Rex Krueger
Published 9 Mar 2023You all have seen it in the background! But what’s actually on the tool wall?
(more…)
March 10, 2023
Build a Tool Wall From Scraps and Junk
The evolution of a slur
Scott Alexander traces the reasons that we can comfortably call British people “Brits” but avoid using the similar contraction “Japs” for Japanese people:
Someone asks: why is “Jap” a slur? It’s the natural shortening of “Japanese person”, just as “Brit” is the natural shortening of “British person”. Nobody says “Brit” is a slur. Why should “Jap” be?
My understanding: originally it wasn’t a slur. Like any other word, you would use the long form (“Japanese person”) in dry formal language, and the short form (“Jap”) in informal or emotionally charged language. During World War II, there was a lot of informal emotionally charged language about Japanese people, mostly negative. The symmetry broke. Maybe “Japanese person” was used 60-40 positive vs. negative, and “Jap” was used 40-60. This isn’t enough to make a slur, but it’s enough to make a vague connotation. When people wanted to speak positively about the group, they used the slightly-more-positive-sounding “Japanese people”; when they wanted to speak negatively, they used the slightly-more-negative-sounding “Jap”.
At some point, someone must have commented on this explicitly: “Consider not using the word ‘Jap’, it makes you sound hostile”. Then anyone who didn’t want to sound hostile to the Japanese avoided it, and anyone who did want to sound hostile to the Japanese used it more. We started with perfect symmetry: both forms were 50-50 positive negative. Some chance events gave it slight asymmetry: maybe one form was 60-40 negative. Once someone said “That’s a slur, don’t use it”, the symmetry collapsed completely and it became 95-5 or something. Wikipedia gives the history of how the last few holdouts were mopped up. There was some road in Texas named “Jap Road” in 1905 after a beloved local Japanese community member: people protested that now the word was a slur, demanded it get changed, Texas resisted for a while, and eventually they gave in. Now it is surely 99-1, or 99.9-0.1, or something similar. Nobody ever uses the word “Jap” unless they are either extremely ignorant, or they are deliberately setting out to offend Japanese people.
This is a very stable situation. The original reason for concern — World War II — is long since over. Japanese people are well-represented in all areas of life. Perhaps if there were a Language Czar, he could declare that the reasons for forbidding the word “Jap” are long since over, and we can go back to having convenient short forms of things. But there is no such Czar. What actually happens is that three or four unrepentant racists still deliberately use the word “Jap” in their quest to offend people, and if anyone else uses it, everyone else takes it as a signal that they are an unrepentant racist. Any Japanese person who heard you say it would correctly feel unsafe. So nobody will say it, and they are correct not to do so. Like I said, a stable situation.
He also explains how and when (and how quickly) the use of the word “Negro” became extremely politically incorrect:
Slurs are like this too. Fifty years ago, “Negro” was the respectable, scholarly term for black people, used by everyone from white academics to Malcolm X to Martin Luther King. In 1966, Black Panther leader Stokely Carmichael said that white people had invented the term “Negro” as a descriptor, so people of African descent needed a new term they could be proud of, and he was choosing “black” because it sounded scary. All the pro-civil-rights white people loved this and used the new word to signal their support for civil rights, soon using “Negro” actively became a sign that you didn’t support civil rights, and now it’s a slur and society demands that politicians resign if they use it. Carmichael said — in a completely made up way that nobody had been thinking of before him — that “Negro” was a slur — and because people believed him it became true.
Tank Chats #168 | Vixen & Fox | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 18 Nov 2022Join David Fletcher as he takes a look at the Vixen and Fox armoured cars.
(more…)
QotD: Wine in French culture
Wine is obviously hugely central to French culture. In 1965 French adults consumed 160 litres per head a year, which perhaps explains their traditionally very high levels of cirrhosis. Despite this, they don’t have the sort of extreme oblivion-seeking alcoholism found in the British Isles. Anglo-Saxon binge drinking is considered uncouth, and the true man of panache and élan instead spends all day mildly sozzled until eventually turning into a grotesque Gérard Depardieu figure. (Although Depardieu’s 14 bottles of wine a day might be on the high side, even for French standards.)
When the French sought to reduce alcohol consumption in the 1950s, the government’s slogan was “No more than a litre of wine a day“, which must have seemed excessively nanny-statish at a time when primary school children were given cider for lunch. Wine consumption has quite drastically fallen in the decades since, by as much as two-thirds by some estimates.
Ed West, “The Frenchest things in the world … Part Deux”, Wrong Side of History, 2022-12-09.
March 9, 2023
“… the French Resistance effect is beginning to appear: After the Nazis leave France, everyone says they were always with the Resistance”
Chris Bray notices what we’re not supposed to be noticing:

French women accused of collaborating with the Germans are paraded through the streets by members of the French Resistance after liberation, Summer 1944.
Original photo from the German Federal Archive via Wikimedia Commons.
Almost two years ago, with a moral panic still consuming the world and the narrative shift far in the future, the journalist Laura Dodsworth published a tough, concise, well-argued book describing the very deliberate efforts of the British government to create a widespread state of fear — that’s the title of the book, by the way — that would paralyze ordinary people and compel them to comply with harsh and repressive public health measures. You’ll be shocked to hear that she was attacked and vilified; one prominent review called State of Fear “an outrageously dumb book selling conspiracy hooey”.
Then, in 2023, Isabel Oakeshott gave us the halfwit government minister Matt Hancock’s pathetic whatsapp messages — in which he clumsily babbles about creating a state of fear to get the public to obey the government — and the rest is history. Laura Dodsworth was demeaned and defamed, and then she was vindicated.
Moral panics always fade. Manufactured crises always crack and collapse. Propaganda always has a “sell by” date, and then it turns rancid. The effect is comparable to what Warren Buffett says about a recession: When the tide goes out, you can see who’s been swimming naked.
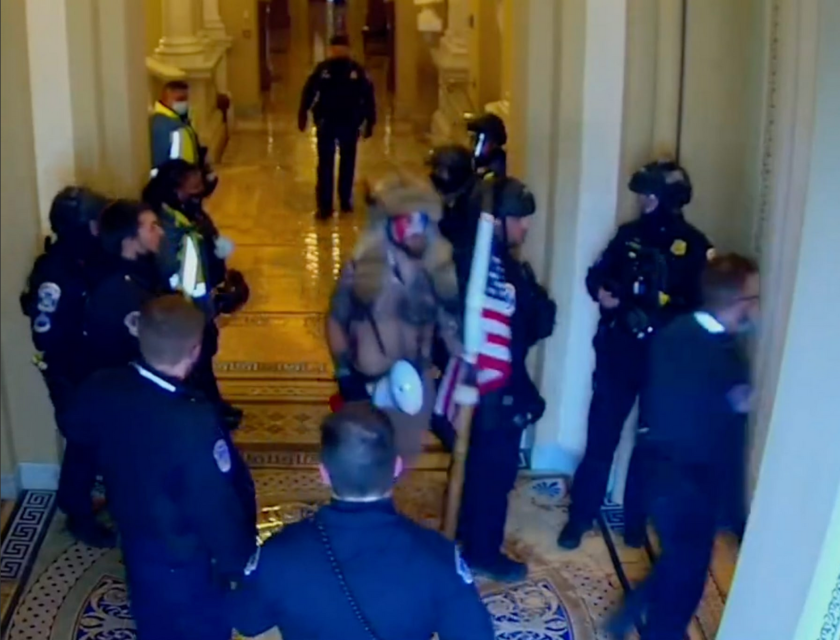
This is where we are with the January 6 narrative, as the most horrible attack on Our Democracy™ since the Civil War collides with the image of a dork in Viking horns calmly wandering the hallways with a police escort. The political class is taking it well.
This image speaks:
That’s violent insurrectionist Jacob Chansley walking calmly through a crowd of police officers who aren’t making the slightest effort to stop him. That’s what happened. Other things also happened, and some of them involved violence and broken windows, but this is the act in the center ring of the circus. Now, the lawyer who represented this violent insurrectionist says plainly that Jacob Chansley was the victim of Brady violations, and other January 6 defendants are racing to raise the same point in court. The tide is going out.
[…]
And it seems possible to me, or rather it seems likely to me, that the French Resistance effect is beginning to appear: After the Nazis leave France, everyone says they were always with the Resistance. As narratives shift, and the moral meaning of an act during a moral panic is recoded, people may begin to remember their choices differently. We’ll see.
Then: “Never be the first to stop clapping”. Now: “In our culture of exhibitionism, silence is suspect”
Chris Bray cross-posted this article by Christopher Gage, who had a painful realization while waiting on hold for a human customer service rep at British Gas:
British Gas has traded the lovely Ludwig van (much too excellent for these advanced times) for a two-chord earwig we once glorified as polyphonic ringtones. Whilst captive to the receiver, British Gas snatches the opportunity to douse you, an innocent and increasingly frozen bystander, in the warm soup of its right-on philosophy.
“British Gas is an inclusive company”, it purrs. “We believe all people, regardless of gender, ethnicity, or background, should be treated with dignity and respect.”
This divination, reader, was news to me. You see, I signed up to British Gas not for warm radiators and gas-lit stoves, but for the surreptitious fascism of a company with “British” in the name.
I assumed British Gas was firmly jackboots, shaved heads, and lumpy knuckles. On hold, I expected not a polyphonic ringtone but the greatest hits of Skrewdriver, with jaunty anthems such as “Keep Britain White” and “It’s All Because of The Jews”.
To my incomprehension, British Gas does not believe that Auschwitz was a holiday camp, nor, like Kanye West, that Hitler had his good points.
The horror. The horror.
Once you notice this culture of Obviousness, this modern theatre in which the captive audience is force-fed a diet of entirely humdrum beliefs shared by absolutely everyone save a few whack-jobs, you cannot unsee it.
A coffee shop I recently and regrettably frequented offered not only espresso and cortado and obscenely priced cheesecake but a syrupy treatise of that coffee shop’s founding beliefs. You’d think a coffee shop’s founding beliefs would be: “Buy coffee. Sell coffee.” No. This coffee shop was against all forms of discrimination.
Relentless is this modern culture of making the most obvious, universal statements and painting them as revolutionary.
When I decide I’d like gas piped into my home, or coffee piped into my stomach, my motivations hover around the middle of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Will this gas warm my home? Will this coffee induce a mild, somewhat enjoyable panic attack?
To reveal, like British Gas did, that one thinks all people should be treated with dignity and with respect is like revealing one doesn’t shit on a bus seat in full view of other passengers. That one is anti-shitting-in-public.
Much of the modern world is that episode of Seinfeld in which Kramer joins an AIDS march but refuses to wear the ribbon proclaiming his opposition to AIDS.
In our culture of exhibitionism, silence is suspect.
Look at Life – The Cherry Pickers (1965)
PauliosVids
Published 20 Nov 2018Following the 11th Hussars from Hanover to Coburg.
QotD: Iron ore mining before the Industrial Revolution
Finding ore in the pre-modern period was generally a matter of visual prospecting, looking for ore outcrops or looking for bits of ore in stream-beds where the stream could then be followed back to the primary mineral vein. It’s also clear that superstition and divination often played a role; as late as 1556, Georgius Agricola feels the need to include dowsing in his description of ore prospecting techniques, though he has the good sense to reject it.
As with many ancient technologies, there is a triumph of practice over understanding in all of this; the workers have mastered the how but not the why. Lacking an understanding of geology, for instance, meant that pre-modern miners, if the ore vein hit a fault line (which might displace the vein, making it impossible to follow directly) had to resort to sinking shafts and exploratory mining an an effort to “find” it again. In many cases ancient miners seem to have simply abandoned the works when the vein had moved only a short distance because they couldn’t manage to find it again. Likewise, there was a common belief (e.g. Plin. 34.49) that ore deposits, if just left alone for a period of years (often thirty) would replenish themselves, a belief that continues to appear in works on mining as late as the 18th century (and lest anyone be confused, they clearly believe this about underground deposits; they don’t mean bog iron). And so like many pre-modern industries, this was often a matter of knowing how without knowing why.
Once the ore was located, mining tended to follow the ore, assuming whatever shape the ore-formation was in. For ore deposits in veins, that typically means diggings shafts and galleries (or trenches, if the deposit was shallow) that follow the often irregular, curving patterns of the veins themselves. For “bedded” ore (where the ore isn’t in a vein, but instead an entire layer, typically created by erosion and sedimentation), this might mean “bell pitting” where a shaft was dug down to the ore layer, which was then extracted out in a cylinder until the roof became unstable, at which point the works were back-filled or collapsed and the process begun again nearby.
All of this digging had to be done by hand, of course. Iron-age mining tools (picks, chisels, hammers) fairly strongly resemble their modern counterparts and work the same way (interestingly, in contrast to things like bronze-age picks which were bronze sheaths around a wooden core, instead of a metal pick on a wooden haft).
For rock that was too tough for simple muscle-power and iron tools to remove, the typical expedient was “fire-setting“, which remained a standard technique for removing tough rocks until the introduction of explosives in the modern period. Fire-setting involves constructing a fuel-pile (typically wood) up against the exposed rock and then letting it burn (typically overnight); the heat splinters, cracks and softens the rock. The problem of course is that the fire is going to consume all of the oxygen and let out a ton of smoke, preventing work close to an active fire (or even in the mine at all while it was happening). Note that this is all about the cracking and splintering effect, along with chemical changes from roasting, not melting the rock – by the time the air-quality had improved to the point where the fire-set rock could be worked, it would be quite cool. Ancient sources regularly recommend dousing these fires with vinegar, not water, and there seems to be some evidence that this would, in fact, render the rock easier to extract afterwards.
By the beginning of the iron age in Europe (which varies by place, but tends to start between c. 1000 and c. 600 BC), the level of mining sophistication that we see in preserved mines is actually quite considerable. While Bronze Age mines tend to stay above the water-table, iron-age mines often run much deeper, which raises all sorts of exciting engineering problems in ventilation and drainage. Deep mines could be drained using simple bucket-lines, but we also see more sophisticated methods of drainage, from the Roman use of screw-pumps and water-wheels to Chinese use of chain-pumps from at least the Song Dynasty. Ventilation was also crucial to prevent the air becoming foul; ventilation shafts were often dug, with the use of either cloth fans or lit fires at the exits to force circulation. So mining could get very sophisticated when there was a reason to delve deep. Water might also be used to aid in mining, by leading water over a deposit and into a sluice box where the minerals were then separated out. This seems to have been done mostly for mining gold and tin.
Bret Devereaux, “Iron, How Did They Make It? Part I, Mining”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-09-18.
March 8, 2023
Perhaps the Prime Minister ran out of glitterbomb distractions?
In The Line, Matt Gurney speculates on why the federal government needed to be “punched in the face” for literally weeks before finally taking (some) action:
Let’s acknowledge something right at the top: no one really knows what the hell the prime minister proposed yesterday. Not in any specific policy sense, at any rate. But boy, did we ever learn something about how the Liberals are viewing this politically.
After weeks of bobbing and weaving and throwing out fistfuls of increasingly ridiculous chaff, Justin Trudeau has belatedly agreed to a series of actions to probe Chinese electoral interference in Canada. And maybe other interference? We don’t know. We do know it’ll involve NSICOP, which is an acronym in desperate need of an agreed-upon pronunciation, if Monday’s press conference was any guide. NSICOP is a joint House-Senate committee that reviews various matters relating to Canada’s national security and intelligence (read this on its website and you’ll know more than 99.9 per cent of Canadians do about NSICOP). There’s also going to be a splash of the National Security and Intelligence Review Agency (NSIRA), plus a special rapporteur. The special rapporteur will apparently be given broad powers and, should they recommend a full public inquiry, the PM will accept that.
Hell of an endorsement for someone who hasn’t been selected yet. It’s almost like the PM decided he had to make an announcement before he was ready to actually share many details about that announcement, for some reason. Like the announcement itself was the point. Weird, eh? Wonder what that was about. In any case, all we know is it’ll be an eminent Canadian.
Shoutout to all you eminent Canadians out there, I guess. Brush up those cover letters.
Winston Churchill frequently has this attributed to him: “You can depend upon the Americans to do the right thing. But only after they have exhausted every other possibility.” Our Canadian version might be that you can depend on Prime Minister Trudeau to do something, but only after he’s exhausted all of his glitterbombs on distracting public attention.
The way that the Liberals responded wasn’t shocking. They only have a few plays left in their playbook, and we’ve seen something just like this only a few weeks ago. (Which is why I’m wondering if they actually only have the single play left, come to think of it.) The Liberals have responded to the barrage of news stories over Chinese interference exactly the way they did over their controversial gun-control amendments from the fall. First, deny there’s a problem. Then accuse anyone saying there’s a problem of being Donald Trump 2.0 or somesuch. Then just cut right to the chase and call them racist. When that doesn’t work, wait a few days to see if the problem goes away. When it doesn’t — indeed, when it gets worse — that’s when you finally admit that you can’t just yell “DISINFORMING MAGA BIGOTS!” at people and watch as your problem magically evaporates.
With guns, after everything else failed, they withdrew the amendments (though I imagine they’ll try again, though probably with no better luck). With China interference, it was agreeing to some kind of process. All the unfilled blanks notwithstanding, even the fact that something is being agreed to shows a dawning of political reality in the PMO: ignoring this and hoping the leaks stop if you called enough people racist Trumpers wasn’t going to work. Clearly, sometime in the last few days, the PM and his staff reached the acceptance stage, and concluded that either they had to admit that there was enough here to warrant some kind of serious process, or they could just start randomly talking about abortion in the hopes that people fell for that.
No, no, wait. They tried that anyway.
It would be fascinating to know what specifically led to the mental breakthrough that enabled Monday’s announcement. Weeks of denials, evasions and counterattacks, a day of performatively fretting about abortion, and then, zap!, we’re getting an rapporteur — an eminent one! — and a process. Maybe they looked at some internal polling. Maybe they’re worried about a big scoop that’s yet to land. Or maybe they’re just tired of being on the defensive and figured that the proposals would stand a decent chance of smothering the issue to death with pillows stuffed with bureaucracy and abbreviations.
Feeding a Medieval Outlaw
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 7 Mar 2023
(more…)
“By fostering intense family loyalties and strong nepotistic urges”, cousin marriage “makes the development of civil society more difficult”
Ed West on what he calls the worst western foreign policy disaster since 1204, the Iraq quagmire:

Mohammed Saeed al-Sahhaf, better known in the West as “Baghdad Bob” or “Comical Ali”, Iraqi Minister of Information for President Saddam Hussein.
This month marks the 20th anniversary of the greatest western foreign policy disaster since the Fourth Crusade. It was the pre-eminent modern-day example of folly, driven by wishful thinking, utopianism and a lack of interest in history and how human societies differ. This was mostly carried out by good people, including our own Tony Blair, and promoted by thoughtful and humanitarian commentators who thought they were making the world a better place.
The White House regime which brought chaos and misery to Iraq were most of all entranced by The Weekly Standard, the now-defunct magazine most associated with neoconservative foreign policy. Had any of them read The American Conservative instead, they might have avoided the whole tragedy. In particular they ought have read Steve Sailer’s “The Cousin Marriage Conundrum“, printed in the run-up to the invasion and in which the author made a seemingly curious argument for why nation-building in Iraq would fail — its high rates of cousin marriage.
Pointing out that between 46 and 53 percent of Iraqis who married did so to first or second cousins, Sailer wrote that: “By fostering intense family loyalties and strong nepotistic urges”, cousin marriage “makes the development of civil society more difficult”. The neocon dream of jumpstarting democracy was therefore clearly doomed to failure.
Even those with a cursory knowledge of the country knew that Iraq was split between Sunni and Shia Arabs, as well as Kurds in the north, each group’s area of dominance roughly corresponding to three former Ottoman provinces. However, these were further subdivided into “smaller tribes, clans, and inbred extended families — each with their own alliances, rivals, and feuds”, in total about 150 tribes comprising some 2,000 clans.
Saddam’s politics were mired in blood, in both senses. He came from the al-Bu Nasir, a tribe comprising some 25,000 people based in the town of Tikrit, and his regime was filled with his relatives. His political career had begun in 1957 when the 20-year-old had joined the revolutionary Ba’ath (“Resurrection”) Party, following his uncle Kharaillah Tulfha, who had fought against the British in the Second World War. Tulfha would become his father-in-law, for Saddam also married his first cousin, although he later took a second wife. Family life wasn’t entirely harmonious, and the man who introduced that couple, Saddam’s food taster, was later stabbed to death by the dictator’s psychotic eldest son Uday at a party thrown by Egyptian president Hosni Mubarak.
The unfortunate food taster was an Assyrian Christian, and within Saddam’s regime religious minorities could rise high, as is often the case in empires, because they presented no threat. His foreign minister, Tariq Aziz, was also a Christian, his birth name being Mikhail Yuhanna.
The family was everything in Saddam’s Iraq. Mark Weiner wrote in The Rule of the Clan of countries governed by “clannism” that: “These societies possess the outward trappings of a modern state but are founded on informal patronage networks, especially those of kinship, and traditional ideals of patriarchal family authority. In nations pervaded by clannism, government is co-opted for purely factional purposes.” The inevitable result of clannism is kin-based corruption whereby resources, positions and other rewards are monopolised by family groups. In these societies, Weiner wrote, “the nuclear family, with its revolutionary, individuating power, has yet to replace the extended lineage group as the principle framework for kinship or household organisation”.
The Weekly Standard was called the in-flight magazine of Air Force One, but presumably there weren’t that many White House staffers reading the American Conservative at the time, a publication started by Pat Buchanan, the great Republican critic of neocon foreign policy. So the Coalition blundered into a disastrous invasion that cost hundreds of thousands of lives, wrecking Iraq and leaving many areas newly-divided along sectarian lines, while minorities like the Christians and Mandaeans were driven almost to extinction.
First to the Fight: The Marines’ Reising M50 SMG
Forgotten Weapons
Published 4 Nov 2022Eugene Reising developed a .45 ACP submachine gun in the late 1930s that was basically the opposite of the Thompson — it was light and handy, fired from a closed bolt with a delayed blowback action, and was inexpensive to produce. Reising contracted with Harrington & Richardson to produce the gun, and when it entered the market in early 1940 it found immediate interest from the USMC. Looking initially to equip the Marine Paratroop Regiment (Paramarines), the Corps wanted a gun that was light and compact. The Reising M55 with its folding stock was certainly those things and since the Thompson was essentially unavailable anyway (all production was going to the Army and foreign contracts), the Corps adopted the Reising with initial purchases of both the M50 and M55 in January and February of 1942.
What we are looking at today is an early production M50. It is blued with 29 barrel fins and the early style of sights, stock screw, trigger guard, magazine release, stock (the lacquer coating and sling swivels having been added by a previous owner), and firing pin. Later production guns would be improved and strengthened in various ways, but the Reising would never quite meet the needs of frontline combat troops, much to the displeasure of the Marines who first used them in the Pacific theater. Lacking interchangeable parts and susceptible to fouling and malfunctions, the Reisings were quickly replaced by other arms — some Johnson M1941 rifles, some M1 and M1A1 carbines, and various other guns. Rotated back to duties like ship boarding parties, guards, and military police, the Reising served very well. They were indeed handy and accurate guns, just not built for the extreme rigors of Pacific beach assaults and jungle foxholes.
(more…)
QotD: Who destroyed the Great Library?
While the Great Library was never as large as some of the more fanciful accounts allege, it is clear that its holdings were large enough that at least some of them were stored outside of the Mouseion. As already noted, this is probably why Caesar’s burning of the dock area was seen as destroying the library collection and why there were at least two “daughter libraries” in the city – one in the Kaisarion or Temple of Caesar, another in the Serapion or Serapeum, the Temple of Serapis and possibly a third. Serapis was a Greek-Egyptian hybrid deity, combining Zeus and Osiris, and his cult and temple were extremely popular in Ptolemaic Alexandria. The Ptolemaic temple burned down sometime in the second century AD and was rebuilt in magnificent style and it is possible that its library was established then. Tertullian mentions that this library included copies of the Old Testament (Tertullian, Apology, 13) and Epiphanius, bishop of Salamis, notes that it was an annex of the Mouseion‘s collection, saying “later another library was built in the Serapeum … which was called the daughter of the first one” (Epiphanius, Weights and Measures, 11). In 391 AD the Serapeum was indeed torn down by Roman soldiers and a Christian mob and it is here, finally, that we find the seed of the myth. There is no “fire” involved and it is this daughter library that was supposedly destroyed not the Great Library itself, which had ceased to exist by this point, but the myth is cobbled together from this episode and some garbled reflections of the story of Caesar’s fire.
The problem, however, is that there is no evidence that the Serapeum still contained any library by 391 AD and some good evidence indicating that it did not.
When the mythic version of the story of the destruction of the Serapeum gets told it usually begins without explaining why the temple was attacked. These retellings focus on the supposed destruction of its library, so they tend to assume that the mob was there simply because they hated learning. But several accounts of the end of the temple note that it came as the climax of a series of attacks by pagans on Christians in reaction to the desecration of pagan idols. Sozomen’s account details what happened next:
They killed many of the Christians, wounded others, and seized the Serapion, a temple which was conspicuous for beauty and vastness and which was seated on an eminence. This they converted into a temporary citadel; and hither they conveyed many of the Christians, put them to the torture, and compelled them to offer sacrifice. Those who refused compliance were crucified, had both legs broken, or were put to death in some cruel manner. When the sedition had prevailed for some time, the rulers came and urged the people to remember the laws, to lay down their arms, and to give up the Serapion (Sozomen, History of the Church, VII.15)
Sozomen was writing in the following century and, as a Christian, may not be reliable on the lurid details, but Socrates Scholasticus, writing a little closer to the events, confirms that many Christians were killed in the unrest. A stand-off followed, with Roman troops surrounding the temple while negotiations went on with the pagan militants inside. This situation must have continued for many weeks, as a petition went to the emperor in Constantinople about the siege and Theodosius ruled that the pagans should be pardoned for their murders and allowed to leave but that the temple should be demolished. Angry at this compromise, as the soldiers began to carry out the order, the Christian mob joined in the destruction, and made sure the great idol of Serapis was also destroyed.
We have no less than five accounts of the destruction of the Serapeum – Rufinius Tyrannius, Socrates Scholasticus, Sozomen, Theodoret and Eunapius of Antioch – which is rare in ancient history and actually makes this one of the best documented events in the period. What is significant about them is that not one of them mentions a library. Some try to argue that the Christian chroniclers would be ashamed of the crime of destroying the last remnant of the Great Library and so hushed it up in their accounts. This argument is hard to sustain. Firstly, Christian historians of the time did record other shameful acts against pagans, including the assassination of Hypatia, so at least one or two of the four Christians who describe the end of the Serapeum could be expected to at least lament the loss of a library. Socrates Scholasticus, who condemned the death of Hypatia, was a Novatian “heretic” and thus no fan of the bishop Theophilus, who urged on the crowd at the temple’s demolition, yet he makes no mention of a library. Even more significantly, Eunapius of Antioch was a pagan, a scholar and a vehement anti-Christian, so had every reason to condemn any destruction of a library, yet he too makes no mention of it. That great defender of New Atheist bad history, the inevitable Richard Carrier, has attempted to dismiss this silence by Eunapius by blithely claiming that “his account is too brief”. Carrier assures his online fan club “[a]ll he describes is the raid on its pagan statues, and some vague looting otherwise. His concern is clearly with the offense to the gods”. This is, as usual with Carrier, total nonsense. Eunapius’ account in his Lives of the Philosophers runs to 548 words in English translation. Of these, a full 245 are not about pagan statues etc, but are devoted wholly to detailed denigration of the ignorant Christian monks who destroyed the temple. He calls them “men in appearance (who) led the lives of swine”, says they “fettered the human race to the worship of slaves” and mocks them for their worship of martyrs’ relics and their general stupidity. Given that around 40% of his account is taken up with this scorning and mocking of these monks, it is still very strange that this scholar neglects to mention in his condemnation that these ignorant oafs also happened to destroy one of the best libraries in the world.
The lack of any mention of a library is most likely explained by concluding that it was no longer there by 391 AD. Temples had begun to be starved of funds with the conversion of the emperors [to] Christianity and the slower but gradual conversion of many rich patrons and city benefactors. The Serapeum survived most of the fourth century, but it is very likely that the expense of maintaining an extensive library would have been a strain. We know that it was ransacked on the orders of the Alexandrian bishop George the Cappodocian c. 360 AD and it is likely the library was looted in this action. Significantly, writing around 378 AD, Ammianus Marcellinus gave a detailed description of the Serapeum and mentions its libraries using the past tense:
In here have been valuable libraries and the unanimous testimony of ancient records declares that seven hundred thousand books, brought together by the unremitting energy of the Ptolemies, were burned in the Alexandrine War when the city was sacked under the dictator Caesar. (Ammianus, Roman History XXII.16-17)
Ammianus is muddling the Serapeum with the main Mouseion library with his reference to Caesar’s fire and the mythical “700,000” books, but the rest of his description is detailed and unique to his work in many respects. Other references in his work indicate that he had visited Egypt himself, probably around 363 AD (or three years after the sacking of the temple by Bishop George), so it is highly possible that his account is that of an eye-witness. This means his use of the past tense about the temple library is significant. Overall, the idea that there was still any library there when the temple was demolished is dubious at best and almost certainly wrong.
Tim O’Neill, “The Great Myths 5: The Destruction Of The Great Library Of Alexandria”, History for Atheists, 2017-07-02.
March 7, 2023
Getting rid of the SAT won’t help low-income or minority students – in fact, it’ll hurt them
Rob Henderson explains why the notion of getting rid of SAT requirements will to the opposite of what is being claimed, based on his own experience:

US Navy Seaman Chanthorn Peou takes the SAT aboard USS Kitty Hawk, 23 February, 2004.
US Navy photograph by Photographer’s Mate 3rd Class Jason T. Poplin via Wikimedia Commons.
I graduated in the bottom third of my high school class with a 2.2 GPA. Didn’t think of myself as “smart”. I thought a lot and read a lot. But I hated homework, teachers, rules, etc. I thought “smart” meant kids who did their homework and raised their hand in class. Those types.
My senior year of high school I took the required test to join the military — the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB). Half my motivation to take this test was because I got to skip class. I spent the night before with my friends drinking Four Loko and playing Fight Night Round 3 on Xbox 360. Woke up with a hangover, chugged 20 ounces of Rockstar energy drink, and took the test. Afterwards, the Air Force recruiter showed me how to convert ASVAB to SAT scores. I got the same score as my smartest friend who always got straight-As and was headed for college. What the fuck? I thought.
At the time, I wasn’t aware these tests are thinly veiled IQ tests. The SAT, ASVAB, and the ACT are all highly correlated with IQ at about r = .8.
A study on Army recruits found that scores on an intelligence test, along with 2-mile run time, were the best predictors of success in infantry training.
Research on tank gunners found that replacing a gunner who scores around the 20th percentile with one who scores around the 55th percentile improves the likelihood of hitting a target by 34 percent.
To qualify, potential military recruits must score higher than roughly one-third of all who take the ASVAB. The lowest acceptable percentile score to join is 36 for the Air Force, 35 for the Navy, 32 for the Marine Corps, and 31 for the Army. By definition, the worst test taker who makes it into the military still scores higher than one-third of his or her peers. The military slices off the bottom third of standardized test-takers, not allowing them to join.
The psychologist and intelligence researcher Linda Gottfredson has written:
IQ 85 … the U.S. military sets its minimum enlistment standards at about this level … The U.S. military has twice experimented with recruiting men of IQ 80-85 (the first time on purpose and the second time by accident), but both times it found that such men could not master soldiering well enough to justify their costs.
In the 1960s, Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara launched Project 100,000 which lowered the testing requirement. This allowed people at the 10th percentile (80~ IQ) — a standard deviation lower than the previous standard — to join.
Supposedly, the aim was to alleviate poverty. LBJ had recently begun his War on Poverty program. The story was that getting more recruits into the military would help them move into the middle class. And they needed more recruits for the Vietnam War. Lowering recruitment standards was an easy way to get them.
Recruits of Project 100,000 were 9 times more likely to require remedial training and training took up to 4 times longer to complete compared to their peers who had entered under the higher score requirement. In Vietnam, men recruited under the lower testing threshold were 2.5 times more likely to die in combat.
Did the veterans who made it home achieve upward mobility? No. Compared to civilians with similar attributes who were not recruited, McNamara’s Morons (as they were later termed) were less likely to be employed, less likely to own a business, and obtained less education. Later, the policy changed to improve the talent pool of the armed forces. Higher ASVAB score thresholds were reinstated. Along with additional rigid requirements.
Today, eight out of ten Americans between 17 and 24 are ineligible for military service. Mostly due to obesity, medical issues, and criminal records.
Anyway, seeing my ASVAB score was the first time I learned I could have been a good student. It was possible. How many kids out there are like this. Kids who have fucked up lives and get bad grades which mask their underlying potential. Potential that a standardized test could reveal.
The SAT is a “barrier” according to that NYT op-ed. But it’s also a gateway. Most poor kids don’t take the SAT. Or any other standardized test. More should.