, “Book Review: Hoover”, Slate Star Codex, 2020-03-17.
June 5, 2024
What Troops Ate On D-Day – World War 2 Meals & Rations
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published May 21, 2024D-Day Scrambled Eggs and Bacon served with toast and D-Day Lemonade
City/Region: United States of America
Time Period: 1944The food in the final days leading up to D-Day was a definite improvement over the sad, dry sandwiches some soldiers had been getting. All-you-can-eat meals of steak, pork chops, sides, lemon meringue pie, ice cream, and even popcorn and candy during movie screenings kept the sequestered troops well fed. The last meal served before the landing was breakfast in the very early hours of the morning, said by many to be scrambled eggs and bacon.
This meal was made in the south of England, but the bacon was from the U.S., so American-style bacon is best here. The eggs don’t taste bad, but the texture is not like fresh scrambled eggs at all (more like tofu). The bacon is real, though, and that really saves the dish. Powdered eggs can be found online and at camping stores.
No. 749. Scrambled Eggs
Water, cold … 2 1/2 quarts (2 1/2 No. 56 dippers)
Eggs, powdered … 1 1/2 pounds (1/2 3-pound can)
Salt … To taste
Pepper … To taste
Lard or bacon fat … 1 pound (1/2 No. 56 dipper)Sift eggs. Pour 1/3 of the water into a utensil suitable for mixing eggs. Add powdered eggs. Stir vigorously with whip or slit spoon until mixture is absolutely smooth. Tip utensil while stirring.
Add salt, pepper, and remaining water slowly to eggs, stirring until eggs are completely dissolved.
Melt fat in baking pan. Pour liquid eggs into hot fat.
Stir as eggs begin to thicken. Continue stirring slowly until eggs are cooked slightly less than desired for serving.
Take eggs from fire while soft, as they will continue to thicken after being removed from heat.No. 750. Diced Ham (or Bacon) and Scrambled Eggs
Add 3 pounds of ham or bacon to basic recipe for scrambled eggs; omit lard. Fry ham or bacon until crisp and brown.
Pour egg solution over meat and fat. Stir and cook as in basic recipe. Additional fat may be needed if ham is used.
— TM 10-412 US Army Technical Manual. Army Recipes by the U.S. War Department, 1946
June 3, 2024
18th Century Spiced Hot Chocolate
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Feb 23, 2024Rich, thick, dark hot chocolate spiced with cinnamon and cardamom
City/Region: England
Time Period: 1747Up until the 19th century, the most popular way to partake of chocolate was to drink it. Aztecs drank a very bitter chocolate, and when Europeans brought it back home, they paved the way for one of the most perfect of food pairings: chocolate and sugar.
This hot chocolate is fairly dark, so feel free to add more sugar if that’s to your taste. It’s super rich and much thicker than most hot chocolates you’d get today, so you may only want to make a small amount of the drink and save the rest of the chocolate for later. The spices jump out at you, and even though mine still had a bit of grittiness from the cocoa nibs (it’s basically impossible to get it completely smooth at home), it was really, really good.
(more…)
May 28, 2024
Why a Tire Company Gives Out Food’s Most Famous Award
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Feb 20, 2024Eugénie Brazier, the chef behind today’s recipe, was a culinary force to be reckoned with. She was described as “a formidable woman with a voice like a foghorn, rough language, and strong forearms”. Both of her restaurants won Michelin stars in the early 20th century, making her the first person to have six. No one else would earn six Michelin stars for 64 years.
By modern Michelin standards, this dish is pretty plain, but it’s still really good. The chicken is cooked simply in butter, and the cream sauce is absolutely fantastic. I was afraid the alcohol would overpower it, but it doesn’t. The sauce takes on a kind of floral woodiness instead of each individual alcohol’s flavor, and it’s so good.
(more…)
May 23, 2024
The Roman Colosseum: What It Was Like to Attend the Games
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Feb 13, 2024Like at sports events today, you could get snacks and souvenirs in and around the Colosseum in ancient Rome. There were sausages and pastries and small sweet snacks, like these dates. Not the same as modern hot dogs and soft serve, but kind of in the same spirit.
These dates are really, really good. You could grind the nuts into a fine paste, but I like the texture a lot when they’re left a little coarse. They’re very sweet from the dates and the honey, but the salt and pepper balance it so well (highly recommend the long pepper here). Definitely give these a try!
(more…)
May 17, 2024
Deviled Bones – The History of Hot Wings
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Feb 6, 2024[Information from the Tasting History page for this video]
Chicken wings tossed in a spicy, complex sauce featuring mushroom ketchup.
The history of hot wings goes much further back than 1964 in Buffalo, New York, as a Google search might have you believe. Deviled bones were a way to use up undesirable chicken wings for centuries before that, calling for leftover cooked joints that still had some meat on them (the bones), and flavorful spices (deviled).
If you’re not a lover of spicy things, like me, then the 1/4 teaspoon of cayenne is plenty. That said, feel free to adjust the amounts of any of the spices to suit your taste. I was afraid that the mustard would be overpowering, but it isn’t. The flavor is complex and full of umami thanks to the mushroom ketchup. This is an easy recipe to do some prep work the day before, as the wings would have originally been leftovers.
Devilled Bones
Take the bones of any remaining joint or poultry, which has still some meat on, which cut across slightly, and then make a mixture of mustard, salt, cayenne, and pepper, and one teaspoonful of mushroom ketchup to two of mustard; rub the bones well with this, and broil rather brownish.
— A Shilling Cookery for the People by Alexis Soyer, 1854.
May 10, 2024
Table Manners in the Ottoman Empire – Acem Pilaf
Text from https://www.tastinghistory.com/recipes/ottomanpilaf:
At an Ottoman banquet, you were only ever meant to eat a few bites of each dish that was brought out (having more was seen as being greedy). But there was no danger of leaving the table hungry, as there could be upwards of dozens of dishes. To European visitors, the order that the dishes were brought out in made no sense. Cakes could be brought out between meat courses, a rich pastry brought out after fish, and fowl after chocolate cake. Amidst this seeming chaos, pilaf was always the last dish served.
Let’s address the elephant in the room and state that yes, the pilaf is supposed to come out layered and all in one piece, but mine did not. Ottoman dishes were meant to be not only flavorful, but beautiful as well. That being said, even if you mold yours in a separate container like I did, it is still delicious (and quite nice looking). The warm spices are a wonderful and unusual combination with the lamb (at least to my palate), and there is a fantastic array of textures.
“Chop a piece of good mutton into small pieces, place them in a pot … add one or two spoonfuls of fresh butter and after frying, take the cooked meat from the pot with a hand strainer. Finely chop three or four onions and fry them, then put the roasted meat on top. Then add plenty of pistachios, currants, cinnamon, cloves, and cardamom on top. After that, according to the old method, one measure of washed Egyptian rice. Add two measures of cold water without disturbing the rice, add sufficient salt, then close the lid of the pot and cover it thoroughly with dough. Boil it slowly on coals and when the water is absorbed, take the cover off, and turn the contents out of the pan onto a dish so it comes out intact. This makes a Pilaw that is very pleasing to the sight, and exceedingly pleasant to the taste.”
— Melceü’t-Tabbâhîn, 1844
May 8, 2024
The cocoa shortage is really the same economic trend that caused the Victorian “servant problem”
Tim Worstall explains not only why your favourite chocolate bar is going to be more expensive, but also why your olive oil will do the same and why it really is the same thing as the Victorian and Edwardian upper class complaints about “the help”:

Upper classes expected maids and other servants to be cheap, eager, and easy to replace. This began to change quickly in the Victorian era, as women found better-paying jobs in commerce and industry that didn’t require bowing and scraping and putting up with constand, casual abuse from oblivious wealthy snobs.
As you might have noticed, cocoa is getting very much more expensive. Futures prices (no, futures are not a good guide to actual market prices but still) have gone from $3,000 a tonne or so (-ish, you understand ) to $12,000 and back to $8,000 or so. According to the usual suspects this is climate change. According to those a little more informed there’s El Nino, there have been a few rusts and plant plagues to deal with. Low prices led to not much planting in recent years — all sorts of little problems that led to that burst of higher prices.
Real prices have changed, the sort of Cadbury’s bar that my wife likes a piece of with her afternoon coffee has gone up by a € a bar in recent weeks (I know, I know, “Send Munnies! Quick!”) and so something must be done.
But there’s a much larger and more significant problem here and one to which there may or may not be a solution. The servant problem.
One of those things you learn when living in foreign is that the poorer a country is the easier it is to get a servant and the cheaper a servant is when you get one. This doesn’t wholly make sense to folk until it’s explained. A poor place is one where wages are low — where wages are low is a poor place. They’re the same statement. So, wages for a servant are low in poor countries.
We can up that a little as well. Poor people spend — truly poor people that is — some 80% of their income on food and shelter. So, when you’re in one of those truly poor places you can gain access to a servant — their fulltime, undivided services — for $2 a day plus a bowl of boiled rice and being allowed to sleep in the barn. Because, if they were out there in the cash economy they’d be paid $2 a day (800 million still live at that level out there) and they’d have to buy their own bowl of rice and a tarpaulin to shelter under out of that.
Servants are cheap in poor places because human labour is cheap in poor places because a place with cheap labour is a poor place. QED.
As places become richer human labour costs more. Which is why the letters pages of The Lady started to fill up with complaints about the uppityness and demands of servants from about the 1880s onwards — about the time that British wages at that low and untrained end first started to substantially rise above mere subsistence. This is also one of our major political problems now that middle class women have the vote. They’re using the franchise to insist that government do something about that servant problem. That’s what all that insistence upon child care subsidies and freebies is about. Those middle class women going off to their terribly important power skirt jobs can no longer afford to hire some working class popsie to look after their kids — so government must be forced to do so instead. The correct answer being look after your own damn kids, obviously.
But cheap labour in poor places:
Britain is at risk of olive oil shortages as the industry is wracked by a production crisis.
Fears are growing over the risk of empty shelves as growers across Europe battle a combination of extreme weather, inflation and high interest rates.
Interest rates matter because you plant, wait some number of years, only then do you gain olives. You will then gain them for many decades even centuries, but that wait without income is more painful the higher interest rates get.
There are rusts, plant plagues, afflicting the crop across much of Europe. Of course we’ve those blaming everything on climate change but that’s just the usual bollocks.
However, low wages in poor places. I live in the middle of an oil producing area. Vast waving acres of olive trees in fact. I’ve also lived, until recently, in an historically poorer area of the same country. Where much of the land — little 2 and 4 acre farms (if they were lucky) which might raise a few goats, a sheep (cheese more than anything) and have a couple or four olive trees — has been simply abandoned. The place is getting richer, no one wants to scrape a living on 4 acres of land these days. Rightly so. 4 acres is an adventurous garden, not a living. The absence of those goats is also why the wildfires are getting so much worse — there’s more scrub to burn.
I can take you to places where there are hundreds of acres of such land. Plenty of olive trees in there too, all fruiting and none of them being picked. Because picking olives from the occasional tree is hard bloody work. Spread a net beneath it, hit the tree hard, a lot. Collect up the net with all the olives. Then sort them. By hand. Each single one needs to be checked (for worms and rot) and then nicked. Then you can take them down to the oil mill (every village has at least one) and you hand over the olives and get back the oil, minus a percentage for the mill owner.
May 7, 2024
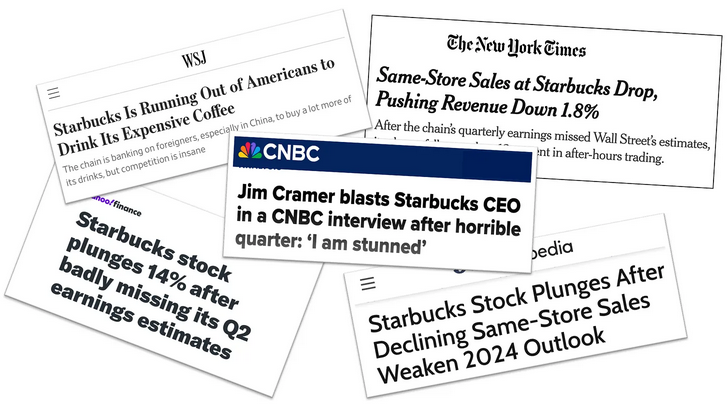
The real problem for Starbucks is that they’ve “turned coffee into something ridiculous”
Ted Gioia will stack his coffee-drinking credentials against anyone, but even he is saddened by what Starbucks did to his favourite hot beverage:
I’ve tried it all, from those crazy hot coffee can dispensers in Tokyo, to Alfred Peet’s humble coffee dispensary in Berkeley (with the master presiding), to actual Colombian in Bogotá and handpicked Kona on the plantations of Hawaii.
Mr. Prufrock has nothing on me. I’ve measured out my entire life in capacious coffee spoons — and make no apologies for it.
But this requires a proper level of gravitas. I don’t just slurp it down. I treat it as a ritual, conducted with mindfulness and reverence. You should do the same.
So I’ve watched with dismay as coffee got turned into a joke.
I mention this in response to the crisis at Starbucks — which reported ugly financial results on Tuesday. Sales are down. Profits are down. Store traffic is down. Everything is down.
Here are some headlines from the last week.
This makes no kind of sense.
How can you lose when you’re selling an addictive substance? Even the most brain-cell-deprived stoner in your high school class eventually figured out how to deal.
When did they get so clueless in Seattle? I’ve heard many explanations.
Some complain that coffee got too expensive — and that’s true. Others will point to the declining quality of the Starbucks experience — and I can’t disagree. I’ve seen things go down in front of the barista straight out of the Battle of Stalingrad.
But the biggest problem is one Starbucks created.
They turned coffee into something ridiculous.
Every comedian now has a five-minute riff on coffee in their routines. In a day when it’s dicey making jokes about people, Starbucks comes to the rescue. Nobody gets offended when those silly beverages are jeered — they are the punchline that keeps on giving.
How did Starbucks become a laughingstock?
Maybe it started with selling a Pumpkin Spice Latte that had zero pumpkin in it. Whatever the reason, there’s something about this beverage that invites mockery — so much so that comedians have actually demanded a moratorium on pumpkin spice latte jokes.
That didn’t stop the drink from gaining a sizable hipster following. Those latte-swilling bros should have been a warning sign. But instead of reading the room, Starbucks pushed ahead with a host of other goofy drinks.
May 4, 2024
Process optimization can definitely be taken too far
Freddie deBoer considers systems that have been overoptimized to the detriment of most users and the benefit of a small, privileged minority:
I know a guy who used to make his living as an eBay reseller. That is, he’d find something on eBay that he thought was underpriced so long as the auction didn’t go above X dollars, buy it, then resell it for more than he paid for it Classic imports-exports, really, a digital junk shop. Eventually he got to the point where, with some items, he didn’t ever have physical possession of them; he had figured out a way to get them directly from whoever he bought an item from to the person he had sold the item to, while still collecting his bit of arbitrage along the way. This buying and selling of items on eBay, looking for deals, was sufficient to be his full-time job and pay for a mortgage. But the last time I saw him, a few years ago, he had gotten an ordinary office job. He told me that it had become too difficult to find value; potential sellers and buyers alike had access to too many tools that could reveal the “real” price of an item, and there was little delta to eke out. He’s not alone. If you search around in eBay-related forums, you’ll find that many longtime sellers have reached similar conclusions. The hustle just doesn’t work anymore.
I don’t suppose there’s any great crime there — it’s all within the rules. And there does appear to still be an eBay-adjacent reselling economy; it’s just that, as far as I can glean, it’s driven by algorithms and bots that average resellers simply don’t have access to. It appears that some super-resellers have implemented software solutions to identify underpriced goods and buy them automatically and algorithmically. They have optimized the system for their own use, giving them an advantage, putting other sellers at a disadvantage, and arguably hurting buyers by eliminating uncertainty that sometimes results in lower-than-optimal-to-sellers prices. This is all in sharp contrast to the early years, when my friend would keep listings for lucrative product categories open – in separate windows, not tabs, that’s how long ago this was – and refresh until he found potential moneymakers. That sort of human searching and bidding work stands at a sharp disadvantage compared to those with information-scraping capacity and automated tools. It’s a good example of how access to data has left systems overoptimized for some users. One of the things that the internet is really good at is price discovery, and these digital tools help determine the “optimal” price of items on eBay, which results in less opportunity for arbitrage for other players.
My current working definition of overoptimization goes like this: overoptimization has occurred when the introduction of immense amounts of information into a human system produces conditions that allow for some players within that system to maximize their comparative advantage, without overtly breaking the rules, in a way that (intentional or not) creates meaningful negative social consequences. I want to argue that many human systems in the 2020s have become overoptimized in this way, and that the social ramifications are often bad.
Getting a restaurant reservation is a good example. Once upon a time, you called a restaurant’s phone number and asked about a specific time and they looked in the book and told you if you could have that slot or not. There was plenty of insiderism and petty corruption involved, but because the system provided incomplete information that was time consuming to procure, there was a limit to how much you could game that system. Now that reservations are made online, you can look and see not only if a specific slot has availability but if any slots have availability. You can also make highly-educated guesses about what different slots are worth on the market through both common sense (weekend evenings are the most valuable etc) and through seeing which reservations get snapped up the fastest in an average week. And being online means that the reservation system is immediate and automatic, so you can train a bot to grab as many reservations as you want, near-instantaneously, and you can do so in a way that the system doesn’t notice. (Unlike, say, if you called the same restaurant over and over again and tried to hide your voice by doing a series of fake accents.) The outcome of all this is that getting a reservation at desirable places is a nightmare and results in a secondary market that, like seemingly everything in American life, is reserved for the rich. The internet has overoptimized getting a restaurant reservation and the result is to make it more aggravating and less egalitarian.
As has been much discussed, nearly the exact same scenario has made getting concert tickets a tedious and ludicrously-pricy exercise in frustration.
May 1, 2024
Lobscouse, Hardtack & Navy Sea Cooks
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Jan 23, 2024Hearty meat and potato stew thickened with crushed hardtack (clack clack)
April 19, 2024
Breakfast in Jane Austen’s England
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Jan 16, 2024What you could tell about someone from their breakfast in Jane Austen’s England, and a recipe for Bath buns as she might have eaten them for her first meal of the day.
Caraway buns topped with glaze, sugar, and caraway, served with butter. Perfect for a Jane Austen inspired breakfast with some hot chocolate
City/Region: England
Time Period: 1769It is a truth universally acknowledged that a person who has recently risen from bed must be in want of breakfast. In Jane Austen’s time, breakfast could be around 8:00 or 9:00 in the morning if you were a manual laborer or servant, or it could be as late as 3:00 or 4:00 in the afternoon if you were upper class.
Jane wrote a letter to her sister Cassandra saying that she wanted to join her on her trip to Bath, but didn’t want to inconvenience their hosts, so she would fill up on bath buns for breakfast. I can see why this would have been a sound strategy. The buns are denser than modern versions, but still soft and very good (they would certainly fill you up). The caraway is present but not overpowering, and they’re sweet but not as sweet as a dessert.
Caraway comfits were candy-coated caraway seeds (think M&Ms), but they don’t use caraway to make them anymore. I mimic them as best I can with caraway seeds and sugar.
To make Bath Cakes.
Rub half a pound of butter into a pound of flour, and one spoonful of good barm, warm some cream, and make it into a light paste, set it to the fire to rise, when you make them up, take four ounces of carraway comfits work part of them in, and strew the rest on the top, make them into a round cake, the size of a French roll, bake them on sheet tins, and send them in hot for breakfast.
— The Experienced English Houskeeper by Elizabeth Raffald, 1769
April 15, 2024
QotD: Cereal cultivation also helped grow the centralized state
Sumer just before the dawn of civilization was in many ways an idyllic place. Forget your vision of stark Middle Eastern deserts; in the Paleolithic the area where the first cities would one day arise was a great swamp. Foragers roamed the landscape, eating everything from fishes to gazelles to shellfish to wild plants. There was more than enough for everyone; “as Jack Harlan famously showed, one could gather enough [wild] grain with a flint sickle in three weeks to feed a family for a year”. Foragers alternated short periods of frenetic activity (eg catching as many gazelles as possible during their weeklong migration through the area) with longer periods of rest and recreation.
Intensive cereal cultivation is miserable work requiring constant toil with little guarantee of a good harvest. Why would anyone leave this wilderness Eden for a 100% wheat diet?
Not because they were tired of wandering around; Scott presents evidence that permanent settlements began as early as 6000 BC, long before Uruk, the first true city-state, began in 3300. Sometimes these towns subsisted off of particularly rich local wildlife; other times they practiced some transitional form of agriculture, which also antedated states by millennia. Settled peoples would eat whatever plants they liked, then scatter the seeds in particularly promising-looking soil close to camp – reaping the benefits of agriculture without the back-breaking work.
And not because they needed to store food. Hunter-gatherers could store food just fine, from salting animal meat to burying fish and letting it ferment to just having grain in siloes like everyone else. There is ample archaeological evidence of all of these techniques. Also, when you are surrounded by so much bounty, storing things takes on secondary importance.
And not because the new lifestyle made this happy life even happier. While hunter-gatherers enjoyed a stable and varied diet, agriculturalists subsisted almost entirely on grain; their bones display signs of significant nutritional deficiency. While hunter-gatherers were well-fed, agriculturalists were famished; their skeletons were several inches shorter than contemporaneous foragers. While hunter-gatherers worked ten to twenty hour weeks, agriculturalists lived lives of backbreaking labor. While hunter-gatherers who survived childhood usually lived to old age, agriculturalists suffered from disease, warfare, and conscription into dangerous forced labor.
Scott Alexander, “Book Review: Against The Grain“, Slate Star Codex, 2019-10-15.