Scenic Routes to the Past
Published 4 Aug 2023This spring, Dr. Andrew Birley gave me a tour of the ongoing excavations at Vindolanda, a Roman fort near Hadrian’s Wall.
Chapters:
0:00 Welcome to Vindolanda
4:41 The wooden underworld
7:13 Layers of history
9:03 Becoming part of the story
November 20, 2023
A Tour of the Excavations at Vindolanda
November 13, 2023
QotD: The “queering-the-museum” movement
The so-called queering-the-museum movement, which was launched in Amsterdam in 2016, is all about contemporary identity politics. It rests on the assumption that museum curation is too “heteronormative”. By queering museum collections, activist curators claim they are including and representing gay and gender non-conforming people.
That at least is the objective. But the actual result is an exercise in narcissism. It turns the past into little more than a mirror reflecting the identitarian obsessions of the present back at us. It tells us less than nothing.
And no wonder. Understanding the past through a “queer” prism is profoundly ahistorical. In the 1500s, “queer” didn’t mean what it does today. It meant “strange, peculiar, odd or eccentric“, and had nothing to do with sexual or gender identity at all. Queer only started to be used as a term for gay men at the turn of the 20th century. And “queer studies” was not named as such until the mid-1990s. Viewing the Mary Rose collection through a “queer” lens is to obscure its historical specificity.
It’s not just the Mary Rose Museum that has succumbed to the cult of queer theory, either. Even more bizarrely, the British Library claimed during Pride month this year that the animal world can be viewed through a queer lens. And so Britain’s national centre of knowledge and learning staged events “celebrat[ing] nature in all its queerness”. In particular, it focussed on animals whose sexual behaviour breaks free from standard “gender roles”, from bisexual penguins and lesbian albatrosses to gender-bending fish. “[Researchers’] discoveries”, stated a press release, “show that animal sexuality is far more diverse than we once thought and has been limited by narrow human stereotypes of heterosexuality, monogamy and gender roles”.
This is obviously absurd. Animals do not experience or possess a sense of identity, sexuality or gender. For a fish to “bend” gender it would need to understand what gender is and how to subvert it – quite an achievement for a creature with a five-second memory recall.
Applying “queer” models to the animal world in this way does a disservice not just to our knowledge of animals, but also to our understanding of humans. Non-human animals aim to remain alive and comfortable and propagate their species. Human sex and sexual identity goes far beyond mere survival and comfort. While there may be many interesting reasons why two female penguins pair off, we can be certain that a sense of lesbian self-identity is not one of them.
As the cases of the Mary Rose Museum and the British Library show, queer methodology does not help us to understand history or nature. This is hardly a surprise. Applying a queer lens to species or epochs where it has no place simply exposes the banality of queer theory. It sees nothing but its own reflection. This narcissistic endeavour is now posing a threat to knowledge itself.
Ann Furedi, “The narcissism of queer theory”, Spiked, 2023-08-12.
November 12, 2023
QotD: Archaeological evidence on the foundation of Rome
The first thing we need to talk about is the physical location of Rome and the peoples directly around it. […] Rome in its earliest history was, essentially, a frontier city, placed at the very northern end of Latium, the region of Italy that was populated by Latin-speakers. Rome’s position on the Tiber River put it at the cultural meeting place of the Etruscan (and Faliscian) cultural zone to the North, Latium to the South and Umbrian-speaking peoples in the Apennine uplands to the North-East. To the West, of course, lay the Sea, which by Rome’s legendary founding date was already beginning to fill with seaborne merchants, particularly Phoenician and Greek ones […] These patterns of settlements and cultural zones are both attested in our literary sources but also show up fairly clearly in the archaeology of the region.
Rome itself, a cluster of hills situated at an important ford over the Tiber (and thus a natural trade and migration route running north-south along Italy’s Western side), was already inhabited by the close of the Neolithic with small settlement clusters on several of its hills. As you might well imagine, excavating pre-historic Rome is difficult, due to the centuries of development piled on top of it and the fact that in many cases pre-historic evidence must exist directly below subsequent ruins which are now cultural heritage sites. Nevertheless, archaeology sheds quite a lot of light. That archaeological evidence allows us to reject the sort of “empty fields” city foundation that Livy implies. Rather than being “founded”, the city of Rome as we know it formed out of the political merger of these communities (the technical term is synoecism from Greek συνοικισμóς, literally “[putting] the houses together”). There is, importantly, no clear evidence of any archaeological discontinuity between the old settlements on the hills and the newly forming city; these seem to have been the same people. The Palatine hill, which is “chosen” by Romulus in the legend and would be the site of the houses of Rome’s most important and affluent citizens during the historical period, seems to have been the most prominent of these settlements even at this early stage.
A key event in this merging comes in the mid-600s, when these hill-communities begin draining the small valley that lay between the Capitoline and Palatine hills; this valley would naturally have been marshy and quite useless but once drained, it formed a vital meeting place at the center of these hill communities – what would become the Forum Romanum. That public works project – credited by the Romans to the semi-legendary king Tarquinius Priscus (Plin. Natural History 36.104ff) – is remarkably telling, both because it signals that there was enough of a political authority in Rome to marshal the resources to see it done (suggesting somewhat more centralized government, perhaps early kings) and because the new forum formed the meeting place and political center for these communities, quite literally binding them together into a single polity. It is at this point that we can really begin speaking of Rome and Romans with confidence.
What does our archaeology tell us about this early community at this point and for the next several centuries?
The clearest element of this early polity is the Latin influence. Linguistically, Rome was of Latium, spoke (and wrote their earliest inscriptions) in Latin and it falls quite easily to reason that the majority of the people in these early hilltop communities around the Tiber ford were culturally and linguistically Latins. But there are also strong signs of Etruscan and Greek influence in the temples. For instance, in the Forum Boarium (between the Tiber and the Palatine), we see evidence for a cult location dating to the seventh century, with a temple constructed there in the early sixth century (and reconstructed again towards the end of that century); votive offerings recovered from the site include Attic ware pottery and a votive ivory figurine of a lion bearing an inscription in Etruscan.
Archaeological evidence for the Sabines is less evident. Distinctive Sabine material culture hasn’t been recovered from Rome as of yet. There are some clear examples of linguistic influence from Sabine to Latin, although the Romans often misidentify them; the name of the Quirinal hill, for instance (thought by the Romans to be where the Sabines settled after joining the city) doesn’t seem to be Sabine in origin. That said, religious institutions associated with the hill in the historical period (particularly the priests known as the Salii Collini) may have some Sabine connections. More notably, a number of key Roman families (gentes in Latin; we might translate this word as “clans”) claimed Sabine descent. Of particular note, several of these are Patrician gentes, meaning that they traced their lineage to families prominent under the kings or very early in the Republic. Among these were the Claudii (a key family in Roman politics from the founding of the Republic to the early Empire; Liv. 2.16), the Tarpeii (recorded as holding a number of consulships in the fifth century), and the Valerii (prominent from the early days of the Republic and well into the empire; Dionysius 2.46.3). There seems little reason to doubt the ethnic origins of these families.
So on the one hand we cannot say with certainty that there were Sabines in Rome in the eighth century as Livy would have it (though nothing rules it out), but there very clearly were by the foundation of the Republic in 509. The Sabine communities outside of Rome (because it is clear they didn’t all move into Rome) were absorbed in 290 and granted citizenship sine suffrago (citizenship without the vote) almost immediately; voting rights came fairly quickly thereafter in 268 BC (Vel. Pat. 1.14.6-7). The speed with which these Sabine communities outside of Rome were admitted to full citizenship speaks, I suspect, to the degree to which the Sabines were already by that point seen as a kindred people (despite the fact that they spoke a language quite different from Latin; Sabine Osco-Umbrian was its own language, albeit in the same language family).
The only group we can say quite clearly that there is no evidence for in early Rome from Livy’s fusion society are the Trojans; there is no trace of Anatolian influence this early (and we might expect the sudden intrusion of meaningful amounts of Anatolian material culture to be really obvious). Which is to say that Aeneas is made up; no great surprise there.
But Livy’s conception of an early Roman community – perhaps at the end of the sixth century rather than in the middle of the eighth – that was already a conglomeration of peoples with different linguistic, ethnic and religious backgrounds is largely confirmed by the evidence. Moreover, layered on top of this are influences that speak to this early Rome’s connectedness to the broader Mediterranean milieu – I’ve mentioned already the presence of Greek cultural products both in Rome and in the area surrounding it. Greek and eastern artistic motifs (the latter likely brought by Phoenician traders) appear with the “Orientalizing” style in the material culture of the area as early as 730 B.C. – no great surprise there either as the Greeks had begun planting colonies in Italy and Sicily by that point and Phoenician traders are clearly active in the region as well. Evidently Carthaginian cultural contacts also existed at an early point; the Romans made a treaty with Carthage in the very first year of the Republic, which almost certainly seems like it must have replaced some older understanding between the Roman king and Carthage (Polybius 3.22.1). Given the trade contacts, it seems likely that there would have been Phoenician merchants in permanent residence in Rome; evidence for such permanently resident Greeks is even stronger.
In short, our evidence suggests that were one to walk the forum of Rome at the dawn of the Republic – the beginning of what we might properly call the historical period for Rome – you might well hear not only Latin, but also Sabine Umbrian, Etruscan and Greek and even Phoenician spoken (to be clear, those are three completely different language families; Umbrian, Latin and Greek are Indo-European languages, Phoenician was a Semitic language and Etruscan is a non-Indo-European language which may be a language isolate – perhaps the modern equivalent might be a street in which English, French, Italian, Chinese and Arabic are all spoken). The objects on sale in the markets might be similarly diverse.
I keep coming back to the languages, by the by, because I want to stress that these really were different people. There is a tendency – we will come back to it next time – for a lot of modern folks to assume that, “Oh well, these are all Italians, right?” But the idea of “Italians” as such didn’t exist yet (and Italy even today isn’t quite so homogeneous as many people outside of it often assume!). And we know that the different languages were mirrored by different religious and cultural practices (although material culture – the “stuff” of daily life, was often shared through trade contacts). Languages thus make a fairly clear and easy marker for a whole range of cultural differences, though – and we will come back to this as well – it is important to remember that people’s identities are often complex; identity is generally a layered, “yes, but also …” affair. I have only glanced over this, but we also see traces of Latin, Etruscan, Greek and Umbrian religious practice in early Roman sanctuaries and our later literary sources; Phoenician influence has also been posited – we know at least that there was a temple to Uni/Astarte in Pyrgi within 30 miles of Rome so Phoenician religious influence could never have been that far away.
We thus have to conclude that Livy is correct on at least one thing: Rome seems to have been a multi-ethnic, diverse place from the beginning with a range of languages, religious practices. Rome was a frontier town at the beginning and it had the wide mix of peoples that one would expect of such a frontier town. It sat at the juncture of Etruria (inhabited by Etruscans) to the north, of Latium (inhabited by Latins) to the South, and of the Apennine mountains (inhabited by Umbrians like the Sabines). At the same time, Rome’s position on the Tiber ford made it the logical place for land-based trade (especially from Greek settlements in Campania, like Cumae, Capua and Neapolis – that is, Naples) to cross the Tiber moving either north or south. Finally, the Tiber River is navigable up to the ford (and the Romans were conscious of the value of this, e.g. Liv 5.54), so Rome was also a natural destination point for seafaring Greek and Phoenician traders looking for a destination to sell their wares. Rome was, in short, far from a homogeneous culture; it was a place where many different peoples meet, even in its very earliest days. Indeed, as we will see, that fact is probably part of what positioned Rome to become the leading city of Italy.
(For those looking to track down some of these archaeological references or get a sense of the source material, though it is now a touch dated, The Cambridge Ancient History, Vol 7.2: The Rise of Rome to 220 B.C., edited by F.W. Walbank, A.E. Astin, M.W. Frederiksen, and R.M. Ogilvie (1990) offers a fairly good overview, particularly the early chapters by Ogilvie, Torelli and Momigliano. For something more suited to regular folks, when I teach this I use M.T. Boatwright, D.J. Gargola, N. Lenski and R.J.A. Talbert, The Romans: From Village To Empire (2012) and it has a decent textbook summary, p. 22-42, covering early Rome with particularly good reference to the archaeology)
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Queen’s Latin or Who Were the Romans? Part I: Beginnings and Legends”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-06-11.
November 3, 2023
QotD: The use of Epigraphy and Papyrology in interpreting and understanding the ancient and classical world
… let’s say you still have a research question that the ancient sources don’t answer, or only answer very incompletely. Where can you go next? There are a few categories, listed in no particular order.
Let’s start with the most text-like subcategories, beginning with epigraphy. Epigraphy is the study of words carved into durable materials like stone or metal. For cultures that do this (so, Mesopotamians, Egyptians, Greeks, Romans: Yes! Gauls, pre-Roman Iberians, ancient Steppe nomads: No!), epigraphy provides new texts to read and unlike the literary texts, we are discovering new epigraphic texts all the time. The downside is that the types of texts we recover epigraphically are generally very limited; mostly what we see are laws, decrees and lists. Narrative accounts of events are very rare, as is the epigraphic preservation of literature (though this does happen, particularly in Mesopotamia with texts written on clay tablets). That makes epigraphy really valuable as a source of legal texts (especially in Greece and Rome), but because the texts in question tend to be very narrowly written (again, we’re talking about a single law or a single decree; imagine trying to understand an act of Congress renaming a post office if you didn’t [know] what Congress was or what a post office was) without a lot of additional context, you often need literary texts to give you the context for the new inscription you are looking at.
The other issue with epigraphy is that it is very difficult to read and use, both because of wear and damage and also because these inscriptions were not always designed with readability in mind (most inscriptions are heavily abbreviated, written INALLCAPSWITHNOSPACESORPUNCTUATIONATALL). Consequently, getting from “stone with some writing on it” to an edited, usable Greek or Latin text generally requires specialists (epigraphers) to reconstruct the text, reconstructing missing words (based on the grammar and context around them) and making sense of what is there. Frankly, skilled epigraphers are practically magicians in terms of being able figure out, for instance, the word that needs to fit in a crack on a stone based on the words around it and the space available. Fortunately, epigraphic texts are published in a fairly complex notation system which clearly delineates the letters that are on the stone itself and those which have been guessed at (which we then all have to learn).
Related to this is papyrology and other related forms of paleography, which is to say the interpretation of bits of writing on other kinds of texts, though for the ancient Mediterranean this mostly means papyrus. The good news is that there is a fairly large corpus of this stuff, which includes a lot of every day documents (tax receipts! personal letters! census returns! literary fragments!). The bad news is that it is almost entirely restricted to Egypt, because while papyrus paper was used far beyond Egypt, it only survives in ultra-dry conditions like the Egyptian desert. Moreover, you have all of these little documents – how do you know if they are typical? Well, you need a very large sample of them. And then we’re back to preservation because the only place you have a very large sample is Egypt, which is strange. Unfortunately, Egypt is quite possibly the strangest place in the Ancient Mediterranean world and so papyrological evidence is frequently plagued by questions of applicability: sure we have good evidence on average household size in Roman Egypt, but how representative is that of the Roman Empire as a whole, given that Egypt is such an unusual place?
Outside of Egypt and a handful of sites (I can think of two) in England? Almost nothing. To top it all off, papyrology shares epigraphy’s problem that these texts are difficult and often require specialists to read and reconstruct them due to damage, old scripts and so on. The major problem is that the quantity of recovered papyrus has vastly outstripped the number of trained papyrologists, bottle-necking this source of evidence (also a lot of ancient papyri get traded on the antiquities black market, potentially destroying their provenance, and there is a special level in hell for people who buy black market antiquities).
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday: March 26, 2021 (On the Nature of Ancient Evidence”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-03-26.
October 17, 2023
An appropriate task for AI – reading the Herculaneum scrolls
Colby Cosh discusses the possibility of finally being able to read the carbonized scolls found in the buried remains of a wealthy Roman’s country villa in 1750:

Unrolled papyrus scroll recovered from the Villa of the Papyri.
Picture published in a pamphlet called “Herculaneum and the Villa of the Papyri” by Amedeo Maiuri in 1974. (Wikimedia Commons)
From the standpoint of fragile human life, a volcanic eruption is the worst possible thing that can happen anywhere in your general vicinity, up to and probably including the detonation of a nuclear weapon.
It goes without saying that pyroclastic flows are also bad for animals or buildings or vegetation … or documents. And yet: as a consequence of the eruption of Vesuvius, there exists a near-complete library of papyrus scrolls retrieved from the buried ruins of a splendid Roman villa.
The “Villa of the Papyri” in Herculaneum was found in 1750 by farmers and was quickly subjected to archeological excavation, an art then in its infancy.
These scrolls, which today number about 1,800 in all, are often described as the only known library to have physically survived from antiquity. The problem, of course, is that they have all been burned literally to a crisp, with only a few easily readable fragments here and there.
The incinerated scrolls are so sensitive that they tend to explode into a cloud of ash at the slightest touch. Occasional attempts to unravel the scrolls — which were rolled very tightly for storage in the first place — have been made over the past 300 years; the chemist Sir Humphry Davy (1778-1829), for example, gave it a shot using newfangled stuff called chlorine. But none of these projects ever came especially close to success, and they typically involved destruction of some of the “books” in the library.
In recent years 3D imaging techniques for “reading” documents like this in a non-invasive way have been making great headway. The leader in the field is a University of Kentucky computer scientist named Brent Seales, who in 2015 led efforts to read a fragile, desiccated Hebrew Bible parchment scroll dating to the third or fourth century AD.
The text was from the book of Leviticus, and proved to be a letter-for-letter match with the Torah of today — which is a disappointment to scholars from one point of view, and a finding of awesome significance from another. (It goes without saying that this scroll came from the territory of Israel, near a kibbutz: this is a fact that would, in any other political context, be regarded as a supreme affirmation of indigeneity.)
Seales has been able to “unroll” some Herculaneum scrolls and detect the presence of inks using CT scanning, but reading the pages is a profound challenge. Roman ink was carbon-based, meaning researchers are trying to “read” traces of carbon on carbonized pages rolled up into three dimensions.
October 2, 2023
The fall and rise of siege warfare
Sieges are probably about a year or so younger than the first fortified village — as soon as someone came up with the bright idea of throwing a wall around it for protection, some equally bright spark likely started coming up with ways to get inside that wall. In The Critic, Peter Caddick-Adams considers the eclipse and return of siege warfare in Europe in reviewing Iain MacGregor’s The Lighthouse of Stalingrad and Prit Buttar’s To Besiege a City: Leningrad 1941-42:

A model of the Vauban fortress at Arras in northern France. Arras is one of the Fortifications of Vauban, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Image via Wikimedia Commons.
The history of war is never far removed from battles for cities. Many of us, of whatever creed, were brought up on the story of the walls of Jericho tumbling after the Israelites marched around the stronghold once a day for six days, seven times on the seventh day, and then blew their trumpets. Though no archaeological evidence at Tell es-Sultan, in modern Palestine, corroborates the arresting visual image related in Joshua, Chapter 6, diggers have uncovered a range of defensive stone and brick walls dating back to 8,000 BC. It indicates that even 10,000 years ago, the ancients indulged in the odd siege when the mood took them. The biblical story also introduces us to the concept of intimidation, today fashionably called “psychological warfare”.
The much younger fortress of Troy provides insights into another city-focussed era of battles. Beneath today’s Hisarlik in northern Turkey are nine archaeological layers. Troy VIII was the alluring city of Classical and Hellenistic times, as portrayed in the Iliad, Homer’s Odyssey and Virgil’s Aeneid. The Romans took the lessons of Homeric Troy seriously and clad all their major settlements with defensive walls, as any exploration of Canterbury, Chester or York will confirm. These acted as magnets for opponents, as in Boudicca’s revolt of AD 60–61. Cities such as Colchester, London and St Albans were sacked, as much for what they represented as for their physical presence.
When the Normans arrived in their longships, they imported the concept of stone castles to control the newly conquered English. Their walled cities would be ungraded and contested scores of times over the succeeding six centuries. Henry V’s siege of Harfleur (modern Le Havre) in 1415, the beginning of the Agincourt campaign famously depicted in Shakespeare’s play, underlined the drawback of traditional sieges. They took longer and were usually far costlier than expected. Several thousand men camped in a small area with no knowledge of hygiene inevitably resulted in a high mortality rate amongst the attackers before a shot was fired.
Harfleur was also the first time an English army made use of gunpowder artillery in a siege, a technology that had trickled its way across the world from China. Powder and fuse heralded events 38 years later, when an Ottoman army shook the Christian world to its core by breaching the massive walls of Constantinople (Istanbul) after a 53-day bombardment using cannons. On Tuesday, 29 May 1453, stone finally gave way to bronze and iron, finishing the last remnant of the Roman Empire. Europe was never quite the same again. Fortress architecture started to employ breadth, using earthen ramparts and ditches, rather than height.
Strategy for urban warfare intensified during the lifetime of the French fortress engineer Vauban (1633–1707), who used landscaped terrain as well as geometrically designed defensive walls to deter would-be besiegers. When viewed from above, his fortification designs resemble starfish. So successful were his tactics that sieges, always costly and time-consuming, lessened in importance. His contemporary Marlborough recognised that on any cost-benefit analysis, Vauban had rendered sieges militarily unprofitable, restoring manoeuvre to campaigns.
Subsequent wars fought in the Napoleonic era, the Crimea, between the American North and South, and by Prussia generally reflected this return to mobility. There was the odd attritional discrepancy with the 1854–55 siege of Sevastopol, that of Petersburg in 1864–65 and Paris in 1870–71. Cities were still fought for, but usually contests were removed away from the walls, where forces could conduct wide sweeping manoeuvres, such as Leipzig in 1813 or Ypres in the Great War. As weapons grew more accurate and their munitions heavier, fortifications broadened and sank into the ground, culminating in the trenches of 1914–18. In this era, dominance of terrain became the hallmark, and it was virtually siege-free.
It was remarkable that urban warfare returned on an industrial scale during the Second World War, a time usually associated with blitzkrieg and rapid tank thrusts. This happened at Leningrad, Sevastopol and Stalingrad in the East; at Ortona and Cassino in Italy, Caen; Carentan and St Lo in Normandy; in Aachen and later assaults on Aschaffenburg and Cologne, Magdeburg, Leipzig and Berlin in 1945. Subsequent NATO doctrine for the defence of central Europe focussed on the threat of more attrition. Plans were devised to defend quite small localities, putting grit in the Soviet steamroller and making the cost of attacking Western towns and cities prohibitive.
Update: Broken URL corrected.
QotD: Who were the Celts?
Now already some of you are noting a curious feature here which is that I keep using the word “Gauls” to describe these folks rather than “Celts” and you are probably wondering why. We’ve actually addressed this question before, but we ought to revisit it here, because I think any approach to “Celtic Warfare” is already potentially begging some pretty important questions (assuming it hasn’t stopped to address them) and, alas, begged the wrong answers (unless it has defined “Celtic” very narrowly). The problem, entirely unaddressed in the original video, is that there is a pretty big gap between what the Greeks meant by the word keltoi, what the keltoi may have meant by the word keltoi and most important what people today understand by the word “Celts”. Instead everyone gets smashed together, with all of the Celtic-language speakers mashed in under the label of “Celts”, a practice that hasn’t been acceptable in serious scholarship for at least 30 years. Let’s talk about why.
From antiquity we have two standard terms. On the one hand, the Greeks encountered a people in the Mediterranean and called them keltoi. From Caesar and Strabo we know that at least some peoples called themselves keltoi (or celtae), though as we’re going to see the people who did this are not actually co-terminus with this military system or with all the people folks (including the original video) think of as Celtic or any identifiable polity or political structure. In particular, Caesar reports that the folks living in what is today France (then Gaul) north of the Garonne and south of the Marne and the Seine called themselves celtae, which he takes to be equivalent to the Latin galli (Caes. BGall. 1.1). Strabo, meanwhile, describes peoples in Spain as both keltoi and also keltiberes (which enters English as Celtiberians, Strabo, Geography 3.2.15) as well as those in Gaul (Geography 4.1ff), but doesn’t make the claim that they call themselves that (instead repeatedly noting these groups broken up into smaller tribal units with their own names). Both Caesar (Caes. BGall. 1.1) and Strabo (Geography 4.1.1) go out of their way to stress that the folks they’re talking about do not have the same languages, institutions or mode of life, even those who are, to Strabo, galatikos – “Gallic” or more precisely “Galatian-like” (referring to the sub-group of Gallic peoples the Greeks were the most familiar with).
Galli, rendered into modern English as “the Gauls” (though the latter is not a descendant of that word, but a wholly different derivation), is likewise tricky. We’re fairly sure that both keltoi and galli are Celtic-language words, meaning that (contrary to the video) they’re both probably “endonyms”, (a thing people call themselves) but it is really common for peoples in history to take the endonym of the first group of people they meet and apply it to a much larger group of “similar” (or not so similar) people. The example I use with my students is “Frank”; – it was common in both the Eastern Mediterranean and later in East Asia to use some derivative of “Frank” or “Frankish” to mean “Western or Central European” – the term got applied to the Portuguese in China, and to both Germans and Sicilian Normans during the Crusades. It’s possible that galli in Latin is connected to the Galatai (Greek) or Galatae (Latin), the Galatians, a Celtic-language speaking La Tène material culture group who migrated into Anatolia in the 270s, but a number of etymologies have been proposed. It certainly wouldn’t be the first time the Romans named a massive ethnic group after the first people they met; this is how we get the word “Greek” when the Greeks call themselves Hellenes. So assuming off the bat that all of these different tribal groups that Caesar or Strabo treat as a cultural unity thought of themselves that way is most unwise. The most we know is that if you called some of these folks (but not all of them, as we’ll see) keltoi or galli, they’d say, “yeah, I guess that more or less describes me”, perhaps in the same way describe a Swiss person as “European” isn’t wrong, but it also isn’t quite right.1
Surely here linguistics will help us out? If we can identify a Celtic language then surely everyone who speaks that language will have that culture? First, this is yet more question begging; English is the official language of South Sudan and yet the South Sudanese are not English, British or American. Linguistic connections do not always imply ethnic or cultural connections extending beyond language. And, in fact, examining the Celtic language family is a brilliant way to illustrate this.
There is, in fact, a family of Celtic languages and indeed it is only in the sense of languages which you will see me use the word Celtic in a formal way precisely to avoid the giant pickle of confusion we are currently working through. Very briefly, it has been shown linguistically that the various surviving Celtic languages are related to each other and also to the extinct languages of pre-Roman continental Europe that were spoken in Gaul, Noricum and parts of Spain. So far so good, right, we have a nice, perfect match between our keltoi and Celtic-language-speakers, right?
Of course not. That would be easy! Because notice there that Irish, Manx, Scottish Gaelic and Welsh are all Celtic languages. But our sources are actually quite clear that at least the Romans and the Greeks did not consider these folks to be galli or keltoi. Indeed, Strabo explicitly defines the people of Britain against the keltoi as two distinct groups, making it clear he doesn’t think the inhabitants of the British Isles were “Celts” (Geography 4.5.2); Caesar doesn’t either (BGall. 4.21ff). Tacitus sees in the britanniae evidence of German, Iberian and Gallic influence, marking them as distinct from all three, but concludes that Gallic settlement is the most likely cause, a point on which we may be quite certain he is wrong, for reasons discussed just below (Tac. Agr. 11). So the groups described as “Celts” don’t entirely overlap with Celtic language speakers.
Well, surely here the archaeologists can help us out, right? Yes and no. On the one hand, we have a collection of object types, artistic motifs and archaeologically visible patterns that we associate with some of the areas settled by people who our sources regard as “Celts” and who were Celtic language speakers. The older of these two material culture groupings we call “Halstatt culture” after the original type-site in Hallstatt, Austria, though we find Hallstatt culture objects (remember, these are objects, not people, a thing to be relevant in a moment) in a territorial range that forms a sort of crescent shape embracing the northern edges of the Alps, from around 1200 BC to around 500 BC. We then shift to a material culture pattern which may have developed out of late Hallstatt culture which we call La Tène culture after its type-site of La Tène in Switzerland; it runs from around 500 BC (very roughly) to around 50 AD, with lots of subdivisions.
And just about all of the folks our sources will identify as “Celts” or “Gauls” tend to live in areas where where we find, by the third century or so, at least some elements of La Tène material culture (and many in places where they have the full package). So do we at last have a way to identify some “Celts”, by matching wherever we find La Tène material culture?
No. Of course not. That would be easy and history is not easy.
First, not all of the people our sources describe as Celts adopt all or even most of the elements of La Tène material culture. Most notably, the folks in Iberia who were keltoi (according to Strabo) or Celtiberians have some elements of La Tène material culture, but are notably missing others. They don’t have, for instance, the whole La Tène military package – mail in particular is absent in Iberia until the Romans arrive, and the La Tène swords they have are local variations of early La Tène I swords by the third and second centuries, not the La Tène II swords we find in most of the rest of the cultural zone.2 The artistic style in “Celtic” Spain is also different and unsurprisingly there’s a lot of Iberian borrowing. As a result, archaeologically, the keltoi of south-western Iberia aren’t some sort of carbon-copy of the keltoi of central France. There’s not no connection here, they are Celtic-language speakers and they have some La Tène stuff, but the Iberian Celtici are quite a bit further from the Helvetii (the folks who probably inhabited the La Tène site) than, say, the Senones.
Meanwhile, we find some La Tène material culture objects in southern Britain, but they don’t fully penetrate the Isles (despite the general assumption that all of the people of Britain and Ireland were Celtic language speakers) and many appear to be expensive, high-status imports. Indeed, while it was once supposed that the arrival of La Tène material culture objects signified some invasion or settlement of Britain by people from Gaul, an analysis of burial patterns3 demonstrates pretty clearly that this isn’t happening in this period, because burial practices in southern Britain remain distinct from those on the continent. Instead, we’re seeing trade.
Meanwhile, we find tons of La Tène material culture objects in cultural contexts that we know were neither “Celtic” in any cultural sense nor filled with Celtic-language speakers. The clearest instance of these are in Illyria and Thrace, who spoke Indo-European but not Celtic language (so a language as close to Celtic languages as Latin or Greek or German), where it’s clear that folks adopted at least some La Tène material culture, including weapons and armor. Of course by the third century, when it came to militaria, we’d have the same problem with the Romans, who by the end of the Second Punic War, had adopted a La Tène sword (albeit from Spain and with a different suspension system), a variant of the La Tène shield, a La Tène helmet type (domestically manufactured), and La Tène body armor (mail). If we didn’t have any surviving Latin language material, I am almost certain there would be nationalist pseudo-archaeologists claiming the Roman Empire was clearly some “pan-Celtic” imperial construct on that basis.4 And of course in the third century, a Greek variant of the La Tène shield, the thureos, begins showing up everywhere in the Hellenistic East, but that doesn’t make them Celts either (they’d be the first to tell you).
Meanwhile, there’s even more complexity than this, because objects of La Tène material culture aren’t the whole of archaeologically visible culture. There are building habits, burial habits, evidence for social organization and on and on. And those vary significantly within the La Tène material culture zone. I put this in the bibliography and I’m afraid it is a (necessarily) difficult and technical read, but if you want to get a sense of just how complex this can get, check out Rachel Pope’s efforts to define the Celts in the Journal of Archaeological Research (2022). To quote some of her conclusions, “In fact, ‘Celts’ as a historical label does not map neatly onto any archaeological tradition; it overlaps with late Hallstatt traditions in northeast France and less ostentatious archaeologies farther west … Nor did the name ‘Celt’ ever equate to all of Gaul, let alone all of Europe.”
So to be clear, we have Celtic-language speakers who aren’t called Celts by our sources and don’t have La Tène material culture (Ireland, N. Britain), Celtic-language speakers who are called Celts by our sources but don’t have the full La Tène material culture package (Spain, Portugal), non-Celtic language speakers who do have some of the La Tène material culture package but who are clearly not Celts to our sources (Thracians, Illyrians, Dacians, etc.), full La Tène material culture-havers who are explicitly not Celts in our sources (Caesar, specifically) and maybe speak a Celtic-language (the Belgae), and partial La Tène material-culture-havers who do speak a Celtic language but are still explicitly not Celts in our sources (S. Britain). Oh, and while we’re here, by the second century we also have La Tène material culture-havers who probably still speak a Celtic-language and are called Celts/galli by our sources but write inscriptions in Greek (the Galatians) and seem to have different religious structures and folks identified as Celts in our sources who are in the process of ditching large parts of La Tène material culture and learning Latin (Cisalpine Gaul), who might, à la Pope (op. cit.), actually be the direct, local descendants of the “original” Celts.
And then of course we have a band across parts of the Alps and central France where everything lines up: Celtic-language speakers with La Tène material culture who our sources call keltoi or galli and live in a place called Gallia by the Romans. But it would be a mistake to assume this is the cultural “heartland” of a “Celtic” people – indeed, La Tène material culture may be more deeply rooted in more Northern parts of France [than in] the Danube region, which has a lot of non-Celtic language speakers in it in this period! Because, to be clear, what we actually have are a host of smaller, tribal societies which share come cultural elements and differ in others, who seem to think of themselves primarily as members of a tribe and who lack notable “pan-Celtic” institutions, to which Greeks and Romans, needing a way to label their neighbors, took whatever ethnic signifiers they had and applied them (over)broadly.
[…]
At no point where all of these people united in a single polity (the closest they get is that most of them get conquered by the Romans) and there’s no indication that they ever saw themselves as a cultural or ethnic unity. And of course we haven’t even gotten into the idea that they might all be somehow closely ethnically related but let’s just go ahead and tag that as “very unlikely” and keep moving.
All of that is to make the point that any treatment of “Celtic” warfare is immediately begging an enormous question because “who were the Celts?” is at best an unanswered question and to be frank, probably an unanswerable question. Crucially, “the Celts” do not share a military system. Warfare among Celtic-language speakers in the British Isles isn’t necessarily based around La Tène material culture, nor is warfare in S. Portugal among peoples identified by our sources as keltoi; both areas seem to have very substantial regional variation. By contrast, the galli of central France and Cisalpine Gaul do seem to share at least substantial elements of a military system with the – according to Caesar – non-celtae of broader Gaul and as well as with the Galatians who live, I must repeat, in Anatolia (having migrated there in the third century). There is thus no “Celtic” military system which maps clearly onto either Celtic-language distribution or peoples described as keltoi by our sources.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Who Were ‘the Celts’ and How Did They (Some of Them) Fight?”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2023-05-12.
1. Especially in the sense that “European” gets used to mean “citizen of a country in the European Union”, which Switzerland is not. Mostly. The EU is complicated.
2. On these differences, see F. Quesada Sanz, “Patterns of Interaction: ‘Celtic’ and ‘Iberian’ weapons in Iron Age Spain” in Celtic Connections, vol. 2, eds. W. Gillies and D.W. Harding (2005) and in even more detail F. Quesada Sanz, “El Armamento Ibérico. Estudio tipológico, geográfico, functional, social y simbólico de las armas en la Cultura ibérica” (siglos VI-I a.C.) (1997). Interestingly, the Roman gladius Hispaniensis seems likely to have been a Roman adaptation of the peculiar Iberian La Tène swords, so you have the La Tène I sword making its way to Iberia, becoming distinctive, being adopted by the Romans instead of the more common (to them) La Tène II sword, thus becoming the gladius. On this, see F. Quesada Sanz, “Gladius Hispaniensis: an Archaeological View from Iberia” JRMES 8 (1997).
3. On this, see S. James, The Atlantic Celts: Ancient People or Modern Invention (1999).
4. On this, see M.J. Taylor, “Panoply and Identity During the Roman Republic” PBSR 88 (2020). On the helmet type and its evolution, see U. Schaaff, “Keltische Helme”, in Antike Helme (1988) for a rundown; P. Connolly Greece and Rome At War (1981), 121 also has a fantastic visual chart of the development of the type in the La Tène material culture zone, where you can see quite clearly where in the fourth century the Italic variants of this helmet type are breaking off from, while the La Tène helmets continue their development in other directions, later to be re-adopted by the Romans who thought it was so nice, they borrowed it twice.
September 2, 2023
QotD: Ancient DNA
… you know I’m always up for the humiliation of a dominant scientific paradigm. I especially like examples where that paradigm in its heyday replaced some much older and unfashionable view that we now know to be correct. It’s important to remind people that knowledge gets lost and buried in addition to being discovered.
The wonderful thing about ancient DNA is it gives us an extreme case of this. Basically, the first serious attempt at creating a scientific field of archaeology was done by 19th century Germans, and they looked around and dug some stuff up and concluded that the prehistoric world looked like the world of Conan the Barbarian: lots of “population replacement”, which is a euphemism for genocide and/or systematic slavery and mass rape. This 19th century German theory then became popular with some 20th century Germans who … uh … made the whole thing fall out of fashion by trying to put it into practice.
After those 20th century Germans were squashed, any ideas they were even tangentially associated with them became very unfashionable, and so there was a scientific revolution in archaeology! I’m sure this was just crazy timing, and actually everybody rationally sat down and reexamined the evidence and came to the conclusion that the disgraced theory was wrong (lol, lmao). Whatever the case, the new view was that the prehistoric world was incredibly peaceful, and everybody was peacefully trading with one another, and this thing where sometimes in a geological stratum one kind of house totally disappears and is replaced by a different kind of house is just that everybody decided at once that the other kind of house was cooler. The high-water mark of this revisionist paradigm even had people saying that the Vikings were mostly peaceful traders who sailed around respecting the non-aggression principle.
And then people started sequencing ancient DNA and … it turns out the bad old 19th century Germans were correct about pretty much everything. The genetic record is one of whole peoples frequently disappearing or, even more commonly, all of the men disappearing and other men carrying off the dead men’s female relatives. There are some exceptions to this, but by and large the old theory wins.
I used to have a Bulgarian coworker, and I asked him one day how things were going in Bulgaria. He replied in that morose Slavic way with a long, sad disquisition about how the Bulgarian race was in its twilight, their land was being colonized by others, their sons and daughters flying off to strange lands and mixing their blood with that of alien peoples. I felt awkward at this point, and stammered something about that being very sad, at which point he came alive and declared: “it is not sad, it is not special, it is the Way Of The World”. He then launched into a lecture about how the Bulgarians weren’t even native to their land, but had been bribed into moving there by the Byzantines who used them as a blunt instrument to exterminate some other unruly tribes that were causing them trouble. “History is all the same,” he concluded, “we invaded and took their land, and now others invade us and take our land, it is the Way Of The World.”
Even a cursory study of history shows that my Bulgarian friend was correct about the Way Of The World. There’s a kind of guilty white liberal who believes that European colonization and enslavement of others is some unique historical horror, a view that has now graduated into official state ideology in America. But that belief is just a weird sort of inverted narcissism. I guess pretending white people are uniquely bad at least makes them feel special, but white people are not special. Mass migration, colonization, population replacement, genocide, and slavery are the Way Of The World, and ancient DNA teaches us that it’s been the Way Of The World far longer than writing or agriculture have existed. It wasn’t civilization that corrupted us, there are no noble savages, “history is all the same”, an infinite history of blood.
Land acknowledgments always struck me as especially funny and stupid: like you really think those people were the first ones there? What about acknowledging the people that they stole it from? Sure enough one of the coolest parts of Reich’s book is his recounting the discovery that there were probably unrelated peoples in the Americas before the ancestors of the American Indians arrived here, and that a tiny remnant of them might even remain deep in Amazonia. So: what does it actually mean to be “indigenous”? Is anybody anywhere actually “indigenous”?
Jane Psmith and John Psmith, “JOINT REVIEW: Who We Are and How We Got Here, by David Reich”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2023-05-29.
August 23, 2023
From “hunter-gatherer” to “settled farmer” as a Just-so story
The latest book review at Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf is James C. Scott’s Against the Grain: A Deep History of the Earliest States by Jane Psmith:
Okay, stop me if you’ve heard this one already. So, there are these hunter-gatherers, right, and one of the things they like to gather, while they’re roaming around the hilly flanks of Anatolia following herds of gazelles, is the large, carbohydrate-rich seeds of local grasses. Then one day some bright soul gets the idea of planting the seeds on purpose, people selectively replant the ones that have exciting mutations like “have really big seeds” and “don’t shatter your stalk and scatter your really big seeds everywhere when they’re ripe, just hang out and wait to be reaped,” and they all start staying in one place to tend their fields. They quickly discover that agriculture can create a lot more calories than foraging, so all of a sudden they have a nice surplus that can go towards supporting non-food-producing specialists like dedicated craftsmen, priests, bureaucrats (but I repeat myself) and kings to expedite and organize all that agricultural labor, and, hey presto! you have civilization.
Oh, cool, you read Guns, Germs, and Steel in high school too?
Only James C. Scott is here to tell you that’s not how it happened. And while you might be excused for thinking (especially if you’ve read our review of The Art of Not Being Governed) that this is Scott doing his contrarian “ooh, look, I’m turning the accepted narrative on its head” thing, you would be wrong. (Don’t worry, though, we definitely will get to the point where he does that.) He’s just offering a summary of the new scholarly consensus: the transition from mobile bands of hunter-gatherers to sedentary agriculturalists didn’t follow that neat logical progression, and it was far patchier, more tenuous, and more bidirectional than generally assumed. In fact, practically since the moment in the late 1920s that V. Gordon Childe coined the term “Neolithic revolution“, archaeological evidence has been accumulating that complicates every aspect of the story I just told you, from agriculture to sedentism to state formation.
To begin with, what constitutes agriculture? Back in the 1960s, paleobotanist Jack Harlan used a flint sickle to harvest enough wild Anatolian wheat in just three weeks to feed a family for an entire year. Now, we can probably agree that just harvesting a stand of wild wheat and storing the grain doesn’t really count as agriculture, but what about pulling up the non-wheat interlopers from a half-ripe stand you hope to harvest later in the year? What about saving some seeds and tossing them on a welcoming plot of soil next spring? What about digging up or burning other plants to make that welcoming plot? And then it turns out that all the harvesting and processing tools — those sickles, winnowing baskets, grindstones, and even purpose-built granaries — seem to have existed before there was any intentional cultivation, suggesting wandering tribes who came together only at harvest time but spent most of the year apart. Also, it seems all like those exciting morphological changes that make grain agriculture so efficient (big seeds and non-brittle rachis) come hundreds and hundreds of years after agriculture was established.1 Our simple story is already getting complicated! But it gets worse.
Archaeologists used to assume that sedentism — that is, people staying in one place year-round — and agriculture necessarily went together. In one direction this is obvious, because once you’re feeding your family from a particular plot of ground you probably want to stick around to weed and water it and keep away any animals (or other people) who might swoop in at the last minute and take your harvest. But it goes the other way, too: we generally assume that pickings as a hunter-gatherer are slim enough that your group needs to keep moving around to find more food. (Or, in the immortal words of the Minnesota Educational Computing Consortium: “if you continue to hunt in this area, game will become scarce.”) This is actually true at higher trophic levels: large animals tend to migrate throughout the year, so people whose subsistence strategies depend heavily on hunting them will follow the herds. But hunter-gatherer mobility is a tendency, not an iron law, and the archaeological (and even historical) record is full of non-agricultural peoples who lived in one place year-round because their environment was rich enough to support it. This was common among the tribes of the Pacific Northwest, who created quite socially and materially complex cultures without agriculture, but it also shows up plenty of other places. The earliest sedentary culture we know about, the Natufians, flourished along the coast of what is now Israel more than thirteen thousand years ago, largely by gathering wild grains and hunting gazelles.
Do note, though, that it would be a mistake to call these non-agricultural environments “natural”, because humans have been actively managing our landscapes for at least a million years. The main tool before the widespread adoption of agriculture was fire, which can be used to stampede prey animals into a trap or to remove unwanted vegetation and make way for the grasses and shrubs that we, or our preferred prey, like to eat. “The game they subsequently bagged,” Scott writes, “represented a kind of harvesting of prey animals they had deliberately assembled by carefully creating a habitat they would find enticing”. It’s even been suggested that the Little Ice Age of the early modern period was due to the sudden cessation of burning activity (and its CO2 emissions) in the Americas when newly-introduced Old World pathogens killed off most of the people who did the burning.
Against the Grain focuses on the region archaeologists call Southwest Asia, people who like reading books about archaeology call the Fertile Crescent, and everyone else calls the Near and Middle East, but it zeroes in specifically on southern Mesopotamia. This wasn’t the first place to host year-round settlements, nor was it the site of the original crop domestications, but it is the home of the third element of the traditional story of the birth of civilization: the state. Scott is unwilling to define the state precisely, describing it instead as an “institutional continuum” where something can be more or less state-like, but he writes that “a polity with a king, specialized administrative staff, social hierarchy, a monumental center, city walls, and tax collections and distribution is certainly a ‘state’ in the strong sense of the term”. It was here, near the mouth of the Euphrates on the Persian Gulf, that the earliest “statelets” arose, and it’s here, once again, that Scott brings up recent archaeological evidence that undermines the usual narrative. This time, the abandoned theory is that the region was as arid at the dawn of agriculture as it is today; an agricultural population might have succeeded in the oases and river valleys, but as numbers swelled they would need to undertake massive irrigation projects, which would in turn require “the mobilization of labor to dig and maintain the canals, which implied the existence of a public authority capable of assembling and disciplining that labor force”. In short, agriculture was assumed to have required a state. But it didn’t.
Scott’s argument draws heavily on the work of Jennifer Pournelle, who reconstructed the landscape of the southern Mesopotamian alluvium in the seventh and sixth centuries BC using a combination of remote sensing, ancient sediments, and climatological history, and concluded that, far from the arid landscape of today, the land between the rivers was in fact an “intricate deltaic wetland.”
The inhabitants of these marshes lived on what are called “turtlebacks,” small patches of slightly higher ground, comparable to cheniers in the Mississippi delta, often no more than a meter or so above the high-water mark. From these turtlebacks, inhabitants exploited virtually all the wetland resources within reach: reeds and sedges for building and food, a great variety of edible plants (club rush, cattails, water lily, bulrush), tortoises, fish, mollusks, crustaceans, birds, waterfowl, small mammals, and migrating gazelles that provided a major source of protein. The combination of rich alluvial soils with an estuary of two great rivers teeming with nutrients, dead and alive, made for an exceptionally rich riparian life that in turn attracted huge number of fish, turtles, birds, and mammals — not to mention humans! — preying on creatures lower on the food chain.
Moreover, the first settlements in the area were right on the border between the brackish water of the coastal estuary and the freshwater ecology upstream, and on the incredibly flat floodplain of the lower Euphrates (the gradient is less than two inches per mile) that seam moved great distances with the tides. “Thus,” Scott writes, “for a large number of communities, the two ecological zones moved across the landscape while they remained stationary, taking sustenance from both”. They didn’t need to roam in search of new food sources; the food came to them. Agriculture — of the flood-retreat form, where seeds are sown in nutrient-rich new soils deposited by the retreating river, and which is the least labor-intensive type possible — was just another of their many diverse and overlapping subsistence strategies. The shift between wet and dry season, with its pulse of migrating animals and harvest of whatever seeds they had sown, can be considered moving zones on a longer timescale: a new habitat arriving on their doorstep to be added to the mosaic of available options. By 6000 BC, Scott says, they were “already agriculturalists and pastoralists as well as hunter-gatherers. It’s just that so long as there were abundant stands of wild foods they could gather and annual migrations of waterfowl and gazelles they could hunt, there was no earthly reason they would risk relying mainly, let along exclusively, on labor-intensive farming and livestock rearing.”
Thus do we, with James C. Scott, reject the old model in which agriculture leads almost at once to both sedentism and the state. Instead, we see sedentism arise in particularly favorable ecological niches as early as 12,000 BC, with most of the main founder crops and animals domesticated between 8000 and 6000 BC, and then a gap of almost four thousand years before the appearance of the state. A naively Whiggish view of history might ask, “What took so long?” But James C. Scott, being James C. Scott (yes, here we’re coming to the “turn it on its head” bit), thinks the more accurate question might be, “What went wrong?”
1. For more on this, Scott suggests this 2013 paper.
August 15, 2023
QotD: Iron ore processing in pre-industrial societies
Once our ore reaches the surface (or is removed from its open pit) it is not immediately ready for smelting, but has to go through a series of preparatory steps collectively referred to as “dressing” to get the ore ready for its date with the smelter […]
Ore removed from the mine would need to be crushed, with the larger stones pulled out of the mines smashed with heavy hammers (against a rock surface) in order to break them down to a manageable size. The exact size of the ore chunks desired varies based on the metal one is seeking and the quality of the local ore. Ores of precious metals, it seems, were often ground down to powder, but for iron ore it seems like somewhat larger chunks were acceptable. I’ve seen modern experiments with bloomeries […] getting pretty good results from ore chunks about half the size of a fist. Interestingly, Craddock notes that ore-crushing activity at mines was sufficiently intense that archaeologists can spot the tell-tale depressions where the rock surface that provided the “floor” against which the ore was crushed have been worn by repeated use.
Ore might also be washed, that is passed through water to liberate and wash away any lighter waste material. Washing is attested in the ancient world for gold and silver ores (and by Georgius Agricola for the medieval period for the same), but might be used for other ores depending on the country rock to wash away impurities. The simple method of this, sometimes called jigging, consisted of putting the ore in a sieve and shaking it while water passed through, although more complex sluicing systems are known, for instance at the Athenian silver mines at Laurium (note esp. Healy, 144-8 for diagrams); the sluices for washing are sometimes called buddles. Throughout these processes, the ore would also probably be hand-sorted in an effort to separate high-grade ore from low-grade ore.
It’s clear that this mechanical ore preparation was much more intensive for higher-value metals where making sure to be as efficient as possible was a significant concern; gold and silver ores might be crushed, sorted, washed and rewashed before being ground into a powder for the final smelting process. Craddock presents a postulated processing set for copper ore for the Bronze Age Timna mines that goes through a primary crushing, hand-sorted division into three grades, secondary crushing, grinding, a winnowing step for the low-grade ore (either air winnowing or washing) before being blended into the final smelter “charge”.
As far as I can tell, such extensive processing for iron was much less common; in many cases it seems it is hard to be certain because the sources remain so focused on precious metal mining and the later stages of iron-working. Diodorus describes the iron ore on Elba as merely being crushed, roasted and then bloomed (5.13.1) but the description is so brief it is possible that he is leaving out steps (but also, Elba’s iron ore was sufficiently rich that further processing may not have been necessary). In many cases, iron was probably just crushed, sorted and then moved straight to roasting […]
Bret Devereaux, “Iron, How Did They Make It? Part I, Mining”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-09-18.
August 11, 2023
Queer Eye for the Tudor ?guy?
At First Things, Carl R. Trueman looks into a recent post from the Mary Rose Museum (where the remains of King Henry VIII’s favourite warship now resides), considering Tudor artifacts recovered from the wreck from a Queer perspective:

“Mary Rose Museum & HMS Victory” by Silly Little Man is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0 .
The anti-Western left has been exposed for its sexual imperialism over the last few months. Evidence is all around. American Muslims have led protests against the imposition of LGBTQ policies and curricula in schools, leaving American progressives uncomfortably caught between two pillars of their favored rhetoric of political thought-crime: transphobia and Islamophobia. The Washington Post opined that anti-LGBTQ moves in the Middle East were “echoing” those of the American culture wars—as if Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan had been listed by the Human Rights Campaign as favored vacation destinations until their ruling elites started reading the website of Moms for Liberty.
It is, of course, the nature of imperialism that everything, everywhere, is always to be measured by the imperialists’ standards. And that is also what makes them so impervious to spotting their own imperialism. “Queering the Mary Rose‘s Collection”, an article on the website of the Mary Rose Museum in Portsmouth, England, is a recent example of this. The Mary Rose was a Tudor warship that sank in 1545 and was raised from the seabed in 1982 in a groundbreaking act of marine archaeology. The museum is dedicated to displaying artifacts retrieved from the wreck, some of which are now been analyzed “through a Queer lens”.
The specific examples are an octagonal mirror, nit combs, a gold ring, and Paternosters. Apparently, looking into a mirror can stir strong emotions for both straight and queer people, and for the latter it can generate, for example, feelings of gender dysphoria or euphoria, depending on whether the reflection matches their gender identity. Combs would have been used by the sailors to remove the eggs of hair lice. Today they are reminders of how hairstyles can be the result of imposed gender stereotypes, but also make possible the subverting of these through hairdos that break with social expectations. Rings are a reminder of marriage and, of course, that the Church of England founded by Henry VIII, king during the Mary Rose‘s working life, still does not allow gay marriage. Finally, the Paternosters remind us that the crew were “practicing” Christians and that, once again, Henry VIII, via his initiation of the English Reformation, facilitated the civil criminalization of homosexual acts.
Two things are striking about the article, in addition to its lack of any intellectual merit. First, the absence of any historical awareness is striking. For example, the category of “practicing Christian” is essentially meaningless when applied to the early sixteenth century. Everybody, bar a few underground Jews, Anabaptists, and radicals, was part of the Catholic Church by baptism. The question of how the crew might have understood themselves, whether in terms of mirrors, rings, combs, or Paternosters, is never asked. To be fair, a short blog post cannot ask all the relevant questions, but this does not even nod in the direction of suggesting that the differences between yesterday and today might be remotely interesting or instructive.
David Thompson also has some thoughts on the Mary Rose artifact interpretations:
It’s quality stuff. Just like being there, in the mists of history. And not at all inept, or jarring, or comically incongruous.
As we have seen, many objects can be viewed through a Queer lens and can indirectly tell LGBTQ+ stories.
And thanks to peering through this “Queer lens”, readers will doubtless find that their understanding of Tudor history has been enriched no end.
We’re told – indeed, assured – by Hannah McCann, of the museum’s collections and curatorial staff,
From the Tate Britain and the Wellcome Collection, to the Rijks Museum in Amsterdam and the Whitney Museum of American Art in New York City, museums are reinterpreting and Queering their objects.
A comfort, I know.
Exactly why such “queering” is underway – what its relevance might be – is not, however, made clear. An explanation for this bolting-on of irrelevant, flimsy tat – in the name of “queer theory” – was not, it seems, deemed necessary. Nor is it entirely obvious how such “queering” of museum contents benefits those who wish to know more about Henry VIII’s favourite warship.
July 13, 2023
QotD: The Annales school of history
The Annales school is a style of historical thinking that emerged in France in the early 1900s; at least for pre-modernists, the dominating figures here tend to be Marc Bloch and Fernand Braudel. It got its name because of its close association with Annales d’Historie Economique et Sociale. Fundamentally, what sets the Annales approach apart is first its focus and then the methods that focus demands.
The big shift in focus for the Annales school was an interest in charting the experience of society below the level of elites (though the elites are not abandoned either), what is sometimes termed “history from below”, as distinct from traditional elite-centered “great man” history or the more deterministic Marxist models of history at the time. You can see the political implications, of course, in the very early 1900s, of declaring the common man worthy of study; this is generally a history from the left but not the extreme left. That focus in turn demanded new approaches because it turned the focus of social history towards people who by and large do not write to us.
In reaching for that experience, Annales scholars tended to frame their thinking in terms of la longue durée (“the long run”); history was composed of three parts: événements (“events”), conjonctures (“circumstances”) and finally la longue durée itself. Often in English this gets rendered as a distinction between “events” (kings, wars, politics, crises) and “structures” (economics, social thought and at a deeper level climate, ecology, and geography). What Annales scholars tended to argue was that those structures were often more important than the events that traditional historians studied: the farmer’s life was far more shaped by very long-term factors like the local ecology, the organization of his farming village, the economic structure of the region and so on. And then the idea goes, that by charting those structures, you can figure things out about the lives of those farmers even if you don’t have many – or any – of those farmers writing to you.
Important to this was the idea of enduring patterns of thought within a society, what Bloch termed mentalités (“mentalities”, like longue durée, this is a technical term usually used in French to make that fact clear). Mentalités – Bloch’s original example was the idea that kings had a holy healing touch, but this could be almost any kind of social construct or pattern of ideas (indeed, one critique of it is that the notion of mentalités is broad and ill-defined) – can last a long time and can inform or constrain the actions of many actors within a society; think of how successive generations of kings can have their decisions shaped or constrained by their societies view – their own view – of kingship. That view of kingship might be more impactful than any one king and so pervasive that even a king would struggle to change it.
So how does this influence my work? I tend to be very much a “history from below” kind of historian, interested in charting the experience of regular farmers, soldiers, weavers and so on. The distinction between the long-term structures that shape life and the short-term events that populate our history is very valuable to think with, especially for identifying when an event alters a structure, because those tend to be very important events indeed. And I think a keen attention to the way people thought about things in the past and how those mentalités can be different than ours is very important.
That said, the Annales stress on mentalités has in some ways been overtaken by more data-driven historical methods on the one hand or a strong emphasis on local or individual experience (“microhistory”) on the other. Mentalités tend to be very big picture, asking how, say, “the French” thought about something over a period of decades or centuries and seeking to know how that shaped their experience. But archaeology, demographics or economic data can reveal patterns of behavior which might not correspond to the mentalités that show up in written texts; this is fundamentally the interaction that informs the “revenge of the archaeologists” in the study of the ancient economy, for instance. On the other hand, not everyone in that big group thinks the same and a microhistory of an individual or a single village might reveal telling local variations not captured in massive-scale structures.
Fortunately, historians do not need to be doctrinaire in our use of theory, we don’t have to pick one and stick to it. Different projects also lend themselves to different approaches. I think the Annales school offers a lot of really useful tools to have my historian’s toolbox, but they sit alongside military theory, archaeological material culture studies methods, philological approaches, a smattering of economic and demographic tools, etc.
Bret Devereaux, “Referenda ad Senatum: January 13, 2023: Roman Traditionalism, Ancient Dates and Imperial Spies”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2023-01-13.
June 1, 2023
Recent discoveries in ancient DNA
The Psmiths, John and Jane, decided to jointly review a book by David Reich called Who We Are and How We Got Here: Ancient DNA and the New Science of the Human Past. This is Jane’s first contribution to an extended email thread between the Psmiths:
The problem with history is that there just isn’t enough of it. We’ve been around for, what, fifty thousand years? Conservatively.1 And we’ve barely written things down for a tenth of that. Archaeological excavation can take you a little farther back, but as the archaeologists always like to remind us, pots are not people. If you get lucky with a society that made things out of durable materials in a cold and/or dry environment (or you get very lucky with anaerobic preservation of organic materials, like in ice or bogs), maybe you can trace a material culture’s expansion and contraction across time and space. But that won’t tell you whether it’s a function of people moving and taking their stuff with them, or people’s neighbors going “ooh, using string to make patterns on your pots, that’s cool” and copying it. It certainly doesn’t tell you what their descendants were doing several thousand years later, potentially in an entirely different place and probably using an entirely different suite of technologies. Trying to understand what happened in the human past based on the historical and archaeological records is like walking into a room where a bomb has gone off and trying to reconstruct the locations of all the objects before the explosion. You can get some idea, but it’s all very broad strokes. And actually it’s worse than that, because it wasn’t just one explosion, it was lots, and we wouldn’t even know how many if we didn’t have a way of winding the clock back. But these days we do, and it’s ancient DNA.
Sometime between when my grandfather gave me a copy of Luca Cavalli-Sforza’s Genes, Peoples, and Languages for my birthday and when you and I decided to read Reich’s book together, two big things happened: humans got really, really good at sequencing and reading genomes, and Svante Pääbo’s lab in Leipzig got really, really good at extracting DNA from ancient bones. (How they developed their procedures is actually a really interesting story, which Pääbo retells in his book, but Reich — whose lab uses the same techniques on an industrial scale — gives a good, brief summary of how it works.) Together, these two advances unlocked … well, not quite everything about the deep past, but an absolutely enormous amount. Suddenly we can track the people, not just the pots, and the story is more complicated and fascinating than anything we might have expected. I’ve written elsewhere about some of the aDNA discoveries about human evolution (Neanderthal admixture, the Denisovans, etc.), but I’m even more excited about what ancient DNA reveals about our more recent past. Luckily, that’s what Reich spends most of the book on, with discussion of ancient ghost populations who now exist only in admixture and then chapters on the specific population genetic histories of Europe, India, North America, East Asia, and Africa, each of which contains some discoveries that would make (at least the more sensible) archaeologists and historical linguists go “well, duh” and others that are real surprises.
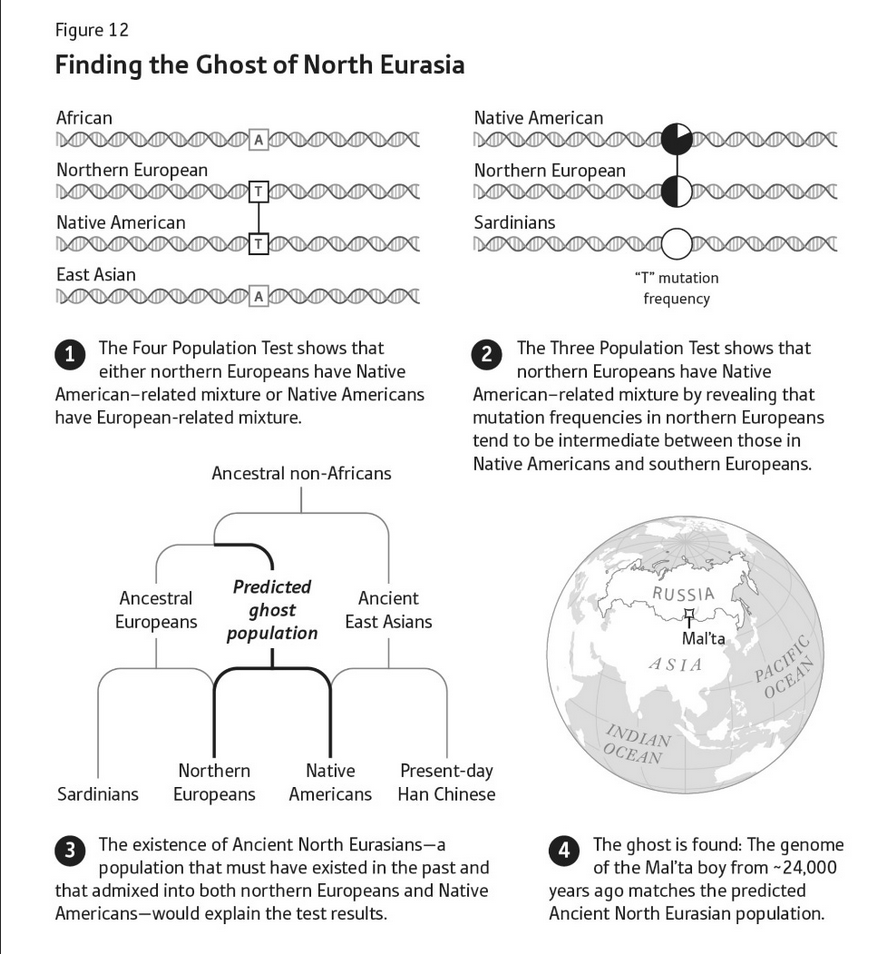
One of the “duh” stories is the final, conclusive identification of the people who brought horses, wagons, and Indo-European languages to Europe with the Yamnaya culture of the Pontic Steppe and their descendants. (David Anthony gives a very good overview of the archaeological case for this in The Wheel, the Horse, and Language, including some very cool experimental archaeology about horse teeth; you have my permission to skim the sections on pots.) My favorite surprising result, though, comes from a little farther north. People usually assume that Native Americans and East Asians share a common ancestor who split from the ancestors of Europeans and Africans before dividing into those two populations, but when Reich’s lab was trying to test the idea they found, to their surprise, that in places where Northern European genomes differ from Africans’, they are closer to Native Americans than to East Asians. Then, using a different set of statistical techniques, they found that Northern European populations were the product of mixture between two groups, one very similar to Sardinians (who are themselves almost-unmixed descendants of the first European farmers) and one that is most similar to Native Americans. They theorized a “ghost” population, which they called the “Ancient North Eurasians”, who had contributed DNA both to the population that would eventually cross the Bering land bridge and to the non-Early European Farmer ancestors of modern Northern Europeans. Several years later, another team sequenced the genome of a boy who died in Siberia 24kya and who was a perfect match for that theorized ghost ANE population.
But we’ve already established that I’m the prehistory nerd in this family; were you as jazzed as I was to read about the discovery of the Ancient North Eurasians?
1. That’s the latest plausible date for the arrival of full “behavioral modernity” in Africa, though our genus goes back about two million years, tool use probably three million, and I think there’s a good case that Homo was meaningfully “us” by 500kya. (That’s “thousand years ago” in “I talk about deep history so much I need an acronym”, fyi.)
May 19, 2023
They made a MOVIE about the discovery of Richard III’s remains!!!
Vlogging Through History
Published 16 Sept 2022Here’s a fantastic hour-long breakdown of the entire search and discovery process – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsTyG…
(more…)
April 23, 2023
My Review of Graham Hancock’s Ancient Apocalypse
Thersites the Historian
Published 17 Jan 2023In this video, I review Graham Hancock’s new series on Netflix, where he presents his case for a globe-spanning prehistoric civilization to a general audience.
(more…)