Picture the scene: it is a dark night in late November. A cross-channel ferry is about to set sail for England. A posh young man, a boy really, boards the ship with his posh mates. They’re not short of money and before long they’re seriously drunk. Some of the other passengers disembark. They hadn’t signed-up for a booze cruise — and, what’s more, the young men are carrying knives. Well, I say “knives” — what I actually mean is swords.
At this point, I ought to mention that the year is 1120; the young man is William Adelin, heir to the throne of England; and the “ferry” is the infamous White Ship.
Anyway, back to the story: the wine keeps flowing and, before long, the crew are drunk too. Not far out of port, the ship hits a submerged rock and rapidly sinks.
In all, hundreds are drowned — and yet that is just the start of the tragedy.
William’s father, King Henry I, had gone to great lengths to proclaim an heir. As the son of William the Conqueror, he knew just how messy succession could get. He had himself inherited the throne from his brother, William Rufus. This second William had died of a chest complaint — specifically, an arrow in the lungs (the result of a hunting “accident”). Henry was determined that his son would inherit the throne without mishap — and so carefully prepared the ground for a smooth transfer. Indeed, the name “Adelin” signified that the third William was the heir apparent.
The sinking of the White Ship left Henry with one remaining legitimate heir, his daughter Matilda. She was a formidable character, also known as Empress Maud (by virtue of her first marriage to the Holy Roman Emperor). She was, nevertheless, a woman — a big problem in an age when monarchs were expected to lead their men in battle. When Henry died in 1135, Maud’s cousin — Stephen of Blois — seized the throne. This was widely welcomed by the English nobility, but Maud wasn’t giving up easily, and she had powerful allies. Her second husband was Geoffrey, Count of Anjou; her illegitimate half-brother, Robert of Gloucester, was a wealthy baron; and her uncle was King David I of Scotland.
Stephen was assailed on all sides — by Geoffrey in Normandy, by Robert in England, by invading Scots and rebellious Welshmen. The civil war (if that’s what you can call this multi-sided free-for-all) dragged on for almost 20 years. There weren’t many set-piece battles, but there was lots of looting and pillaging in which countless nameless peasants perished.
In the end it was the death of another heir — Stephen’s son, Eustace — that opened the way to peace. The war-weary king agreed that Maud’s son (the future Henry II) would succeed him. And thus “The Anarchy” came to end: two decades of pointless devastation — and all because some young fool got pissed on a boat.
Peter Franklin, “Why Boris needs an heir apparent”, UnHerd, 2020-08-17.
March 2, 2026
QotD: King Stephen and “the anarchy”
March 1, 2026
The American Revolutionaries – when you don’t want a king, but you do want someone king-ish
On Substack Notes, John Carter shared this post by Theophilus Chilton, saying:
Fascinating. The American founders were explicitly trying to revive a stronger form of monarchical executive authority with the presidency, as a deliberate corrective to the relatively powerless Crown of the British Constitution, which had been effectively neutered by the doctrine of parliamentary supremacy.
Along similar lines, the American Bill of Rights was in most ways simply a restatement of the ancient rights of Englishmen.
So, of course, I had to go read the post:

Too “kingly” but also not “kingly” enough for America’s Founding Fathers.
King George III in his Coronation robes.
Oil painting by Allan Ramsay (1713-1784) circa 1761-1762. From the Royal Collection (RCIN 405307) via Wikimedia Commons.
Recently, I’ve been reading an interesting book about 18th century political philosophy entitled The Royalist Revolution: Monarchy and the American Founding. In this work the author, Eric Nelson, guides the reader through the various aspects of the great inter-whiggish debates that roiled the American colonies prior to independence, and which then continued afterwards. One of the main premises is that a major faction within this debate — and indeed the one which ended up prevailing in the end — understood the relationship between colonies and mother country to be founded upon the king of Britain’s personal proprietorship over the colonies. This Patriot position was opposed by the Loyalist position which saw the colonies as existing under the laws and rule of Parliament.
Now this might seem strange to generations of Americans who grew up learning in school that the American revolutionaries fought against the great tyrant King George III who was set upon grinding the American colonies under his bootheel of oppression. That view would be quite surprising to many of the participants on the Patriot side, many of whom actually appealed to King George, both publicly and in private correspondence, to exercise kingly prerogative and overturn the various duties, laws, and taxes which Parliament had laid upon the colonies. This, indeed, was the crux of the Patriot argument, which is that because the colonies were originally founded under the personal demesne of the British King, they remained so even despite the temporary abolishment of the monarchy after the execution of Charles I in 1649. In the interregnum between that and the Glorious Revolution and restoration of a stable monarchy that was accepted by all classes as legitimate in 1688, Parliament had illegitimately usurped authority over the colonies. Because it was Parliament which was laying the Intolerable Acts and all the other complaints which the Americans had, it was Parliament against whom they wished to be protected.
But these Patriots were pining after a situation which no longer existed. In point of fact, the British kings since the Glorious Revolution had left whatever prerogative powers they might still have had unused. So it was with George III, who rejected the American colonists’ calls for him to intervene, knowing that doing so would have provoked a constitutional crisis in Britain which he would not have won. As a result, the American colonists chose to make their final break with the British monarchy and throw in their lot for independence, buttressed by Thomas Paine’s fleetingly persuasive but ultimately ineffectual pamphlet Common Sense.
However, after independence, the colonists were faced with providing their own governance. Initially, this was attempted under the Articles of Confederation, as well as their state constitutions, all of which were very whiggish in principle. They were also inadequate to the task. As every student who took high school civics knows, the solution to this was the Constitution of 1789.
Typically, students are taught that the new Constitution was designed to strengthen the ability of the federal government to handle the various issues that applied to the confederation of states as a whole. What we don’t generally hear, however, is that much of this included strengthening the roles and powers of the president to include several areas of prerogative powers which exceeded even the powers then available to the kings of Britain. The stock view of the Constitution is that it “was created to prevent anyone from getting too much power!” The actuality is that the Constitution was crafted, in part, to expand presidential power and create what was viewed at the time as a literally monarchical chief executive. Opponents of this described the proposed executive as “the foetus of monarchy”. Supporters often defended it on the basis that parliaments and congresses, if left unchecked by a strong executive whose interest was drawn from the body of the whole people, would themselves become the greatest threats to the liberties of the people.
The Founders who proposed this enhancement of the executive didn’t do this in a vacuum. Indeed, they had a century and a half of history about this very subject to draw from first-hand. Fresh in the collective mind of every Englishmen, both in the home country and in the colonies, were the English Civil Wars of the previous century. Beginning with the revolt of the parliamentarian army in 1642 through the regicide of Charles I in 1649, the protectorate of Oliver Cromwell, the attempted restoration of the House of Stuart under James II, until the final deposition of James and his replacement with William, Prince of Orange in the Glorious Revolution of 1688, Englishmen had a long series of examples from which to draw various conclusions.
So yes, they could see the parliamentarian excesses that took place during the Protectorate. Current in the collective national mind were the overreaches (whether real or imagined) of Parliament both during the interregnum and in the century since the acquisition of the throne by the House of Hanover. As noted above, among these overreaches, at least as viewed by many in the American colonies, was parliamentary interference in the affairs of the colonies, viewed as transgressions into the rightful domain of the king’s purview. Hence, by a strange twist, the Loyalists who opposed American independence before and during the Revolution were generally the more whiggish of the two sides, throwing in their lot with the parliamentary oligarchies. The Patriots, on the other hand, were desperately trying to get the king to reassert his royal prerogatives and intervene by reasserting his perceived rights to directly rule the colonies, something of a modified “high/low vs. the middle” type of scenario.
December 28, 2025
QotD: The Middle Ages saw rebellions but no revolutions
At some point in this space, we discussed the difference between a rebellion and a revolution. Drawing on Michael Walzer’s key work The Revolution of the Saints, I argued that a true revolution requires ideology, as it’s an attempt to fundamentally change society’s structure.
Therefore there were no revolutions in the Middle Ages or the Ancient World, only rebellions — even a nasty series of civil wars like The Wars of the Roses were merely bloody attempts to replace one set of rulers with another, without comment on the underlying structure. A medieval usurpation couldn’t help but raise questions about “political theory” in the broadest sense — how can God’s anointed monarch be overthrown? — but medieval usurpers understood this: They always presented the new boss as the true, legitimate king by blood. I forget how e.g. Henry IV did it — Wiki’s not clear — but he did, shoehorning himself into the royal succession somehow.
Combine that with Henry’s obvious competence, Richard II’s manifest in-competence, and Henry’s brilliant manipulation of the rituals of kingship, and that was good enough; his strong pimp hand took care of the rest. Henry IV was a legitimate king because he acted like a legitimate king.
A revolution, by contrast, aims to change fundamental social relations. That’s why medieval peasant rebellions always failed. Wat Tyler had as many, and as legitimate, gripes against Richard II as Henry Bolingbroke did, but unlike Henry’s, Tyler’s gripes couldn’t really be addressed by a change of leadership — they were structural. 200 years later, and the rebels were now revolutionaries, willing to give structural change a go.
Severian, “¡Viva la Revolución!”, Founding Questions, 2025-02-27.
November 24, 2025
Algeria: France’s War It Refused to Name – W2W 054
TimeGhost History
Published 23 Nov 2025This episode tracks how the doctrine “Algeria is France” — departments, settler power, and forced assimilation — breeds dispossession, mass violence, and a new Algerian nationalism: from conquest and the Sétif massacres to the FLN’s launch in 1954 and Philippeville in 1955. As Paris doubles its forces and passes Special Powers, Suez intertwines with the war, bombings in Algiers begin, and Lacoste hands police powers to General Massu — opening the Battle of Algiers and a system of torture.
(more…)
October 24, 2025
The Picnic at the Battle of Bull Run
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 20 May 2025Nutmeg and brandy pound cake with roast beef sandwiches, lemonade, and berries
City/Region: United States of America
Time Period: 1824In the beginning of the American Civil War, no one expected the fighting to go on for very long. Not wanting to miss out on any of the action, a crowd of spectators gathered a couple of miles from the battlefield at the First Battle of Bull Run. They enjoyed the boom of cannon fire and picnic lunches of sandwiches, pies, and cakes, before fleeing for their lives in a mad dash when the battle turned against the Union.
This pound cake is denser than modern versions because it contains no chemical leavener, but it’s not stodgy and is delicious. The nutmeg comes through and you get the flavor of the brandy without it being boozy.
To complete your picnic and recreate some simple sandwiches from 1857, butter slices of white bread, layer on sliced roast beef and Dijon mustard, then trim off the crusts. I don’t usually put butter on my sandwiches, but it was really nice.
Pound Cake.
Wash the salt from a pound of butter and rub it till it is soft as cream, have ready a pound of flour sifted, one of powdered sugar, and twelve eggs well beaten; put alternately into the butter, sugar, flour and the froth from the eggs; continuing to beat them together till all the ingredients are in, and the cake quite light; add some grated lemon peel, a nutmeg, and a gill of brandy; butter the pans and bake them.
— The Virginia House-Wife by Mary Randolph, 1824.Sandwiches for travelling may be made of the lean of cold beef, (roast or boiled,) cut very thin, seasoned with French mustard, and laid between two slices of bread and butter.
— Miss Leslie’s New Cookery Book, 1857
October 16, 2025
The hereditary aristocrats of the People’s Republic of China
To many western liberals, an aristocratic system is a disparaged and vestigial remnant of the distant past. An echo of the “bad old days” of anti-meritocratic wealth and privilege enjoyed by the lucky descendants of ancient conquerors and oppressors. Yet among the most well-connected and powerful people in China can only be described as “princelings”, as they are literally the children and grandchildren of the leaders of the Communist Party, especially those who took part in the “Long March”:

“The Chinese People’s Liberation Army is the great school of Mao Zedong Thought”, 1969.
A poster from the Cultural Revolution, featuring an image of Chairman Mao, published by the government of the People’s Republic of China.
Image via Wikimedia Commons.
In 1926, five years after becoming one of the founders of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), Mao Zedong listed China’s enemies as “the warlords, the bureaucrats, the comprador class [businessmen dealing with foreign interests] and the reactionary section of the intelligentsia attached to them”. It is ironic that Mao would eventually create a new aristocracy, often referred to as the “princelings” (taizidang), every bit as hierarchical as that against which he had previously railed.
Perversely, when Mao Zedong came to power in China in 1949, there were not many structures of authority left to destroy. In the period of warlordism that succeeded the overthrow of the Qing dynasty by Sun Yat-sen in 2011 and ended with the consolidation of nationalist (Kuomintang) power by Chiang Kai-shek in 1936, the aristocracy of imperial China had been swept away. So too the Mandarin class, the Chinese bureaucrats selected by civil service examination, a system that started with the Sui dynasty in AD 581. As for the Chinese aristocracy, its last vestiges ended with the abolition in 1935 of the Dukedom of Yansheng which belonged to the descendants of Confucius.
So, in terms of social hierarchies, Mao inherited a clean sheet when he established the People’s Republic of China on October 1, 1949. The CCP leadership soon proved that, in the immortal words of George Orwell in his novel Animal Farm, “all animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others”. In Beijing, Mao and China’s CCP leaders took residence in the palatial compounds located in Zhongnanhai, a waterside park established by the Yuan dynasty in the 13th century.
There is not even equality within the “red aristocracy”. Gradations are as clear-cut as if there were princes, dukes or marquises. The highest rank is accredited to the offspring of those CCP leaders who participated in the Long March. This iconic fighting retreat to a remote plateau in Shaanxi province followed the defeat of the Red Army in October 1934.
It is perhaps difficult for people in the West to understand the scale of Chinese veneration for the individuals who completed the Long March. With the possible exception of the migratory treks along the Oregon Trail, there is no comparable event in American or European history. Throughout their lives, leaders of the Long March enjoyed unparalleled prestige; it was a prestige that passed down to their children – hence the princelings.
The creation of the red aristocracy started with Mao himself. Within a few years of the establishment of the People’s Republic of China, Mao became a de facto emperor. On occasions he even referred to himself as such. He certainly lived the life of an emperor. At his commodious palace in Zhongnanhai, Mao surrounded himself with a harem of dancing girls who would occupy his bed and his swimming pool. In time-honoured fashion, China’s head of security and intelligence, Kang Sheng, procured girls for Mao as well as thousands of volumes of pornography.
[…]
My own experience of the princeling world confirmed that in China, despite its vast population a very small group of families form a governing nexus that has power far beyond its numbers. It is a group that seem to be getting stronger. The princeling proportion of the CCP central committee rose from 6 per cent in 1982 to 9 per cent in 2012. When I spoke to a princeling friend about the politburo standing committee that was elected in 2012, she told me that she personally knew five of its seven members; to her great delight three of them were princelings. It was through her that I met Deng Xiaoping’s daughters and spent a “country house” weekend with them and her princeling pals.
Here it became clear that, while most of the princelings I met were reformists in the Deng mode, there are also factions that are hard-line Maoists, like the one led by Xi Jinping. At the moment it appears that the reformist princelings have gained the upper hand. More light on Xi Jinping’s future and the outcome of this princeling tug of war may be shed at the Fourth Plenum of the 20th CCP Congress starting on October 20.
October 14, 2025
White Hoods, Bloody Hands: The Klan as America’s First Terrorists – W2W 048
TimeGhost History
Published 12 Oct 2025From Pulaski to Stone Mountain to Brown v. Board, the Ku Klux Klan evolves from Reconstruction terror to a decentralized, Cold War–era movement that bombed churches, lynched citizens, and hid behind “anti-communism”. We trace the First, Second, and Third Klans — rituals, networks, and the brutal campaign against desegregation and civil rights.
(more…)
October 12, 2025
October 4, 2025
Warner Carbine
Forgotten Weapons
Published 8 Sept 2015The Warner carbine was another of the weapons used in small numbers by the Union cavalry during the Civil War. It is a pivoting breechblock action built on a brass frame. These carbines were made in two batches, known as the Greene and Springfield. The first guns were chambered for a proprietary .50 Warner cartridge, which was replaced with .56 Spencer in the later versions (for compatibility with other cavalry arms).
This particular Warner shows some interesting modification to its breechblock, which has been converted to use either rimfire or centerfire ammunition. This was not an uncommon modification for .56 Spencer weapons, as the centerfire type of Spencer ammunition could be reloaded (unlike the rimfire cartridges). With this modification, the firing pin can be switched from rimfire to centerfire position fairly easily.
October 1, 2025
The Battle of Actium – We can at least agree ships were involved!
Drachinifel
Published 12 Oct 2022Today we take a look at the battle that decided if Rome was to be a Republic or an Empire, and also examine why its incredibly hard to work out just exactly what happened between the start and the end!
Sources:
https://www.amazon.co.uk/Battle-Actiu…
https://www.amazon.co.uk/Actium-31-BC…
https://www.amazon.co.uk/War-That-Mad…
https://www.amazon.co.uk/Roman-Histor…
http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/10452/
(more…)
September 26, 2025
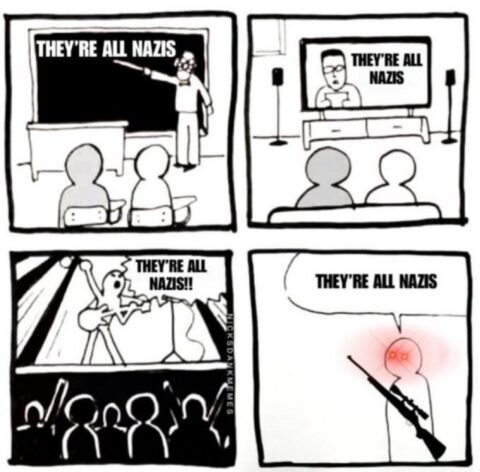
“Create no-go zones for federal forces”
On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, ESR responds to a comment about his three possible futures after the Charlie Kirk assassination (linked here):
Mike Benz @MikeBenzCyber
Antifa websites totally open to the public explicitly call to so utterly terrorize ICE that federal agents are physically afraid to enter a city. If the Proud Boys wrote this about the FBI how fast would every single person around that website be indicted by Merrick Garland.
“Create no-go zones for federal forces.’
In one of my previous analysis postings, I outlined three possible scenarios for the future after the assassination of Charlie Kirk.
This corresponds to scenario 3, the one where insurrection edges into a simmering civil war a la Bosnia. I caught some flak in my replies at the time from people who thought an insurrection based in urban areas isn’t practical under modern conditions.
Antifa thinks it is. It’s what they’re planning for.
One of the things I have to remind myself of occasionally is that most people know essentially nothing about Communist theory and Communist revolutionary tactics.
Antifa is running the classic Communist playbook. Make the enemy fight you where you are strong and they are weak — where you have support among the people and (when possible) cover from sympathetic local officials.
Historically that has usually meant fighting from rural areas where the reach of the government is weak. But the Russian Revolution was an exception, and the revolution Antifa is trying to fight is another. Their natural home ground is large coastal cities run by left-wing Democrats.
September 22, 2025
HBO’s Rome – Ep 12 “Kalends of February” – History and Story
Adrian Goldsworthy. Historian and Novelist
Published 30 Apr 2025Today, we look at the final episode of Season One, which deals with the last days of the conspiracy against Julius Caesar and his murder on the Ides of March — not that the date gets a mention. There is quite a lot of soap-opera stuff in this one, the culmination of character arcs, so less time for politics.
One day, we may do Season Two, but for the moment, that’s all folks!
September 19, 2025
After the Charlie Kirk assassination, here are three possible futures
On the social media site formerly known as Twitter, ESR lays out what he sees are the three most likely short-term futures for the United States after the assassination of Charlie Kirk:
I’m a student of history. Here are three possible futures following the assassination of Charlie Kirk. They’re based on historical examples of what happens when a Communist subversion campaign or insurgency overplays its hand and triggers broad popular resistance.
1. Popular revulsion against aboveground leftists celebrating the murder gives the Trump administration political cover to go after Antifa and its shadow funding network hard. Both are smashed.
Communist agents of influence in the mainstream media and academia continue to self-discredit.
Relatively few Communists are arrested, but their millions of aboveground tools become isolated and demoralized.
Propelled by a huge swing in voter registrations that we are already seeing happen, the Democrats get crushed in the 2026 midterms.
The long period of fever, madness, and Left ascendancy that began with the assassination of JFK by a Soviet agent in 1963 ends not with a bang but with a whimper.
This is the best case scenario for everybody, including the Communists who don’t get thrown out of helicopters or shot down in the streets.
If things don’t go this way it will likely be because Democratic lawfare prevents the counter-subversion push from being fully effective. An obvious index of this failure would be another high-profile political assassination or attempt against a conservative target after about 4 months out.
What happens in the event of that failure, especially if the third public attempt to kill Trump succeeds:
2. A period of Caudillismo. A charismatic strongman rides popular anger into power. If this happens, the Left better pray that the strongman is an infuriated JD Vance, because any alternative to him is likely to be worse for them.
The crackdown against the Communist network becomes brutal and routinely uses extra-Constitutional means, possibly thinly covered by a declared state of emergency.
At the harder end of this range of possibilities, right-wing death squads not exactly formed by government but winked at by it go after Communist public figures that are out of reach of the law because they’ve carefully preserved deniability. Many journalists are at the top of this target list.
It is not likely that the Communist network can survive this future. The only way it happens is if they have enough popular support to develop a semi-militarized resistance — in effect making certain parts of the country no go regions for Federal agents.
Going by historical precedents, the index of this failure would be a resurgence of banditry by armed groups, initially with overtly political goals but decaying into general predation.
This would land us at:
3. Low-grade civil war, a la Bosnia or the Irish troubles. Anybody wishing for this has no idea how bloody, ugly, and brutal it would probably be. Especially if the Left succeeds at what it will with absolute certainty try to do, which is racialize the conflict.
I don’t think there is any realistic scenario in which the Communists win any of these confrontations. Not in the U.S., not in the 21st century. The question is how much blood and agony the rest of us will go through before they are finally defeated.
Update, 20 September: Welcome, Instapundit readers! Please do have a look around at some of my other posts you may find of interest. I send out a daily summary of posts here through my Substack – https://substack.com/@nicholasrusson that you can subscribe to if you’d like to be informed of new posts in the future.
September 16, 2025
No sensible person wants to start a civil war
There are always angry folks online who take any current event as a conversational pretext for talking about taking up arms against … whoever they always seem to want to take up arms against. In decades past, you could more easily find tantrums like that among the conspiratorial right but today it seems that the left is leading the charge, so to speak. As a bit of a follow-on to this post, here’s more from Tom Kratman and Harry Kitchener on what might need to be done to start that unwanted-by-all-sensible-folks conflict:
Let’s assume, though, that you people want to kick off what we might call a hard debate – that you plan to use organized and precise violence to combat your enemies and promote your views.
Actually doing it is pretty easy – a patsy with a hunting rifle has a pretty good chance, assuming a bit of talent, to take out any given public figure (assuming no Secret Service protection, that makes things much more difficult). He’ll almost certainly be caught, of course; in a best case, arrested, tried and sentenced to life … or death, in a worst case, killed during the arrest. If you’ve got an inexhaustible supply of these patsies I suppose that’s sustainable – it’s meaningless, of course, as it’ll just bring the other side to the conclusion that if this is the game in future, they’ll happily play along (and they have more guns, more training and probably more immediate support than you do. And they’re starting to really hate you, too).
If you actually *want* to kick off a low-level civil war (I have to say I can’t understand why you would want this, but, hey ho, your call), you need to think in more sustainable terms. Read back on our pieces for some hints on the operational, logistic and security considerations you need to establish a covert, violent organization. Particularly consider the issue of finance – this stuff costs big money to organize and execute and I’m not sure you have access to the sort of volumes of laundered cash you’re going to need.
You’re also going to need to be tough, properly tough in order to cope with the immense pressure you’re going to feel from government and the Right alike, to say nothing of the moral (and morale) impact of inevitable casualties, not just those arrested and sentenced, but also those killed and maimed. Don’t underestimate the impact on one of your “active service units” losing one or two of their members, or of the occasional need just to abandon them in order to get away.
Assuming – and, to be frank, I don’t see this working – but, assuming you do manage to organize some sort of covert violent organization, what would it be *for*? What’s the end state you’re looking to achieve? Proletarian revolution, the righteous rage of the mobilized working class? Not a fucking chance, not in the USA. Every historical example we have of the left trying this kind of thing to raise an oppressive right wing government, to mobilize the masses for the left, shows, instead, massive cheering from those masses for the government that then proceeds to exterminate you.
Cowing the Right through violence? Again, not a hope – the Right (as you call it, a better term might be “the majority of the US population”) tends to be pretty much OK with justified violence, tends to have a larger proportion of people who’ve seen the elephant (this is military slang for “the greatest show on earth”, which is to say, war) and tends to be much better armed than your folks are. On the plus side, you’re in America so becoming better armed is easy. Becoming better armed without leaving a trail pointing straight at you, on the other hand, is hard. And you don’t have the criminal connections to avoid this.
Your base is relatively small and relatively concentrated in certain areas and in certain sectors – soft states, academia, the media, that kind of thing. Don’t believe a word big tech says, they’ll drop you and switch immediately as their share price is adversely affected. And note that the “disciplines” your sort of people tend to undertake in college – gender studies, ethnic studies, gay studies, feminist interpretive dance – are great for motivation to act for the left, but not very good for competence in action.
This makes your base incredibly vulnerable. No matter how effective your “active service units” might be in doing dreadful things to individuals on the Right, you’ll always be outgunned – and every single successful operation you carry out will generate greater support for your opponents. What’s that? Yes, of course it’s unfair and unjust. Deal with it.
What you have, always, to remember is that however important some things are to you, most people are either indifferent to them, or actively hostile to them. No amount of killing is going to change that, probably quite the contrary.
Update, 17 September: Welcome, Instapundit readers! Please do have a look around at some of my other posts you may find of interest. I send out a daily summary of posts here through my Substack – https://substack.com/@nicholasrusson that you can subscribe to if you’d like to be informed of new posts in the future.
September 15, 2025
HBO’s Rome – Ep 11 “The Spoils” – History and Story
Adrian Goldsworthy. Historian and Novelist
Published 23 Apr 2025This time we look at episode 11 — and only this episode as there is more to talk about when it comes to the historical background. Some of the plot doesn’t fit too well to the actual history, but there are some nice details that crop up and make it worthwhile. In the main, I get excited about a coin and a court.