Real Time History
Published Mar 15, 2024Fall 1945: the Second World War is over, but there is fresh fighting in Vietnam. Now, former enemies become allies as British-Indian troops, French Commandos, and surrendered Japanese soldiers join in a rag-tag alliance against Ho Chi Minh’s Communists in Saigon. The outcome will shape Vietnam’s future for decades to come, in Great Britain’s weird Vietnam War.
(more…)
July 21, 2024
Britain’s Weird Vietnam War
QotD: There’s no recovery mode from being a Basic College Girl
Do you have any examples of BCGs recuperating?
Sadly, very few. Part of this is just in the nature of the biz — I don’t see too many former students out and about, since they all leave College Town for the big wide world — but I do know this: Scratch a Karen, find a BCG. In fact, you could go so far to say that “Karen” simply IS the BCG after she hits The Wall. The faster the impact, the bigger the Karen (this is a testable hypothesis — given that our gal Taylor Swift is currently impacting The Wall at about Mach 3, if I’m right, she’ll soon unleash the kraken of Karens on an unsuspecting world).
I also strongly suspect that BCGs can’t recover. As any shrink will tell you, Narcissistic and Borderline Personality Disorders are almost impossible to treat. For one thing, treatment requires believing that you have a problem, and believing you don’t have a problem is pretty much diagnostic of those two syndromes. And while I’m not sure the BCG is clinically diagnosable with either of those, what they actually are is close enough that I’m betting whatever therapies “work” on actual clinical cases would “work” on them … but see above.
Finally, I guess I can’t really blame the BCG for not realizing she’s got a problem, because she obviously doesn’t have a problem. Look around — society rewards this shit. AOC, for example, is going to be La Presidenta por Vida de los Estados Unidos here in a decade or so; if that’s a problem, I can’t really blame them for not fixing it. Eventually, of course, reality will intrude, and your BCG will be screaming for a real man to come save her … but, thanks to her BCG antics, there won’t be any real men around. Or, you know, we’ll all be in the OPFOR, so good luck with that, beeyatch.
Severian, “Friday Mailbag /Grab Bag”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-06-25.
July 20, 2024
When diversity and competence requirements conflict
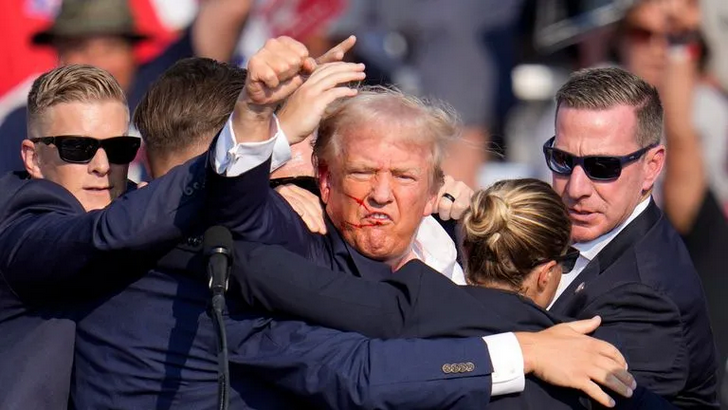
Janice Fiamengo compares the iconic Trumpian reaction after being wounded by a sniper with the cries for diversity at all costs from others:

Donald Trump, surrounded by Secret Service agents, raises his fist after an attempt on his life during a campaign speech in Butler, PA on 13 July, 2024.
Many observers have had harsh words for the female Secret Service agents who performed poorly in response to the attempt on Trump’s life last Saturday (see this Wired article for a catalogue of the charges, in which the author cannot muster a single rebuttal). Some noted that Trump’s security detail for the Republican National Convention is now, it appears, exclusively male. And rightly so. There is no equality when bullets start to fly, and it is lethal to pretend there is.
When the first shot rang out, 50-year-old Pennsylvanian firefighter Corey Comperatore is reported to have done what men typically do in such situations: he shielded his wife and daughters, taking a bullet to the head. Women far more rarely perform such acts of self-sacrifice.
Comperatore lost his life because of a multitude of errors on the part of the Secret Service, including a long hesitation by snipers tasked with neutralizing threats. Video shows that at least one of these snipers, seemingly with the gunman in his sites, failed to take action until seconds after the gunman began firing. The agent seemed befuddled, scrambling back when the first shot came. Was he new on the job, inadequately trained, or sub-par in his skills? Or directed not to fire?
I am not equipped to answer these or the many other, darker, questions about the bungled security operation. What can be said for certain is that if some element of the Secret Service was not treasonously complicit in the attempt on Trump’s life, it was certainly massively inadequate to its task of protecting him and others at the rally. The gunman was allowed to gain access to his rooftop shooting position, and Trump was not extracted the moment the shooter’s presence became known.
Director Kimberly A. Cheatle, who expressed to CBS News in interview her concern with “developing and giving opportunities to everyone in our work force, and particularly women“, has a lot to answer for.
Perhaps the women we saw in Trump’s security detail were new recruits helping Cheatle reach her target of 30% women by 2030. They looked amateur, panicked, and unpracticed. One of the women attempting to remove Trump from the stage was simply too small, and hesitant, for the task; she looked at one point as if she were engaged in a group hug at a United Church reconciliation ceremony. (As many have noted, her small stature enabled Trump’s fist-raised gesture of masculine defiance and his exhilarating “Fight! Fight! Fight!”). As Trump was being taken into the security vehicle, the four women surrounding the car looked jumpy and confused, scared and awkward. One woman was visibly unable to holster her gun.
I’ve never seen so many women guarding a former president, and I’ve never seen so many women obviously incapable.
We know that men and women have different strengths and aptitudes. Nearly a decade ago, the United States Marine Corps demonstrated through a year-long study of hundreds of Marines that even women who could pass the physical exam simply could not carry out standard military tasks as efficiently as men. The study found, unsurprisingly, that “The males were more accurate hitting targets, faster at climbing over obstacles, better at avoiding injuries.” The women struggled to carry weapons and ammunition, and even to use the weaponry properly. Women’s higher injury rate was marked: “The well documented comparative disadvantage in upper and lower-body strength resulted in higher fatigue levels of most women, which contributed to greater incidents of overuse injuries such as stress fractures.”
Counting citation numbers in “Chomskys”
The latest anonymous reviewer in Astral Codex Ten‘s “Your Book Review” series considers the work of Noam Chomsky, and notes just how his works dominate the field of linguistics:

Noam Chomsky speaks about humanity’s prospects for survival in Amherst, Massachusetts, United States on 13 April 2017.
Original photo by Σ, retouched by Wugapodes via Wikimedia Commons.
You may have heard of a field known as “linguistics”. Linguistics is supposedly the “scientific study of language“, but this is completely wrong. To borrow a phrase from elsewhere, linguists are those who believe Noam Chomsky is the rightful caliph. Linguistics is what linguists study.
I’m only half-joking, because Chomsky’s impact on the study of language is hard to overstate. Consider the number of times his books and papers have been cited, a crude measure of influence that we can use to get a sense of this. At the current time, his Google Scholar page says he’s been cited over 500,000 times. That’s a lot.
It isn’t atypical for a hard-working professor at a top-ranked institution to, after a career’s worth of work and many people helping them do research and write papers, have maybe 20,000 citations (= 0.04 Chomskys). Generational talents do better, but usually not by more than a factor of 5 or so. Consider a few more citation counts:
- Computer scientist Alan Turing (65,000 = 0.13 Chomskys)
- Neuro / cogsci / AI researcher Matthew Botvinick (83,000 = 0.17 Chomskys)
- Mathematician Terence Tao (96,000 = 0.19 Chomskys)
- Cognitive scientist Joshua Tenenbaum (107,000 = 0.21 Chomskys)
- Nobel-Prize-winning physicist Richard Feynman (120,000 = 0.24 Chomskys)
- Psychologist and linguist Steven Pinker (123,000 = 0.25 Chomskys)
- Two-time Nobel Prize winner Linus Pauling (128,000 = 0.26 Chomskys)
- Neuroscientist Karl Deisseroth (143,000 = 0.29 Chomskys)
- Biologist Charles Darwin (182,000 = 0.36 Chomskys)
- Theoretical physicist Ed Witten (250,000 = 0.50 Chomskys)
- AI researcher Yann LeCun (352,000 = 0.70 Chomskys)
- Historian and philosopher Hannah Arendt (359,000 = 0.72 Chomskys)
- Karl Marx (458,000 = 0.92 Chomskys)
Yes, fields vary in ways that make these comparisons not necessarily fair: fields have different numbers of people, citation practices vary, and so on. There is also probably a considerable recency bias; for example, most biologists don’t cite Darwin every time they write a paper whose content relates to evolution. But 500,000 is still a mind-bogglingly huge number.
Not many academics do better than Chomsky citation-wise. But there are a few, and you can probably guess why:
- Human-Genome-Project-associated scientist Eric Lander (685,000 = 1.37 Chomskys)
- AI researcher Yoshua Bengio (780,000 = 1.56 Chomskys)
- AI researcher Geoff Hinton (800,000 = 1.60 Chomskys)
- Philosopher and historian Michel Foucault (1,361,000 = 2.72 Chomskys)
…well, okay, maybe I don’t entirely get Foucault’s number. Every humanities person must have an altar of him by their bedside or something.
Chomsky has been called “arguably the most important intellectual alive today” in a New York Times review of one of his books, and was voted the world’s top public intellectual in a 2005 poll. He’s the kind of guy that gets long and gushing introductions before his talks (this one is nearly twenty minutes long). All of this is just to say: he’s kind of a big deal.
[…]
Since around 1957, Chomsky has dominated linguistics. And this matters because he is kind of a contrarian with weird ideas.
Build the Square-Leg Craftsman Table (Part 1)
Rex Krueger
Published Apr 3, 2024A satisfying project starts with square pieces.
(more…)
QotD: Comparing gun crime in Canada and the United States
That may explain the extraordinary amount of sucking up to Canada in this movie [Bowling for Columbine], which, while gratifying to insecure Canucks and self-loathing Americans, may be of less interest to third parties. Moore’s thesis, such as it is, is that America’s murder rate is the consequence not just of the country’s love of guns but of deeper currents of paranoia and fear in the American psyche. To that end, he crosses the Michigan border into Ontario, where one Canadian after another tells him that they don’t lock their doors. The level of guns per capita in Canada is similar to America but the murder rate is much, much lower. Ergo, it must be because Americans are living in fear while Canadians are much more socially progressive.
Whatever, dude. Unlike Moore, I have homes on both sides of the border and it’s the Quebec one I keep locked. By the time you read this, I’ll be in New York, but my home in New Hampshire will be unlocked, and so will my car at the airport, the key in the ignition, so I’ll know where to find it. By contrast, in Quebec it’s illegal to leave your car unlocked, even if you stop for a pee on an ice floe up by Hudson’s Bay. Pace Moore, Canada has vastly lower rates of handgun ownership. Long-gun ownership is much closer, but, statistically, Canadians are slightly more murderous than Americans in this sphere: in the US, there are 1.7 homicides per 100,000 long guns; in Canada, it’s 1.9. So European visitors to North America should be aware they’re more likely to be killed by a homicidal Canadian rifleman than an American one.
On the overall murder rate, if Moore’s interested in “cultural differences”, it seems odd that he should avoid the most obvious one. Alberta Report‘s Colby Cosh, a braver man than I, points out that black Americans are 13 per cent of the US population but commit over half the murders. Once you factor those out, non-black Americans murder at about the same rate as Canadians.
Mark Steyn, “Bowling for Columbine”, Steyn Online, 2002-11-30.
July 19, 2024
Argentina’s decades-long struggle with inflation
At the Foundation for Economic Education, Marcos Falcone provides an update on President Javier Milei’s ongoing efforts to drag the Argentine economy back from hyperinflation:
As Javier Milei rose to power in December of last year, Argentina suffered from an annual inflation rate of over 211 percent, only behind Venezuela and Lebanon. Having risen consistently for over two decades, a combination of perpetually unbalanced budgets and investors’ distrust made money creation (and thus inflation) almost unavoidable.
In that context, Javier Milei’s first promise in his inaugural address was to avoid hyperinflation. In order to do that, his highest priority was to balance the budget so as to stop monetizing the deficit. And indeed, after just one month, the government announced in January that Argentina achieved its first financial surplus in 16 years. In successive months, the budget has been kept balanced.
Quick action seems to be causing quick effects. Indeed, inflation has plunged from 25 percent in December to an expected 4 percent in July. This is happening in a context of price readjustments, with prices like rent going down (after the government repealed rent control laws) and energy and transport prices going up (as the government is cutting subsidies). Even the IMF has admitted that inflation is falling faster than expected. In fact, inflation is coming down so fast that banks have started offering mortgages for the first time in seven years. This signals that the market expects inflation to stay down.
Milei told Argentines that the process of defeating inflation would hurt—and it has. The downside of the government’s economic plan is that the country has entered a recession which is likely to last until at least the end of the year. Amid some layoffs, the country’s industrial output is decreasing. The spending cuts that allowed the country to balance the budget have resulted in less income for provinces and specific groups like retirees.
The rise of the reactionaries – Gen X poised to pounce and seize
Andrew Potter tries to explain why Gen X are much more likely to support conservative policies than the groovy fossil Boomers and the painfully Socialized Millennials and GenZ’ers:

Generation X Word Cloud Concept collage background
Best Motivation Blog: What Generation Is X
As North American politics continues its rightward lurch, it is becoming increasingly commonplace to note the outsized role of Gen Xers in pushing this trend. In 2022, a Politico essay tried to explain “How Gen X became the Trumpiest generation“. That same year, an essay in Salon lamented how “of course Gen X was always going to sell out and vote Republican”. Writing in The Line last year, Rahim Mohamed wondered “how Generation MTV became Generation GOP?” These aren’t outliers – there is a whole sub genre of cultural commentary devoted to trying to explain just why Gen Xers are so right wing, compared to both their Boomer predecessors and the Millennials and Zs who followed.
This raises a couple of questions, the first of which is: is it even true? And if so, why?
On the facts of the matter, it appears that members of Generation X are, on the whole, more conservative than other generations, and this is especially true in the United States. For the past three or four years, polls have consistently shown that Gen Xers are more likely to see the country as going in the wrong direction, more likely to disapprove of Joe Biden, and more likely to support Donald Trump and vote Republican, than any other generational cohort. And while every generation tends to become more conservative as it ages, it is a tendency that accelerated under Gen X.
Pollsters have found similar support for these trends in Canada. An Abacus survey conducted last August found Gen Xers had the highest level of support for the Conservatives, with 41 per cent of those surveyed intending to vote CPC. And just this past June, the pollster Frank Graves released a series of charts tracking sentiment in Canada on a number of issues, including national attachment, social cohesion, and voter intention. He found significant intergenerational discord, with members of Gen X showing the highest level of support for smaller government, and Gen X males having the highest level of support for the CPC.
So why is this the case? How did the generation that fought (and won) the first culture war against conservatives, that launched the antiglobalization movement, that made heroes out of left wing icons like Kurt Cobain and Naomi Klein, become the most right wing cohort of all? Did we follow our Boomer parents’ hippies-to-yuppies trajectory in selling out? Or is there something else at work, beyond crass financial self-interest?
There’s probably at least something to be said for the “crass self-interest” angle. Despite the long-standing claim to being the first generation to do worse than their parents, the truth is, Gen X is raking it in. Starting right around the pandemic, Canadian Gen Xers quietly overtook Boomers as the generation with the highest average household net worth. It may also explain why alone amongst the generations, members of Gen X list “cost of living” as their most salient political issue, in contrast with both the older and younger cohorts who identify things like climate change, health care, and the environment as the most important issues facing Canada.
Airline Food During the Golden Age of Air Travel
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Apr 9, 2024Back before airlines could compete with lower prices, they competed with the quality of atmosphere, service, and, of course, food.
I’d be happy to have this pot roast on the ground, let alone on an airplane. The meat is so tender that it falls apart, the vegetables and herbs give it wonderful flavor, and you get the added bonus of it making your house smell awesome as it simmers.
(more…)
QotD: The value of contemporary music
The music piped into the men’s locker room at my gym puts me in touch with contemporary culture, and, in so doing, gives me an incentive to change as quickly as I can.
Bruce Ivar Gudmundsson, “The Timelessness of Elle Cordoba”, Extra Muros, 2024-04-18.
July 18, 2024
An elite luxury belief – “Diversity Is Our Strength”
In a guest-post at Postcards from Barsoom, Spaceman Spiff lists some of the cargo cult notions that have captured the imagination of many “elites” in western nations, like “Diversity Is Our Strength“:
Multiculturalism is pursued in Western countries with a religious mania. It is difficult to imagine anything closer to a belief system for today’s upwardly mobile professional than advocating for diversity and inclusion.
Most of the world views ethnic and cultural mixing as a dangerous, civilization ending activity. A threat to be guarded against, not an opportunity to be embraced. This has been the conventional view throughout history in almost every society.
The modern Western formulation has challenged this. Mixing cultures, especially those hostile to assimilation, is not just to be tolerated but encouraged. Alien peoples must be sought out and imported to increase the ethnic and cultural mix. We must extend every courtesy to those fundamentally incompatible with us in customs and manners. The ultimate expression of this ambition is open borders, a concept viewed with deep hostility by almost all non-Western countries.
Whatever the origins of such policies, the implementers of these ideas are everywhere. They work in corporations, public sector bodies, and NGOs. We find them in Starbucks and Walmart. Diversity is everywhere even though it makes little sense as an end in itself.
How do we explain the enthusiasm with which middle managers and HR workers have embraced such a destructive idea, including its corporate version of job and education quotas?
Competency itself can be hard to find even in ideal conditions, so why hobble your chances like this? Why intentionally seek to create brittle heterogeneous environments that reduce productivity and increase strife?
The simple answer is that sophisticates don’t succumb to primitive notions like preferring their own. These are urges to be resisted, like hunger while dieting. Racism is old hat and any noticing of differences is racism. After all, our elites do not behave like this, so the goal is to be observably anti-racist, just like them.
Some look at our globalist elites and see them mixing with an international set. As they hobnob around the world they certainly socialize with foreigners. Indian elites, Arab elites, and Chinese elites all mix with their Western equivalents. We see them at events like Davos or the global climate change meetings. A multicoloured constellation of traitors from every country, all getting along with each other because they are nothing like their fellow countrymen, and everything like each other.
What the dullards in the corporate HR world miss is that this is not a celebration of diversity. Most of those elites are nearly identical. Many attended the same universities. All speak English, the international language. They have similar views, including contempt for their respective compatriots.
There is no diversity at the very top, just an elitist outlook most of them share, and contempt for the peasants who surround them. White, brown, or black, we all look the same from the cultural stratosphere. Cannon fodder for their Olympian ideas, but nothing more. The elite view of mass migration is indifference, not enthusiasm.
The street-level version takes the superficial aspects of this phenomenon and worships it as the end goal since the underlying homogeneity of the elites is largely absent. Their goal is not to seek out that which we have in common with others but the less sophisticated observation of what makes us different, what makes us more “diverse.”
The midrange talent in the West have therefore convinced themselves celebrating overt differences in the form of multiculturalism is modernity. It is the future promised by Star Trek and other communist dreams. Colour won’t matter, just like Martin Luther King promised, so long as we overlook the long predicted consequences of their dream, the lowered wages, the erosion of trust and the eventual polarization of competing groups within our own nations we once kept at bay with more considered immigration policies.
What is a Battle Rifle?
Forgotten Weapons
Published Apr 10, 2024“Battle rifle” is not a formally recognized term like “assault rifle”, but it is widely used, and I think it has a lot of utility. It is intended to differentiate between intermediate-caliber and full-power military rifles, and to that end I propose these four criteria to define a “battle rifle”:
1 – A military style or pattern rifle
2 – Intended primarily to be fired from the shoulder
3 – Self-loading (either semi- or fully automatic)
4 – Chambered for a full power rifle cartridge
(more…)
QotD: Culture in the late western Roman Empire
This vision of the collapse of Roman political authority in the West may seem a bit strange to readers who grew up on the popular narrative which still imagines the “Fall of Rome” as a great tide of “barbarians” sweeping over the empire destroying everything in their wake. It’s a vision that remains dominant in popular culture (indulged, for instance, in games like Total War: Attila; we’ve already talked about how strategy games in particular tend to embrace this a-historical annihilation-and-replacement model of conquest). But actually culture is one of the areas where the “change and continuity” crowd have their strongest arguments: finding evidence for continuity in late Roman culture into the early Middle Ages is almost trivially easy. The collapse of Roman authority did not mark a clean cultural break from the past, but rather another stage in a process of cultural fusion and assimilation which had been in process for some time.
The first thing to remember, as we’ve already discussed, is that the population of the Roman Empire itself was hardly uniform. Rather the Roman empire as it violently expanded, had absorbed numerous peoples – Celtiberians, Iberians, Greeks, Gauls, Syrians, Egyptians, and on and on. Centuries of subsequent Roman rule had led to a process of cultural fusion, whereby those people began to think of themselves as Romani – Romans – as they both adopted previously Roman cultural elements and their Roman counterparts adopted provincial culture elements (like trousers!).
In particular, by the fifth century, the majority of these self-described Romani, including the overwhelming majority of elites, had already adopted a provincial religion: Christianity, which had in turn become the Roman religion and a core marker of Roman identity by the fifth century. Indeed, the word paganus, increasingly used in this period to refer to the remaining non-Christian population, had a root-meaning of something like “country bumpkin”, reflecting the degree to which for Roman elites and indeed many non-elites, the last fading vestiges of the old Greek and Roman religions were seen as out of touch. Of course Christianity itself came from the fringes of the Empire – a strange mystery cult from the troubled frontier province of Judaea in the Levant which had slowly grown until it had become the dominant religion of the empire, receiving official imperial favor and preference.
The arrival of the “barbarians” didn’t wipe away that fusion culture. With the exception of the Angles, Saxons and Jutes who eventually ended up in England, the new-comers almost uniformly learned the language of the Roman west – Latin – such that their descendants living in those lands, in a sense still speak it, in its modern forms: Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, etc. alongside more than a dozen local regional dialects. All are derived from Latin (and not, one might note, from the Germanic languages that the Goths, Vandals, Franks and so on would have been speaking when they crossed the Roman frontier).
They also adopted the Roman religion, Christianity. I suspect sometimes the popular imagination – especially the one that comes with those extraordinarily dumb “Christian dark age” graphs – is that when the “barbarians invade” the Romans were still chilling in their Greco-Roman temples, which the “barbarians” burned down. But quite to the contrary – the Romans were the ones shutting down the old pagan temples at the behest of the now Christian Roman emperors, who busied themselves building beautiful and marvelous churches (a point The Bright Ages makes very well in its first chapter).
The “barbarians” didn’t tear down those churches – they built more of them. There was some conflict here – many of the Germanic peoples who moved into the Roman Empire had been converted to Christianity before they did so (again, the Angles and Saxons are the exception here, converting after arrival), but many of them had been converted through a bishop, Ulfilias, from Constantinople who held to a branch of Christian belief called “Arianism” which was regarded as heretical by the Roman authorities. The “barbarians” were thus, at least initially, the wrong sort of Christian and this did cause friction in the fifth century, but by the end of the sixth century nearly all of these new kingdoms created in the wake of the collapse of Roman authority were not only Christian, but had converted to the officially accepted Roman “Chalcedonian” Christianity. We’ll come back later to the idea of the Church as an institution, but for now as a cultural marker, it was adopted by the “barbarians” with aplomb.
Artwork also sees the clear impact of cultural fusion. Often this transition is, I think, misunderstood by students whose knowledge of artwork essentially “skips” Late Antiquity, instead jumping directly from the veristic Roman artwork of the late republic and the idealizing artwork of the early empire directly to the heavily stylized artwork of Carolingian period and leads some to conclude that the fall of Rome made the artists “bad”. There are two problems: the decline here isn’t in quality and moreover the change didn’t happen with the fall of the Roman Empire but quite a bit earlier. […]
Late Roman artwork shows a clear shift into stylization, the representation of objects in a simplified, conventional way. You are likely familiar with many modern, highly developed stylized art forms; the example I use with my students is anime. Anime makes no effort at direct realism – the lines and shading of characters are intentionally simplified, but also bodies are intentionally drawn at the wrong proportions, with oversized faces and eyes and sometimes exaggerated facial expressions. That doesn’t mean it is bad art – all of that stylization is purposeful and requires considerable skill – the large faces, simple lines and big expressions allow animated characters to convey more emotion (at a minimum of animation budget).
Late Roman artwork moves the same way, shifting from efforts to portray individuals as real-to-life as possible (to the point where one can recognize early emperors by their facial features in sculpture, a task I had to be able to perform in some of my art-and-archaeology graduate courses) to efforts to portray an idealized version of a figure. No longer a specific emperor – though some identifying features might remain – but the idea of an emperor. Imperial bearing rendered into a person. That trend towards stylization continues into religious art in the early Middle Ages for the same reason: the figures – Jesus, Mary, saints, and so on – represent ideas as much as they do actual people and so they are drawn in a stylized way to serve as the pure expressions of their idealized nature. Not a person, but holiness, sainthood, charity, and so on.
And it really only takes a casual glance at the artwork I’ve been sprinkling through this section to see how early medieval artwork, even out through the Carolingians (c. 800 AD) owes a lot to late Roman artwork, but also builds on that artwork, particularly by bringing in artistic themes that seem to come from the new arrivals – the decorative twisting patterns and scroll-work which often display the considerable technical skill of an artist (seriously, try drawing some of that free-hand and you suddenly realize that graceful flowing lines in clear symmetrical patterns are actually really hard to render well).
All of the cultural fusion was effectively unavoidable. While we can’t know their population with any certainty, the “barbarians” migrating into the faltering western Empire who would eventually make up the ruling class of the new kingdoms emerging from its collapse seem fairly clearly to have been minorities in the lands they settled into (with the notable exception, again, of the Angles, Saxons and Jutes – as we’re going to see this pattern again and again, Britain has an unusual and rather more traumatic path through this period than much of the rest of Roman Europe). They were, to a significant degree, as Guy Halsall (op. cit.) notes, melting into a sea of Gallo-Romans, or Italo-Romans, or Ibero-Romans.
Even Bryan Ward-Perkins, one of the most vociferous members of the decline-and-fall camp, in his explosively titled The Fall of Rome and the End of Civilization (2005) – this is a book whose arguments we will come back to in some detail – is forced to concede that “even in Britain the incomers [sic] had not dispossessed everyone” of their land, but rather “the invaders entered the empire in groups that were small enough to leave plenty to share with the locals” (66-7). No vast replacement wave this, instead the new and old ended up side by side. Indeed, Odoacer, seizing control of Italy in 476, we are told, redistributed a third of the land; it’s unclear if this meant the land itself or the tax revenue on it, but in either case clearly the majority of the land remained in the hands of the locals which, by this point in the development of the Roman countryside, will have mostly meant in the hands of the local aristocracy.
Instead, as Ralph Mathisen documents in Roman aristocrats in barbarian Gaul: strategies for survival in an age of transition (1993), most of the old Roman aristocracy seems to have adapted to their changing rulers. As we’ll discuss next week, the vibrant local government of the early Roman empire had already substantially atrophied before the “barbarians” had even arrived, so for local notables who were rich but nevertheless lived below the sort of mega-wealth that could make one a player on the imperial stage, little real voice in government was lost when they traded a distant, unaccountable imperial government for a close-by, unaccountable “barbarian” one. Instead, as Mathisen notes, some of the Gallo-Roman elite retreat into their books and estates, while more are co-opted into the administration of these new breakaway kingdoms, who after all need literate administrators beyond what the “barbarians” can provide. Mathisen notes that in other cases, Gallo-Roman aristocrats with ambitions simply transferred those ambitions from the older imperial hierarchy to the newer ecclesiastical one; we’ll talk more about the church as an institution next week. Distinct in the fifth century, by the end of the sixth century in Gaul, the two aristocracies: the barbarian warrior-aristocracy and the Gallo-Roman civic aristocracy had melded into one, intermarried and sharing the same religion, values and culture.
In this sense there really is a very strong argument to be made that the “Romans” and indeed Roman culture never left Rome’s lost western provinces – the collapse of the political order did not bring with it the collapse of the Roman linguistic or cultural sphere, even if it did fragment it.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Rome: Decline and Fall? Part I: Words”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-01-14.