Rex Krueger
Published 12 Nov 2025The Secret History of Wood – Rubber wood
(more…)
November 14, 2025
This is in your house … and you’ve never noticed
May 9, 2025
May 21, 2024
Tribalism
Theophilus Chilton pulls up an older essay from the vault, discussing tribalism, how it likely arose, and examples of cultures that relapsed into tribalism for various reasons:
In this post, I’d like to address the phenomenon of tribalism. There can be two general definitions of this term. The first is attitudinal – it refers to the possession by a group of people of a strong ethnic and cultural identity, one which pervades every level and facet of their society, and which serves to separate (often in a hostile sense) the group’s understanding of itself apart from its neighbours. The second definition is more technical and anthropological, referring to a group of people organised along kinship lines and possessing what would generally be referred to as a “primitive” governmental form centered around a chieftain and body of elders who are often thought to be imbued with supernatural authority and prestige (mana or some similar concept). The first definition, of course, is nearly always displayed by the second. It is this second definition which I would like to deal with, however.
Specifically, I’d like to explore the question of how tribalism relates to the collapse of widely spread cultures when they are placed under extreme stresses.
There is always the temptation to view historical and pre-historical (i.e., before written records were available) people-groups which were organised along tribal lines as “primitives” or even “stupid”. This is not necessarily the case, and in many instances is certainly not true. However, tribalism is not a truly optimal or even “natural” form of social organisation, and I believe is forced onto people-groups more out of necessity than anything else.
Before exploring the whys of tribalism’s existence, let’s first note what I believe can be stated as a general truism – Mankind is a social creature who naturally desires to organise himself along communal lines. This is why cities, cultures, civilisations even exist in the first place. Early in the history of Western science, Aristotle expressed this sentiment in his oft-quoted statement that “Man is by nature a political animal” (ὁ ἄνθρωπος φύσει πολιτικὸν ζῷον). This aphorism is usually misunderstood, unfortunately, due to the failure of many to take its cultural context into account. Aristotle was not saying that mankind’s nature is to sit around reading about politicians in the newspaper. He was not talking about “politics” in some sort of demotic or operational sense. Rather, “political” means “of the polis” [” rel=”noopener” target=”_blank”>link]. The polis, in archaic and classical Greece, was more than just a city-state – it was the very sum of Greek communal existence. Foreigners without poleis were not merely barbarians, they were something less than human beings, they lacked a crucial element of communal existence that made man – capable of speech and reason – different from the animals and able to govern himself rationally. “Political” did not mean “elections” or “scandals”, as it does with us today. Instead, it meant “capable of living with other human beings as a rational creature”. It meant civilisation itself. Tribalism, while perhaps incorrectly called “primitive”, nevertheless is “underdeveloped”. It is in the nature of man to organise himself socially, and even among early and technologically backwards peoples, this organisation was quite often more complex than tribal forms. While modern cities may be populated by socially atomised shells of men, the classical view of the city was that it was vital to genuine humanity.
My point in all of this is that I don’t believe that tribal organisation is a “natural” endpoint for humanity, socially speaking. The reason tribes are tribes is not because they are all too stupid to be capable of anything else, nor because they have achieved an organisation that truly satisfies the human spirit and nature. As the saying goes, “The only morality is civilisation”. The direction of man’s communal association with man is toward more complex forms of social and governing interactions which satisfy man’s inner desire for sociability.
So why are tribal peoples … tribal? My theory is that tribalism arises neither from stupidity or satisfaction, but as a result of either environmental factors such as geography, habitability, etc. which inhibit complexification of social organisation, or else as a result of civilisation-destroying catastrophes which corrode and destroy central authority and the institutions necessary to maintain socially complex systems.
The first – environmental factors – would most likely be useful for explaining why cultures existing in more extreme biomes persist in a tribal state. For example, the Arctic regions inhabited by the Inuit would militate against building complexity into their native (i.e. pre-contact with modern Europeans) societies. The first great civilisations of the river valleys – Egypt, Mesopotamia, the Indus valley, and China – all began because of the organisation needed to construct and administer large scale irrigation projects for agriculture. Yet, the weather in the Arctic precludes any sort of agriculture, as well as many other activities associated with high civilisation such as monumental architecture and large scale trade. The Inuit remained tribal hunter-gatherers not because they were inherently incapable of high culture, but because their surroundings inhibited them from it. Likewise, the many tribal groups in the Rub’ al-Khali (the Empty Quarter of the Arabian peninsula) were more or less locked into a semi-nomadic transhumant existence by their environment, even as the racially and linguistically quite similar peoples of Yemen and the Hadramaut were developing complex agricultural and commercial cultures along the wadis.
However, I believe that the more common reason for tribalism in history is that of catastrophes – of various types, some fast-acting and others much slower – which essentially “turned the world upside down” for previous high civilisations which were affected by them. I believe that there are many examples of this which can be seen, or at least inferred, from historical study. I’ll detail five of them below.
The first is an example which would formerly have been considered to fall into the category of tribes remaining tribal because of geographical factors, but which recent archaeological evidence suggests is not the case. This would be the tribes (or at least some of them) of the Amazon jungles, especially the Mato Grosso region of western Brazil. Long considered to be one of the most primitive regions on the planet, one could easily make the argument that these tribes were such because of the extreme conditions found in the South American jungles. While lush and verdant, these jungles are really rather inhospitable from the standpoint of human habitability – the jungle itself is extremely dense, is rife with parasites and other disease-carriers, and is full of poisonous plants and animals of all kinds. Yet, archaeologists now know that there was an advanced urban culture in this region which supported large-scale root agriculture, build roads, bridges, and palisades, and dammed rivers for the purpose of fish farming – evidently the rumours told to the early Spanish conquistadores of cities in the jungle were more than just myth. This culture lasted for nearly a millennium until it went into terminal decline around 1550 AD, the jungle reclaiming it thoroughly until satellite imaging recently rediscovered it.
What happened? We’re not sure, but the best theory seems to be that diseases brought by Europeans terminated this Mato Grosso culture, destroying enough of its population that urban existence could no longer be sustained. The result of this was a turn to tribalism, a less complex form more easily sustained by the post-plague population. The descendants of this culture are the Kuikuro people, a Carib-speaking tribe living in the region, and probably also other tribes living in the greater area around the Matto Grosso. In the case of the Mato Grosso city culture, the shock of disease against which they had no immunity destroyed their population, and concomitantly their ability to maintain more complex forms of civilisation.
The conical tower inside the Great Enclosure at Great Zimbabwe.
Photo by Marius Loots via Wikimedia Commons.The second example would be that of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe, centered around its capital of “Great Zimbabwe,” designated as such so as to distinguish it from the 200 or so smaller “zimbabwes” that have been scattered around present-day Rhodesia and Mozambique. Great Zimbabwe, at its peak, housed almost 20,000 people and was the nucleus of a widespread Iron Age culture in southern Africa, and this Bantu culture flourished from the 11th-16th centuries AD before collapsing. It is thought that the decline of Zimbabwean culture was due to the exhaustion of key natural resources which kept them from sustaining their urban culture. The result, if the later state of the peoples in the area is any indicator, was a conversion to the tribal structures more typically associated with sub-Saharan Africa. The direct descendants of the Zimbabwean culture are thought to be the various tribes in the area speaking Shona, a Bantu language group with over 8 million speakers now (post Western medicine and agriculture, of course). Once again, though, we see that when conditions changed – the loss of key resource supports for the urban culture – the shock to the system led to a radical decomplexification of the society involved.
February 22, 2024
Allied War Crimes, Latin American Troops, and Top-Secret Proximity Fuzes – WW2 – OOTF 033
World War Two
Published 21 Feb 2024Did the Western Allies commit war crimes? What did Latin American troops do during the war? And, how did the top-secret proximity fuze change the face of warfare? Find out in this episode of Out of the Foxholes.
(more…)
November 7, 2022
“We are the descendants of good team players”
Rob Henderson considers the Male-Warrior hypothesis:
The male-warrior hypothesis has two components:
- Within a same-sex human peer group, conflict between individuals is equally prevalent for both sexes, with overt physical conflict more common among males
- Males are more likely to reduce conflict within their group if they find themselves competing against an outgroup
The idea is that, compared with all-female groups, all-male groups will (on average) display an equal or greater amount of aggression and hostility toward one another. But when they are up against another group in a competitive situation, cooperation increases within male groups and remains the same among female groups.
Rivalries with other human groups in the ancestral environment in competition for resources and reproductive partners shaped human psychology to make distinctions between us and them. Mathematical modeling of human evolution suggests that human cooperation is a consequence of competition.
Humans who did not make this distinction — those who were unwilling to support their group to prevail against other groups — did not survive. We are the descendants of good team players.
It used to be accepted as a given that males were more aggressive toward one another than females. This is because researchers often used measures of overt aggression. For instance, researchers would observe kids at a playground and record the number of physical altercations that occurred and compare how they differed by sex. Unsurprisingly, boys push each other around and get into fights more than girls.
But when researchers expanded their definition of aggression to include verbal aggression and indirect aggression (rumor spreading, gossiping, ostracism, and friendship termination) they found that girls score higher on indirect aggression and no sex differences in verbal aggression.
The most common reasons people give for their most recent act of aggression are threats to social status and reputational concerns.
Intergroup conflict has been a fixture throughout human history. Anthropological and archaeological accounts indicate conflict, competition, antagonism, and aggression both within and between groups. But violence is at its most intense between groups.
A cross-cultural study of 31 hunter-gatherer societies found that 64 percent engaged in warfare once every 2 years.
Men are the primary participants in such conflicts. Human males across societies are responsible for 90 percent of the murders and make up about 80 percent of the victims.
The evolution of coalitional aggression has produced different psychological mechanisms in men and women.
Just as with direct versus indirect aggression, though, homicide might be easier to observe and track with men. When a man beats another man to death, it is clear what has happened. Female murder might be less visible and less traceable.
Here’s an example.
There’s a superb book called Yanoama: The Story of Helena Valero. It’s a biography of a Spanish girl abducted by the Kohorochiwetari, an indigenous Amazonian tribe. She recounts the frequent conflicts between different communities in the Amazon. After decades of living in various indigenous Amazonian communities, Valero manages to leave and describes her experiences to an Italian biologist, who published the book in 1965.
In the book, Helena Valero describes arriving in a new tribe. Some other girls were suspicious of her. One girl gives Valero a folded packet of leaves containing a foul-smelling substance. She tells Valero that it’s a snack, but that if she doesn’t like it she can give it to someone else. Valero finds the smell repulsive and sets it aside. Later, a small child picks up the leaf packet, takes a bite, and falls deathly ill. The child tells everyone that he got the leaf packet from Valero. The entire community accuses Valero of trying to poison the child, and banishes her from the tribe, with some firing arrows at her as she runs deep into the forest.
The girl who gave Valero the poisonous leaf packet formed a win-win strategy in her quest to eliminate her rival:
- Valero eats the leaf packet and dies
- Or she gives it to someone else who dies and she is blamed for it, followed by being ostracized or killed by the community
This is some high-level indirect aggression. Few men would ever think that far ahead (supervillains in movies notwithstanding). For most men, upon seeing a newcomer they view as a potential rival, they would just physically challenge him. Or kill him in his sleep or something, and that would be that.
Point is, this girl would have been responsible for Valero’s demise had she died. But no one would have known. If a man in the tribe, enraged at the death of the small child, had killed Valero, then he would be recorded as her killer. Or if Valero had been mauled by a jaguar while fleeing, then her death wouldn’t have been considered a murder.
Interestingly, the book implies that Valero was viewed as relatively attractive by the men, which likely means the girl who attempted to poison her was also relatively attractive (because she viewed her as a rival). Studies demonstrate that among adolescent girls, greater attractiveness is associated with greater use of aggressive tactics (both direct and indirect) against their rivals.
November 16, 2021
Pineapple: the King of Fruits
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 15 Nov 2021Pineapples are so culturally significant that pineapples adorn the tops of cathedrals, and serve as the domicile of one of the world’s most popular cartoon characters. An estimated 300 billion pineapples are farmed each year, and a 2021 YouGov poll lists pineapples as the sixth most favorite fruit, ahead of all varieties of apples and oranges.
This is original content based on research by The History Guy. Images in the Public Domain are carefully selected and provide illustration. As very few images of the actual event are available in the Public Domain, images of similar objects and events are used for illustration.
You can purchase the bow tie worn in this episode at The Tie Bar:
https://www.thetiebar.com/?utm_campai…All events are portrayed in historical context and for educational purposes. No images or content are primarily intended to shock and disgust. Those who do not learn from history are doomed to repeat it. Non censuram.
Find The History Guy at:
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TheHistoryGuy
Please send suggestions for future episodes: Suggestions@TheHistoryGuy.netThe History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered is the place to find short snippets of forgotten history from five to fifteen minutes long. If you like history too, this is the channel for you.
Awesome The History Guy merchandise is available at:
https://teespring.com/stores/the-hist…Script by THG
#history #thehistoryguy #Pineapple
August 27, 2021
On Which Side is Brazil? – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 26 Aug 2021Brazilian President, Getúlio Vargas, has led his country as dictator since the 1930s. He has embraced European fascist ideas and fostered close ties with Germany and Italy. Yet, he also maintains a close relationship with the United States. After skilfully playing both sides, he must now choose Axis or Allies.
(more…)
August 25, 2021
Tanks Chats #121 | The Cascavel | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 2 Apr 2021The Tank Museum’s Curator David Willey presents a Tank Chat on the EE-9 Cascavel, a Brazilian Armoured Car developed during the 1970s, primarily for reconnaissance. David also touches upon the EE-11 Urutu, which shares many of the Cascavel’s components. Join him to find out more.
(more…)
March 25, 2021
Modern Artists: The Original Shitposters! | B2W: ZEITGEIST! I E.14 – Winter 1922
TimeGhost History
Published 24 Mar 2021The interwar era has seen an explosion of art movements all vying to offer the most revolutionary response to modern society. The competition is intense and, as we shall see, often spills over into open conflict.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Francis van Berkel
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Francis van Berkel
Edited by: Michał Zbojna
Sound design: Marek KamińskiColorizations:
Daniel Weiss – https://www.facebook.com/TheYankeeCol…Sources:
Some images from the Library of CongressSoundtracks from Epidemic Sound:
“Epic Adventure Theme 3” – Håkan Eriksson
“Crimp” – Hysics
“Substage” – Jay Varton
“Appeased Soundscape 01” – August Wilhelmsson
“Stranger Days” – Alexandra Woodward
“Superior” – Silver Maple
“Rememberance” – Fabien Tell
“Ghost Dungeons” – Ethan Sloan
“Ancient Discoveries” – Gabriel LewisArchive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
TimeGhost History
2 days ago (edited)
The original idea for this episode came from me (Francis here, hello) stumbling across a passing reference to the 1922 trial of André Breton buried deep in a Wikipedia article. It led me down a huge rabbit hole on the history of the chaotic artists milling around in Paris, New York, Zurich, and beyond.Considering that it also takes place in the same season as the publication of Ulysses, the release of Nosferatu, the birth of Brazillian Modernism, and more, I realized that it was the perfect opportunity to dedicate an entire episode to the weird and wonderful artistic movements of the modern era. If this kind is new to you then consider this episode your introduction to the topic. Indy talks about the Cubist revolution, then Dadaism, Expressionism, and more.
In case all that seems a bit too niche for your liking then look at it this way: if you want to understand how people processed the horrors of the Great War, the rise of mass production, and modern geopolitical machinations, then diving into the art of the time is a great place to start.
Watch the video to find out why.
March 17, 2021
Sunny Beaches, Fascist Leaders, and Nazi Spies – WW2 – Spies & Ties 01
World War Two
Published 16 Mar 2021South America is home to one of Germany’s most effective spy-networks. In Operation Bolivar, dozens of German operatives transmit information from and to the USA, Brazil, Argentina, and other South and Central American countries, giving the Abwehr and SD access to crucial information on politics, economics, and military business.
(more…)
January 23, 2021
History Summarized: Atlantic Exploration
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 22 Jan 2021So you just conquered Iberia, and you’re wondering where to go from here? It’s a more common conundrum than you might think. Consider: a big wooden floaty house that goes splish-splash in the Atlantic Ocean. Anyway, this is a video about Portuguese and Spanish (erm, Castilian) exploration in the Atlantic during the 1400s. Please note my deliberate decision to Nope on out at the turn of the 1500s.
This topic was requested by our longtime patron Antonio Juarez! Thank you Antonio for supporting our work and helping to provide entertaining educational content.
SOURCES & Further Reading: Ornament of the World by Maria Rosa Menocal; lectures from Great Courses Plus “1571: Spain, Portugal Encircle the Globe” by Donald J. Harreld, “Renaissance and Exploration: New Horizons” by Jennifer McNabb, “Portugal’s Great Leap Forward” by “Vejas Gabriel Liulevicius”
TRACKLIST: “Scheming Weasel (faster version),” “Monkeys Spinning Monkeys”, “Local Forecast – Elevator” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
PODCAST: https://overlysarcasticpodcast.transi…
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/osp
MERCH LINKS: http://rdbl.co/osp
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
August 28, 2020
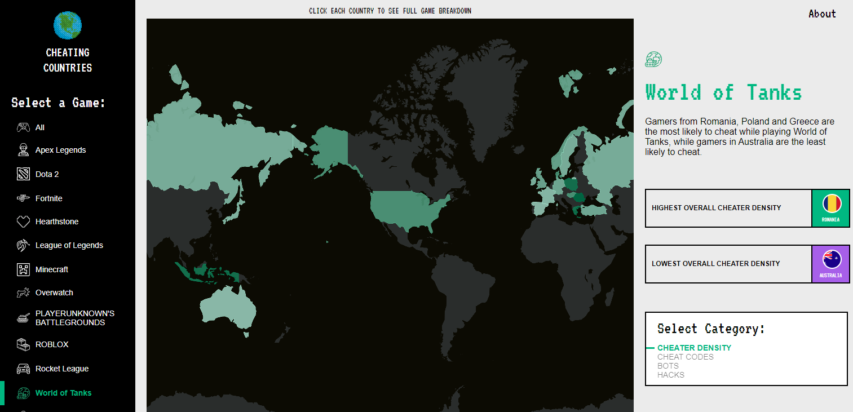
National “cheater density” for popular online games
Richard Currie summarizes the findings of Ruby Fortune’s cheater research (note that there’s no data on China because reasons):
Ever torn your keyboard from the desk and flung it across the room, vowing to find the “scrub cheater” who ended your run of video-gaming success? Uh, yeah, us neither, but a study into the crooked practice might help narrow down the hypothetical search.
The research, carried out by casino games outfit Ruby Fortune, has produced a global heatmap of supposed cheater density.
According to the website, this was done by analysing “search trend and search volume data to reveal where in the world is most likely to cheat while playing online multiplayer video games”. The report looks at the frequency of search engine queries for the most-played video games and measures them against searches for related cheat codes, hacks and bots, to show which country has the highest density of cheaters, and which cheat categories are the most popular in each location.
[…]
There is a massive hole in the data, however, thanks to the Great Firewall of China, which has a terrible reputation for ruining the experience of online games.
If there was any doubt that the Middle Kingdom would otherwise take Brazil’s crown, consider that Dell once advertised a laptop for the market by saying it was especially good for running PUBG plugins to “win more at Chicken Dinner”, a reference to the “Winner winner chicken dinner” message that comes up on a victory screen.
Data from the Battle Royale granddad’s anti-cheat tech provider, BattlEye, has also suggested that at one point 99 per cent of banned cheaters were from China.
June 4, 2020
Tank Chats #71 M3 Stuart Hybrid | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 29 Mar 2019David Fletcher talks about the Second World War M3 Stuart and why this particular version is a hybrid.
The M3 Stuart was built by the USA for WW2 and went into service in 1941. The tank in this video was gifted to The Tank Museum by the Brazilian Army.
Support the work of The Tank Museum on Patreon: ► https://www.patreon.com/tankmuseum
Visit The Tank Museum SHOP: ► https://tankmuseumshop.org/
Twitter: ► https://twitter.com/TankMuseum
Tiger Tank Blog: ► http://blog.tiger-tank.com/
Tank 100 First World War Centenary Blog: ► http://tank100.com/ #tankmuseum #tanks #tankchats
October 5, 2019
Legends Summarized: El Dorado
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 4 Oct 2019El Dorado! A shining golden city packed with promises of wealth, power and everlasting glory. An unspoiled paradise deep in the jungle, the PERFECT destination for treasure-hunters and anthropologists alike. Something that perfect is something EVERYONE wants to be real.
Aaaaand that’s the trick, isn’t it? Wanting something that badly isn’t healthy. Just ask the conquistadors!
(Oh wait, we can’t – because so many of them died on fruitless quests for El Dorado. And also it’s been five hundred years and they’d all be dead anyway)PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
MERCH LINKS: https://www.redbubble.com/people/OSPY…
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
March 29, 2019
Smoking Snakes – Brazilian Expeditionary Force – Sabaton History 008
Sabaton History
Published on 28 Mar 2019You don’t generally think about Brazil when talking about World War Two. Still, they joined the Allied powers in 1942, after which the Brazilian Expeditionary Force played a role in the battle for Italy. The Sabaton song “Smoking Snakes” (from the Heroes album) is about the Brazilian effort during World War Two and especially about three Brazilian soldiers who wouldn’t surrender.
Support Sabaton History on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/sabatonhistory
Watch more videos on the Sabaton YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/Sabaton?…
Listen to Sabaton on Spotify: http://smarturl.it/SabatonSpotify
Official Sabaton Merchandise Shop: http://bit.ly/SabatonOfficialShopHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Markus Linke and Indy Neidell
Directed by: Astrid Deinhard and Wieke Kapteijns
Produced by: Pär Sundström, Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Executive Producers: Pär Sundström, Joakim Broden, Tomas Sunmo, Indy Neidell, Astrid Deinhard, and Spartacus Olsson
Maps by: Eastory
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Sound Editing by: Marek KaminskiEastory YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by: Reuters/Screenocean https://www.screenocean.com
Music by Sabaton.
Research contribution: Leitura ObrigaHISTÓRIA – Check out their channel: https://www.youtube.com/obrigahistoria
The Mariners’ Museum and Park
Brazilian casualty chugs milk
https://catalogs.marinersmuseum.org/o…
P0003/01-#W-14256An OnLion Entertainment GmbH and Raging Beaver Publishing AB co-Production.
© Raging Beaver Publishing AB, 2019 – all rights reserved.