TimeGhost History
Published 5 May 2025In early 1949, the Arab-Israeli War finally comes to an uneasy end. After brutal fighting, armistice talks in Rhodes redraw borders with a green pencil line, displacing hundreds of thousands and reshaping the Middle East. Egypt, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon reluctantly sign ceasefires, leaving core issues — Jerusalem, refugees, and recognition — unresolved. But can forced armistices really bring lasting peace, or is Palestine fated to endless conflict?
(more…)
May 6, 2025
1949: How the Arab-Israeli War Ended – W2W 27
January 15, 2025
Desert Storm: The Gulf War 1990-1991
Real Time History
Published 6 Sept 2024When Saddam Hussein invaded Kuwait in the summer of 1990, he didn’t anticipate a massive international backslash and unanimous Security Council response. Soon a broad military Coalition under leadership of the United States assembled and kicked the Iraqi Army out of Kuwait. In the aftermath several Iraqi groups rose up against Saddam but the Coalition didn’t support a regime change.
CHAPTERS:
00:00 Intro
00:29 Saddam Hussein Victorious (but Broke)
03:49 Iraqi Invasion of Kuwait
06:02 The Coalition Against Iraq Forms
08:37 Operation Desert Shield
10:55 Operation Desert Storm
20:26 Iraqi Highway of Death
21:39 Iraqi Uprisings
(more…)
December 6, 2024
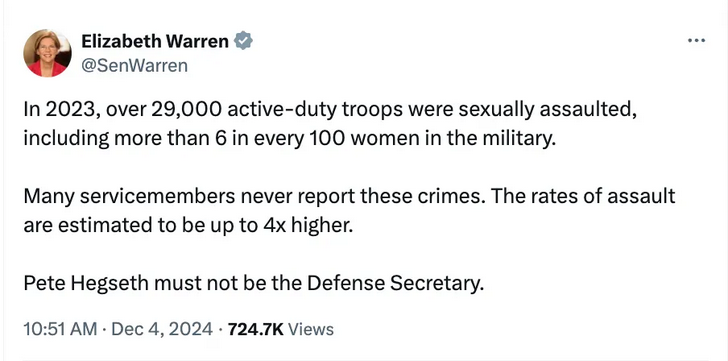
Hegseth is clearly unfit to be Secretary of Defense because LOOK! A SQUIRREL!
I don’t recall having heard Pete Hegseth’s name before Trump nominated him to be the next Secretary of Defense, but Chris Bray clearly thinks the accusations are purely partisan:
Pete Hegseth is being Kavanaughed. And the only people dumb enough to fall for it are Republican senators.
I was willing to hear arguments that Hegseth wasn’t the best choice for Secretary of Defense. In his 40s, he’s on his third marriage, and while the rape allegation from his visit to a conservative conference in Monterey is clearly false, I was wide open to the argument that his actions demonstrated poor judgment. I was prepared to hear an argument. Like many combat veterans, Hegseth had some post-war chaos in his life. Discussion was merited.
But the more these arguments have been made, the dumber they’ve become. We’ve seen this play, and we know the third act: more heat, less light, the descent into completely irrational ranting.
Let’s pretend to take this number at face value, for the sake of argument, though Warren is egregiously misrepresenting the estimate about unreported assaults. Let’s just look at the structure of the claim: In 2023, while Lloyd Austin was the Secretary of Defense, 29,000 troops were sexually assaulted. Therefore, Pete Hegseth must never become the Secretary of Defense.
This is the kind of argument people make when they’re piling on, in an atmosphere of hysteria. It has no logic or order to it, and it does the opposite of the thing it’s intended to do: It depicts current leadership as failures, while arguing against a course correction. Bob punched me in the face, which proves that John is very bad. This is currently the logical structure of half the “news”.
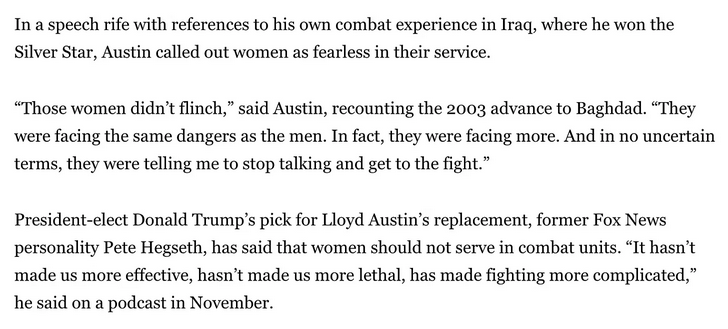
In another Martha-do-you-hear-yourself moment, Lloyd Austin himself recently attacked Hegseth for arguing that women shouldn’t serve in the combat arms:
But read this carefully, and look for the own-goal:
Women serving in combat are facing more danger than men, Austin said.
Therefore, women should serve in combat. Explain the logic, Lloyd. Amazingly, the journalist who reported Austin’s comments missed the implications, mindlessly typing up the claim that women in combat are in more danger than men, then — next paragraph! — framing that statement as a rebuke to someone who warned that the service of women in combat “made fighting more complicated.” We’re not discussing; we’re ritually lining up behind our teams.
July 24, 2024
Chieftain V T-62 | Operation Nasr, Iran – Iraq War, 1981
The Tank Museum
Published Apr 13, 2024Two tanks designed to fight each other in Northern Europe would face each other during the Iran-Iraq war in 1981. On one side, the British built Chieftain MBT. On the other, the Soviet-built T-62.
In this video, we examine what happened during Operation Nasr to find out which tank came out on top …
00:00 | Intro
01:19 | Meet the Tanks
02:15 | The T-62
03:26 | The Chieftain
06:21 | From Paper to the Battlefield
09:25 | The Outcome and Findings
(more…)
July 23, 2024
Claim – “Everybody wants Gaza’s gas”
Tim Worstall explains why the popular idea that it’s demand for the natural gas reserves that sit under Palestine that is driving much of the situation in the Middle East is utter codswallop:

“Oil Platform in the Santa Barbara Channel, California” by Ken Lund is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0 .
So we’ve a big thing about how all this fighting in Gaza is really about fossil fuels. @JamesMelville seems to think it’s true:
“Everybody wants Gaza’s gas.”
Oil and gas reserves – that’s the real proxy war in the Middle East.
This video provides a really succinct summary of the situation.
This “really succinct” summary includes the idea that the invasion of Iraq was all about access to that country’s oil. Which is very silly indeed. Before the war people paid Iraq for the oil. During the war people paid Iraq for the oil. After the war people are paying Iraq for the oil. The war hasn’t changed Iraq’s oil price — the global oil price has changed it, but not the war — and so the effect of the war upon access to Iraq’s oil has been, well, it’s been zero.
No, it’s not possible to then go off and say that Iraq wouldn’t sell to Americans and that’s why or anything like that. The US didn’t buy much Middle East oil anyway — mainly West African instead. But more than that, this is idiocy about how commodity markets work.
This is something we can test with a more recent example. So, there are sanctions on Russian oil these days over Ukraine. Western Europe, the US, doesn’t buy Russian oil. Russia is still exporting about what it used to. Because it’s a commodity, oil is.
What’s happening is that the Russian oil that used to come to Europe now goes to — say — India. And the Far East, or Middle East, whatever, oil that used to go to India now comes to Europe (the US is now a net exporter itself). Because that’s what happens with commodities. The very name, commodity, means they are substitutable. So, if one particular source cannot sell to one particular user then there’s a bit of a reshuffle. The same oil gets produced, the same oil gets consumed, it’s just the consumption has been moved around a bit and is now by different people. The net effect of sanctions on Russian oil has been, more or less, to increase the profits of those who run oil tankers. Ho Hum.
We’re also treated to the revelation that the US wants everyone to use liquefied natural gas because the US is the big exporter of LNG (well, it’s one). Therefore the US insists that Israel must develop the LNG fields off Gaza. Which is insane. If you’re an exporter you don’t want to start insisting on the start up of your own competition. The US demanding that the LNG not be produced at all would make logical sense but that’s not how conspirazoid ignorance works, is it? It has to be both a conspiracy and also a ludicrous one.
And a third claim. That this natural gas off Gaza is really worth $500 billion. That’s half a trillion dollars. We’ve looked at this value of gas off Gaza claim before and it’s tittery. $4 billion (that’s four billion, not five hundred billion) might be a reasonable claim and that’s just not enough to go to war over.
May 9, 2024
How the First World War Created the Middle East Conflicts
The Great War
Published Dec 8, 2023The modern Middle East is a region troubled by war, terrorism, weak and failed states, and civil unrest. But how did it get this way? The map of today’s Middle East was mostly drawn after the First World War, and the war that planted many of the seeds of conflict that still plague Israel, Palestine, Iraq, Syria and even Iran today.
(more…)
January 31, 2024
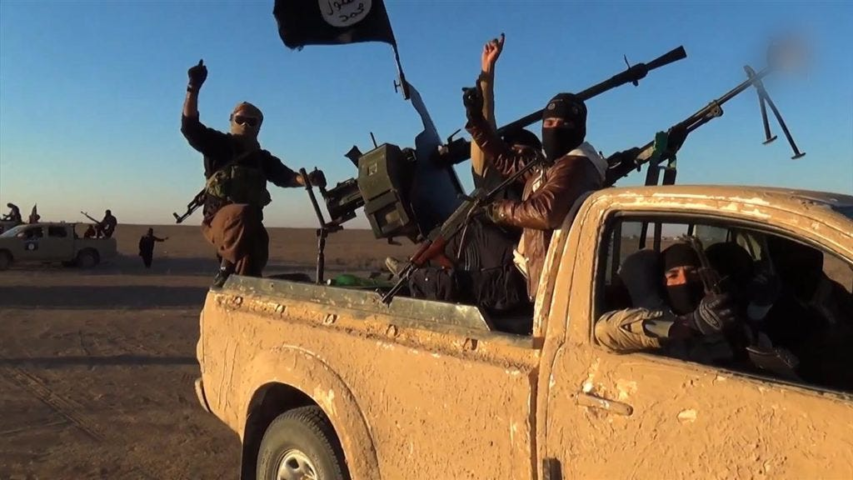
The rise of the “Technical”
Kulak at Anarchonomicon considers the innovation and adaptability that Chad’s ragtag forces displayed in the late 1980s to drive Libyan forces out of their territory, specifically the military use of Toyota pickup trucks as improvised gun carriages:
The Great Toyota War of 1987 was the final phase of the Chadian-Libyan conflict. Gadhafi’s Libyan forces by all rights should have dominated the vast stretches of desert being fought over: the Chadian military was less than a 3rd the size of the Libyan, and the Libyans were vastly better equipped fielding hundreds of tanks and armored personnel carriers, in addition to dozens of aircraft … to counter this the Chadians did something unique … They mounted the odds and ends heavy weapons systems they had in the truck beds of their Toyota pickups, and using the speed and maneuverability of the Toyotas, managed to outperform Libya’s surplus tanks and armored vehicles. By the end of the Chadian assault to retake their northern territory, the Libyans had suffered 7500 casualties to the Chadians 1000, with the Libyan defeat compounded by the loss of 800 armored vehicles, and close to 30 aircraft captured or destroyed.
The maneuverability and speed of the pickups made them incredibly hard to hit, and the tanks in particular struggled to get a sight picture … strafing within a certain range the pickups moved faster across the horizon than the old soviet tanks’ main gun could be hand cranked around to shoot them.
Since then Technology has become the backbone of insurgencies, militias, poorer militaries, and criminal cartels around the world. The ready availability of civilian pickups, with the ability of amateur mechanics to mount almost any weapon system in their truck-bed means that this incredibly simple system is about the most cost-effective and easy way for a small force to make the jump to mounted combat and heavy weapon.
But these weapons are far less asymmetric than motorcycles. The increasing importance of mobility means even the most advanced armies are getting in on the game. The US Army is currently converting a portion of its Humvees to have their rear seat and trunk cut out for a truck bed so that they can run a mobile light artillery out of it:
Popular Mechanics article – https://www.popularmechanics.com/military/weapons/a28288/hawkeye-humvee-mounted-howitzer/
The importance of instant maneuverability far outstretches any advantage armor can give in this application. Since artillery shells are radar-detectable, and, follow a parabolic arc, their origin point is easily calculable. Thus shoot and Scoot tactics are necessary since it may only be a minute or two from firing a volley that counter artillery fire might be inbound.
Aside from The bemused jokes that the US is finally catching up with the tech Chad had in the 80s, The truth is most advanced forces have always had something light with a heavy gun that can travel at highway speeds … the fact the US is now converting Humvees to have full light artillery pieces is only really a continuation of the trend of semi-auto grenade launchers, TOW missiles, or anti-tank guns being placed on light fast vehicles since WW2.
The remarkable thing about the technical isn’t that they’re some unique capability militaries can’t use … most poorer countries field something equivalent (the Libyans seemed to have screwed up the unit composition of their force) … Rather the unique advantage is how easy and cheap they are for non-conventional or poorer forces to home assemble.
US combat-ready Humvees cost the military into the hundreds of thousands of dollars, a cost that is presumably even higher as they’re modified to carry heavy weapons systems.
As ridiculous as a Toyota with an Air-to-Ground rocket pod, or a repurposed anti-air gun might be, they’re cheap. The pickup truck new is $20,000-50,000, though I suspect any irregular force would pay closer to 1000-5,000 for something decades old, if they pay at all. Likewise, they’re trivial to source, which is good if sanctions or anti-money laundering laws are trying to stop you from buying anything, and as the Chadians proved: pretty much any captured or surplus heavy weapon will go on it.
This gets irregular forces into the mounted combat game … but it does slightly more than that. Pickup trucks, as any perturbed Prius driver will tell you, are shockingly common … perhaps one in 10 or more vehicles out there are some form of pickup truck. This not only makes them easy to source, but it disguises them and allows them to operate hidden amongst the rolling stock of civilian vehicles, requiring either visual identification or extensive intelligence work to tell them from mere civilians.
This combination of mobility, resemblance to civilian vehicles, and ability to deploy heavy weapons was used to devastating effect by the Islamic State during the 2014 Fall of Mosul. Striking quickly while Iraqi national tanks were deployed elsewhere the small Islamic force entered the city at 2:30 am, striking in small convoys that overwhelmed checkpoints with their firepower, executing and torturing captured Iraqi soldiers and targeted enemies as they went. Even after taking into account desertions and “ghost soldiers” (fake soldiers meant to pad unit numbers so corrupt officials could collect their pay) which significantly reduced the 30,000 Iraqi army and 30,000 police within the city … Even after allowing for all that, the Iraqi national forces still outnumbered the 800-1500 ISIS fighters at a rate of 15 to 1.
YET ISIS was able to achieve a total victory and take the whole of the city within 6 days.
2 years later it would take the Iraqi government with American backing 9 months to retake it.
How? How does a force of 1500 at most, most without any formal training, overwhelm and defeat a force of 12,000-23,000, which at least has some training, better equipment, and has an entire state behind it? How did ISIS do this entirely without air support? Even as the Iraqi government bombed them from helicopters?
How did they take in 6 days what would take the Iraqi government with full American backing 9 months to retake?
Well, they made the Iraqis break and run.
January 29, 2024
Peter Hitchens isn’t onboard with the march to yet another war
Writing in the Daily Mail, Peter Hitchens decries the apparent drift by western politicians into yet another war:
Are we the baddies? What if the Ukraine war is just as stupid and wrong as the Iraq war, but the state propaganda has been more successful and hardly anybody has realised … yet?
Many people to this day still think the damaging and morally dubious Western attacks on Serbia and Libya were justified. Many still think the gory attempt to destroy Syria was a good thing. It took ages for opinion to swing on the Vietnam war, back in the 1960s. And, as one who opposed the Iraq war, I remember only too well just how many (who now think they were against it all the time) were fooled into backing Sir Anthony Blair and George W. Bush.
The issue is more pressing as generals and admirals warn we must live in a militarised society and prepare for what they think is an inevitable war against Russia. They could get their way. If you go on backing this policy, you could be condemning yourself, your children or grandchildren to a world of war, privation and perhaps conscription into some sort of military service.
[…]
This is what I have never been able to work out. We have a Defence Secretary, Grant Shapps, who has perfected the art of shouting loudly while carrying a very small stick – thunderous, belligerent declarations while our Armed Forces melt away thanks to neglect and badly targeted spending. Perhaps, if the long-feared Russian invasion of Western Europe takes place, we can fend it off by dispatching our troops on the pestilential e-scooters and e-bikes which are this former Transport Secretary’s major contribution to the nation.
Certainly these vehicles are terrifying to those not riding them. They have nearly killed me more than once. And, piled up in heaps, they make formidable obstacles, as the people of London are finding.
What Mr Shapps does not seem to grasp is that Britain became great by staying out of continental conflicts, and letting others do the fighting. Even in the battle against Bonaparte, we paid our European allies to do most of the hard work.
Our greatness ceased when bombastic moralising took over, in 1914. We flung ourselves, supposedly nobly, into a Russo-German war. Within two years we were bankrupt, and bereft of the flower of our young manhood.
People still refuse to believe me when I say accurately that Britain has not paid off its huge 1914-18 war debts (now worth about £40 billion) to the USA. But I promise you it is true.
Four years of terrible loss left the Russo-German problem unsolved and we had to do it all again in 1939. After that we were even more bankrupt, and in 1946 had to ration bread, like some desperate People’s Republic. But for many years afterwards we were largely governed by grown-ups who had fought in actual wars and been wounded, and had seen death very near them, or endured bombing and a war economy. And so we largely stayed out of major foreign trouble.
May 28, 2023
This Gun Could Reach Space
Real Engineering
Published 18 Feb 2023
(more…)
April 26, 2023
Tanks Chats #169 | Scimitar Mark 1 & Scimitar Mark 2 | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 20 Jan 2023In this week’s video, David Willey continues David Fletcher’s CVRT Tank Chats series, delving into the fascinating history of the Scimitar Mark 1 & Scimitar Mark 2. David provides an in-depth look at the development of these two iconic tracked vehicles, exploring their unique features and capabilities. He also examines how they have evolved over the years, and been used in various military operations.
(more…)
April 4, 2023
Tank Chats Reloaded | Challenger 1 | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 16 Dec 2022In the first episode of Tank Chats Reloaded we hear from Major General Patrick Cordingley who both commanded Challenger 1 during the First Gulf War and was involved in its design. Also introducing our new presenter Chris Copson, host of the new Tank Chats Reloaded series — where we’ll be revisiting old favourites from Tank Chats.
(more…)
March 20, 2023
“The New American Empire lasted, at most, twenty years, if one counts the two falls of Kabul as brackets”
Ed West on the brief — and largely unacknowledged by Americans — high-water mark of the 21st century’s biggest empire:

A Boeing CH-47 Chinook transport helicopter appears over the U.S. embassy compound in Kabul, 15 Aug 2021. Image from Twitter via libertyunyielding.com
This century has already seen its fair share of great delusions, society-changing disasters built on wishful thinking: you can loan mortgages to people who obviously can’t pay them back; you can cure pain with an opiate that won’t make people addicted; and now the unstoppable idea of equality of outcomes between races, a project doomed to failure and tragedy.
But none was perhaps so spectacularly disastrous as liberal imperialism. Twenty years ago, George W Bush sent the most powerful military the world had ever seen into the birthplace of Abraham to overthrow Saddam Hussein, and as Niall Ferguson wrote in the Wall Street Journal at the time: “the greatest empire of the modern times has come into existence without the American people even noticing”.
The New American Empire lasted, at most, twenty years, if one counts the two falls of Kabul as brackets. This was despite enormous technological supremacy, and genuine goodwill and benevolence among many of the state-builders.
The United States was “born liberal”, as historian Louis Hartz said, even if the crime wave of the late 20th century made that a dirty word, and the “New American Empire” would spread the benefits of liberalism to grateful beneficiaries around the world.
Yet what is so striking about the imperialists of the 21st century, compared to their forebears in the 19th, was just how little interest they seemed to show in the subject people. Their naivety about human nature, and their utopian belief that people around the world just wanted “freedom”, chimed with a lack of curiosity about humanity.
To think that people around the world might not be the same, that they might not want “freedom” nor have the social structure or culture that suited democracy, might be to venture into dangerous territory. To suggest that Iraq was incapable of democracy was insulting to Iraqis, since as the US president said ahead of the war: “There was a time when many said that the cultures of Japan and Germany were incapable of sustaining democratic values. Well, they were wrong. Some say the same of Iraq today. They are mistaken.”
Yet the defeated nations in 1945 had very old, well-established institutions and very strong national identities, something Iraq did not. The latter was extremely clannish, something no one seemed to consider. Sovereignty and strong institutions take generations to build, and cannot just be imposed by foreigners working on abstract principles like “democracy”.
Bush was not alone. That same year, John McCain had said: “There is not a history of clashes that are violent between Sunnis and Shias, so I think they can probably get along”. And on March 1, 2003, two weeks before the war started, Bill Kristol, editor of the Weekly Standard, had dismissed warnings about sectarian conflict: “We talk here about Shiites and Sunnis as if they’ve never lived together. Most Arab countries have Shiites and Sunnis, and a lot of them live perfectly well together.” On top of that, “Very few wars in American history were prepared better or more thoroughly than this one by this president.” He was totally wrong, while in contrast the American Conservative‘s pessimistic warnings about Iraq’s social fabric proved correct.
March 8, 2023
“By fostering intense family loyalties and strong nepotistic urges”, cousin marriage “makes the development of civil society more difficult”
Ed West on what he calls the worst western foreign policy disaster since 1204, the Iraq quagmire:

Mohammed Saeed al-Sahhaf, better known in the West as “Baghdad Bob” or “Comical Ali”, Iraqi Minister of Information for President Saddam Hussein.
This month marks the 20th anniversary of the greatest western foreign policy disaster since the Fourth Crusade. It was the pre-eminent modern-day example of folly, driven by wishful thinking, utopianism and a lack of interest in history and how human societies differ. This was mostly carried out by good people, including our own Tony Blair, and promoted by thoughtful and humanitarian commentators who thought they were making the world a better place.
The White House regime which brought chaos and misery to Iraq were most of all entranced by The Weekly Standard, the now-defunct magazine most associated with neoconservative foreign policy. Had any of them read The American Conservative instead, they might have avoided the whole tragedy. In particular they ought have read Steve Sailer’s “The Cousin Marriage Conundrum“, printed in the run-up to the invasion and in which the author made a seemingly curious argument for why nation-building in Iraq would fail — its high rates of cousin marriage.
Pointing out that between 46 and 53 percent of Iraqis who married did so to first or second cousins, Sailer wrote that: “By fostering intense family loyalties and strong nepotistic urges”, cousin marriage “makes the development of civil society more difficult”. The neocon dream of jumpstarting democracy was therefore clearly doomed to failure.
Even those with a cursory knowledge of the country knew that Iraq was split between Sunni and Shia Arabs, as well as Kurds in the north, each group’s area of dominance roughly corresponding to three former Ottoman provinces. However, these were further subdivided into “smaller tribes, clans, and inbred extended families — each with their own alliances, rivals, and feuds”, in total about 150 tribes comprising some 2,000 clans.
Saddam’s politics were mired in blood, in both senses. He came from the al-Bu Nasir, a tribe comprising some 25,000 people based in the town of Tikrit, and his regime was filled with his relatives. His political career had begun in 1957 when the 20-year-old had joined the revolutionary Ba’ath (“Resurrection”) Party, following his uncle Kharaillah Tulfha, who had fought against the British in the Second World War. Tulfha would become his father-in-law, for Saddam also married his first cousin, although he later took a second wife. Family life wasn’t entirely harmonious, and the man who introduced that couple, Saddam’s food taster, was later stabbed to death by the dictator’s psychotic eldest son Uday at a party thrown by Egyptian president Hosni Mubarak.
The unfortunate food taster was an Assyrian Christian, and within Saddam’s regime religious minorities could rise high, as is often the case in empires, because they presented no threat. His foreign minister, Tariq Aziz, was also a Christian, his birth name being Mikhail Yuhanna.
The family was everything in Saddam’s Iraq. Mark Weiner wrote in The Rule of the Clan of countries governed by “clannism” that: “These societies possess the outward trappings of a modern state but are founded on informal patronage networks, especially those of kinship, and traditional ideals of patriarchal family authority. In nations pervaded by clannism, government is co-opted for purely factional purposes.” The inevitable result of clannism is kin-based corruption whereby resources, positions and other rewards are monopolised by family groups. In these societies, Weiner wrote, “the nuclear family, with its revolutionary, individuating power, has yet to replace the extended lineage group as the principle framework for kinship or household organisation”.
The Weekly Standard was called the in-flight magazine of Air Force One, but presumably there weren’t that many White House staffers reading the American Conservative at the time, a publication started by Pat Buchanan, the great Republican critic of neocon foreign policy. So the Coalition blundered into a disastrous invasion that cost hundreds of thousands of lives, wrecking Iraq and leaving many areas newly-divided along sectarian lines, while minorities like the Christians and Mandaeans were driven almost to extinction.
November 25, 2022
Our old, comfortable geopolitical certainties are becoming less comfortable and less certain
In The Line, Matt Gurney discusses a few of the things he heard at the recent Halifax International Security Forum:
First, though, I wanted to explore that grim feeling that swept over me as Forum president Peter Van Praagh stepped up to the lectern and opened the formal proceedings with a review of the geopolitical situation, and how we got here.
From his prepared remarks (slightly trimmed):
Last year … we marked the 20th anniversary of 9/11. It was not an auspicious anniversary. Just months earlier, the United States and its allies withdrew their troops from Afghanistan and discarded the hopes and dreams of so many Afghans … [it] was a low point for Afghanistan and indeed, for all of us. … It was the culmination of 20 years of good intentions. And bad results:
The decisions made in the immediate aftermath of 9/11, North Korea going nuclear, Russia’s invasion of Georgia, the Great Recession, Iran, the Arab Spring and the Syrian civil war, the surge of refugees — more than at any time in human history, the successful rise of populist politics, the higher than necessary death toll from coronavirus, Hong Kong losing its freedoms, January 6 and its wake, climate-change disasters, and our withdrawal from Afghanistan …
It was a tragic end to a 20-year tragic era.
That’s a pretty depressing list. Right?
As a student of history, I always strive to avoid too much recency bias. Most of the things you hear described as “unprecedented” aren’t anything remotely close to that. The general public has a memory of a few years — maybe a generation. We definitely do face some novel challenges today, but we are still better off than most generations in human history, and it’s not even close.
Still. Van Praagh offered a bleak if concise catalogue of tragedy and struggle. And there are some notable absences. The Iraq War, for instance, is probably worth noting as a specific event, not just part of the Sept. 11th fallout. Perhaps the Libyan intervention as well. Some of China’s more aggressive actions, especially at home, also come to mind.
But as I mulled over that terse version of early-21st-century history, something else jumped out at me: most of those threats were things that happened far away and to other people.
I mentioned recency bias above, so it’s only fair to note a different bias: “far away” and “other people” depends on the vantage point, doesn’t it? Every event listed above was a direct and local tragedy for the people caught in the middle of it, who don’t have the luxury of viewing these events at a comfortable remove, the way the West generally has.
The pandemic, of course, did not spare the West. Nor did the Great Recession, the toll of a changing climate and the populist upheavals roiling the democracies. Those are local problems for us all.
The military challenges, though, are getting more and more local, aren’t they? North Korea seemed far away once; today it’s using the Pacific Ocean’s vital sealanes for target practice and providing some of the munitions being used against civilians in Europe. Libya, Syria and the other migration crises posed real societal and political challenges for Europe, but nothing like what the continent has been bracing for in the event of either crippling energy shortages or an outright escalation into a military conflict, potentially nuclear conflict, with Russia. China’s growing ambitions and willingness to use force pose direct challenges to the West and its prosperity; American financier Ken Griffin recently made the headlines when he observed that if Chinese military action were to cut off or disrupt American access to Taiwanese semiconductor chips, the immediate impact on the U.S. economy would be between five and 10 per cent of GDP. That would be a Great Depression-sized bodyblow, and it could happen almost instantly and without much warning.
Pondering Van Praagh’s list later on, it occurred to me that the more remote threats to core Western security and economic interests were also more remote in time. The closer Van Praagh’s summation of crises came to the present, the more immediate and near to us they became.
November 2, 2022
QotD: Being “the world’s policeman”
The British spent most of the 19th and the first half of the 20th centuries as the world’s policeman, responsible for keeping the peace, and for maintaining a balance of power. They were usually pilloried by all about them for this role, particularly by up and coming powers who wanted a “place in the sun” — Germany and the United States being the stand-out examples (though there is a lot of whinging from old allies like Russia). For the last half of that period, the British voter was having serious second thoughts about the whole concept.
The United States took on the mantle of world’s policeman in the post-Second World War world. They have spent much of the last 60 years trying to keep the peace, and, interestingly, to maintain the balance of power. (Do not be fooled by the concept of the overwhelming superpower. Britain was a lot closer to being able to take on the rest of the world in the 19th century, when it really could defeat every other navy in the world combined; than the US is now, where it could perhaps face Iran, Russia and India simultaneously, as long as the European Union is friendly. Whoops, forgot China, the Balkans, Palestine, Syria, North Korea, Iraq, Afghanistan, Somalia and other little blips on the US horizon. Well let’s be honest, no one has ever been able to take on more than a few of the other powers simultaneously. NO one.)
For their troubles, they are usually pilloried by those all about them, particularly by up and coming powers who want their “place in the sun” – the Soviet Union and China being the stand-out examples. (Though there is a lot of whinging from old allies like France). For the last forty years (since Vietnam, and certainly since Gulf War One), there have been signs that the US voter is having serious second thoughts about the whole concept.
Britain was quite reluctant to take over later imperial dependencies, particularly leftover states of defeated Empires like Turkey, such as Iraq and Palestine: but also parts of Africa and Asia “of interest to no bugger”. They were never part of the British ideal of commercial empire, and were almost impossible to govern. They were abandoned as soon as possible.
The United States is currently experiencing the joys of taking over, or being responsible for unwanted bits of empire. Strangely the names Iraq and Palestine are occurring on that list, as well as Afghanistan and possibly other commitments to come. (The US has interfered in these areas far longer than Britain had before she was stuck with them). They cannot be considered part of a logical geopolitical empire (not even for oil conspiracy nuts), and will be abandoned as soon as possible.
The British voter responded to the world wars by wanting out of empire. Now. Some of the states thus “released” were well-developed societies with decent infrastructure and good literacy and rule of law concepts. India, Malta, Ceylon, Bermuda and Singapore spring to mind. Others were abandoned prematurely: without literacy, rule of law, good infrastructure, a developed civil service, practice of voting, or any of the other minor necessities for establishing a democratic state. See any list of African dictatorships.
The US voter is responding to current events by wanting out of the Middle East ASAP. They are intent on abandoning states to “democracy”, regardless of a lack of literacy, rule of law, good infrastructure, a developed civil service, practice of voting, or any of the other minor necessities for establishing a democratic state. Whoops.
Britain suffered from an immense artificial economic high after the Napoleonic war. This left the British economy extremely artificially inflated for eighty years, and still well above its realistic weight in the world for another fifty (and only really brought back to the field by the immense economic losses of two world wars). In the last twenty years Britain has held a more realistic place in the world economy for its population and industrial level (though still relatively inflated by an immense backlog of prestige and sometimes reluctant respect.).
The US suffered from an immense artificial economic high after WWII. This left the US economy artificially inflated for the rest of the century, and still well above its realistic weight in the world to the present. … Sometime in the next few decades, the US will probably return to a more realistic place in the world economy for its population and industrial level. (Minor variables like World War III may make this projection uncertain as to actual timing, but it will happen: simply because the US will not be able to largely sit out most of the next world wars and profiteer from everyone else’s ruin the way she could in the last two).
Nigel Davies, “The Empires of Britain and the United States – Toying with Historical Analogy”, rethinking history, 2009-01-10.