BFBS Creative
Published 24 Jun 2021We take you behind the scenes on a BFBS creative shoot, 8000 miles from home. With access all areas, we take a look at the current military presence on the Falkland Islands as well as the incredible wildlife.
May 21, 2023
What Are The Falklands Like Today? | BFBS
March 10, 2023
Tank Chats #168 | Vixen & Fox | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 18 Nov 2022Join David Fletcher as he takes a look at the Vixen and Fox armoured cars.
(more…)
February 12, 2023
Avro Vulcan: What made the Vulcan the best V bomber?
Imperial War Museums
Published 28 Apr 2021The Avro Vulcan Bomber, the most famous of the British V bombers, is known for its distinctive howl and delta wing. Initially one of the delivery agents of Britain’s independent nuclear deterrent during the Cold War, the Vulcan later fulfilled another role, undertaking the longest bombing raid in history for Operation Black Buck in the Falklands Campaign of 1982. One of the first operational RAF aircraft with a delta wing, this impressive Cold War jet has never lost its appeal. In this video, events and experiences coordinator Liam Shaw takes us through the extraordinary history and technological achievements of the Avro Vulcan. We go into the cockpit and hear first-hand from the people who flew this unique machine throughout its long and remarkable history.
(more…)
February 1, 2023
What’s the Greatest Machine of the 1980s … the FV107 Scimitar?
Engine Porn
Published 19 Jan 2015Light, agile and very fast on all types of terrain, the fabulous Scimitar FV107 armoured reconnaissance vehicle was developed by car manufacturer Alvis, who were asked to build a fast military vehicle that was light enough to be airdropped — simply not an option for full sized battle tanks at the time, which averaged around 13 tonnes. [NR: I think they mean “light tanks” here, as MBTs of the era would have been more like 50+ tons.]
Alvis got the weight down to under 8 tonnes by using a new type of aluminium alloy and minimising armour rating in favour of speed. They built the Scimitar around a 220 horsepower, six cylinder, 4.2 litre Jaguar sports car engine with ground-breaking transmission that allowed differential power to each set of tracks. The result was a sports car of the the military world that might not be the toughest in the field, but could race its way out of trouble at speeds of up to 70 miles an hour.
What makes it great: A revolutionary armoured vehicle that brought the very best of British sports car performance to the battlefield.
Time Warp: The Scimitar was the only armoured vehicle to be used by the British Army in the Falklands War.
This short film features Chris Barrie taking the Scimitar for a spin.
(more…)
December 4, 2022
L39A1: British Service Target Rifle Before the L42A1
Forgotten Weapons
Published 5 Aug 2022The story of the conversion of the Lee Enfield to 7.62mm NATO would not be complete without the L39A1. This is essentially the civilian competition version of what would become the L42A1. It was actually in British service as a target rifle — not intended for combat. It followed the L8 (the first British military attempts at a 7.62mm precision version of the Enfield) and the L42A1. It was basically a copy of the conversions done by civilian competition shooters in the British NRA.
Sights were made by several different companies, as the rifles were not issued with sights — they were obtained by the unit they went to, whatever particular model that unit preferred. This example has Parker Hale diopter sights. The L39A1 also used a .303 caliber magazine, as they were intended for slow-fire, single-loaded competition but the magazine was used as a loading tray. The .303 magazine will not reliably hold 7.62mm cartridges, but 7.62mm conversion magazines can be put in the L39A1 and will then work just fine. They also sometimes are fitted with .303 extractors. The stock here has a semi-pistol grip a bit less substantial than the L8 .22 rifle, although most had standard No4 stocks.
The original sights were removed, and remarked as L39A1. They were made in 1969, 1970, and 1972, with a single serial number range used for the L39A1, the pretrial trials examples of the L39, and the “7.62 Conv” rifles. A total of 1,213 L39A1 rifles were made, with the other types accounting for about 28 additional rifles.
(more…)
November 6, 2022
QotD: Thatcher and the Falklands
Mrs Thatcher saved her country — and then went on to save an enervated “free world”, and what was left of its credibility. The Falklands were an itsy bitsy colonial afterthought on the fringe of the map, costly to win and hold, easy to shrug off — as so much had already been shrugged off. After Vietnam, the Shah, Cuban troops in Africa, Communist annexation of real estate from Cambodia to Afghanistan to Grenada, nobody in Moscow or anywhere else expected a western nation to go to war and wage it to win. Jimmy Carter, a ditherer who belatedly dispatched the helicopters to Iran only to have them crash in the desert and sit by as cocky mullahs poked the corpses of US servicemen on TV, embodied the “leader of the free world” as a smiling eunuch. Why in 1983 should the toothless arthritic British lion prove any more formidable?
And, even when Mrs Thatcher won her victory, the civilizational cringe of the west was so strong that all the experts immediately urged her to throw it away and reward the Argentine junta for its aggression. “We were prepared to negotiate before” she responded, “but not now. We have lost a lot of blood, and it’s the best blood.” Or as a British sergeant said of the Falklands: “If they’re worth fighting for, then they must be worth keeping.”
Mrs Thatcher thought Britain was worth fighting for, at a time when everyone else assumed decline was inevitable. Some years ago, I found myself standing next to her at dusk in the window of a country house in England’s East Midlands, not far from where she grew up. We stared through the lead diamond mullions at a perfect scene of ancient rural tranquility — lawns, the “ha-ha” (an English horticultural innovation), and the fields and hedgerows beyond, looking much as it would have done half a millennium earlier. Mrs T asked me about my corner of New Hampshire (90 per cent wooded and semi-wilderness) and then said that what she loved about the English countryside was that man had improved on nature: “England’s green and pleasant land” looked better because the English had been there. For anyone with a sense of history’s sweep, the strike-ridden socialist basket case of the British Seventies was not an economic downturn but a stain on national honor.
A generation on, the Thatcher era seems more and more like a magnificent but temporary interlude in a great nation’s bizarre, remorseless self-dissolution. She was right and they were wrong, and because of that they will never forgive her. “I have been waiting for that witch to die for 30 years,” said Julian Styles, 58, who was laid off from his factory job in 1984, when he was 29. “Tonight is party time. I am drinking one drink for every year I’ve been out of work.” And when they call last orders and the final chorus of “Ding Dong! The Witch Is Dead” dies away, who then will he blame?
During the Falklands War, the Prime Minister quoted Shakespeare, from the closing words of King John:
And we shall shock them: naught shall make us rue,
If England to itself do rest but true.For eleven tumultuous years, Margaret Thatcher did shock them. But the deep corrosion of a nation is hard to reverse: England to itself rests anything but true.
Mark Steyn, “The Uncowardly Lioness”, SteynOnline.com, 2019-05-05.
November 1, 2022
Britain’s Final Assault – Falklands War
Historigraph
Published 29 Oct 2022In the closing days of May 1982, the British land campaign to recapture the Falkland Islands began, after an eight thousand mile voyage and weeks of battles at sea and in the air. With a beachhead established, British troops were now charged with rapidly defeating an Argentinian force that was more numerous and had spent weeks preparing defences. The Battle for the Falklands was about to begin.
(more…)
October 19, 2022
South Atlantic D-Day: Battle of San Carlos – Falklands War
Historigraph
Published 15 Oct 2022On May 21st 1982, the United Kingdom landed thousands of troops at San Carlos Water in the Falkland Islands, to begin their recapture from Argentina. But only hours after arriving, British forces were under intense attack, as the Argentine air force attempted to push the troops clambering ashore back into the sea. This was the Battle of San Carlos.
0:00 – Intro
0:37 – Britain’s Invasion Plans
2:59 – Bespoke Post
4:16 – The Argentine Onslaught
8:46 – Attack on Coventry and Conveyer
(more…)
June 4, 2022
Falklands Conflict Aftermath | The global impact of a 74-day conflict
Imperial War Museums
Published 1 Jun 2022The Falklands Conflict of 1982 only lasted for 74 days, but it had lasting consequences which continue to be felt today. Prior to 1982, Margaret Thatcher’s government was planning major defence cuts including withdrawing the military from the South Atlantic. Instead, they spent nearly £3 billion defending British sovereignty of the Falkland Islands, and to this day maintain a garrison there. What was the effect of this short conflict for Argentina, Britain and the Falkland Islands, and what impact did it have around the world?
Correction: The video states that Port Stanley was granted city status in 2002, this should be 2022.
Thanks for watching IWM’s 5 part series on the Falklands Conflict. Please like and subscribe for more, and let us know in the comments below what you’d like to see next.
Explore and licence the archive films in this video: https://film.iwmcollections.org.uk/c/…
CREDITS
Mount Pleasant images, Crown copyright, April 2022
Margaret Thatcher images © University of Salford Press Office
Landmine clearance photos via Safe Lane Global
Sound effects via ZapSplat
May 1, 2022
Sinking of the General Belgrano – Falklands War Documentary
Historigraph
Published 30 Apr 2022Go to https://squarespace.com/historigraph to get a free trial and 10% off your first purchase of a website or domain.
Falklands War series:
[1] Invasion of the Falklands https://youtu.be/BUYp3Wqz00A
[2] Recapture of South Georgia https://youtu.be/4mCZBpX4pxsTo help support the creation of more videos, consider supporting on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/historigraph#FalklandsWar #Historigraph #Belgrano
Come join the historigraph discord: https://discord.gg/ygypfs3BEB
Buy Historigraph Posters here! historigraph.creator-spring.com
This video was sponsored by Squarespace.
► Twitch: https://www.twitch.tv/historigraph
► Second Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpIj…
► Twitter: https://twitter.com/historigraph
► Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/historigraphSources for the Falklands War Series (so far):
Max Hastings & Simon Jenkins, Battle for the Falklands
https://archive.org/details/battlefor…
Martin Middlebrook, Operation Corporate
Martin Middlebrook, Battle for the Malvinas
Mike Norman, The Falklands War There and Back Again: The Story of Naval Party 8901
Kenneth Privratsky, Logistics in the Falklands War
Sandy Woodward, One Hundred Days
Paul Brown, Abandon Ship
Julian Thompson, No Picnic
John Shields, Air Power in the Falklands Conflict
Edward Hampshire, The Falklands Naval Campaign 1982
Hugh McManners, Forgotten Voices of the Falklands
Cedric Delves, Across an Angry Sea: The SAS in the Falklands War
Rowland White, Vulcan 607
Vernon Bogdanor, “The Falklands War 1982” lecture https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9bWw…
Arthur Gavshon, The sinking of the Belgrano https://archive.org/details/sinkingof…
Gordon Smith, Battle Atlas of the Falklands War 1982 by Land, Sea and Air
http://www.naval-history.net/NAVAL198…
Hansard- https://api.parliament.uk/historic-ha…
Recording of Thatcher’s statement to the Commons is from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HvbhV…Music Credits:
“Rynos Theme” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Crypto” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Stay the Course” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Other music and SFX from Epidemic Sound
April 28, 2022
Britain’s Incredible Recapture of South Georgia – Falklands War Documentary
Historigraph
Published 27 Apr 2022Go to https://squarespace.com/historigraph to get a free trial and 10% off your first purchase of
a website or domain.In just three weeks after the Argentinian invasion of the Falkland islands, Britain threw together a task force out of thin air, sailed it 8000 miles around the world and started taking its territory back. This is how it happened.
Made with thanks to the Fleet Air Arm Musuem in Yeovilton, Somerset. https://www.fleetairarm.com/
To help support the creation of the rest of the Falklands series, consider supporting on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/historigraph#Falklands40 #Historigraph
Come join the historigraph discord: https://discord.gg/ygypfs3BEB
Buy Historigraph Posters here! historigraph.creator-spring.com
► Twitch: https://www.twitch.tv/historigraph
► Second Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpIj…
► Twitter: https://twitter.com/historigraph
► Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/historigraph
Thumbnail credit Daniel Behennec: https://www.naval-history.net/FxDBMis…Sources for the Falklands War Series (so far):
Max Hastings & Simon Jenkins, Battle for the Falklands
https://archive.org/details/battlefor…
Martin Middlebrook, Operation Corporate
Martin Middlebrook, Battle for the Malvinas
Mike Norman, The Falklands War There and Back Again: The Story of Naval Party 8901
Kenneth Privratsky, Logistics in the Falklands War
Sandy Woodward, One Hundred Days
Paul Brown, Abandon Ship
Julian Thompson, No Picnic
John Shields, Air Power in the Falklands Conflict
Edward Hampshire, The Falklands Naval Campaign 1982
Hugh McManners, Forgotten Voices of the Falklands
Cedric Delves, Across an Angry Sea: The SAS in the Falklands War
Rowland White, Vulcan 607
Vernon Bogdanor, “The Falklands War, 1982” lecture https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9bWw…
Arthur Gavshon, “The sinking of the Belgrano” https://archive.org/details/sinkingof…
Gordon Smith, Battle Atlas of the Falklands War 1982 by Land, Sea and Air
http://www.naval-history.net/NAVAL198…
Hansard- https://api.parliament.uk/historic-ha…
Recording of Thatcher’s statement to the Commons is from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HvbhV…Music Credits:
“Rynos Theme” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Crypto” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Stay the Course” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Other music and SFX from Epidemic Sound
April 4, 2022
The Falklands War — the first postmodern war or the last colonial war?
Dominic Sandbrook in UnHerd says Britain “needed the Falklands War”:
On the morning of Monday, 5 April 1982, the aircraft carrier Invincible slipped its moorings and eased into Portsmouth Harbour, bound for the South Atlantic. It was barely ten o’clock, yet the shoreline was packed with tens of thousands of flag-waving onlookers, singing and cheering for all they were worth, many of them in tears. From every building in sight flew the Union Jack, while well-wishers brandished dozens of homemade banners: “God Bless, Britannia Rules”, “Don’t Cry for Us, Argentina”. In the harbour, a flotilla of little boats, crammed with spectators, bobbed with patriotic enthusiasm. And as the band played and the ship’s horn sounded, red flares burst into the sky.
It is 40 years now since the outbreak of the Falklands War, one of the strangest, most colourful and most popular conflicts in British military history. Today this ten-week campaign to free the South Atlantic islands from Argentine occupation seems like a moment from a vanished age. But that was how it felt at the time, too: a scene from history, a colossal costume drama, a self-conscious re-enactment of triumphs past.
On the day the Invincible sailed, Margaret Thatcher quoted Queen Victoria: “Failure? The possibilities do not exist.” In the Sun, executives put up Winston Churchill’s portrait. And as the travel writer Jonathan Raban watched the departure of the Task Force on television, he thought it was like a historical pageant, complete with “pipe bands, bunting, flags, kisses, tears, waved handkerchiefs”. He regarded the whole exercise with deep derision, until the picture blurred and he realised that, despite himself, he was crying.
For many people the Falklands War was only too real. There were serious issues and genuine lives at stake, not just for the 1,813 islanders who had woken to find military vehicles roaring down their little streets, but for the tens of thousands of Argentine conscripts and British servicemen who were soon to be plunged into the nightmare of combat. And although polls suggest that about eight out of ten Britons strongly supported it, there were always those who considered it a mistake, a tragedy, even a crime. A certain Jeremy Corbyn thought it a “Tory plot to keep their money-making friends in business”. The novelist Margaret Drabble considered it a “frenzied outburst of dying power”. A far better writer, Argentina’s Jorge Luis Borges, famously called it “two bald men arguing over a comb”. That seems an odd analogy, though, for almost 2,000 blameless sheep farmers, who had no desire to be ruled by a junta that threw dissenters out of helicopters.
One common view of the Falklands campaign is that it was Britain’s last colonial war. But this strikes me as very unpersuasive. When we think of colonial wars, we think of wars of conquest by white men in pith helmets against brown-skinned underdogs. We think of embattled imperialists struggling to stave off a nationalist uprising, or fighting in defence of white settlers against a native majority. But the Falklands War was none of those things. There was no oppressed indigenous majority — except perhaps for the islanders themselves, some of whom had been there since the 1830s. As for the Argentines, their Spanish and Italian surnames were a dead giveaway. Indeed, few countries in the Americas had done a more thorough job of eliminating their original inhabitants.
April 2, 2022
Falklands War 82: How Argentina Seized the Islands
Historigraph
Published 31 Mar 2022For up to 60% off a subscription to Babbel, head over to https://bit.ly/historigraph_babbel
To help support the creation of the rest of the Falklands series, consider supporting on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/historigraphCome join the historigraph discord: https://discord.gg/ygypfs3BEB
Buy Historigraph Posters here! historigraph.creator-spring.com
This video was sponsored by Babbel.
► Twitch: https://www.twitch.tv/historigraph
► Second Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpIj…
► Twitter: https://twitter.com/historigraph
► Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/historigraphSources for the Falklands War Series (so far):
Max Hastings & Simon Jenkins, Battle for the Falklands
https://archive.org/details/battlefor…
Martin Middlebrook, Operation Corporate
Martin Middlebrook, Battle for the Malvinas
Mike Norman, The Falklands War There and Back Again: The Story of Naval Party 8901
Kenneth Privratsky, Logistics in the Falklands War
Sandy Woodward, One Hundred Days
Paul Brown, Abandon Ship
Julian Thompson, No Picnic
John Shields, Air Power in the Falklands Conflict
Edward Hampshire, The Falklands Naval Campaign 1982
Hugh McManners, Forgotten Voices of the Falklands
Cedric Delves, Across an Angry Sea: The SAS in the Falklands War
Rowland White, Vulcan 607
Vernon Bogdanor, “The Falklands War 1982” lecture https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9bWw…
Arthur Gavshon, The sinking of the Belgrano https://archive.org/details/sinkingof…
Gordon Smith, Battle Atlas of the Falklands War 1982 by Land, Sea and Air
http://www.naval-history.net/NAVAL198…
Hansard – https://api.parliament.uk/historic-ha…
Recording of Margaret Thatcher’s statement to the commons is from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HvbhV…Music Credits:
“Rynos Theme” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Crypto” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…“Stay the Course” Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 4.0 License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b…Other music and SFX from Epidemic Sound
From the comments:
Historigraph
1 day agoThis series has been about four months in the making, and is by far the most ambitious project I’ve set out to complete on Historigraph. It’s going to be 8 (possibly 9) videos over the next three months, charting the course of the Falklands War as it happened 40 years ago.
If you liked this video and want to help support the creation of the remaining seven videos, it would meant the world to me if you could consider supporting on Patreon https://www.patreon.com/historigraph, become a channel member, or even just share this video far and wide.
December 9, 2021
The sequel to the British disaster at the Battle of Coronel, the German disaster at the Battle of the Falkland Islands
On December 8th, the people of the Falkland Islands observe “Battle Day” to commemorate the British naval victory off the islands in 1914. This is the bookend to the Battle of Coronel the previous month (described here and here), where a Royal Navy squadron was almost annihilated by Imperial Germany’s East Asia Squadron under Vice-Admiral Graf Maximilian von Spee. At the Battle of the Falkland Islands, an equally lop-sided victory eliminated von Spee’s ships with minimal damage to Rear Admiral Sir Frederick Doveton Sturdee’s squadron. In The Critic, A.S.H. Smyth outlines the events as shown in a British film released in 1927:
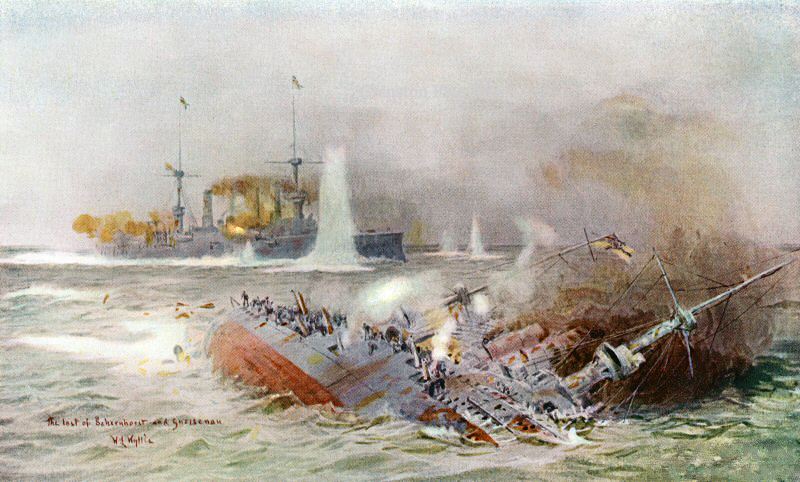

Battle of the Falkland Islands, 1914 by William Lionel Wyllie. SMS Scharnhorst rolls over and sinks while SMS Gneisenau continues to fight.
Originally published in 1918 by Cassel & Company. Retouched image via Wikimedia Commons
Rear Admiral Sir Frederick Doveton Sturdee (unimprovably British, isn’t it?), Chief of War Staff at the Admiralty, and at distinct risk of being scapegoated for the Coronel catastrophe, was summarily appointed Commander-in-Chief South Atlantic and Pacific(!) and despatched posthaste by [First Sea Lord John “Jackie”] Fisher (with whom he did not get on), on something of a do-or-die mission as the commander of new, eight-cruiser squadron.
The Admiral Superintendent of Devonport warns that Sturdee’s two battle cruisers, Invincible and Inflexible, cannot be ready before Friday the 13th November. First Lord of the Admiralty Winston Churchill balks at that ill-omened date, and orders that they sail on the 11th, ready or not. (Students of the 1982 conflict may see more than a couple of parallels here.) Cue: dockyard refitting montage.
Cut to the German colony at Valparaiso, where his countrymen fête von Spee’s glorious German victory in their first naval battle. “Damnation to the British Navy!” they want to toast. No, says, von Spee: “to a gallant enemy.” Handed a bouquet of flowers, he says he’ll keep them for his funeral “when my time comes.” For “when were the British ever content to leave an enemy to his triumph?”
Von Spee was well aware, it seems, that running the gauntlet up through the Atlantic was going to be a torrid prospect, even without a veangeful enemy on the look-out for him personally. But homeless (Tsingtau had fallen to the Japanese), in need of fuel, and down to half their ammunition, von Spee’s captains urged him now to head for Germany, and he agreed.
Von Spee’s ships were in need of dockyard maintenance and not steaming efficiently, but thanks to a captured British collier they were not in need of coal to be able to get home. Before setting off from where they’d been refuelling, Spee decided to strike another blow against the British and raid the Royal Navy’s supply base at Port Stanley in the Falkland Islands where only local militia were expected to be defending.
It was, among other things, sheer bad luck that von Spee came up to Stanley just a few hours after Sturdee had arrived with his group of cruisers — all newer, faster, and better-gunned than their fatigued German counterparts — and was busily refuelling. Likewise, that the sea was calm, there was little wind, and visibility was excellent. Too late, Gneisenau observes that there are British warships in the harbour! (The acting here is particularly terrible.)
It has been suggested that von Spee had not known that the British ships were “waiting” there (they hardly were); but it has also been alleged that he was misled by poor German intelligence, or even false British cryptography. [The Wikipedia article on the battle credits misinformation by British intelligence for leading von Spee into the trap.]
In Britain, meanwhile, the Admiralty is under the impression that Sturdee is the one who has been caught unawares in the Falkland Islands. Von Spee is a mere 12 miles away, and none of the British ships have their steam up. The FIVF [the Falklands Islands Volunteer Force] are called out, as the ships are ordered to go from zero to hero. One poor lad has to run up the Union Jack in local weather conditions (I’ve been that lad: he has my sympathies); another forgets his rifle, as emphasised by a heavily-asterisked title card.
As so often happens, Fate now played its hand, and Canopus, parked, with her fully-functioning 12-inch guns (so missed at Coronel) in Stanley Harbour, as the Islands’ main defensive battery, came into her own. As the Germans turn and run, Canopus opens fire, and soon enough the “grimly purposeful” cruiser group — “fittingly bearing names from the four corners of Britain … Kent, Cornwall, Glasgow and Carnarvon” — set off in pursuit.
The maths was simply not on the Germans’ side. Sturdee even sent his men below to eat. At midday, he called them back to Action Stations. Von Spee responded by ordering his light cruisers to scatter and make for neutral ports, while Scharnhorst and Gneisenau remained to “accept action to cover their escape”. Flashback to the presentation of those flowers.
October 8, 2021
ARA General Belgrano – Guide 047
Drachinifel
Published 18 Dec 2019The ARA Belgrano of the Argentine Navy is today’s ship.
Want to support the channel? – https://www.patreon.com/Drachinifel
Want a shirt/mug/hoodie – https://shop.spreadshirt.com/drachini…
Want a medal? – https://www.etsy.com/uk/shop/Drachinifel
Want to talk about ships? https://discord.gg/TYu88mt
Want to get some books? www.amazon.co.uk/shop/drachinifel
Drydock Episodes in podcast format – https://soundcloud.com/user-21912004