BBC Archive
Published 5 Mar 2023“The ration book has done its job. It’s been a long job. Indeed, children up to school-leaving age have never known life without the ration book.”
On the fourth of July, the rationing of meat in Britain came to an end, the final step in dismantling Britain’s whole wartime system of food distribution. After fourteen long years, Britons can at last tear up their ration books.
Richard Baker looks back at some of the key moments in the story of rationing and de-rationing.
Originally broadcast 5 July, 1954.
June 8, 2023
1954: The END of RATIONING
May 24, 2023
The Original PB&J from 1901
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 23 May 2023
(more…)
December 26, 2022
2nd Canadian Infantry Brigade Christmas celebrations in Ortona, 1943
The folks at the World War Two channel on YouTube posted this to their community page on Christmas Day:
On Christmas Day, 25 December 1943, the 1st Canadian Infantry Division is still engaged in brutal urban combat against the 1. Fallschirmjäger-Division for control over the town of Ortona. But among the rubble of the “Italian Stalingrad”, soldiers of the Seaforth Highlanders of Canada, along with other units [of the 2nd Canadian Infantry Brigade], manage to keep the Christmas spirit alive.
Colonel S. W. Thomson will recount this most unusual Christmas celebration many years later:
“I knew that we would be fully engaged with the enemy on Christmas day. However our most enterprising Quartermaster, Captain Bordon Cameron, was anxious to provide something special for the men at Christmas. Three companies were in the line with one in reserve, often the norm. We decided to feed the reserve company first and feed the remaining companies in relays. as one company finished it would go forward some 300 or 400 yards and relieve the next. Tables, linen, chinaware and candles were scrounged by the reserve company. The tables were set up in rows in our great church Santa Maria with four foot thick walls and my rear H.Q. What a picture, what an appropriate setting for a Christmas dinner on Dec. 25.
“Soup, roast pork, vegetables and Christmas pudding along with a bottle of beer for each of the tattered, scruffy, war weary soldiers was served by HQ and B echelon staff. The Q.M. boys excelled themselves, the impossible had happened. There was a spirit of good-fellowship throughout the church. The signals officer Lieutenant Wilf Gildersleeve played the organ, and our much loved padre Roy Durford led the carol singing. Pipe Major Esson played his pipes several times during the meals drowning out the odd enemy shell burst outside.
“Christmas in Ortona, the meal, yes, but the spirit of the occasion, the look on the faces of those exhausted, gutsy men on entering the church is with me to-day and will live forever.”
To all our followers, readers, and viewers: We wish you a Merry Christmas!
From: Canadian Military History, Vol. 2 (1993)
Picture: Canadian soldiers celebrate Christmas in Ortona, Italy
Source: Canadian Armed Forces
December 15, 2022
Christmas in the WWI Trenches – Xmas Rations
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 13 Dec 2022
December 3, 2022
This Is What A British Sailor Ate In Nelson’s Royal Navy!
History Hit
Published 23 Oct 2021‘This Is What A British Sailor Ate In Nelson’s Royal Navy!’
200 years ago, Britain’s Royal Navy was the most technologically advanced and supremely efficient force in the history of naval warfare.
But what was it like to live and work on board these ships? What did the men eat? How did the ships sail? What were the weapons they used?
In our latest documentary on History Hit TV, to commemorate the Battle of Trafalgar, Dan Snow explores what life would have been like for those whose served in the Nelson’s Navy.
(more…)
November 9, 2022
How-to Eat Like a Marine in the Field
Munchies
Published 11 Jul 2018Lieutenant Glenn-Roundtree shows us how to make his ideal MRE (Meal, Ready-to-Eat), which includes a beef ravioli taco and cherry blueberry cobbler.
(more…)
October 30, 2022
“The Economist is the most over-rated publication in the English language”
I started reading The Economist when I was in college, and became a subscriber for nearly 20 years. Over the last few years, the tone of the articles shifted away from classical liberal toward communitarian or even full-blown socialist cheerleading, so I sadly ended my subscription and haven’t picked up a copy in at least 15 years. According to Ken Whyte in the SHuSH newsletter, things haven’t improved since I stopped paying attention:
The Economist recently said that book publishing in today’s economy resembles book publishing during the Second World War when “paper imports collapsed” and “publishers printed only sure-fire hits”.
The Economist is the most over-rated publication in the English language, especially by itself. I give it marks for its broad range of interests, ability to cover a lot of ground in relatively tight articles, and occasionally solid reporting, but if you’re going to boast incessantly about how smart you are …
… you’d better back it up. The Economist seldom does. It tends to glib, obvious, and sloppy. Most of its articles are written by anonymous b-level freelancers whose best stuff goes to outlets that afford bylines. Their work is edited to a stultifying homogeneity by a haughty grad student with a Financial Times subscription. Or so it reads.
This piece — “Books are Physically Changing Because of Inflation” — is a case in point. Paper imports to the UK were reduced during WW2 but they did not collapse. The problem for the book trade was rationing. The government restricted publishers to 60 percent of their pre-war paper volumes (later falling to 35 percent) and itself used far more tonnage for propaganda than the book industry normally required. Manpower shortages were another factor limiting the production of new titles.
Nor is it true that publishers released “only sure-fire hits”. While much of their paper allotment went to keeping hot-selling books in stock, many bets were placed on new titles and most of them paid. It was wartime and leisure activities were limited. “British publishers found that they could sell virtually any title,” writes Zoe Thomson in The Journal of Publishing Culture.
The article isn’t all bad. It reports that British book publishers are paying 70% more for paper than they were a year ago: “Supplies are erratic as well as expensive: paper mills have taken to switching off on days when electricity is too pricey. The card used in hardback covers has at times been all but unobtainable.”
To cope with the price increases, publishers are printing smaller books on cheaper paper and jamming more words onto the page. Writers are being asked to write shorter and are being held to their word limits.
That reflects the current state of the industry. It’s hardly news, though. SHuSH readers are probably sick of hearing me on rising paper and printing costs, and I’ve just been following what others have written. The cost of printing has more or less doubled since before COVID. Many smaller publishers are already releasing fewer and slimmer titles. If we are headed into a recession, the trend will continue.
September 7, 2022
Tamale Pie: What did WW2 Food Ration Stamps Look Like?
YesterKitchen
Published 3 Nov 2019I hope you enjoy this special trip back in food history!! WW2 brought food rationing to America and American housewives needed recipes to accommodate the scarcity. Never fear, warm, hearty dishes such as this were created to feed the nation. This Tamale Pie is classic war ration cooking and is just YUM!
(more…)
June 4, 2022
Cheese propaganda, 1940 | Archive Film Favourites
Imperial War Museums
Published 14 May 2022With rationing introduced early in 1940 in Britain, this public information film was created to advocate the advantages of eating cheese over meat. The film explains not only the health benefits of cheese with some (unverified) experiments, but also its versatility in cooking, from grilled cheese to califlower cheese, “a meal in itself.” Film curator Matt Lee introduces us to this brilliant cheese propaganda.
You can watch the full Choose Cheese film on IWM’s Film Archive: https://film.iwmcollections.org.uk/re…
Subscribe to our channel for more films from the archives every Thursday!Browse the full IWM film collection and find out more about licencing this film or many others: https://bit.ly/iwmfilms
While our doors are temporarily closed, we still have millions of unforgettable stories to share with you. Your support is invaluable to help ensure we can share them with generations to come – please consider supporting Imperial War Museums today. Support us: https://www.iwm.org.uk/support-us/don…
Follow IWM on social media:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/I_W_M
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/imperialwar…
March 22, 2022
West Germany’s Wirtschaftwunder — the staggering economic postwar recovery
Christian Monson debunks the common tale taught in western schools of reason for the amazing recovery of West Germany’s economy after World War Two:
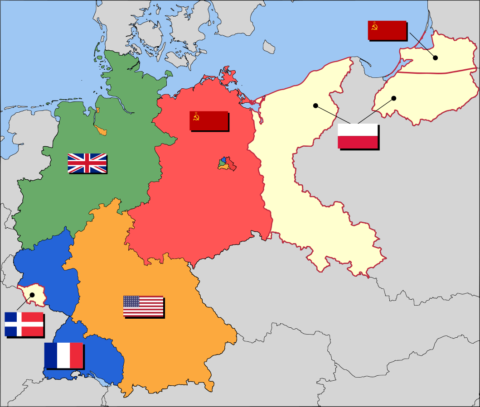
Occupation zone borders in Germany, 1947. The territories east of the Oder-Neisse line, under Polish and Soviet administration/annexation, are shown as cream as is the likewise detached Saar protectorate. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone.
Image based on map data of the IEG-Maps project (Andreas Kunz, B. Johnen, and Joachim Robert Moeschl of the University of Mainz) — www.ieg-maps.uni-mainz.de, via Wikimedia Commons.
This “economic miracle” is commonly referred to as die Wirtschaftswunder. But how did Germany go from rubble to riches in just a decade while neutral countries like Spain merely treaded economic water? If you ask your average American history student, they will say the Marshall Plan, of course!
Unfortunately, the ubiquity of the myth that the Marshall Plan rebuilt Germany is proof that state-controlled education favors propaganda over economic literacy. Despite the fact that most modern historians don’t give the Marshall Plan much credit at all for rebuilding Germany and attribute to it less than 5 percent of Germany’s national income during its implementation, standard history textbooks still place it at the forefront of the discussion about post-war reconstruction.
Consider this section from McDougal Littell’s World History (p. 968), the textbook I was given in high school:
This assistance program, called the Marshall Plan, would provide food, machinery, and other materials to rebuild Western Europe. As Congress debated the $12.5 billion program in 1948, the Communists seized power in Czechoslovakia. Congress immediately voted approval. The plan was a spectacular success.
Of course, the textbook makes no mention of the actual cause of the Wirtschaftwunder: sound economic policy. That’s because, for the state, the Marshall Plan makes great statist mythology.
Not only is it frequently brought up to justify the United States getting involved in foreign conflicts, but it simply gives support for central planning. Just look at the economic miracle the government was able to create with easy credit, they say.
And of course, admitting that the billions of dollars pumped into Germany after WWII accomplished next to nothing, especially when compared to something as simple as sound money, would be tantamount to admitting that the government spends most of its time making itself needed when it isn’t and thereby doing little besides getting in the way.
Credit for the turnaround should be accorded to Ludwig Erhard, according to Alasdair Macleod at the Cobden Centre:
Anyone who favours regulation needs to explain away Germany’s post-war success. Her economy had been destroyed, firstly by the Nazi war machine, and then by Allied bombing. We easily forget the state of ruin the country was in, with people in the towns and cities actually starving in the post-war aftermath. The joint British and American military solution was to extend and intensify war-time rationing and throw Marshall aid at the problem.
Then a man called Ludwig Erhard was appointed director of economics by the Bizonal Economic Council, in effect he became finance minister. He decided, against British and American misgivings, as well as opposition from the newly-recreated Social Democrats, to do away with price controls and rationing, which he did in 1948. These moves followed his currency reform that June, which contracted the money supply by about 90%. He also slashed income tax from 85% to 18% on annual incomes over Dm2,500 (US$595 equivalent).
Economists of the Austrian school would comprehend and recommend this strategy, but it goes wholly against the bureaucratic grain. General Lucius Clay, who was the military governor of the US Zone, and to whom Erhard reported, is said to have asked him, “Herr Erhard, my advisers tell me what you have done is a terrible mistake. What do you say to that?”
Erhard replied, “Herr General, pay no attention to them! My advisers tell me the same thing.”
About the same time, a US Colonel confronted Erhard: “How dare you relax our rationing system, when there is a widespread food shortage?”
Erhard replied, “I have not relaxed rationing, I have abolished it. Henceforth the only rationing ticket the people will need will be the deutschemarks. And they will work hard to get those deutschemarks, just wait and see.”
The US Colonel did not have to wait long. According to contemporary accounts, within days of Erhard’s currency reform, shops filled with goods as people realised the money they sold them for would retain its value. People no longer needed to forage for the basics in life, so absenteeism from work halved, and industrial output rose more than 50% in the second half of 1948 alone.
March 2, 2022
Duck Tape – WW2 Secret Weapon – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 1 Mar 2022This war has seen a huge amount of scientific and technological innovation. New ways of taking lives, and new ways of saving lives abound. But what about the more ordinary, everyday, products of the war? Would you be surprised to hear that people in the 21st century will still be using WWII inventions in daily life.
(more…)
January 14, 2022
The Revenge Bombing of Germany – WAH 050 – January 1943, Pt. 1
World War Two
Published 13 Jan 2022While Nazi Germany keeps on escalating its War Against Humanity, the United Nations alliance decides that they will escalate their war on Germany.
(more…)
October 20, 2021
Chocolate | British Pathé
British Pathé
Published 22 Sep 2016BON APPETIT – FOOD MONTH ON BRITISH PATHÉ (SEPTEMBER 2016): Chocolate.
We all love a bit of chocolate, so have a watch of these vintage films which show different chocolates being made, as well as the celebrations when sweet rationing came to an end.
(Film Ids: 1601.11, 313.13, 1108.14, 1401.17)
Music:
The Show Must Be Go (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…A NEW THEME EVERY MONTH!
Each month, a range of new uploads and playlists tell the story of a particular topic through archive footage. Let us know what themes you’d like to see by leaving us a comment or connecting with us on social media.BRITISH PATHÉ’S STORY
Before television, people came to movie theatres to watch the news. British Pathé was at the forefront of cinematic journalism, blending information with entertainment to popular effect. Over the course of a century, it documented everything from major armed conflicts and seismic political crises to the curious hobbies and eccentric lives of ordinary people. If it happened, British Pathé filmed it.Now considered to be the finest newsreel archive in the world, British Pathé is a treasure trove of 85,000 films unrivalled in their historical and cultural significance.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
A VIDEO FROM BRITISH PATHÉ. EXPLORE OUR ONLINE CHANNEL, BRITISH PATHÉ TV. IT’S FULL OF GREAT DOCUMENTARIES, FASCINATING INTERVIEWS, AND CLASSIC MOVIES. http://www.britishpathe.tv/
FOR LICENSING ENQUIRIES VISIT http://www.britishpathe.com/
British Pathé also represents the Reuters historical collection, which includes more than 136,000 items from the news agencies Gaumont Graphic (1910-1932), Empire News Bulletin (1926-1930), British Paramount (1931-1957), and Gaumont British (1934-1959), as well as Visnews content from 1957 to the end of 1984. All footage can be viewed on the British Pathé website. https://www.britishpathe.com/
August 7, 2021
The Black Markets of World War Two – WW2 – On the Homefront 012
World War Two
Published 6 Aug 2021With the scarce food supply brought about by war, many turn to the black market and its astronomic prices as supplements. It is a place for opportunists and patriotic protesters, but mainly it’s a means to survive.
(more…)
April 12, 2021
“War Communism” in the Soviet Union, 1917-1921
J.W. Rich outlines the economic and humanitarian disaster of Soviet “War Communism” that eventually forced Lenin to bring back some limited elements of capitalism to save the country:
In 1917, the Bolsheviks seized power in Moscow after the deposition of the democratic provisional government which had replaced the Tsar. However, the Bolsheviks’ hold on power was far from secure. There was little affection anywhere for the Tsar, but there was no agreement on what form of government should replace the monarchy. Bolshevism had been on the rise for years, but ideas of democracy and liberalism were gaining popularity as well. Shortly after the 1917 revolution, the Russian Civil War broke out between the Reds, the Bolsheviks, and the Whites, a coalition of anti-Bolsheviks that were generally democratic.
Through the course of the civil war, the Bolsheviks gained more power and control over increasingly large amounts of Russia. With this control, they began to implement their Marxist economic ideas into reality. On January 28, 1918, it was decreed that all factories should be directed by state-appointed managers. In effect, this amounted to a near-complete nationalization of industry. In one fell swoop, the vast majority of the production of Russia’s consumer goods was now under the purview and direction of the state.
On May 9, 1918, a grain monopoly was announced over grain production in the country. All grain harvested across the country was now the property of the state. This was extended even further when a general food levy was announced in January 1919. Any and all food was now the property of the state. In addition, local farm authorities were no longer allowed to set the levy based on harvest estimates. In essence, the state would take however much it wanted from the peasants without any concern if they had enough food to feed themselves and their families.
It was at this point that large-scale forced rationing was introduced. Money was made worthless overnight as ration cards were mandated to the entire population. No longer could you buy whatever you wished with the money you had. The goods allocated for you were predetermined on your ration card.
By late 1920, going into 1921, the Russian Civil War was all but over. The Whites had been soundly defeated by the Reds, giving the Bolsheviks control of nearly the entirety of the country. However, despite the victory in the Civil War, the economy at home was beginning to fall apart. Industrial production was at 20% of pre-war levels by 1920. As a result of this lagging production, there were few goods in the cities available. This resulted in a flight from the cities to the countryside. From 1918 to 1920, eight million people emigrated from the cities to the villages, where there was better hope of finding food or some goods. In Moscow and Petrograd, the population declined by 58.2%
The agricultural situation was not much better. Sheldon Richman records that from 1909-1913, gross agricultural output averaged 69 million tons. By 1921, it was just 31 million. From 1909-1913, sown area was over 224 million acres. In 1921, only 158 million acres were sown. This lack of food resulted in a mass loss of population. From 1917 to 1922, the entire population declined by 16 million, not counting immigration and deaths from the civil war.
War Communism was now fully implemented and the Marxist aspirations of Lenin and the Bolsheviks were now fulfilled. For the people that had to live under War Communism, however, the conditions had become intolerable. In February 1921, labor strikes began to emerge all over Russia. With the end of the civil war and living standards continuing to fall, resistance to the Bolsheviks began to spread throughout the country. Moscow was the first city to strike, with other large cities, such as Petrograd, following. The protestors demanded an end to War Communism and a restoration of private enterprise and civil liberties, such as the freedom of speech and assembly.
The protests escalated when the Kronstadt Naval Base mutinied against the government. Once a bastion of Bolshevik support and fervor, the sailors joined with the laborers in demanding reform and change. A force led by Trotsky was dispatched to deal with the mutiny, but Lenin knew that change was needed. The writing was on the wall for War Communism.