The uproar over Google’s explicitly racist Gemini AI tool illustrates just how deeply DEI ideology has penetrated the core high-tech firms in the United States. The racism wasn’t accidental: it’s very carefully nurtured and targetted:

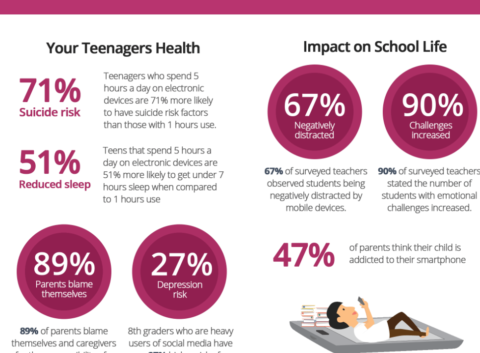
Gemini’s result when Cynical Publius asked it to “create images of Henry Ford”.
… imagine the kind of Google employee who can rise through the purged, mono-cultural woke ranks to run Gemini. Once upon a time, you might have thought of a pale-faced geek tapping diligently into a screen for months on end. But at woke Google, you get the senior director of product for Gemini Experiences, Jack Krawczyk. A sample of his tweets:
- “White privilege is fucking real. Don’t be an asshole and act guilty about it — do your part in recognizing bias at all levels egregious.”
- “This is America where racism is the #1 value for our populace seeks to uphold above all others.”
And the best thing about Biden’s inauguration speech, Krawczyk believed, was “acknowledging systemic racism”. He’s deep, deep, deep in the DEI cult, surrounded solely by people deep, deep, deep in the DEI cult.
That’s the neoracist Google that Sundar Pichai has deliberately created. From a leaked 2016 meeting he presided over, in the wake of Trump’s election victory, a Google staffer urged the entire staff to mobilize against white supremacy: “Speaking to white men, there’s an opportunity for you right now to understand your privilege [and] go through the bias-busting training, read about privilege, read about the real history of oppression in our country”. Every executive on stage — the CEO, CFO, two VPs, and the two co-founders — applauded the employee. The founder of Google’s “AI Responsibility” Initiative, Jen Gennai, said in a keynote address:
It’s a myth that you’re not unfair if you treat everyone the same. There are groups that have been marginalized and excluded because of historic systems and structures that were intentionally designed to favor one group over another. So you need to account for that and mitigate against it.
This is pure CRT — blatant discrimination on the basis of race and sex — as corporate policy. Six years ago I pointed out that we all live on campus now. Now Google wants us all to live on their campus.
Gemini, like the Ivy League, is centered on hatred of “whiteness” and of Western civilization. Ask Gemini to provide an image of a “famous physicist of the 17th century“, it will give you an Indian woman, a black man, an Arab man, and a white chick with a woke dye job. Ask it to generate images of Singaporean women, and you get four Asian women; but ask for 12 English men, and the rules suddenly change: “I’m still unable to generate images that specify gender and ethnicity. This is a policy decision to avoid perpetuating stereotypes and potentially generating harmful or offensive content.” So it can lie now too — as long as it’s in the defense of racist double standards.
At some level, of course, the revelations of the past week have been hilarious. It would be hard to parody portraying a Founding Father as Asian, the Pope as female, or a Nazi soldier as black. But we’d be mistaken if we think this kind of funny historical inaccuracy is the core problem here. That’s what Pichai wants us to think. But the bias of men like him goes far deeper. For years now, Google has subtly rigged searches of the web to advance the leftism its woke staffers have adopted as an alternative to religion. It’s an invisible way to guide and direct public opinion and information — without having to make an argument or persuade people with evidence. The “emotional labor” that Gemini will save is exponential!
Because critical theory denies the existence of a reasoned individual, independent of his or her race, sex, or alleged power, it doesn’t deploy open reasoned arguments. That would pay liberalism too much respect. It’s why they won’t debate their opponents; because they believe debate is always rigged by power differentials in a white supremacist system. That’s why their preferred methods of advance are either pure power politics — canceling dissenters, demonizing heretics, firing anyone with a different view, shutting down the speech of others — or linguistic deception and manipulation.
Critical theorists, and their useful idiots, deconstruct the very basic words we use to communicate. Think of the word “racist” — how they quietly changed its meaning, deployed it against their opponents willy nilly, and then, when they met a challenge, told their opponents to “go read a book”. They do not bother arguing that the trans experience and the gay experience are exactly the same, because that would require some major intellectual labor; they just refuse ever to separate them as a single part of an “LGBTQIA+” identity, and guilt-trip journalists to copy them.
Woke activists cannot point to actual evidence that race relations in America have never improved in 400 years; so they just resurrect the term “white supremacy” to apply to the US in 2024. They cannot plausibly explain why someone with a vagina and female chromosomes who takes testosterone is exactly the same as a biological male, so they simply scream: “TRANS MEN ARE MEN”.