Ted Gioia describes the plight of a young man who had to move home after college and falls into a state of depression thanks to his hopeless situation and his dysfunctional home and social life. His name is Hamlet:
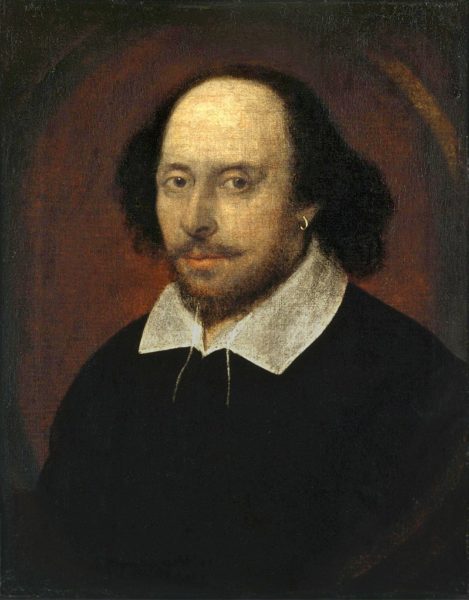

This was long thought to be the only portrait of William Shakespeare that had any claim to have been painted from life, until another possible life portrait, the Cobbe portrait, was revealed in 2009. The portrait is known as the “Chandos portrait” after a previous owner, James Brydges, 1st Duke of Chandos. It was the first portrait to be acquired by the National Portrait Gallery in 1856. The artist may be by a painter called John Taylor who was an important member of the Painter-Stainers’ Company.
National Portrait Gallery image via Wikimedia Commons.
It’s almost uncanny how relevant it feels right now.
So if I were directing Hamlet in the current moment, I’d give the title character an iPhone and game console. I’d have the characters onstage share photos on Instagram — and put up a big screen so the audience could see them posted in real time.
Hamlet could add pithy captions to his social media images. What a piece of work is a man! or maybe The lady doth protest too much!
Yes, Hamlet is many things, but one of them is, perhaps, a failed influencer.
Along the way, we may have answered the classic question about this play. For generations, critics have wondered why Hamlet wastes so much time, and can’t be bothered to take action.
Maybe he’s just too busy gaming and scrolling.
Okay, it sounds ridiculous. But is it really? Shakespeare possessed tremendous insight into the human condition — perhaps more than any author in history. So maybe he really did grasp the dominant personality types of our own time.
The Prince of Denmark still walks in our midst. And maybe — just maybe — careful attention to this play might help us, in some small degree, to heal the Hamlets all around us. Their number is legion.
Of course, the larger reality is that Shakespeare has proven himself relevant to every time and place. We can see that easily be examining how other generations viewed this same play.
Hamlet‘s original audience, four hundred years ago, clearly enjoyed the spectacle of violence and adultery. Nine key characters die during the course of the play — most of them murdered. Audiences loved these kinds of dramas back then, and Shakespeare always knew how to please the crowd.
But more sophisticated viewers, circa 1600, would have seen Hamlet as a political commentary — a reflection of all the tensions and rivalries of Elizabethan England. Nobody knew better than Shakespeare that monarchy is a dangerous game, and he always looked for opportunities to refer to current events in roundabout ways.
But two hundred years later, the Romanticists were in ascendancy, and they saw Hamlet as a very different kind of play. They ditched the politics, and embraced the Prince of Denmark for his pathos and personality. They tapped into the intense emotional currents of Shakespeare’s heroes — and the plays seemed perfectly suited for this kind of interpretation.
It’s no exaggeration to say that Hamlet continued to change for each new generation. He always feels timely and relevant.
A hundred years ago, critics began grappling with psychology and the unconscious — and Hamlet was a perfect character for these kinds of interests. In his 1900 book The Interpretation of Dreams, Freud focused on Hamlet as a case study in repression.
And who could disagree?
But fifty years later, Hamlet changed again. It now was the perfect play for those who had survived World War II. Jan Kott insists, in his book Shakespeare, Our Contemporary, that these old plays were more relevant than ever during the Cold War — just as timely as Beckett or Sartre or Brecht or Ionesco.