The Great War
Published 10 Apr 2020
Sign up for Curiosity Stream and Nebula – and get 40% off annual plans right now: https://curiositystream.com/thegreatwar
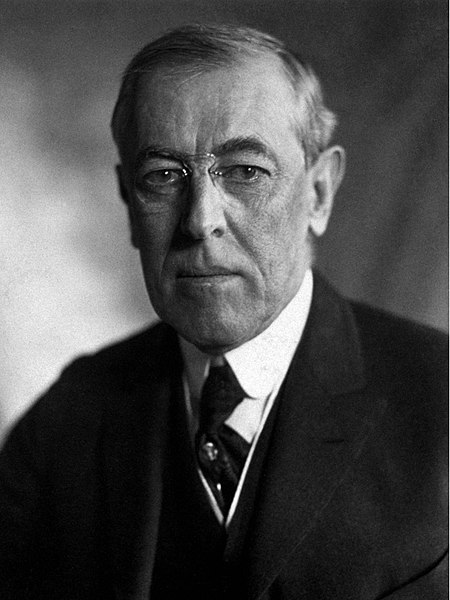
The League of Nations was US President Woodrow Wilson’s tool for a new and peaceful world after the war of 1914-1918 — and the US should have been their most important member. But the United States never joined and today the League of Nations is often seen as a failure. Was it doomed from the start?
» SUPPORT THE CHANNEL
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thegreatwar
Merchandise: https://shop.spreadshirt.de/thegreatwar/
» SOURCES
“The Treaty of Peace with Germany (The Treaty of Versailles),” June 28, 1919, United States Statutes at Large, art. 1-440.
Walters, F.P. A History of the League of Nations. (Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 1952)
Link, Arthur et al., eds., The Papers of Woodrow Wilson, vol. 45 (1984)
Ray S. Baker and William E. Dodd, eds, The Public Papers of Woodrow Wilson: Authorized Edition, Vol. 1, (New York, 1924)
Matz, Nele, “Civilization and the Mandate System under the League of Nations as Origin of Trusteeship” in von Bogdandy, A and Wolfrum, R (eds.), Max Planck Yearbook of United Nations Law, Volume 9, 2005
Braumoeller, Bear F. “The Myth of American Isolationism”, Foreign Policy Analysis Vol. 6, No. 4 (OCTOBER 2010), pp. 349-371
“March 19, 1920: Senate Rejects Treaty of Versailles for Second and Final Time” New York Times, https://learning.blogs.nytimes.com/20… /march-19-1920-senate- rejects-treaty-of-versailles-for-second-and-final-time/
Egerton, George W, “The Lloyd George Government and the Creation of the League of Nations”, The American Historical Review, Vol. 79, No. 2 (Apr., 1974), pp. 419-444
Burkman, Thomas W. “Japan and the League of Nations: AN ASIAN POWER ENCOUNTERS THE ‘EUROPEAN CLUB'”, World Affairs, Vol. 158, No. 1, Woodrow Wilson and the League of Nations: Part Two (SUMMER 1995), pp. 45-57
Rappart, William E. “Small States in the League of Nations”, Political Science Quarterly Vol. 49, No. 4 (Dec., 1934), pp. 544-575
Cox, James Middleston, Journey Through My Years, (Simon & Schuster: New York, 1946)
“THE BRITISH EMPIRE, THE LEAGUE OF NATIONS, AND THE UNITED STATES”, Advocate of Peace through Justice, Vol. 82, No. 7 (JULY, 1920), pp. 229-231
Dorsey, Leeroy G, “Woodrow Wilson’s Fight for the League of Nations: A Reexamination”, Rhetoric and Public Affairs, Vol. 2, No. 1 (Spring 1999), pp. 107-135
“The Covenant of the League of Nations” AVALON PROJECT, Yale Law School, https://avalon.law.yale.edu/20th_cent…
“Woodrow Wilson’s 14 Points”, AVALON PROJECT, Yale Law School, https://avalon.law.yale.edu/20th_cent…
Riddell, George Allardice, The Riddell diaries, 1908-1923, (London ; Dover, N.H. : Athlone Press, 1986)
» SOCIAL MEDIA
Instagram: https://instagram.com/the_great_war
Twitter: https://twitter.com/WW1_Series
Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/TheGreatWarChannel
»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Mark Newton, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Toni Steller
Editing: Toni Steller
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Daniel Kogosov (https://www.patreon.com/Zalezsky)
Research by: Jesse Alexander
Fact checking: Florian Wittig
Channel Design: Alexander Clark
Original Logo: David van Stephold
A Mediakraft Networks Original Channel
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2020