Real Engineering
Published 28 Mar 2020In the debut episode of the Logistics of D-Day we explore the logic and planning that resulted in Normandy being chosen as the location for the largest amphibious invasion in the history of human kind.
(more…)
June 3, 2023
Why Was Normandy Selected For D-Day?
April 28, 2023
QotD: The high-water mark of the Panzerarmee Afrika
The Gazala-Tobruk sequence was the greatest victory of Rommel’s career, not merely a triumph on the tactical level, but an operational level win, a victory that even General Halder could love. Call it Rommel’s Rule #1, which is still a recipe for success today: “Be sure to erupt into your opponent’s rear with an entire Panzer army in the opening moments of the battle.”
Even here, however, let us be honest. Smashing 8th Army at Gazala and taking tens of thousands of prisoners at Tobruk did little to solve the strategic problem. Unless the British were destroyed altogether, they would reinforce to a level the Axis could not match. Many later analysts argue that the Panzerarmee should have paused now, waited until some sort of combined airborne-naval operation had been launched against Malta to improve the logistics, and only then acted. Such arguments ignore the dynamic of the desert battle, however; they ignore the morale imperative of keeping a victorious army in motion; above all they ignore the personality of Rommel himself.
Pause? Halt? Wait? Anyone who expected Rommel to ease up on the throttle clearly hadn’t been paying attention. Instead, the Panzerarmee vaulted across the border into Egypt with virtually no preparation. To Rommel, to his men, and even to Hitler and Mussolini, it must have looked like a great victory lay just over the next horizon: Cairo, Alexandria, the Suez Canal, the British Empire itself.
In reality, it is possible today to see what the great Prussian philosopher of war Karl von Clausewitz once called the “culmination point” — that moment in every campaign when the offensive begins to lose steam, run down, and eventually stop altogether. The Panzerarmee was exhausted, its equipment was worn out and in desperate need of repair. Captured British stores and vehicles had become its life-blood, Canadian Ford trucks in particular. The manpower was breaking down. A chronic shortage of potable water had put thousands of soldiers on the sick rolls. Colonel Siegfried Westphal, the Panzerarmee‘s operations chief (the “Ia”, in German parlance), was yellow with jaundice. The army’s intelligence chief (the “Ic”), Colonel Friedrich Wilhelm von Mellenthin, was wasting away with amoebic dysentery. Rommel had a little of both, as well as a serious blood-pressure problem (no doubt stress-induced) and a chronic and bothersome sinusitis condition. While it would be easy to view all these illnesses as simple bad luck, they were, in fact, the price Rommel and all the rest of them were paying for fighting an overseas expeditionary campaign with inadequate resources.
The same might be said for the rest of the campaign. The Panzerarmee made an ad hoc attempt to break thought the British bottleneck at El Alamein in July. It failed, coming to grief against British defenses on the Ruweisat ridge. There was a second, more deliberate, attempt in August. After an initial breakthrough, it crashed into strong British defenses at Alam Halfa ridge and it, too, failed. After yet another long pause, a “third battle of El Alamein” began in late October. This time, it was the well supplied British on the attack, however, and they managed to smash through the Panzerarmee and drive Rommel and company back, not hundreds of miles, but more than a thousand, out of the desert altogether and into Tunisia. There was still fighting to be done in Africa, but the “desert war” was over.
Robert Citino, “Drive to Nowhere: The Myth of the Afrika Korps, 1941-43″, The National WWII Museum, 2012. (Originally published in MHQ, Summer 2012).
March 30, 2023
The use and mis-use of wargames
Cheating in wargames must be approximately five minutes younger than wargames themselves … famously, the Imperial Japanese Navy didn’t like the outcome of wargaming what became the Battle of Midway and “cheated” by refloating the aircraft carriers shown as sunk in the simulation and Wehrmacht General Paulus ran a wargame that showed Operation Barbarossa would fail and he was also told to ignore the results and ended up in Stalingrad. Lessons can be learned from formal wargames, but as CDR Salamander points out, a wargame outcome can be custom-tailored as the leaders require:
One of the things that will get my eye twitching faster than about anything else is when someone responds to a question or concern with a, “Well, in our wargames …”
Bullshit.
That may work for civilians or under-briefed lawmakers who lack the depth in military matters, but anyone who has run or been part of a wargame knows that you can design one to give you the outcomes you want.
Planning assumptions etc … it is all flexible.
Wargames, done right, don’t tell you the future, but they do help inform gaps in your OPLAN, thinking, or expectations of the enemy … and shortfalls you might have.
At the POLMIL level — where our most senior uniformed and civilian leaders live — you have distinctly different concerns than Tactical, Operational, or — if your Planning Confession separates Strategic from the POLMIL level — Strategic level.
For the senior uniformed leader to make this statement, as if it were a bolt out of the blue, is simply gobsmacking;
A “big lesson learned comes out of Ukraine, which is the incredible consumption rates of conventional munitions in what really is a limited regional war,” General Mark Milley, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, told the House Armed Services Committee.
“If there was a war on the Korean peninsula or a great power war between United States and Russia, United States and China, those consumption rates would be off the charts,” he said.
Whose charts? Who made them and using what metrics and dataset?
Yes … that is a lesson for most out there … but it should not be for the CJCS. Hell, I remember certain aspects of updating the OPLAN for Korea a quarter century ago when we beat the drum that, “We don’t have enough ____ and only a few days of ____ before we are combat ineffective.”
This. Is. Not. New.
As we mentioned last July, magazine depth has been a chronic shortfall for a long time.
I have trouble believing that the CJCS is shocked, SHOCKED, that this is an issue.
It isn’t a “lesson learned” — it is a lesson ignored.
One of the easiest, most obvious-to-the-accountants economy any military can make is to scrimp on the inventory of live ammunition … if there’s no war, much of the stored munitions must be disposed of at a cost, and what’re the chances they’ll throw a war before the next election? Plus, if there’s only so much in storage, it’s not economical to have the training allowance of ammunition go up, so you can reduce the resupply levels and free up money in the budget for sexier, more mediagenic toys.
February 24, 2023
Up Close and Personal – Mountain Warfare in Italy – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 23 Feb 2023Thanks to Curiosity Stream for sponsoring today’s video
Even as the Allied and Axis commanders focus on the sweeping warfare of the Eastern Front and the planning for the invasion of Europe, their men continue to fight a grinding war of attrition high in the Italian mountains. It’s a war of merciless terrain, brutal close-quarters combat, and vast quantities of artillery and bombs. They may be playing second fiddle, but the soldiers on the Italian front will never forget these battles.
(more…)
February 22, 2023
True Size of a Roman Legion
Invicta
Published 29 Oct 2022The True Size of a Roman Legion.
A history documentary on the True Size of a Roman Legion. This is our first episode in the new True Size series which seeks to bring history to life in 3D using Unreal Engine 5. In this episode we cover the organization of a Roman Legion from the soldier to the Contubernium, the Century, the Cohort, and the Legion. Along the way we not only include the troops and their officers but all the slaves, mules, support, staff, and gear which accompanied them. This makes for a much better understanding of the Roman army structure.
We then put these into context by looking at a Roman army camp, a Roman army on the march, and a Roman army in battle order. This gives the viewer a full 3D history of a legion like never before.
(more…)
January 26, 2023
Ukraine to receive Challenger II, M1 Abrams, and Leopard 2 tanks … both a solution and a new set of problems
In The Line, Matt Gurney outlines some of the benefits Ukraine will receive with this new transfusion of AFVs … and also the new and exacerbated set of practical problems that goes along with fielding so many different makes and models of tanks:

A British army Challenger Main Battle Tank, of 1 Royal Regiment of Fusiliers (1RRF), is shown returning to base after completing a firing mission as part of Exercise MedMan.
1RRF Battle group were based at the British Army Training Unit Suffield (BATUS) in Canada.
MOD photo by Mike Weston via Wikimedia Commons.
A column getting into all the details of why [the German government] were withholding said blessing would be several times longer than this one will be. Suffice it to say this is just the latest manifestation of Germany’s extreme discomfort with this war. Some of it relates to the lingering fallout of Germany’s blood-soaked history. But we would be naïve not to attribute at least some of the reluctance to Russia’s deep influence among some segments of the German ruling elite.
Germany has contributed to the defence of Ukraine, and it would be unfair to deny that. It would not be unfair to note that Germany has typically only done so later than the other allies, and under enormous pressure.
As part of the deals being announced, the United States will be sending several dozen of its M1 Abrams tanks, and Germany will send Leopards. Berlin will also allow other allies to send further Leopards. (Canada hasn’t committed to sending any of ours yet, but our few remaining Leopards are reported to be in poor shape, and are also all the way across an ocean, so we might not even be asked.) The British will send the Challengers. This gives Germany the ability to claim, with a reasonably straight face, that it has not chosen to escalate the conflict. Heavens, no! It’s simply moving in lockstep with its allies! As fig leaves go, it’s a pretty small and transparent one, but for the purposes of diplomacy and maintaining the appearance of allied solidarity, it’ll do.
And this brings us to the problem that the plan is exacerbating. A year ago, the Ukrainian military was largely armed and equipped along Russian lines — both militaries were, after all, descendants of the Soviet Red Army. Since then, much of its original equipment has been destroyed or lost, but this has generally been offset by an influx of Western weapons into the country as the allies empty their arsenals and get their production lines running again. This has allowed Ukraine to keep fighting, far more effectively than the Russians, among many others, expected. Despite huge losses of manpower, the Ukrainian military seems to actually have grown stronger as the war has gone on, thanks to the power of its new weapons.
Sending news is good news to that extent. It will make Ukraine stronger still. But it is also producing a situation where the Ukrainians are armed with an absurdly unwieldy mix of weapon systems. This is laying the groundwork for a future logistics disaster.
Any individual soldier can learn to use any specific piece of equipment. That’s just a matter of training and experience. Soldiers are smart. The longer they serve, the quicker they’ll get at picking up new pieces of equipment and kit. The challenge is more on the backend. The logistics of sustaining an arsenal of completely mixed weapon systems is a nightmare. Not only must Ukraine procure a huge variety of calibers of ammunition, it must also procure, sort, and then distribute a bewildering array of spare parts to keep all these weapons running. It’s not that this is impossible. The fact that Ukraine fights on is proof that it is not. But it adds tremendous cost and complexity, and requires a much larger effort to sustain than would be the case if Ukrainian units were equipped with standard weapons across comparable units.
The numbers of NATO tanks are initially small enough that only a few battalions can be re-equipped with the donated AFVs, but each different “brand” needs its own specialized support in the way of maintenace, repair, and re-supply. Ukraine is going to have to have at least a company-sized, fully trained maintenance unit for each battalion of NATO tanks and the logistics system will have to ensure that the different types of ammunition and ordinary wear-and-tear maintenance spares are delivered quickly enough to keep those battalions combat-ready. Some NATO nations with much better facilities sometimes struggle to do this for a single type of AFV, never mind for several different types.
Update: Can’t help but agree with Matt here.
January 22, 2023
Where The British Army Figured Out Tanks: Cambrai 1917
The Great War
Published 20 Jan 2023The Battle of Cambrai in 1917 didn’t have a clear winner, but the conclusions that Germany and Britain drew from it, particularly about the use of the tank (in combination with other arms), would have far reaching consequences in 1918.
(more…)
January 7, 2023
QotD: The “camp followers” of a pre-modern army
It is worth keeping in mind that an army of 10,000 or 20,000 men was, by ancient or medieval standards, a mid-sized town or city moving across the landscape. Just as towns and cities created demand for goods that shaped life around them, so did armies (although they’d have to stay put to create new patterns of agriculture, though armies that did stay put did create new patterns of agriculture, e.g. the Roman limes). Thousands of soldiers demand all sorts of services and often have the money to pay for them and that’s in addition to what the army as an army needs. That in turn is going to mean that the army is followed by a host of non-combatants, be they attached to the soldiers, looking to turn a profit, or compelled to be there.
We can start with sutlers, merchants buying or selling from the soldiers themselves (the Romans called these fellows lixae, but also called other non-soldiers in the camp lixae as well, see Roth (2012), 93-4; they also call them mercatores or negotiatores, merchants). Sutlers could be dealing in a wide array of goods. Even for armies where ration distribution was regular (e.g. the Roman army), sutlers might offer for sale tastier and fancier rations: meat, better alcohol and so on. They might also sell clothing and other goods to soldiers, even military equipment: finding “custom” weapons and armor in the archaeology of military forts and camps is not uncommon. For less regularly rationed armies, sutlers might act as a supplement to irregular systems of food and pay, providing credit to soldiers who purchased rations to make up for logistics shortfalls, to collect when those soldiers were paid. By way of example, the regulations of the Army of Flanders issued in 1596 allowed for three sutlers per 200-man company of troops (Parker, op. cit.), but the actual number was often much higher and of course those sutlers might also have their own assistants, porters, wagons and so on which moved with the army’s camp. Women who performed this role in the modern period are often referred to by the French vivandière.
For some armies there would have been an additional class of sutlers: slave dealers. Enslaved captives were a major component of loot in ancient warfare and Mediterranean military operations into and through the Middle Ages. Armies would abduct locals caught in hostile lands they moved through or enemies captured in battles or sieges; naturally generals did not want to have to manage these poor folks in the long term and so it was convenient if slave-dealer “wholesalers” were present with the army to quickly buy the large numbers of enslaved persons the army might generate (and then handle their transport – which is to say traffic them – to market). In Roman armies this was a regularized process, overseen by the quaestor (an elected treasury official who handled the army’s finances) assigned to each army, who conducted regular auctions in the camp. That of course means that these slave dealers are not only following the army, but are doing so with the necessary apparatus to transport hundreds or even thousands of captives (guards, wagons, porters, etc.).
And then there is the general category of “camp follower”, which covers a wide range of individuals (mostly women) who might move with the camp. The same 1596 regulations that provided for just three sutlers per 200-man Spanish company also provided that there could be three femmes publiques (prostitutes), another “maximum” which must often have been exceeded. But prostitutes were not the only women who might be with an army as it moved; indeed the very same regulations specify that, for propriety’s sake, the femmes publiques would have to work under the “disguise of being washerwomen or something similar” which of course implies a population of actual washerwomen and such who also moved with the army. Depending on training and social norms, soldiers may or may not have been expected to mend their own clothes or cook their own food. Soldiers might also have wives or girlfriends with them (who might in turn have those soldier’s children with them); this was more common with professional long-service armies where the army was home, but must have happened with all armies to one degree or another. Roman soldiers in the imperial period were formally, legally forbidden from marrying, but the evidence for “soldier’s families” in the permanent forts and camps of the Roman Empire is overwhelming.
The tasks women attached to these armies have have performed varied by gender norms and the organization of the logistics system. Early modern gunpowder armies represent some of the broadest range of activities and some of the armies that most relied on women in the camp to do the essential work of maintaining the camp; John Lynn (op. cit., 118-163) refers to the soldiers and their women (a mix of wives, girlfriends and unattached women) collectively as “the campaign community” and it is an apt label when thinking about the army on the march. As Lynn documents, women in the camp washed and mended clothes, nursed the sick and cooked meals, all tasks that were considered at the time inappropriate for men. Those same women might also be engaged in small crafts or in small-scale trade (that is, they might also be sutlers). Finally, as Lynn notes, women who were managing food and clothing seem often to have become logistics managers for their soldiers, guarding moveable property during battles and participating in pillaging in order to scrounge enough food and loot for they and their men to survive. I want to stress that for armies that had large numbers of women in the camp, it was because they were essential to the continued function of the army.
And finally, you have the general category of “servants”. The range of individuals captured by this label is vast. Officers and high status figures often brought either their hired servants or enslaved workers with them. Captains in the aforementioned Army of Flanders seem generally to have had at least four or five servants (called mozos) with them, for instance; higher officers more. But it wasn’t just officers who did this. Indeed, the average company in the Army of Flanders, Parker notes, would have had 20-30 individual soldiers who also had mozos with them; one force of 5,300 Spanish veterans leaving Flanders brought 2,000 such mozos as they left (Parker, op. cit. 151).
Looking at the ancient world, many – possibly most – Greek hoplites in citizen armies seem to have very often brought enslaved servants with them to carry their arms and armor; such enslaved servants are a regular feature of their armies in the sources. The Romans called these enslaved servants in their armies calones; it was a common trope of good generalship to sharply restrict their number, often with limited success. At Arausio we are told there were half as many servants (calonum et lixarum) as soldiers (Liv. Per. 67, on this note Roth (2013), 105), though excessive numbers of calones et lixae was a standard marker of bad general and the Romans did lose badly at Arausio so we ought to take those figures with a grain of salt, as Livy (and his sources) may just be communicating that the generals there were bad. That said, the notion that a very badly led army might have as many non-combatants following it as soldiers is a common one in the ancient sources. And while Roman armies were considered notable in the ancient world for how few camp servants they relied on and thus how much labor and portage was instead done by the soldiers, getting Roman aristocrats to leave their vast enslaved household staff at home was notoriously difficult (e.g. Ps.Caes. BAfr. 54; Dio Cass. 50.11.6). Much like the early modern “campaign community”, our sources frequently treat these calones as part of the army they belonged to, even though they were not soldiers.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Logistics, How Did They Do It, Part I: The Problem”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-07-15.
January 3, 2023
1943 in Numbers – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 1 Jan 2023This war is massive. Our chronological coverage helps give us an understanding of it, but sometimes statistics help us understand the bigger picture.
(more…)
December 14, 2022
QotD: The “tooth-to-tail ratio” in armies
The first issue is what in military parlance is called the “tooth to tail” ratio. This is the ratio of the number of actual combat troops (the “tooth”) to logistics and support personnel (the “tail”) in a fighting force. Note that these are individuals in the fighting force – the question of the supporting civilian economy is separate. The thing is, the tooth to tail ratio has tended to shift towards a longer tail over time, particular as warfare has become increasingly industrialized and technical.
The Roman legion, for instance, was essentially all tooth. While there was a designation for support troops, the immunes, so named because they were immune from having to do certain duties in camp, these fellows were still in the battle line when the legion fought. The immunes included engineers, catapult-operators, musicians, craftsmen, and other specialists. Of course legions were also followed around by civilian non-combatants – camp-followers, sutlers, etc. – but in the actual ranks, the “tail” was minimal.
You can see much the same in the organization of medieval “lances” – units formed around a single knight. The Burgundian “lance” of the late 1400s was composed of nine men, eight of which were combatants (the knight, a second horsemen, the coustillier, and then six support soldiers, three mounted and three on foot) and one, the page, was fully a non-combatant. A tooth-to-tail ratio of 8:1. That sort of “tooth-heavy” setup is common in pre-industrial armies.
The industrial revolution changes a lot, as warfare begins to revolve as much around mobilizing firepower, typically in the form of mass artillery firepower as in mobilizing men. We rarely in our fiction focus on artillery, but modern warfare – that is warfare since around 1900 – is dominated by artillery and other forms of [indirect] fires. Artillery, not tanks or machine guns, after all was the leading cause of combat death in both World Wars. Suddenly, instead of having each soldier carry perhaps 30-40kg of equipment and eat perhaps 1.5kg of food per day, the logistics concern is moving a 9-ton heavy field gun that might throw something like 14,000kg of shell per day during a barrage, for multiple days on end. Suddenly, you need a lot more personnel moving shells than you need firing artillery.
As armies motorized after WWI and especially after WWII, this got even worse, as a unit of motorized or mechanized infantry needed a small army of mechanics and logistics personnel handling spare parts in order to stay motorized. Consequently, tooth-to-tail ratios plummeted, inverted and then kept going. In the US Army in WWI, the ratio was 1:2.6 (note that we’ve flipped the pre-industrial ratio, that’s 2.6 non-combat troops for every front line combat solider), by WWII it was 1:4.3 and by 2005 it was 1:8.1. Now I should note there’s also a lot of variance here too, particularly during the Cold War, but the general trend has been for this figure to continue increasing as more complex, expensive and high-tech weaponry is added to warfare, because all of that new kit demands technicians and mechanics to maintain and supply it.
[NR: Early in WW2, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill frequently harassed his various North African generals for the disparity between the “ration strength” of their commands and the much-smaller number of combat troops deployed. If General Wavell had 250,000 drawing rations, Churchill (who last commanded troops in the field in mid-WW1) assumed that this meant close to 200,000 combat troops available to fight the Italians and (later) the Germans. This almost certainly contributed to the high wastage rate of British generals in the Western Desert.]
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday, April 22, 2022”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-04-22.
November 28, 2022
Mulberry Harbours – Rhinos, Whales, Beetles, Phoenixs and Spuds against the Axis
Drachinifel
Published 13 Jul 2022Today we take a look at the artificial harbours designed, built and then installed on the Normandy beaches in 1944.
Many thanks to @Think Defence for finding and collating so many images and letting me use them! Follow them on Twitter or on their website for more interesting articles!
(more…)
November 20, 2022
A Conspiracy to kill America’s President? – WW2 – 221 – November 19, 1943
World War Two
Published 19 Nov 2022A torpedo attack against the President; a Marine invasion in the central Pacific that turns very bloody in a hurry; German counterattacks in the Soviet Union; a bombing raid in Italy against a secret weapons site — all of that this week.
(more…)
October 22, 2022
Battle of the Bulge 1944: Could the German Plan Work?
Real Time History
Published 21 Oct 2022Sign up for Nebula and watch Rhineland 45: https://nebula.tv/realtimehistory
The Battle of the Bulge was one of the last German offensives during the Second World War. It caught the US Army off guard in the Ardennes sector but ultimately the Allies prevailed. But did Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein (“Operation Watch on the Rhine”) ever have a chance to succeed and reach Antwerp?
(more…)
October 13, 2022
QotD: “Russia is a nation built for tank warfare”
Some nations possess very large numbers of tanks indeed — others barely any. Russia, China and North Korea are some of the worlds largest tank fleet operators, with thousands of tanks listed on their order of battle. Russia is a nation built for tank warfare — large open borders, and endless steppes that have over the last century played host to some of the biggest armoured battles ever seen. Having visited the Kursk salient many years ago, Humphrey can personally attest to the sheer size of the Eastern Front, and how a militarized society can make good use of armour.
Russia also benefits from an outstanding rail network able to quickly move tanks and other heavy elements of military power such as APCs and self-propelled guns around easily, and has the space and reserves of conscript manpower from previous generations to draw on to crew its simple but effective designs, such as the T64 and T72.
This is underpinned by a national philosophy which is best summed up as “don’t throw away any military asset that, no matter how old it is, could be used to kill an invader”. There are storehouses across Russia full of elderly tanks that with a bit of TLC could, probably function as a last gasp capability. Russia regularly exercises its armoured capability, mobilising forces and moving them around the country to test readiness against the theoretical threat of a NATO invasion.
Russia then is a nation intended for operating tanks, but only when supported by a logistics chain that can support the front. Start moving away from the Russian landmass and their ability to sustain a force at any distances is quickly called into doubt. While Russia may “rank” as the largest tank operator in the world, much of this is only a threat to any nation foolish enough to invade Russia in the first place.
Sir Humphrey, “Tanks for nothing — Why it does not matter if the British Army has fewer tanks than Cambodia”, Thin Pinstriped Line, 2019-04-24.
September 29, 2022
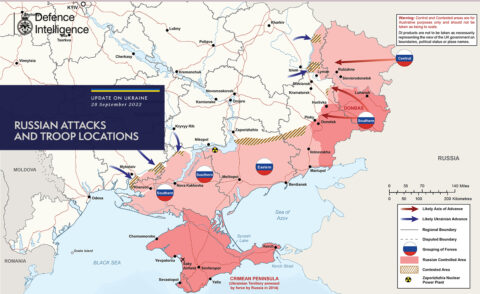
Considering weird possible scenarios in Ukraine
In The Line, Matt Gurney walks through some until recently unimaginable outcomes of the Russian invasion of Ukraine:
It’s probably time for us to start thinking through some weird possible scenarios for what’s happening in Russia. Because the spectrum of what could happen is a lot broader than it seemed only six months ago.
But let’s start with an important exercise in accountability. In previous commentary, I predicted a lot of things well: that Ukrainian resistance would be very effective, that Russia would have major logistics problems, that the Russians would use mass artillery fire against civilians in place of military advances. I was quick to grasp that Ukraine was overperforming and that Russia was struggling early in the conflict.
But getting some details right didn’t help me avoid blowing the conclusion: I thought Russia would win. Not a total victory, but I thought Russia would seize a lot more of the country before its logistical problems and Ukrainian resistance brought their offensives to a halt, leaving Ukraine with some kind of rump state in the west. I certainly didn’t believe in February that Russia could lose, and I never would have believed that Ukraine could actually win on the battlefield, as it now seems more than capable of doing.
I don’t know if I underestimated Ukrainian capabilities, per se. I always expected them to fight bravely and well, and understood the lethality of modern man-portable weapons against tanks and armoured vehicles. It’s probably closer to the mark to say that I overestimated Russia’s capabilities — I was a cynic on their military and expected it to perform badly, but it’s somehow fallen well short of my already low expectations. It is absolutely delightful to be wrong on this one, but readers deserve the truth: I expected Russia’s military to perform better and grab a much bigger chunk of Ukraine before having to stop in the face of logistical dysfunction and Ukrainian resistance. Part of me wonders if the Russians themselves are surprised by how hollowed out their military had become.
With that on the record, let’s flash forward to the present. As noted above, Ukraine now seems fully able to win the war. As I write this, Ukrainian forces are on the move again in the northeast, and seem to be encircling Russian positions in occupied Lyman. If able to complete this latest manoeuvre, Ukrainian forces will cut off a large force of Russian troops and will also seize control of an important local rail junction, threatening Russian logistics (such as they are) in the surrounding area. Perhaps more importantly to the overall conduct of the war, Russia’s effort to mobilize 300,000 men for the war is running into obvious challenges. Men of military age are fleeing the country. Reports from Russia reveal that the army has little in the way of equipment and weapons for the new draftees, and no system in place to train them. There have been comically bizarre stories of infirm old men getting call-up notices, and of draftees being sent to the front after only a day or two of training … at best.
This isn’t a solution to Putin’s problems. It’s a new problem being created in real time. Even if Putin can find 300,000 men, it seems unlikely he can equip them, and even less likely that he can train them. Whether or not he can transport what men he does round up into the battle area is an open question, as is whether or not he can supply them once they get there.
This is the long way of saying something I’ll now just state bluntly: Russia is losing. Putin’s latest actions reveal that he knows he’s losing. If the mobilization flops, as seems likely, he’ll be losing even worse than he was losing before, and he’ll have damn few options to turn that around.
And this is why we need to start thinking through some weird scenarios.