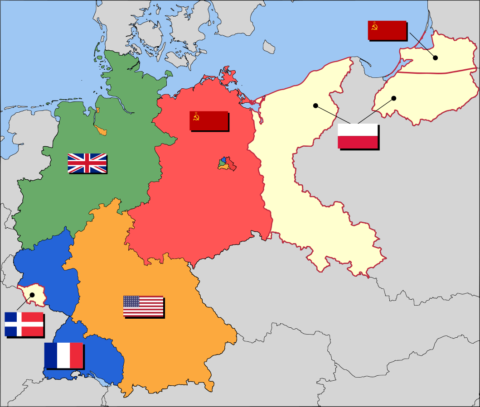
I started reading The Economist when I was in college, and became a subscriber for nearly 20 years. Over the last few years, the tone of the articles shifted away from classical liberal toward communitarian or even full-blown socialist cheerleading, so I sadly ended my subscription and haven’t picked up a copy in at least 15 years. According to Ken Whyte in the SHuSH newsletter, things haven’t improved since I stopped paying attention:
The Economist recently said that book publishing in today’s economy resembles book publishing during the Second World War when “paper imports collapsed” and “publishers printed only sure-fire hits”.
The Economist is the most over-rated publication in the English language, especially by itself. I give it marks for its broad range of interests, ability to cover a lot of ground in relatively tight articles, and occasionally solid reporting, but if you’re going to boast incessantly about how smart you are …
… you’d better back it up. The Economist seldom does. It tends to glib, obvious, and sloppy. Most of its articles are written by anonymous b-level freelancers whose best stuff goes to outlets that afford bylines. Their work is edited to a stultifying homogeneity by a haughty grad student with a Financial Times subscription. Or so it reads.
This piece — “Books are Physically Changing Because of Inflation” — is a case in point. Paper imports to the UK were reduced during WW2 but they did not collapse. The problem for the book trade was rationing. The government restricted publishers to 60 percent of their pre-war paper volumes (later falling to 35 percent) and itself used far more tonnage for propaganda than the book industry normally required. Manpower shortages were another factor limiting the production of new titles.
Nor is it true that publishers released “only sure-fire hits”. While much of their paper allotment went to keeping hot-selling books in stock, many bets were placed on new titles and most of them paid. It was wartime and leisure activities were limited. “British publishers found that they could sell virtually any title,” writes Zoe Thomson in The Journal of Publishing Culture.
The article isn’t all bad. It reports that British book publishers are paying 70% more for paper than they were a year ago: “Supplies are erratic as well as expensive: paper mills have taken to switching off on days when electricity is too pricey. The card used in hardback covers has at times been all but unobtainable.”
To cope with the price increases, publishers are printing smaller books on cheaper paper and jamming more words onto the page. Writers are being asked to write shorter and are being held to their word limits.
That reflects the current state of the industry. It’s hardly news, though. SHuSH readers are probably sick of hearing me on rising paper and printing costs, and I’ve just been following what others have written. The cost of printing has more or less doubled since before COVID. Many smaller publishers are already releasing fewer and slimmer titles. If we are headed into a recession, the trend will continue.