Real Time History
Published 3 Jan 2025In the summer of 1940, Great Britain is under attack in the air and at sea. German U-Boat wolf packs prowl the Atlantic and sink over a million tons of shipping. German skippers call this the “happy time” — but was the German Navy actually that successful early in the Battle of the Atlantic?
(more…)
May 17, 2025
Battle of the Atlantic, 1939-1940
January 21, 2025
November 28, 2024
Town-class destroyers – Guide 400
Drachinifel
Published Aug 3, 2024The Town class destroyers, old Wickes, Clemson and Cadwell class vessels of the US Navy, transferred to the British Royal Navy and others, are today’s subject.
(more…)
October 7, 2023
Eastern Front Tank Warfare 1944
World War Two
In this conflict, we’ve seen armored warfare on a greater scale than anything before or since. Indy takes a look at some of the tanks slugging it out on the Eastern Front, from the long-serving Panzer III and IV, to the newer and more powerful Tiger and T-34 85, and the monstrous IS-2.
(more…)
June 28, 2023
How to Fund a War: Lend Lease, Billion Dollar Gift, and Aid to Britain
OTD Military History
Published 27 Jun 2023Programs like Lend Lease, Mutual Aid, and the Billion Dollar Gift were support from Canada and the United States that helped Britain with war supplies and material in the darkest days of World War 2.
(more…)
June 5, 2022
Banzai Charges in Alaska – WW2 – 197 – June 4, 1943
World War Two
Published 4 Jun 2022The Chinese defeat the Japanese at Shipai Fortress and the Americans maul the Japanese in the Aleutians. The Japanese are also worried about the possibility of the USSR joining the war against them. Meanwhile the Allies still plan to invade Sicily, but have no idea what they’ll do after that.
(more…)
February 12, 2022
Stemple 76/45 + Russian Lend-Lease Thompson Kit = STG-M1A
Forgotten Weapons
Published 8 Oct 2021http://www.patreon.com/ForgottenWeapons
https://www.floatplane.com/channel/Fo…
Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.forgottenweapons.com
The modularity and clever design of the Stemple Takedown Gun is perhaps best illustrated by the STG-M1A and STG-1928 (these are the same gun with either a horizontal or vertical front grip). In the early 2000s a bunch of Thompson parts kits came into the US, WW2 vintage lend-lease guns sent to Russia. They were M1 and M1A1 models, and had intact barrels but torch-cut receivers. BRP, who makes the Stemple, realized that the sear-to-magwell dimensions on the Thompson were almost identical to the Suomi and Stemple — and that he could make a version of the STG that was a nearly perfect clone of the M1 Thompson.
The registered Stemple receiver slides into a square Thompson lookalike housing, and original Thompson grips, stocks, and hand guards are used. It is chambered for .45ACP, using original Thompson stick magazines (naturally). The result is a submachine gun that almost perfectly duplicates the handling of a true Thompson, without the historical value that makes the Thompson so expensive and keeps many owners from wanting to actually take their Thompsons out to the range.
Note that the gun in this video is an early example, and models made today are able to take both stick and drum magazines. Also, due to the design of the disconnector in the original Thompson FCG, the semiauto setting is not functional in the Stemple version — it’s only full automatic.
Contact:
Forgotten Weapons
6281 N. Oracle 36270
Tucson, AZ 85740
September 28, 2021
Debunking the notion that Stalin was an innocent victim of Hitler
At Instapundit, Ed Driscoll links Jakub Grygiel’s review of a new look at World War 2 in Europe, Stalin’s War by Sean McMeekin, which includes a bit of debunking about the relationship between Hitler and Stalin from 1939 to 1941:

Translation of the Russian caption for this image:
People’s Commissar of Foreign Affairs of the USSR V.M. Molotov signs a friendship and border treaty between the USSR and Germany. Among those present: I.V. Stalin, translator of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs V.N. Pavlov, German diplomat G. Hilger (“truncated” version of the photograph of M. Kalashnikov distributed on the net)
Photograph attributed to Mikhail Mikhaylovich Kalashnikov (1906-1944) via Wikimedia Commons.
Stalin was always interested in a war, especially one that would pit the other powers against each other. The expansion of Soviet influence and control required the weakening of the other powers, in particular the Western ones that were opposed to the Communist virus. For Stalin, therefore, the growth of Nazi Germany was a great opportunity: a violent and expansionistic power in the middle of Europe that could take the first swing against the polities standing on his path. Unsurprisingly, the Soviet tyrant was deeply disappointed when France and Britain signed the Munich Agreement with Nazi Germany in 1938 postponing the great European war that he desired. The 1939 Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact coordinated the efforts of Hitler and Stalin, but it benefited the latter more, allowing him to conquer a large swath of Polish territory with minimal effort, eliminating one of the staunchest opponents to Russian westward expansion. A year later, by murdering almost 22,000 Polish officers in Soviet captivity, Stalin further weakened the Polish obstacle to his expansion. “Nations which had been ruled by powerful aristocracies,” Stalin told once to the Yugoslav Milovan Djilas, “like the Hungarians and the Poles, were strong nations” — and, fearing them, he sought to eliminate them. Then, while Germany invaded France, Stalin took over the three Baltic states in a further step westward.
Hitler’s decision to invade Russia in mid-1941 was a surprise to Stalin, but not because he was expecting a lasting peace on his western frontier. Rather, as McMeekin documents, Stalin had ordered very rapid and large military preparations, building airbases and placing forces near the border with the Third Reich in the first half of 1941. None of them were in a defensive posture, and presented a vulnerable high value target to Nazi attacks. When Hitler decided to attack the USSR in June 1941, these Soviet forces were easy pickings for the well-organized, trained, and war tested German army. McMeekin here expands and amends a bold thesis offered in 1990 by Viktor Suvorov, a pseudonym for a GRU agent who defected to the West in the late ’70s and became a historian, that argued that Stalin was actively planning an attack on Germany but was preempted by Hitler. While Suvorov was excessive in his claim that the Red Army was ready for an offensive campaign in 1941 (because, among other reasons, the officer corps was still in shambles after Stalin’s purges) and that Stalin had plans to conquer Europe, he argued that the USSR was never a status quo power satisfied in its borders. After all Soviet Russia had already attempted to march westward in 1920 and was stopped only by the Poles in a desperate battle near Warsaw (the “Miracle on the Vistula”). This westward vector and ambition of Moscow did not abate, and had to pause because of Hitler’s rise and the might of Nazi Germany. As McMeekin points out, the Soviet military posture in 1941 makes no sense if the goal was to defend Soviet-held lands, suggesting that Stalin was thinking of pouncing on Berlin, now the last remaining continental power in Europe. As the Soviet tyrant himself put it, the USSR no longer needed to be locked in a defensive posture, and was “a rapacious predator, coiled in tense anticipation, waiting for the chance to ambush its prey.”
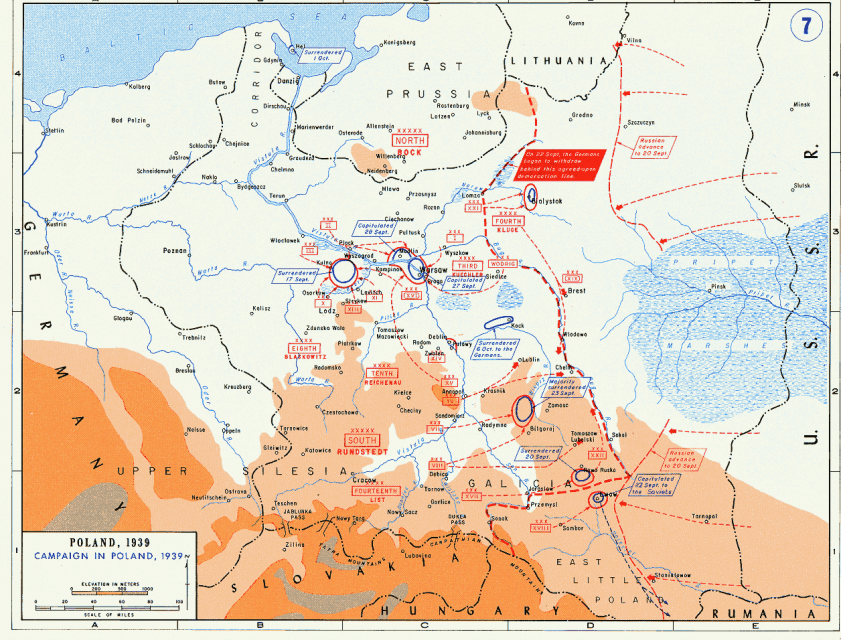
Military situation in Poland, 14 September 1939 (map does not show Slovak Army activity in southern Poland).
United States Military Academy, Department of History via Wikimedia Commons.Stalin, that is, was not an innocent victim of Hitler. Not only he was an active partner from 1938 until 1941, but also he had geopolitical aspirations that were more ambitious than those held by Hitler. And he pursued them methodically and ruthlessly, leaving a trail of death that dwarfed the one produced by the Nazis.
McMeekin then focuses on how the Western allies, Churchill but especially FDR, abetted Stalin’s ambitions. This part of the book is fascinating and depressing at the same time. In a nutshell, Stalin obtained from FDR more than he expected: territory, influence, and materiel. And he did not give anything in exchange for it because FDR and his advisors never asked him for it. For instance, FDR supported the Lend-Lease program, putting his friend Harry Hopkins in charge. Under this program of military aid, the United States supplied a massive amount of weapons, trucks, airplanes, tanks, foodstuff to the Soviet Union in the months of its greatest need, as German troops were driving deep into Russia while the vaunted Soviet armies were melting away. Without such aid, the USSR would have likely been unable to stop the German onslaught and certainly would have been incapable of mustering the resources necessary to push westward. Hence, in this moment there was a good strategic rationale for the American support of Stalin’s defensive efforts against Nazi Germany.
Prior to the launch of Operation Barbarossa, you’d have been hard-pressed to find a more anti-Soviet leader than Winston Churchill, but he immediately recognized that Stalin was more useful to the British as an ally than as a passive enemy. Earlier this year, McMeekin wrote that Stalin “could not have asked for a friendlier British government” than Churchill’s wartime coalition. As Connor Daniels wrote in response at The Churchill Project:

The “Big Three” meet at Tehran, 28 November-1 December, 1943.
Photo attributed to US Army photographer, via Wikimedia Commons.
Churchill’s support for Stalin during the Second World War followed from a simple calculus of the lesser of two evils. Britain could only take on one evil empire at a time, and, of the two, Churchill believed that Nazi Germany posed the greater threat to liberty. He famously remarked, “If Hitler invaded Hell I would make at least a favourable reference to the Devil in the House of Commons.” McMeekin attempts to sidestep this harsh reality, writing: “Whether or not the payoff was worth the price is a question well worth debating.” Churchill’s alliance with the Soviets stands or falls on this question: was Nazi Germany or the Soviet Union the greater danger in 1939?
With hindsight, one can easily marshal facts that portray Soviet communism as the greater evil. According to the best available estimates, the Stalin regime killed 20 millions of its own citizens. Nearly six million of those deaths occurred during the 1932–33 famine brought about by Stalin’s collectivization policies. While Nazi Germany also killed 17 million civilians, most of those deaths occurred after Hitler’s invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941. Thus, on the eve of the Second World War, one could argue — as Chamberlain and the appeasers did — that Nazi Germany served as a useful bulwark against a greater danger: the Soviet Union.
This analysis, however, misses a crucial point — one that Churchill recognized. Until 1939, the horrors of the Soviet regime had been primarily restricted to its own borders, while Nazi Germany had already made its expansionist ambition clear. In 1938, Germany annexed Austria. Later that year, Germany seized the Sudetenland. In 1939, the rest of Czechoslovakia passed under Hitler’s control. The Nazi doctrine of Lebensraum dictated even greater expansion. By contrast, Stalin’s doctrine of “socialism in one country” had kept the Soviet Union relatively peaceful until the Second World War began.
August 27, 2021
On Which Side is Brazil? – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 26 Aug 2021Brazilian President, Getúlio Vargas, has led his country as dictator since the 1930s. He has embraced European fascist ideas and fostered close ties with Germany and Italy. Yet, he also maintains a close relationship with the United States. After skilfully playing both sides, he must now choose Axis or Allies.
(more…)
June 23, 2021
QotD: Churchill’s support for Stalin
Churchill threw all of his support behind Stalin’s armies despite Stalin’s alliance with Hitler during the first 21 months of the war — the USSR having invaded the same number of countries as Nazi Germany (seven), having supplied the German Wehrmacht as it invaded France and the Low Countries, and having literally fueled the Luftwaffe as it bombed London in 1940.
This support was more than rhetorical. In a gesture of astonishing (and short-sighted) selflessness, Churchill responded to news of Nazi Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union by sending Stalin 200 brand-new Hawker Hurricane pursuit planes which had been pledged to defend Singapore against Japanese attack. Churchill then “re-gifted” Stalin 200 Tomahawk fighters and 300 Douglas A-20 Havoc bombers from Britain’s own Lend-Lease consignments, and shipped Stalin 2,000 tonnes of processed aluminum for Soviet warplane factories, despite it being desperately needed at home.
Even more striking was Churchill’s decision to ship Stalin nearly 600 tanks, which helped tip the balance in the Battle of Moscow in December 1941. Churchill even agreed to strip Cairo command of hundreds more tanks in 1942, routing them to Stalin’s USSR via Iran to bail out the Red Army at Stalingrad, which left Egypt vulnerable to Rommel’s Afrika Korps.
Churchill doubled down on his pro-Soviet policies even in areas where Britain had her own clients, such as Yugoslavia. Despite hosting the Yugoslav exile government in London, by September 1943, Churchill abandoned that government’s commander on the ground and threw his full support behind Stalin’s man, Josip Broz (“Tito”). Bamboozled by a Soviet smear campaign against Colonel Draža Mihailovic, Churchill cut off Mihailovic’s Chetniks and shipped Tito more than 100 times more war materiel over the next nine months than Mihailovic had received in the previous two years.
Sean McMeekin, “Churchill’s enigma: the real riddle is why he cozied up to Stalin”, Spectator, 2021-03-21.
January 13, 2021
Waking the Sleeping Giant – America Prepares for War – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 12 Jan 2021As the United States enters World War Two, a huge industrial giant awakens from hibernation. This episode covers industrial mobilization plans, their execution, and their potential.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Joram Appel
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Joram Appel
Edited by: Karolina Dołęga
Sound design: Marek Kamiński
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
Norman Stewart – https://oldtimesincolor.blogspot.com/Sources:
– Library of Congress
– National Archives NARA
– Picture of the first class of the Army Industrial College from National Defense University
– FDR Presidential Library & Museum
– Icons from the Noun Project: Artillery by Creative Mania, Douglas SBD Dauntless by Lluisa Iborra, Man by Milinda Courey, Factory Workers by Gan Khoon Lay, Soldier by Wonmo Kang, Old Car by Andri Graphic, progress 20% & 40% by Roberto Chiaveri.Soundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
– “The Inspector 4” – Johannes Bornlöf
– “London” – Howard Harper-Barnes
– “Break Free” – Fabien Tell
– “Last Point of Safe Return” – Fabien Tell
– “Force Matrix” – Jon BjorkArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
October 4, 2020
September 30, 2020
America First – Patriots or Nazis? – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 29 Sep 2020In 1941, the question of whether America should join the European War still isn’t settled. Different groups whip up opposition to it, and those such as the America First Committee seem suspiciously sympathetic to Hitler’s message and cause.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Francis van Berkel and Indy Neidell
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: James Newman
Edited by: Miki Cackowski
Sound design: Marek Kamiński
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
Daniel Weiss
Norman Stewart – https://oldtimesincolor.blogspot.com/Sources:
from the Noun Project: people by ProSymbolsSoundtracks from the Epidemic Sound:
Reynard Seidel – “Deflection”
Johannes Bornlof – “The Inspector 4”
Philip Ayers – “Trapped in a Maze”
Johannes Bornlof – “Deviation In Time”
Phoenix Tail – “At the Front”Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
June 11, 2020
World War Two Heats Up: The M1928A1 Thompson SMG
Forgotten Weapons
Published 11 Oct 2018https://www.forgottenweapons.com/worl…
http://www.patreon.com/ForgottenWeapons
Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.bbtv.com/collections/forg…
By 1939, Auto-Ordnance was thoroughly bankrupt, having about $400 in assets and a debt of more than $1.2 million to the estate of the late Thomas Ryan, it’s original financier. Ryan had died in 1929, but the company shareholders had prevented his estate from forcing the sale of the company for a decade. In 1939 they could hold out no longer, and the company was sold to one Russell Maguire, a high profile corporate raider.
Maguire, however, saw the potential of a submachine gun company on the brink of a new world war, and negotiated a contract with the Savage Arms Company to begin new production of Thompsons (the original Colt guns from 1921 having finally all sold). Orders began to come in from Europe, and new Model of 1928 Thompsons were sold to France, Sweden, and most substantially, the United Kingdom. The US military would also start buying Thompsons in quantity (designated the M1928A1), but the UK orders (paid for in bullion) were a massive source of profits for the company.
Auto-Ordnance would roll some of these profits back into the company, buying an old automotive brake factory in Bridgeport Connecticut and tooling up their own production of receivers and trigger frames to supplement Savage’s production. A number of changes were progressively made to the guns to simplify and speed up their manufacture, including smooth barrels, stamped ejectors, vastly simplified rear sights, and horizontal front grips. By the time the M1928A1 was replaced by the M1 Thompson, more than 1.1 million had been made by AO and Savage combined. The Thompson had at last found it’s purpose!
This is the third of a 5-part series on the development of the Thompson…
Contact:
Forgotten Weapons
PO Box 87647
Tucson, AZ 85754If you enjoy Forgotten Weapons, check out its sister channel, InRangeTV! http://www.youtube.com/InRangeTVShow
June 7, 2020
Why determining the Impact of Lend-Lease is so complicated
Military History Visualized
Published 14 Aug 2018Determining the impact of the Western Aid that was provided to the Soviet Union in the Second World War is quite controversial. This aid was provided under the Lend-Lease act, as such it is usually just called Lend-Lease. The majority of the support was provided by the United States, yet other countries like the United Kingdom and Canada aided the Soviet Union as well.
Thank you to VonKickass for the Thumbnail Design!
»» SUPPORT MHV ««
» patreon – https://www.patreon.com/join/mhv
» paypal donation – https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr…»» MERCHANDISE – SPOILS OF WAR ««
» shop – https://www.redbubble.com/people/mhvi…»» SOCIAL MEDIA ««
» twitter – https://twitter.com/MilHiVisualized
» twitch – https://www.twitch.tv/militaryhistory…» SOURCES «
Boris V. Sokolov: “The role of lend‐lease in Soviet military efforts, 1941–1945”, The Journal of Slavic Military Studies, 7:3 (1994) p. 567-586
Hill, Alexander: The Red Army and the Second World War. Armies of the Second World War. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017.
Glantz, David M.; House, Jonathan M.: When Titans Clashed. How the Red Army stopped Hitler. Revised and Expanded Edition. University Press of Kansas: USA, 2015
Harrison, Mark: THE SOVIET ECONOMY AND RELATIONS WITH THE UNITED STATES AND BRITAIN, 1941-1945, Draft 25 August, 1993
Hill, Alexander: “British Lend Lease Aid and the Soviet War Effort, June 1941 June 1942”, in: The Journal of Military History, Vol. 71, No. 3 (Jul., 2007), pp. 773-808
Cambridge History of the Second World War. Volume 1: Fighting the War. Cambridge University Press: UK (2015)
Broadberry, Stephen; Howlett, Peter: “The United Kingdom: ‘Victory at all costs'”, in: Harrison, Mark (ed.): The Economics of World War II. Cambridge University Press: UK (1998), p. 43-80
Strydwolf: Lend-Lease to Soviet Union, significance, impact and myths
Protocol and Area Information Staff of the U.S.S.R. Branch and the Division of Research and Reports: REPORT ON WAR AID FURNISHED BY THE UNITED STATES TO THE U.S.S.R, November 28, 1945
Harrison, Mark: “The USSR and Total War: Why Didn’t the Soviet Economy Collapse in 1942?” In: Chickering, Roger (ed.); Förster, Stig (ed.); Greiner, Bernd (ed.): A World at Total War: Global Conflict and the Politics of Destruction, 1939-1945, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press (2005), p. 137-156.
Tooze, Adam: The Wages of Destruction. The Making and Breaking of the Nazi Economy. Penguin Books: United Kingdom (2006).
Overy, Richard: Why the Allies Won. Pimlico: London, UK (2006).
Higham, Robin (ed.); Kagan, Frederick W. (ed.): The Military History of the Soviet Union. Palgrave: New York, 2002
Havlat, Denis: Western aid for the Soviet Union during World War II, Wien, 2015 (Master Thesis)
» DATA CHAIN «
Made with Natural Earth. Free vector and raster map data @ naturalearthdata.com.» CREDITS & SPECIAL THX «
Song: Ethan Meixsell – “Demilitarized Zone”