World War Two
Published 31 Oct 2020Operation Typhoon is halted until the coming winter can freeze enough ground to increase mobility. But the ever colder weather is a disaster waiting to happen for an already over-stretched German supply line.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @ww2_day_by_day – https://www.instagram.com/ww2_day_by_day
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Director: Astrid Deinhard
Producers: Astrid Deinhard and Spartacus Olsson
Executive Producers: Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson, Bodo Rittenauer
Creative Producer: Maria Kyhle
Post-Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Indy Neidell
Edited by: Miki Cackowski
Sound design: Marek Kamiński
Map animations: Eastory (https://www.youtube.com/c/eastory)Colorizations by:
Mikolaj Uchman
Dememorabilia – https://www.instagram.com/dememorabilia/
Jaris Almazani (Artistic Man) – https://instagram.com/artistic.man?ig…Sources:
Bundesrchiv
Narodowe Archiwum Cyfrowe
Yad Vashem 7283/146Soundtracks from the Epidemic Sound:
Johannes Bornlof – “Death And Glory 2”
Johan Hynynen – “Dark Beginning”
Johannes Bornlof – “The Inspector 4”
Hakan Eriksson – “Epic Adventure Theme 4”
Farell Wooten – “Blunt Object”
Fabien Tell – “Last Point of Safe Return”Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
November 1, 2020
October 25, 2020
July 20, 2020
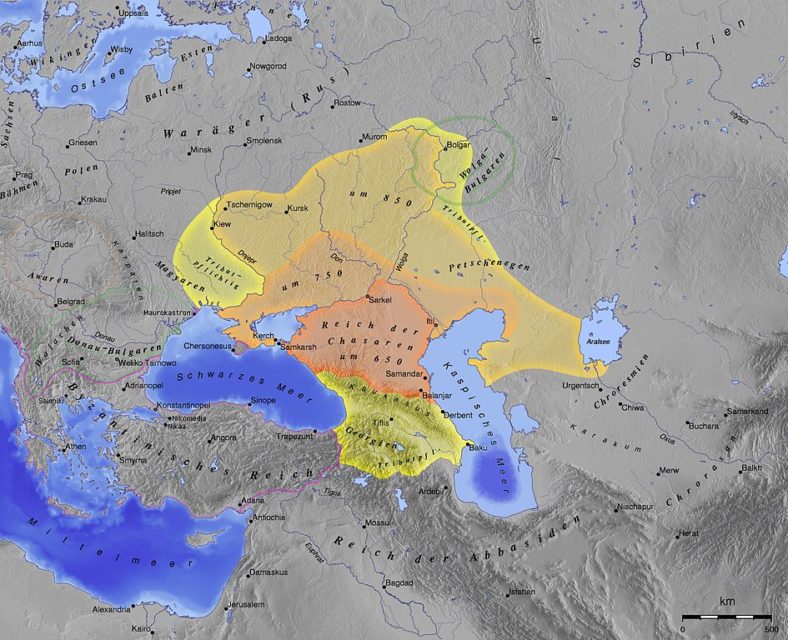
A lost nation that lasted for 300 years in (relative) peace and prosperity
I’d heard of the Khazar Khaganate occasionally, but didn’t know much about it until I read a useful summary by Lawrence W. Reed:
The list of extinct countries includes the better known ones like the USSR (aptly dubbed “the Evil Empire” by Ronald Reagan) and Yugoslavia, as well as hundreds of largely forgotten others like Majapahit, Assyria, Babylonia, Burgundy, and the Ottoman Empire. Far more countries are long gone, in fact, than the 195 on the map today. As a history lover, I’ve never yet discovered a country whose inhabitants’ experience was devoid of interesting facts and lessons.
Take Khazaria, for example. It lasted over 300 years (650 to 965 AD) and covered more territory than the combined Scandinavian nations of our time. It spanned the eastern half of modern-day Ukraine, the steppes of the Volga-Don region of present Russia, the entire Crimean Peninsula, and the northern Caucasus. Its southern portion took in most of the shorelines of three seas: the Black, the Caspian and the Aral.
It’s my thesis that for a country to be “successful” for a considerable period — success being defined loosely here as economically prosperous, politically stable, and militarily defensible — it must possess substantial TTD. That’s not a pronounceable acronym, unfortunately, but it stands for trade, tolerance and decentralization.
Each of these three criteria for success is worth volumes of discussion but here’s the nub of it: When economic freedom and private property exist, trade flourishes. And trade is what peaceful humans do to satisfy wants and improve material well-being. Choke it off and living standards plummet. Tolerance is a sign that people appreciate the benefits derived from diversity in personal choices. An intolerant people deprive themselves of what others can offer and waste time and resources fighting instead of collaborating. Decentralization preserves the rich identities of local communities and stymies the concentration of authority with its inevitable corruption. Power dispersed is power tamed.
So a successful country is one that can boast a lot of TTD. It encourages exchange, celebrates diversity and avoids top-down, political command-and-control. Almost every “failed state” in history did just the opposite by stifling commerce; stoking racial, ethnic or nationalistic hatred; and/or installing a dictatorship.
Khazaria, to its great credit, practiced remarkable measures of trade and tolerance and enough decentralization to prevent its government from sabotaging either one. In the end, it met its demise not from internal decay but from foreign assault.
October 3, 2019
The Crimean War – History Matters
History Matters
Published on 7 Apr 2019Twitter: https://twitter.com/Tenminhistory
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/user?u=4973164This episode covers the Crimean War (1853-1856) between the Russian Empire and the Ottomans, the British, the French and the Sardinians. It began largely out of Russo-Ottoman rivalry and because French Emperor Napoleon III had been appointed the protector of Christians within the Ottoman Empire, at the expense of the Russian Emperor Nicholas I. The war really kicked off in 1854 with the British and French invasion of Crimea and largely ended with the capture of Sevastopol in 1855, after which the Russians sued for peace.
August 8, 2019
QotD: Austrians – strudel-eating surrender monkeys
Oh yes, did I mention the Austrians? A grand military tradition. The Radetzky march, all that stuff. Let’s look at their record more closely, shall we?
The Austrians (or rather the Habsburgs) built up a moderately large empire by persuading the Magyars that they could be sort of equal partners in the empire in an unequal sort of way, expert politicking and setting one lot of Slavs against another in the Balkans and central Europe, and marrying into the right ducal families in bits of what was later to become Italy. They never quite managed to sort out the Serbs, however, who felt that fighting nobly against the Turks was their speciality, and they were forced out of Switzerland early on by a small boy with an apple on his head.
The year 1683 may reasonably be considered a turning point for Western Christendom. Over the preceding century or so the Turkish Ottoman Empire had steadily advanced up the Balkan peninsula and after being balked, as it were, for many years by Macedonians, Bulgars, Albanians, Serbs, Bosnians, Croats, Slovenians, Slavonians and some I’ve probably forgotten, finally got as far as the Habsburg capital, Vienna, to which they laid siege. The siege failed, and the Turks were repelled, never again to return. Why? Because Austria was rescued by the Poles under Jan III Sobieski.
Under the noted and renowned Empress Maria Theresa, a War of the Austrian Succession was held. In keeping with tradition, it was mainly fought between the French and the English in Belgium (the French, opposed to Austria, won), except for an unimportant sideshow which appears to have been between the French and the Indians in Saratoga. The upshot was naturally that the Austrians let the Prussians have Silesia. Twice, to be on the safe side. A few years later the Seven Years War, largely fought between the English and the French in Belgium (the English, opposed to the Austrians, won) confirmed the result.
When it came to the French revolutionary and the Napoleonic wars, the Habsburgs were naturally on the side of the divine right of kings (well, Marie-Antoinette was a Habsburg herself) and against mob rule, liberty, fraternity, and most certainly equality. In furtherance of this cause, the Austrians fought the French at such places as Marengo, Austerlitz, and Wagram – among other names listed on the Arc de Triomphe in Paris. By 1812 the Austrians decided to try being on the same side as Napoleon for a change. Napoleon promptly invaded Russia, with predictable results. Following Napoleon’s final defeat at a battle in Belgium which the Austrians fortunately weren’t in time to get to, they regained most of their possessions in Italy at the peace talks due to diplomatic manoeuvrings by the master of the art, Metternich, but lost influence in Germany.
In the 1850s Austria failed to back her treaty partner Russia when the latter was invaded by the Turks, French and English in the Crimean war. Sardinia/Savoy/Piedmont, the leading state in the Italian peninsula, fought with the Allies, gaining international favour when it came to removing the Austrian influence during the subsequent wars of the Italian unification. Austria lost battles at places like Magenta and Solferino, and with them most of its Italian possessions except Venice.
In 1864 the Austrians did actually win a battle, a small naval engagement near Heligoland in the North Sea, against the Danes, against whom they were fighting in support of the Prussians over the Schleswig-Holstein question, of course. Emboldened by this masterstroke, they promptly came to blows with their erstwhile allies and were soundly whipped at the battle of Sadowa-Königgratz. The Italians got most of the rest of their country back in the resulting confusion.
The Austrians managed to stay out of trouble for another few decades after that, building up a national economy based on cheap dance music and diplomatic manoeuvrings in the Balkans. Unfortunately they got out of their depth in this respect; in 1914 the foreign minister [actually Chief of the General Staff] Conrad von Hötzendorff, believing himself to be the reincarnation of Metternich, decided to start the First World War to impress a woman he fancied. It could reasonably be argued that all the countries involved lost the First World War, even the winners, but Austria, after some Pyrrhic successes against the Serbs, a certain amount of back-and-forth against the Russians in Galicia and a cheap and ultimately futile win at Caporetto after the Russians had pulled out and the Germans had sent rather a lot of extra troops, ended up losing its entire empire, its monarchy, access to the sea and any self-respect whatsoever. It also managed to export Adolf Hitler to Germany during this period, which was singularly unfortunate; he absorbed Austria into a Greater Germany and then lost a rather big war in the most spectacular of fashions, as you are probably aware. This ended the military involvement of Austria in world affairs, at least for the moment.
I rest my case.
Albert Herring, “Why neither the French nor the Italians are the worst military nation”, Everything2, 2002-01-07.
November 29, 2018
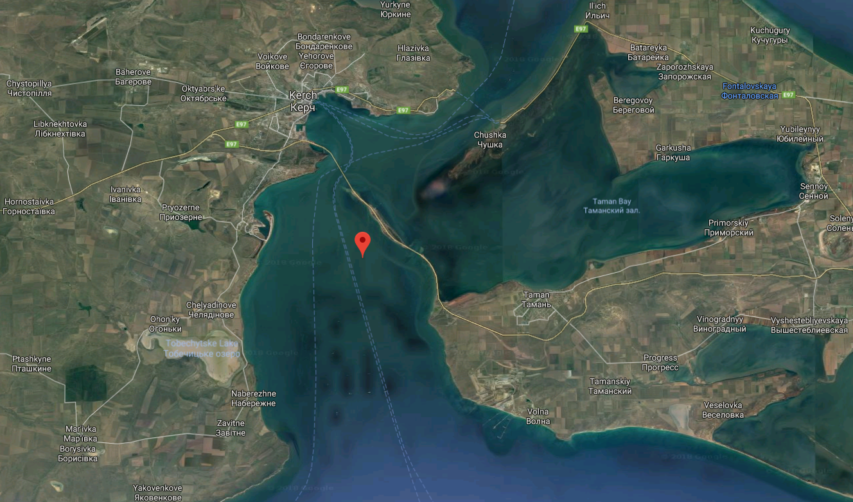
The Kerch Strait stand-off
The Russians are attempting to cut off Ukrainian access to the Sea of Azov, cloaking that action in standard disinformation to claim that Ukraine is the aggressor, etc. Shoshana Bryen outlines the situation at the moment:
Every story has a starting point. Don’t start with the Russian capture this week of two (or three) Ukrainian ships and the injury to three (or six) Ukrainian sailors. The Russian habit is to do as it likes with smaller countries and then announce that the other guy did it (or it never happened at all). That is the story of the Russian war in Ukraine and the 2014 illegal annexation of Crimea, and that is the Russian story of the Ukrainian ships – two ships, not three, three injured not six; anyhow, Ukraine was sailing out of its lane.
Start instead with the bridge over the narrow Kerch Strait that opened earlier in 2018. It is the only entrance to the Azov Sea from the Black Sea, spanning the Taman Peninsula in Russia and the Kerch Peninsula in Crimea. Earlier plans for the bridge were completed between Russia and Ukraine, but that was before the Russians occupied Crimea. There is an agreement for Ukrainian passage to its two ports along the Azov Sea, but Ukraine has complained that the bridge is the beginning of a blockade that would ultimately control or end Ukrainian shipping. There have been delays for Ukrainian ships passing through, sometimes days, and oh, by the way, the bridge is very low – nearly flat – over the water, meaning that Ukrainian ships over 115 feet can’t pass at all. And now there is a Russian ship parked under the bridge, blocking traffic.
It is estimated that Ukrainian shipping through the strait is down nearly 25% since the bridge opened – as the Ukrainians feared and as the Russians planned.
Austin Bay looks at the military and diplomatic side:
Closing the Kerch Strait effectively blockades Berdyansk and Mariupol, two Ukrainian ports on the Sea of Azov’s north coast.
In 2015, while visiting Crimea, Vladimir Putin himself said he hoped there would be no “full-scale direct clashes” between Ukrainian and Russian forces.
But on Nov. 25, Russia’s war against Ukraine escalated as verifiably Russian coast guard forces under the command of the Russian Federal Security Service intercepted (rammed says Ukraine), boarded and seized two verifiably Ukrainian naval vessels and a Ukrainian tugboat. The 24 Ukrainians on board the ships became Russian prisoners.
The Kremlin claimed the Ukrainian vessels had conducted “dangerous maneuvers” in Russian territorial water.
Putin’s Kremlin specializes in adding complex twists to blatant falsehoods. There is no evidence the Ukrainian ships did anything but try to avoid being intercepted. Russian territorial water? To buy that you must accept Russia’s illegal seizure of the peninsula. However, the strait is an internationally recognized waterway open to transit by commercial shipping and naval vessels. Kerch is comparable to other straits around the globe, like the Strait of Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf. Iran routinely threatens to close Hormuz to shipping, but to do so would violate freedom of navigation and constitute an act of war.
Defense One reported that Kiev had informed Moscow that its naval vessels would transit the strait. Moreover, the Russians who boarded the Ukrainian ships were special operations commandos.
The Ukrainian ships were making a legal transit. As recently as 2003, Russia guaranteed Ukraine’s right to transit the strait. The 2003 treaty made the strait and Sea of Azov shared territory.
Like invading Crimea, the Russian seizure of Ukrainian ships is a calculated act of war. Russia has now anchored an oil tanker in the main sealane beneath the bridge, blocking all ship traffic.
Ukrainian Foreign Minister Pavlo Klimkin said ramming a Ukrainian vessel was an “act of armed aggression” and that Russia had violated “the freedom of maritime traffic.” He also cited specific articles in the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea that “bans the obstruction of peaceful transit across the Kerch Strait.”
Several articles referenced the possibility that NATO would … do something. Other than the usual diplomatic protests, I doubt that there’s much NATO can do in a situation like this. Direct military action should not even be considered an option (not that it’ll stop the odd wild-eyed editorial writer), as NATO does not have a direct interest at risk here. All western nations do have an interest in preserving and upholding freedom of the seas, but Russia knows that the west won’t likely risk getting into a shooting war over incidents like this.
You can get a very useful list of links including the current Kerch Strait confrontation from MILNEWS.ca.
June 28, 2018
Mary Seacole – II: Mother Seacole in the Crimea – Extra History
Extra Credits
Published on 16 Jan 2016Unable to find any official sponsors, Mary Seacole decided to send herself to the Crimea. She recruited her husband’s cousin, a fellow business person, and the two of them set off for the war zone. Unlike London, where she’d met a chilly reception, Mary’s help was welcomed by the overworked doctors and suffering soldiers. She built a new version of her British Hotel and invited officers to dine or shop there, using their money to buy medical supplies and creature comforts for the poorer soldiers. She had set herself up next to the army camp, and during battles she helped provide emergency care. But when at last the city of Sevastopol fell, Mary’s medical services were no longer in much demand. She enjoyed a few months of prosperity as the soldiers celebrated their newfound time off, but in March of 1856, a treaty was signed and troops began returning home. Many of them left unpaid debts, and Mary could no longer sell her supplies, so she and her business partner were forced to return home to London and declare bankruptcy. When that news got out, the soldiers she’d cared for rallied to her aid, donating money to help pay her debts. Although Mary tried to continue serving soldiers in warzones, the government never recognized her and in the end, only her homeland of Jamaica remembered her contributions after her death. In the 2000s, her story came back to light in the United Kingdom and she was recognized in 2004 as the Greatest Black Briton.
June 27, 2018
Mary Seacole – I: A Bold Front to Fortune – Extra History
Extra Credits
Published on 9 Jan 2016Mary Seacole treated soldiers during the Crimean War – but she took a long path to get there. She grew up in Jamaica, the daughter of a local hotel owner and a Scottish soldier. She admired her doctress mother and wanted to be like her, but she also yearned to travel and see the world. In 1821 she accepted a relative’s invitation to visit London, and turned herself from a tourist to a businesswoman by importing Jamaican food preserves. She traveled with her business for several years before returning home to Jamaica, where she married a white man named Edwin Seacole and started a general store. Their venture failed, and disaster struck: fire destroyed most of Kingstown, and both Mary’s husband and her mother died in 1843. Mary survived and rebuilt the hotel, but she set out to start a new life in Panama and was immediately greeted by a cholera epidemic. She helped contain it, and earned a reputation that helped her start her own business across the street from her half-brother’s. When word reached her that the Crimean War back in Europe needed nurses, she left her business behind and went to sign up. Both the War Office and Florence Nightingale’s expedition rejected her, but Mary determined to find her own way there.
May 8, 2018
Charge of the Light Brigade | Animated History
The Armchair Historian
Published on 28 Dec 2017The Charge of the Light Brigade, Animated History
March 21, 2017
Catherine the Great – V: Potemkin, Catherine’s General, Advisor, and Lover – Extra History
Published on 25 Feb 2017
Catherine had many lovers during her life, but perhaps none meant so much to her as Grigory Potemkin. Although their romance did not last a lifetime, it did form the basis of a working relationship that would change the face (and future) of Europe.
March 26, 2015
Tsar Vladimir is merely following the pattern of Philip of Macedon and Napoleon
When he’s not droning on about domestic politics, Victor Davis Hanson has interesting historical patterns to point out:
Nothing that Vladimir Putin has done in gobbling up territories of the former Soviet Union is new. In fact, he simply apes every tyrant’s time-honored four-step plan of aggression.
From Philip of Macedon to Napoleon, aggressors did not necessarily have a grand timetable for creating an empire. Instead, they went at it ad hoc. They took as much as they could at any given time; then backed away for a bit, if they sensed strong opposition was building — only to go back on the offensive when vigilance waned.
Hitler did not realistically believe in 1936 that he would within five years create an empire from the Atlantic to the Volga. Instead, he started out by moving incrementally — in the Rhineland, Austria, and Czechoslovakia — testing where he might grab land without a war, always both surprised at the ease of his success and full of contempt for the appeasers who had so empowered him.
So too Putin. Once the Obama administration had reset the mild punishments of the Bush administration for carving out parts of Ossetia, Putin went back on the move. Obama’s reset was a green light for Putin. Who in the real world of serious diplomacy shows up in Geneva with a red plastic toy reset button, complete with a mistranslated Russian label? When Putin soon sized up the Obama administration’s appeasement around the globe — from fake red lines for Syria, to a scramble out of Iraq, to chaos in Libya — he moved into Crimea. And then he waited.
Western sermons followed; outrage grew. Then the Western hysterics predictably passed, as popular attention went back to the Kardashians and Miley Cyrus’s metamorphosis from Disney girl to vamp. After a bit of digestion, Putin was ready for his next Anschluss. He repeated the formula in Ukraine: a persecuted Russian-speaking minority, an anti-Russian illiberal government, civil unrest, denial of a just and much-needed new plebiscite, a need for paramilitaries to help out their brethren, a Russian army standing nearby just in case, a few bombers buzzing the West, and magnanimous promises to leave crumbs for the victims.
January 22, 2015
QotD: The practice of selling army commissions
A lot has been said about the purchase of commissions — how the rich and incompetent can buy ahead of better men, how the poor and efficient are passed over — and most of it, in my experience, is rubbish. Even with purchase abolished, the rich rise faster in the Service than the poor, and they’re both inefficient anyway, as a rule. I’ve seen ten men’s share of service, through no fault of my own, and can say that most officers are bad, and the higher you go, the worse they get, myself included. We were supposed to be rotten with incompetence in the Crimea, for example, when purchase was at its height, but the bloody mess they made in South Africa recently seems to have been just as bad — and they didn’t buy their commissions.
George MacDonald Fraser, Flashman, 1969.
December 17, 2014
QotD: The mark of a true-born nobleman
Now, no one in my life that I could remember had ever been so damned civil to me, except toad-eaters like Speedicut who didn’t count. I found myself liking his lordship, and did not realize that I was seeing him at his best. In this mood, he was a charming man enough, and looked well. He was taller than I, straight as a lance, and very slender, even to his hands. Although he was barely forty, he was already bald, with a bush of hair above either ear and magnificent whiskers. His nose was beaky and his eyes blue and prominent and unwinking — they looked out on the world with that serenity which marks the nobleman whose uttermost ancestor was born a nobleman, too. It is I the look that your parvenu would give half his fortune for, that unrufflable gaze of the spoiled child of fortune who knows with unshakeable certainty that he is right and that the world is exactly ordered for his satisfaction and pleasure. It is the look that makes underlings writhe and causes revolutions. I saw it then, and it remained changeless as long as I knew him, even through the roll-call beneath Causeway Heights when the grim silence as the names were shouted testified to the loss of five hundred of his command. ‘It was no fault of mine,’ he said then, and he didn’t just believe it; he knew it.
George MacDonald Fraser, Flashman, 1969.
November 16, 2014
QotD: James Brudenell, Earl of Cardigan
The 11th Light Dragoons at this time were newly back from India, where they had been serving since before I was born. They were a fighting regiment, and — I say it without regimental pride, for I never had any, but as a plain matter of fact — probably the finest mounted troops in England, if not in the world. Yet they had been losing officers, since coming home, hand over fist. The reason was James Brudenell, Earl of Cardigan.
You have heard all about him, no doubt. The regimental scandals, the Charge of the Light Brigade, the vanity, stupidity, and extravagance of the man — these things are history. Like most history, they have a fair basis of fact. But I knew him, probably as few other officers knew him, and in turn I found him amusing, frightening, vindictive, charming, and downright dangerous. He was God’s own original fool, there’s no doubt of that — although he was not to blame for the fiasco at Balaclava; that was Raglan and Airey between them. And he was arrogant as no other man I’ve ever met, and as sure of his own unshakeable rightness as any man could be — even when his wrongheadedness was there for all to see. That was his great point, the key to his character: he could never be wrong.
They say that at least he was brave. He was not. He was just stupid, too stupid ever to be afraid. Fear is an emotion, and his emotions were all between his knees and his breastbone; they never touched his reason, and he had little enough of that.
For all that, he could never be called a bad soldier. Some human faults are military virtues, like stupidity, and arrogance, and narrow-mindedness. Cardigan blended all three with a passion for detail and accuracy; he was a perfectionist, and the manual of cavalry drill was his Bible. Whatever rested between the covers of that book he could perform, or cause to be performed, with marvellous efficiency, and God help anyone who marred that performance. He would have made a first-class drill sergeant — only a man with a mind capable of such depths of folly could have led six regiments into the Valley at Balaclava.
However, I devote some space to him because he played a not unimportant part in the career of Harry Flashman, and since it is my purpose to show how the Flashman of Tom Brown became the glorious Flashman with four inches in Who’s Who and grew markedly worse in the process, I must say that he was a good friend to me. He never understood me, of course, which is not surprising. I took good care not to let him.
George MacDonald Fraser, Flashman, 1969.
April 16, 2014
Russia’s long and brutal relationship with Crimea
In History Today, Alexander Lee talks about the historical attitude of Russia toward the Crimean peninsula and some of the terrible things it has done to gain and retain control over the region:
… Russia’s claim to Crimea is based on its desire for territorial aggrandizement and – more importantly – on history. As Putin and Akysonov are keenly aware, Crimea’s ties to Russia stretch back well back into the early modern period. After a series of inconclusive incursions in the seventeenth century, Russia succeeded in breaking the Ottoman Empire’s hold over Crimea with the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (1774), before formally annexing the peninsula in 1784. It immediately became a key factor in Russia’s emergence as a world power. Offering a number of natural warm-water harbours, it gave access to Black Sea trade routes, and a tremendous advantage in the struggle for the Caucasus. Once gained, it was not a prize to be willingly surrendered, and the ‘Russianness’ of Crimea quickly became a cornerstone of the tsars’ political imagination. When a spurious dispute over custody of Christian sites in the Holy Land escalated into a battle for the crumbling remnants of the Ottoman Empire in 1853, Russia fought hard to retain its hold over a territory that allowed it to threaten both Constantinople and the Franco-British position in the Mediterranean. Almost a century later, Crimea was the site of some of the bitterest fighting of the Second World War. Recognising its military and economic importance, the Nazis launched a brutal attempt to capture the peninsula as a site for German resettlement and as a bridge into southern Russia. And when it was eventually retaken in 1944, the reconstruction of Sevastopol – which had been almost completely destroyed during a long and bloody siege – acquired tremendous symbolic value precisely because of the political and historical importance of the region. Even after being integrated into the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic and – later – acknowledged as part of an independent Ukraine after the fall of the USSR, Crimea’s allure was so powerful that the new Ukrainian President, Leonid Kraychuk, claimed that Russia’s attempts to assert indirect control of the peninsula betrayed the lingering force of an ‘imperial disease’.
[…]
The non-Russian population of Crimea was to suffer further even worse under the Soviet Union, and between 1921 and 1945, two broad phases of persecution devastated their position in the peninsula. The first was dominated by the fearsome effects of Stalinist economic policy. In keeping with the centralised aims of the First Five-Year Plan (1928-32), Crimean agricultural production was collectivised, and reoriented away from traditional crops such as grain. On top of this, bungling administrators imposed impossibly high requisition quotas. The result was catastrophic. In 1932, a man-made famine swept through the peninsula. Although agronomists had warned their political masters of the danger from the very beginning, the Moscow leadership did nothing to relieve the situation. Indeed, quite the reverse. As starvation began to take hold, Stalin not only prosecuted those who attempted to collect left-over grain from the few remaining collectivised farms producing grain, but also hermetically sealed regions afflicted by shortages. He was using the famine to cleanse an ethnically diverse population. A true genocide, the Holodmor (‘extermination by hunger’) – as this artificial famine is known – killed as many as 7.5 million Ukrainians, including tens of thousands of Crimeans. And when it finally abated, Stalin took the opportunity to fill the peninsula with Russians, such that by 1937, they accounted for 47.7% of the population, compared to the Tatars’ 20.7%.
The second phase – covering the period between 1941 and 1945 – compounded the terrible effects of the Holodmor. On its own, the appalling casualties caused by the savage battle for Crimea would have decimated the peninsula. Some 170,000 Red Army troops were lost in the struggle, and the civilian population suffered in equal proportion. But after the Soviet Union regained control, the region was subjected to a fresh wave of horror. Accusing the Tatars of having collaborated with the Nazis during the occupation, Stalin had the entire population deported to Central Asia on 18 May 1944. The following month, the same fate was meted out to other minorities, including Greeks and Armenians. Almost half of those subject to deportation died en route to their destination, and even after they were rehabilitated under Leonid Brezhnev, the Tatars were prohibited from returning to Crimea. Their place was taken mostly by ethnic Russians, who by 1959 accounted for 71.4% of the population, and – to a lesser extent – Ukrainians.