seangabb
Published Apr 28, 2024This seventh lecture in the course covers the career of Alexander the Great and its consequences for the world.
(more…)
April 29, 2024
Greek History and Civilization, Part 7 – Alexander
March 6, 2024
QotD: Mansa Musa’s disastrous foreign aid to Cairo
Mansa Musa’s good intentions may be the first case in history of failed foreign aid. Known as the “Lord of the Wangara Mines”, Mansa Musa I ruled the Empire of Mali between 1312 and 1337. Trade in gold, salt, copper, and ivory made Mansa Musa the richest man in world history.
As a practicing Muslim, Mansa Musa decided to visit Mecca in 1324. It is estimated that his caravan was composed of 8,000 soldiers and courtiers — others estimate a total of 60,000 — 12,000 slaves with 48,000 pounds of gold and 100 camels with 300 pounds of gold each. For greater spectacle, another 500 servants preceded the caravan, and each carried a gold staff weighing between 6 and 10.5 pounds. When totaling the estimates, he carried from side to side of the African continent approximately 38 tons of the golden metal, the equivalent today of the gold reserves in Malaysia’s central bank — more than countries like Peru, Hungary or Qatar have in their vaults.
On his way, the Mansa of Mali stayed for three months in Cairo. Every day he gave gold bars to the poor, scholars, and local officials. Mansa’s emissaries toured the bazaars paying at a premium with gold. The Arab historian Al-Makrizi (1364-1442) relates that Mansa Musa’s gifts “astonished the eye by their beauty and splendor”. But the joy was short-lived. So much was the flow of golden metal that flooded the streets of Cairo that the value of the local gold dinar fell by 20 percent and it took the city about 12 years to recover from the inflationary pressure that such a devaluation caused.
Orestes R Betancourt Ponce de León, “5 Historic Examples of Foreign Aid Efforts Gone Wrong”, FEE Stories, 2021-06-06.
February 19, 2024
QotD: Cleopatra VII Philopator
This week on the blog we’re going to talk about Cleopatra or to be more specific, we’re going to talk about Cleopatra VII Philopator, who is the only Cleopatra you’ve likely ever heard of, but that “seven” after her name should signal that she’s not the only Cleopatra.1 One of the trends in scholarship over the years towards larger than life ancient historical figures – Caesar, Alexander, Octavian, etc. – has been attempts to demystify them, stripping away centuries of caked-on reception, assumptions and imitation to ask more directly: who was this person, what did they do and do we value those sorts of things?2
Cleopatra, of course, has all of that reception layered on too. In antiquity and indeed until the modern era, she was one of the great villains of history, the licentious, wicked foreign queen of Octavian’s propaganda. More recently there has been an effort to reinvent her as an icon of modern values, perhaps most visible lately in Netflix’ recent (quite poorly received) documentary series. A lot of both efforts rely on reading into gaps in the source material. What I want to do here instead is to try to strip some of that away, to de-mystify Cleopatra and set out some of what we know and what we don’t know about her, with particular reference to the question I find most interesting: was Cleopatra actually a good or capable ruler?
Now a lot of the debate sparked by that Netflix series focused on what I find the rather uninteresting (but quite complicated) question of Cleopatra’s heritage or parentage or – heaven help us – her “race”. But I want to address this problem too, not because I care about the result but because I am deeply bothered by how confidently the result gets asserted by all sides and how swiftly those confident assertions are mobilized into categories that just aren’t very meaningful for understanding Cleopatra. To be frank, Cleopatra’s heritage should be a niche question debated in the pages of the Journal of Juristic Papyrology by scholars squinting at inscriptions and papyri, looking to make minor alterations in the prosopography of the Ptolemaic dynasty, both because it is highly technical and uncertain, but also because it isn’t an issue of central importance. So we’ll get that out of the way first in this essay and then get to my main point, which is this:
Cleopatra was, I’d argue, at best a mediocre ruler, whose ambitious and self-interested gambles mostly failed, to the ruin of herself and her kingdom. This is not to say Cleopatra was a weak or ineffective person; she was very obviously highly intelligent, learned, a virtuoso linguist, and a famously effective speaker. But one can be all of those things and not be a wise or skillful ruler, and I tend to view Cleopatra in that light.
Now I want to note the spirit in which I offer this essay. This is not a take-down of the Netflix Queen Cleopatra documentary (though it well deserves one and has received several; it is quite bad) nor a take-down of other scholars’ work on Cleopatra. This is simply my “take” on her reign. There’s enough we don’t know or barely know that another scholar, viewing from another angle, might well come away with a different conclusion, viewing Cleopatra in a more positive light. This is, to a degree, a response to some of the more recent public hagiography on Cleopatra, which I think air-brushes her failures and sometimes tries a bit too hard to read virtues into gaps in the evidence. But they are generally gaps in the evidence and in a situation where we are all to a degree making informed guesses, I am hardly going to trash someone who makes a perfectly plausible but somewhat differently informed guess. In history there are often situations where there is no right answer – meaning no answer we know to be true – but many wrong answers – answers we know to be false. I don’t claim to have the right answer, but I am frustrated by seeing so many very certain wrong answers floating around the public.
Before we dive in briefly to the boring question of Cleopatra’s parentage before the much more interesting question of her conduct as a ruler, we need to be clear about the difficult nature of the sources for Cleopatra and her reign. Fundamentally we may divide these sources into two groups: there are inscriptions, coins and papyrus records from Egypt which mention Cleopatra (and one she wrote on!) but, as such evidence is wont to be, [they] are often incomplete or provided only limited information. And then there are the literary sources, which are uniformly without exception hostile to Cleopatra. And I mean extremely hostile to Cleopatra, filled with wrath and invective. At no point, anywhere in the literary sources does Cleopatra get within a country mile of a fair shake and I am saying that as someone who thinks she wasn’t very good at her job.
The problem here is that Cleopatra was the target of Octavian’s PR campaign, as it were, in the run up to his war with Marcus Antonius (Marc Antony; I’m going to call him Marcus Antonius here), because as a foreign queen – an intersecting triad of concepts (foreignness, monarchy and women in power) which all offended Roman sensibilities – she was effectively the perfect target for a campaign aimed at winning over the populace of Italy, which was, it turns out, the most valuable military resource in the Mediterranean.3 That picture – the foreign queen corrupting the morals of good Romans with her decadence – rightly or wrongly ends up coloring all of the subsequent accounts. Of course that in turn effects the reliability of all of our literary sources and thus we must tread carefully.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: On the Reign of Cleopatra”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2023-05-26.
1. Or even just the seventh!
2. This is not to diminish the value of reception studies that trace the meaning a figure – or the memory of a figure – had over time. That’s a valuable but different lens of study.
3. It’s not all Octavian, mind. Cicero’s impression of Cleopatra was also sharply negative, for many of the same reasons: Cicero was hardly likely to be affable to a foreign queen who was an ally of Julius Caesar.
February 13, 2024
“I am a proud member of the Airfix generation”
I didn’t realize that Peter Caddick-Adams is the same age as me, but it does seem that our interests pretty much ran parallel for a while:

Re-enactors in Roman legionary gear, 19 May, 2021.
Original photo from https://pxhere.com/en/photo/883133 via Wikimedia Commons.
I am a proud member of the Airfix generation. The desire (less so the ability) to assemble and paint plastic model kits of aircraft, tanks and ships hit me squarely between the eyes on my tenth birthday in 1970. Several aunts and uncles had arrived at the same solution to bring out my inner Spitfire on the same day. Who needed the high of polystyrene cement and Humbrol enamel when you could refight D-Day across your bedroom floor with kits costing as little as 1/6d? Although Airfix was the premium producer of scale kits, other competing brands included Frog, Tamiya, Monogram, Hasegawa and Revell. I wish I knew what I did with them all, but many of the aircraft I recall casting out of upstairs windows, set on fire by match and candle. Looking back, I can see how it sewed the seeds of my becoming a professional military historian decades later. From little acorns, eh?
Two years later, I discovered I was interested in anything historical when my parents packed us into a train (great excitement in itself) for a trip to London. Although long past the days of steam, I can remember my father walking me down to thank the engine driver for getting us safely into Euston and then the true adventure began. The arrival at the British Museum to see the Tutankhamun Exhibition, which ran from March to December 1972. When it ended, besides the young Caddick-Adams, 1.6 million visitors had passed through the exhibition doors, making it the most popular attraction in the museum’s history. My favourite art class activity thereafter altered from drawing Spitfires and Messerschmitts chasing each other across every page to depicting ghostly, golden burial masks. Ever since, I have held an unbelievably soft spot for the old BM, always remembering that due to its vastness, it is best to go there to see something specific, rather than wander hither and thither, lost in its many treasures.
Then in 1977, when studying Ancient History for “A” Level, it was the turn of the Royal Academy in Piccadilly to capture my imagination with its Pompeii AD 79 exhibition. Mosaics, personal possessions, wall paintings and plaster casts of Romans and their animals caught in the moment of death as toxic gases, ashes, molten rock and pulverized pumice froze them forever, like insects in amber, likewise left a profound mark on my understanding of the bigger wheels of history.
The other day I was more than happy to be reunited with my old friend, the British Museum, this time hosting another Roman exhibition, which promises to be every bit as impactful as the Tutankhamun and Pompeii antecedents. Just unveiled, Legion: Life in the Roman Army is an inspired portrayal of an institution which numbered around 450,000 at its peak in AD 211 (33 legions and c. 400 auxiliary regiments), although numbers always fluctuated. The first amazing realisation is how little archaeological evidence remains of this vast organisation that endured for many centuries. The second is how well the scanty remnants in this exhibition have been preserved and interpreted.
Here, the British Museum has assembled the best surviving examples of arms, armour and personal possessions from collections around the world, in over 200 artefacts from 28 lenders. Though we view gleaming bronze helmets, swords long-rusted into scabbards, a pile of near-fossilised chainmail, it is incredible to think that there is only one intact example remaining of all those hundreds of thousands of rectangular and curved legionary shields (called a scutum), still bearing its decoration and crimson dye. This one comes from Syria.
There are some fine funerary carvings of Roman officers from around the empire, then we encounter some of the battlefield detritus including breastplate armour found near Kalkriese, in the Teutoburgerwald of Lower Saxony. This is where a coalition of Germanic tribes led by a rebel chieftain called Arminius ambushed 3 legions led by Publius Quinctilius Varus in 9 AD. The story of discovering this battle terrain was as dramatic as the assault itself. It was the result of a meticulous British soldier who combed an area north of his base at Osnabrück with a metal detector in 1987. Major Tony Clunn recorded each discovery of Roman coins and sling shot, making it possible to reconstruct the route taken by Roman legionaries under Varus and determine where they were ambushed and massacred.
February 9, 2024
His Year: Julius Caesar (59 BC)
Historia Civilis
Published Jul 5, 2016
(more…)
February 7, 2024
The Magician Who Fooled the Nazis (and all of us)
World War Two
Published 7 Nov 2023Military deception is tricky. Sometimes you need to destroy a crucial piece of war industry or make an entire harbour disappear. Who do you call for this sort of job? Well, someone who knows a thing or two about tricking the eye. You need a professional magician. You need Jasper Maskelyne. But is there more to this illusionist than meets the eye?
(more…)
November 20, 2023
QotD: Flax and linen in the ancient and medieval world
Linen fabrics are produced from the fibers of the flax plant, Linum usitatissimum. This common flax plant is the domesticated version of the wild Linum bienne, domesticated in the northern part of the fertile crescent no later than 7,000 BC, although wild flax fibers were being used to produce textiles even earlier than that. Consequently the use of linen fibers goes way back. In fact, the oldest known textiles are made from flax, including finds of fibers at Nahal Hemar (7th millennium BC), Çayönü (c. 7000 BC), and Çatalhöyük (c. 6000 BC). Evidence for the cultivation of flax goes back even further, with linseed from Tell Asward in Syria dating to the 8th millennium BC. Flax was being cultivated in Central Europe no later than the second half of the 7th millennium BC.
Flax is a productive little plant that produces two main products: flax seeds, which are used to produce linseed oil, and the bast of the flax plant which is used to make linen. The latter is our focus here so I am not going to go into linseed oil’s uses, but it should be noted that there is an alternative product. That said, my impression is that flax grown for its seeds is generally grown differently (spaced out, rather than packed together) and generally different varieties are used. That said, flax cultivated for one purpose might produce some of the other product (Pliny notes this, NH 19.16-17)
Flax was a cultivated plant (which is to say, it was farmed); fortunately we have discussed quite a bit about farming in general already and so we can really focus in on the peculiarities of the flax plant itself; if you are interested in the activities and social status of farmers, well, we have a post for that. Flax farming by and large seems to have involved mostly the same sorts of farmers as cereal farming; I get no sense in the Greco-Roman agronomists, for instance, that this was done by different folks. Flax farming changed relatively little prior to mechanization; my impression reading on it is that flax was farmed and gathered much the same in 1900 BC as it was in 1900 AD. In terms of soil, flax requires quite a lot of moisture and so grows best in either deep loam or (more commonly used in the ancient world, it seems) alluvial soils; in both cases, it should be loose, unconsolidated “sandy” (that is, small particle-sized) soil. Alluvium is loose, often sandy soil that is the product of erosion (that is to say, it is soil composed of the bits that have been eroded off of larger rocks by the action of water); the most common place to see lots of alluvial soil are in the flood-plains of rivers where it is deposited as the river floods forming what is called an alluvial plain.
Thus Pliny (NH 19.7ff) when listing the best flax-growing regions names places like Tarragona, Spain (with the seasonally flooding Francoli river) or the Po River Basin in Italy (with its large alluvial plain) and of course Egypt (with the regular flooding of the Nile). Pliny notes that linen from Sætabis in Spain was the best in Europe, followed by linens produced in the Po River Valley, though it seems clear that the rider here “made in Europe” in his text is meant to exclude Egypt, which would have otherwise dominated the list – Pliny openly admits that Egyptian flax, while making the least durable kind of linen (see below on harvesting times) was the most valuable (though he also treats Egyptian cotton which, by his time, was being cultivated in limited amounts in the Nile delta, as a form of flax, which obviously it isn’t). Flax is fairly resistant to short bursts of mild freezing temperatures, but prolonged freezes will kill the plants; it seems little accident that most flax production seems to have happened in fairly warm or at least temperate climes.
Flax is (as Pliny notes) a very fast growing plant – indeed, the fastest growing crop he knew of. Modern flax grown for fibers is generally ready for harvesting in roughly 100 days and this accords broadly with what the ancient agronomists suggest; Pliny says that flax is sown in spring and harvested in summer, while the other agronomists, likely reflecting practice further south suggest sowing in late fall and early winter and likewise harvesting relatively quickly. Flax that is going to be harvested for fibers tended to be planted in dense bunches or rows (Columella notes this method but does not endorse it, De Rust. 2.10.17). The reason for this is that when placed close together, the plants compete for sunlight by growing taller and thinner and with fewer flowers, which maximizes the amount of stalk per plant. By contrast, flax planted for linseed oil is more spaced out to maximize the number of flowers (and thus the amount of seed) per plant.
Once the flax was considered ready for harvest, it was pulled up out of the ground (including the root system) in bunches in handfuls rather than as individual plants […] and then hung to dry. Both Pliny and Columella (De Rust. 2.10.17) note that this pulling method tended to tear up the soil and regarded this as very damaging; they are on to something, since none of the flax plant is left to be plowed under, flax cultivation does seem to be fairly tough on the soil (for this reason Columella advises only growing flax in regions with ideal soil for it and where it brings a good profit). The exact time of harvest varies based on the use intended for the flax fibers; harvesting the flax later results in stronger, but rougher, fibers. Late-pulled flax is called “yellow” flax (for the same reason that blond hair is called “flaxen” – it’s yellow!) and was used for more work-a-day fabrics and ropes.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Clothing, How Did They Make It? Part I: High Fiber”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-03-05.
November 12, 2023
Who Destroyed The Library of Alexandria? | The Rest is History
The Rest is History
Published 21 Jul 2023Step back in time with renowned historians Dominic Sandbrook and Tom Holland as they embark on an enthralling journey to explore the enigmatic tale of the Library of Alexandria’s destruction. Join them as they uncover the who, what, and why behind one of history’s greatest losses.
#LibraryOfAlexandria #DominicSandbrook #TomHolland
November 3, 2023
QotD: The use of Epigraphy and Papyrology in interpreting and understanding the ancient and classical world
… let’s say you still have a research question that the ancient sources don’t answer, or only answer very incompletely. Where can you go next? There are a few categories, listed in no particular order.
Let’s start with the most text-like subcategories, beginning with epigraphy. Epigraphy is the study of words carved into durable materials like stone or metal. For cultures that do this (so, Mesopotamians, Egyptians, Greeks, Romans: Yes! Gauls, pre-Roman Iberians, ancient Steppe nomads: No!), epigraphy provides new texts to read and unlike the literary texts, we are discovering new epigraphic texts all the time. The downside is that the types of texts we recover epigraphically are generally very limited; mostly what we see are laws, decrees and lists. Narrative accounts of events are very rare, as is the epigraphic preservation of literature (though this does happen, particularly in Mesopotamia with texts written on clay tablets). That makes epigraphy really valuable as a source of legal texts (especially in Greece and Rome), but because the texts in question tend to be very narrowly written (again, we’re talking about a single law or a single decree; imagine trying to understand an act of Congress renaming a post office if you didn’t [know] what Congress was or what a post office was) without a lot of additional context, you often need literary texts to give you the context for the new inscription you are looking at.
The other issue with epigraphy is that it is very difficult to read and use, both because of wear and damage and also because these inscriptions were not always designed with readability in mind (most inscriptions are heavily abbreviated, written INALLCAPSWITHNOSPACESORPUNCTUATIONATALL). Consequently, getting from “stone with some writing on it” to an edited, usable Greek or Latin text generally requires specialists (epigraphers) to reconstruct the text, reconstructing missing words (based on the grammar and context around them) and making sense of what is there. Frankly, skilled epigraphers are practically magicians in terms of being able figure out, for instance, the word that needs to fit in a crack on a stone based on the words around it and the space available. Fortunately, epigraphic texts are published in a fairly complex notation system which clearly delineates the letters that are on the stone itself and those which have been guessed at (which we then all have to learn).
Related to this is papyrology and other related forms of paleography, which is to say the interpretation of bits of writing on other kinds of texts, though for the ancient Mediterranean this mostly means papyrus. The good news is that there is a fairly large corpus of this stuff, which includes a lot of every day documents (tax receipts! personal letters! census returns! literary fragments!). The bad news is that it is almost entirely restricted to Egypt, because while papyrus paper was used far beyond Egypt, it only survives in ultra-dry conditions like the Egyptian desert. Moreover, you have all of these little documents – how do you know if they are typical? Well, you need a very large sample of them. And then we’re back to preservation because the only place you have a very large sample is Egypt, which is strange. Unfortunately, Egypt is quite possibly the strangest place in the Ancient Mediterranean world and so papyrological evidence is frequently plagued by questions of applicability: sure we have good evidence on average household size in Roman Egypt, but how representative is that of the Roman Empire as a whole, given that Egypt is such an unusual place?
Outside of Egypt and a handful of sites (I can think of two) in England? Almost nothing. To top it all off, papyrology shares epigraphy’s problem that these texts are difficult and often require specialists to read and reconstruct them due to damage, old scripts and so on. The major problem is that the quantity of recovered papyrus has vastly outstripped the number of trained papyrologists, bottle-necking this source of evidence (also a lot of ancient papyri get traded on the antiquities black market, potentially destroying their provenance, and there is a special level in hell for people who buy black market antiquities).
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday: March 26, 2021 (On the Nature of Ancient Evidence”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-03-26.
October 19, 2023
Why there are no regional refuges available to Gazan civilians
Ed West outlines the sad story of Palestinian civilians uprooted from their homes by the many conflicts that have convulsed the region:
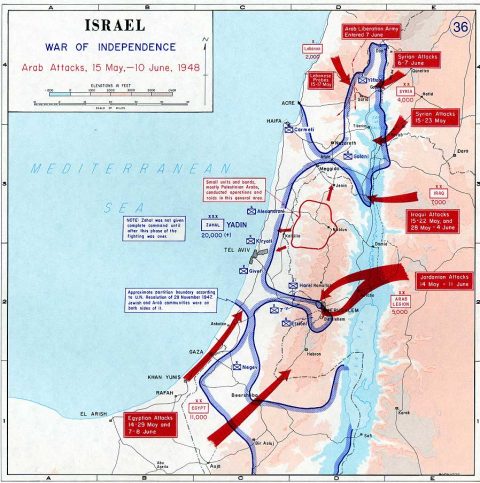
Arab attacks in May and June 1948.
United States Military Academy Atlas, Link.
It is generally a good idea for refugees to be housed in neighbouring countries rather than on different continents, for a number of reasons, but we should be wary of casually stating that Arab states should house Gazans. In a difficult region many of these countries have already put themselves under enormous strain through acts of immense generosity, and none more so than Jordan.
[…]
The survival of Jordan’s monarchy has been one of the more surprising outcomes of the past few decades, and experts have repeatedly bet against it. The country has an unusually bad hand in many ways. Situated beside the disputed Holy Land, it lacks the natural resources of neighbouring Saudi Arabia and Iraq, while also being more remote than Lebanon or Syria, which had long been at the heart of Mediterranean trading networks and far more plugged into European markets.
But most of all it has suffered the destabilising effect of refugees. Abdullah is named after his great-grandfather, the first King of Jordan, whose assassination in 1951 forms the opening of Hussein’s autobiography; indeed he calls it “the most profound influence of my life”. He was just 15 years-old when he travelled with his grandfather to Jerusalem to perform Friday prayers, where the monarch was shot dead by a Palestinian. The gunman then fired at Hussein but the bullet struck a medal his grandfather had given him.
Abdullah I had ruled the new kingdom for just five years, and it endured an incredibly bad start with defeat in the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, which led to a surge of refugees. Estimates of exact numbers seem to vary hugely, but in Lion of Jordan, Avi Shlaim writes that 700,000 Palestinians left in 1948, and of these “450,000 ended up in Jordan, which did more than any other Arab state to help them resettle and integrate with the rest of society”.
He wrote: “The refugees in Jordan wanted to preserve their separate Palestinian identity, but this ran counter to Abdullah’s policy of ‘Jordanization’.” He gave them citizenship rights “but the refugees were a great burden on the weak Jordanian economy; it simply did not have the financial resources to cope with a humanitarian tragedy on such a vast scale.” Many ended up in resentful poverty and “the Palestinians thus became an important factor in domestic Jordanian politics”.
Another source suggests that in 1949, “Jordan welcomed approximately 900,000 refugees by amending the country’s 1928 Law of Nationality to grant equal citizenship to Palestinians; the 1954 Law of Jordanian Nationality later extended citizenship to Palestinians who arrived in Jordan after the 1949 addendum.”
After another defeat against Israel in 1967, up to 300,000 displaced Palestinians in the West Bank retained Jordanian citizenship, and today around 40% of the Jordanian population descend from Palestinian refugees, although the figure may be higher (again, they vary hugely). What seems certain is that about 40% of displaced Palestinians and their descendants live in Jordan, with another 10% in Syria (although many of those have since fled to Lebanon).
The Hashemites, unlike some Arab countries, were keen to integrate the newcomers and to avoid them having to endure a permanent refugee existence; that is why three-quarters of Palestinians in Jordan are Jordanian citizens, although Palestinians from Gaza aren’t, that area having been part of Egypt before the Six-Day War.
In contrast Palestinians who fled to Syria were not given citizenship, for all the talk of solidarity, and often remained in refugee camp-cities for decades (many of which were heavily affected by the Syrian war).
In Lebanon it was even worse; there the Palestinians could neither gain citizenship, nor in many cases access things like healthcare, education or work. The situation here was uniquely dangerous, because their arrival tipped the country’s incredibly delicate balance between Christians, Shia, Sunni and Druze; in 1975 the country descended into civil war, a horror that saw a modern example of shibboleths where Christian militiamen would present tomatoes to suspected Palestinians and ask them to pronounce the name.
This refugee surge had a destabilising effect on Jordan. Already in 1958 things were so bad that Hussein hoped to form a tripartite union with Saudi Arabia and Iraq to counter the influence of Gamal Abdel Nasser’s Egypt. Neither neighbour was too keen on the idea, and Saudi prince Abd al-Ilah remarked that “Hussein’s trouble stemmed from the fact that 70 per cent of his subjects were Palestinians with no loyalty to the throne”.
But in 1970, three years after the Six-Day War, it reached a crisis point, with the British ambassador commenting that “the mixture became so volatile that the container exploded”. There now came full civil war in Jordan between the army and the Palestinian fedayeen.
Jordan had become home to the Palestinian Liberation Organisation, but this umbrella group was itself split into different factions, Fatah being the largest and most moderate. They were reluctant to get involved in the internal affairs of other Arab states, but this was not the case with the more extreme Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine led by Dr George Habash (who, as his name suggests, was a Christian) and the Marxist-Leninist Popular Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine (yes, it does get very Life of Brian).
September 30, 2023
Why did the North Africa Campaign Matter in WW2?
The Intel Report
Published 8 Jun 2023As Erwin Rommel’s Afrika Korps rolled into Egypt in 1942, the only thing standing between them and Cairo and the Suez Canal was the British 8th Army. In this video we look at what was at stake for both sides, and why the North African campaign made a crucial impact on the outcome of the Second World War.
(more…)
August 7, 2023
The Longest Year in Human History (46 B.C.E.)
Historia Civilis
Published 24 Apr 2019
(more…)
QotD: How do we determine Roman dates like “46 BC”?
So this is actually a really interesting question that we need to break into two parts: what do historians do with dates that are at least premised on the Roman calendar and then what do we do with dates that aren’t.
Now the Roman calendar is itself kind of a moving target, so we can start with a brief history of that. At some very early point the Romans seem to have had a calendar with ten months, with December as the last month, March as the first month and no January or February. That said while you will hear a lot of folk history crediting Julius Caesar with the creation of two extra months (July and August) that’s not right; those months (called Quintilis and Sextilis) were already on the calendar. By the time we can see the Roman calendar, it has twelve months of variable lengths (355 days total) with an “intercalary month” inserted every other year to “reset” the calendar to the seasons. That calendar, which still started in March (sitting where it does, seasonally, as it does for us), the Romans attributed to the legendary-probably-not-a-real-person King Numa, which means in any case even by the Middle Republic it was so old no one knew when it started (Plut. Numa 18; Liv 1.19.6-7). The shift from March to January as the first month in turn happens in 153 (Liv. Per. 47.13), probably for political reasons.
We still use this calendar (more or less) and that introduces some significant oddities in the reckoning of dates that are recorded by the Roman calendar. See, because the length of the year (355 days) did not match the length of a solar year (famously 365 days and change), the months “drifted” over the calendar a little bit; during the first century BC when things were so chaotic that intercalary months were missed, the days might drift a lot. This problem is what Julius Caesar fixed, creating a 365 day calendar in 46; to “reset” the year for his new calendar he then extended the year 46 to 445 days. And you might think, “my goodness, that means we’d have to convert every pre-45 BC date to figure out what it actually is, how do we do that?”
And the answer is: we don’t. Instead, all of the oddities of the Roman calendar remain baked into our calendar and the year 46 BC is still reckoned as being 445 days long and thus the longest ever year. Consequently earlier Roman dates are directly convertible into our calendar system, though if you care what season a day happened, you might need to do some calculating (but not usually because the drift isn’t usually extreme). But in expressing the date as a day, the fact that the Gregorian calendar does not retroactively change the days of the Julian calendar, which also did not retroactively change the days of the older Roman calendar means that no change is necessary.
Ok, but then what year is it? Well, the Romans counted years two ways. The more common way was to refer to consular years, “In the year of the consulship of X and Y.” Thus the Battle of Cannae happened, “in the year of the consulship of Varro and Paullus,” 216 BC. In the empire, you sometimes also see events referenced by the year of a given emperor. Conveniently for us, we can reconstruct a complete list of all of the consular years and we know all of the emperors, so back-converting a date rendered like this is fairly easy. More rarely, the Romans might date with an absolute chronology, ab urbe condita (AUC) – “from the founding of the city”, which they imagined to have happened in in 753 BC. Since we know that date, this also is a fairly easy conversion.
Non-Roman dates get harder. The Greeks tend to date things either by serving magistrates (especially the Athenian “eponymous archon”, because we have so many Athenian authors) or by Olympiads. Olympiad dates are not too bad; it’s a four-year cycle starting in 780 BC, so we are now in the 700th Olympiad. Archon dates are tougher for two reasons. First, unlike Roman consuls, we have only a mostly complete list of Athenian archons, with some significant gaps. Both dates suffer from the complication that they do not line up neatly with the start of the Roman year. Olympiads begin and end in midsummer and archon years ran from July to June. If we have a day, or even a month attached to one of these dates, converting to a modern Gregorian calendar date isn’t too bad. But if, as is often the case, all you have is a year, it gets tricky; an event taking place “in the Archonship of Cleocritus” (with no further elaboration) could have happened in 413 or 412. Consequently, you’ll see the date (if there is no month or season indicator that lets us narrow it down), written as 413/2 – that doesn’t mean “in the year two-hundred and six and a half” but rather “413 OR 412”.
That said, with a complete list of emperors, consuls and Olympiads, along with a nearly complete list of archons, keeping the system together is relatively easy. Things get sticky fast when moving to societies using regnal years for which we do not have complete or reliable king’s lists. So for instance there are a range of potential chronologies for the Middle Bronze Age in Mesopotamia. I have no great expertise into how these chronologies are calculated; I was taught with the “Middle” chronology as the consensus position and so I use that and aim just to be consistent. Bronze Age Egyptian chronology has similar disputes, but with a lot less variation in potential dates. Unfortunately while obviously I have to be aware of these chronology disputes, I don’t really have the expertise to explain them – we’d have to get an Egyptologist or Assyriologist (for odd path-dependent reasons, scholars that study ancient Mesopotamia, including places and cultures that were not Assyria-proper are still called Assyriologists, although to be fair the whole region (including Egypt!) was all Assyria at one point) to write a guest post to untangle all of that.
That said in most cases all of this work has largely been done and so it is a relatively rare occurrence that I need to actually back convert a date myself. It does happen sometimes, mostly when I’m moving through Livy and have lost track of what year it is and need to get a date, in which case I generally page back to find the last set of consular elections and then check the list of consuls to determine the date.
Bret Devereaux, “Referenda ad Senatum: January 13, 2023: Roman Traditionalism, Ancient Dates and Imperial Spies”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2023-01-13.
June 24, 2023
QotD: The plight of miners in pre-industrial societies
Essentially the problem that miners faced was that while mining could be a complex and technical job, the vast majority of the labor involved was largely unskilled manual labor in difficult conditions. Since the technical aspects could be handled by overseers, this left the miners in a situation where their working conditions depended very heavily on the degree to which their labor was scarce.
In the ancient Mediterranean, the clear testimony of the sources is that mining was a low-status occupation, one for enslaved people, criminals and the truly desperate. Being “sent to the mines” is presented, alongside being sent to work in the mills, as a standard terrible punishment for enslaved people who didn’t obey their owners and it is fairly clear in many cases that being sent to the mines was effectively a delayed death sentence. Diodorus Siculus describes mining labor in the gold mines of Egypt this way, in a passage that is fairly representative of the ancient sources on mining labor more generally (3.13.3, trans Oldfather (1935)):
For no leniency or respite of any kind is given to any man who is sick, or maimed, or aged, or in the case of a woman for her weakness, but all without exception are compelled by blows to persevere in their labours, until through ill-treatment they die in the midst of their tortures. Consequently the poor unfortunates believe, because their punishment is so excessively severe, that the future will always be more terrible than the present and therefore look forward to death as more to be desired than life.
It is clear that conditions in Greek and Roman mines were not much better. Examples of chains and fetters – and sometimes human remains still so chained – occur in numerous Greek and Roman mines. Unfortunately our sources are mostly concerned with precious metal mines and those mines also seem to have been the worst sorts of mines to work in, since the long underground shafts and galleries exposed the miners to greater dangers from bad air to mine-collapses. That said, it is hard to imagine working an open-pit iron mine by hand, while perhaps somewhat safer, was any less back-breaking, miserable toil, even if it might have been marginally safer.
Conditions were not always so bad though, particularly for free miners (being paid a wage) who tended to be treated better, especially where their labor was sorely needed. For instance, a set of rules for the Roman mines at Vipasca, Spain provided for contractors to supply various amenities, including public baths maintained year-round. The labor force at Vipasca was clearly free and these amenities seem to have been a concession to the need to make the life of the workers livable in order to get a sufficient number of them in a relatively sparsely populated part of Spain.
The conditions for miners in medieval Europe seems to have been somewhat better. We see mining communities often setting up their own institutions and occasionally even having their own guilds (for instance, there was a coal-workers guild in Liege in the 13th century) or internal regulations. These mining communities, which in large mining operations might become small towns in their own right, seem to have often had some degree of legal privileges when compared to the general rural population (though it should be noted that, as the mines were typically owned by the local lord or state, exemption from taxes was essentially illusory as the lord or king’s cut of the mine’s profits was the taxes). It does seem notable that while conditions in medieval mines were never quite so bad as those in the ancient world, the rapid expansion of mining activity beginning in the 15th century seems to have coincided with a loss of the special status and privileges of earlier medieval European miners and the status associated with the labor declined back down to effectively the bottom of the social spectrum.
(That said, it seems necessary to note that precious metal-mining done by non-free Native American laborers at the order of European colonial states appears to have been every bit as cruel and deadly as mining in the ancient world.)
Bret Devereaux, “Iron, How Did They Make It? Part I, Mining”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-09-18.
June 20, 2023
QotD: When kings and emperors become gods
Nothing in ancient religion strikes my students as so utterly strange and foreign as that idea [of divinized kings and emperors]. The usual first response of the modern student is to treat the thing like a sham – surely the king knows he is not divine or invested with some mystical power, so this most all be a con-job aimed at shoring up the legitimacy of the king. But as we’ve seen, the line between great humans and minor gods is blurry, and it is possible to cross that line. It is not necessary to assume that it was all an intentional sham.
Divine rulership was not universal however – it was subject to cultural context. In Egypt, the Pharaoh was the Living Horus, a physical incarnation of the divine; when he died he became Osiris, the ruler over the underworld. The mystery of the duality whereby a Pharaoh was both a specific person (and might be a different person in the future) but also the same god each time seems to owe something to the multipart Egyptian conception of the soul. Naram-Sin, an Akkadian King (2254-2218 B.C.) represents himself as divine (shown by his having horns) on his victory stele; future kings of Akkad followed suit in claiming a form of divinity, albeit a lesser one than the big-time great gods.
But in Mesopotamia, the rulers of Akkad were the exception; other Mesopotamian kings (Sumerian, Babylonian, etc) did not claim to be gods – even very great kings (at least while alive – declaring a legendary ruler a god is rather more like a divine founder figure). Hammurabi (king of Babylon, c.1810-c.1750 B.C.) is shown in his royal artwork very much a man – albeit one who receives his mandate to rule from the gods Shamash and Marduk. Crucially, and I want to stress this, the Achaemenid kings of Persia were not considered gods (except inasmuch as some of them also occupied the position of Pharaoh of Egypt; it’s not clear how seriously they took this – less seriously than Alexander and Ptolemy, quite clearly). The assumption that the Persians practiced a divine kingship is mostly a product of Greek misunderstandings of Persian court ritual, magnified in the popular culture by centuries of using the Persian “other” as a mirror and (usually false) contrast for European cultures.
But the practice that my students often find most confusing is that of the Roman emperors. To be clear, Roman emperors were not divinized while they were alive. Augustus had his adoptive father, Julius Caesar divinized (this practice would repeat for future emperors divinizing their predecessors), but not himself; the emperor Vespasian, on his deathbed, famously made fun of this by declaring as a joke, “Alas! I think I’m becoming a god” (Suet. Vesp. 23.4). And yet, at the same time, outside of Rome, even Augustus – the first emperor – received cult and divine honors, either to his person or to his genius (remember, that’s not how smart he is, but the divine spirit that protects him and his family).
I think it is common for us, sitting outside of these systems, to view this sort of two-step dance, “I’m not a god, but you can give me divine honors in the provinces and call me a god, just don’t do it too loudly” as fundamentally cynical – and to some degree it might have been; Augustus was capable of immense cynicism. But I think it is possible to view this relationship outside of that cynicism through the lens of the ideas and rules we’ve laid out.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Practical Polytheism, Part IV: Little Gods and Big People”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-11-15.



